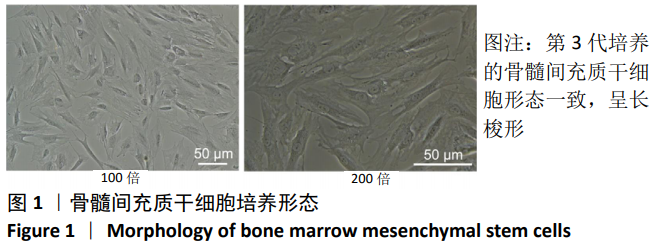
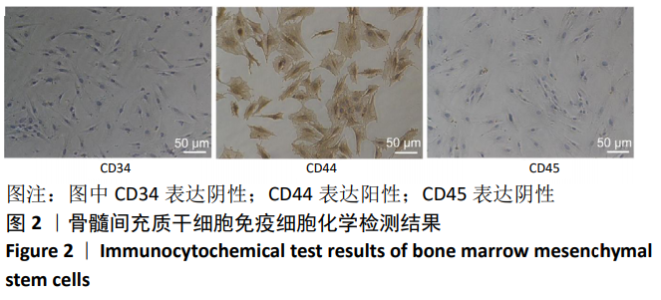
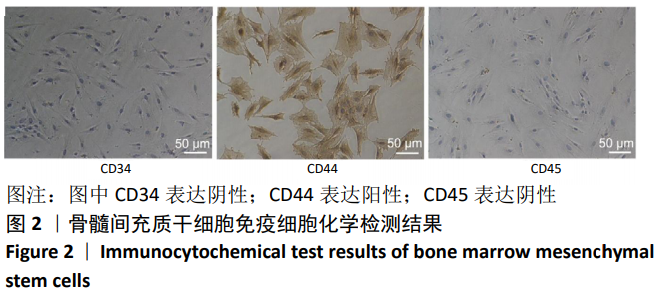
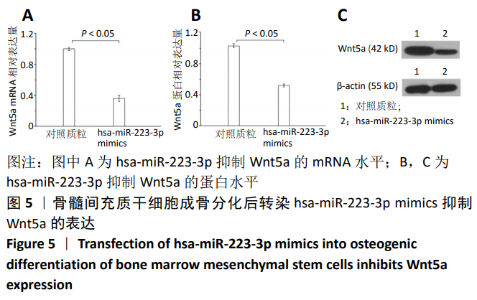
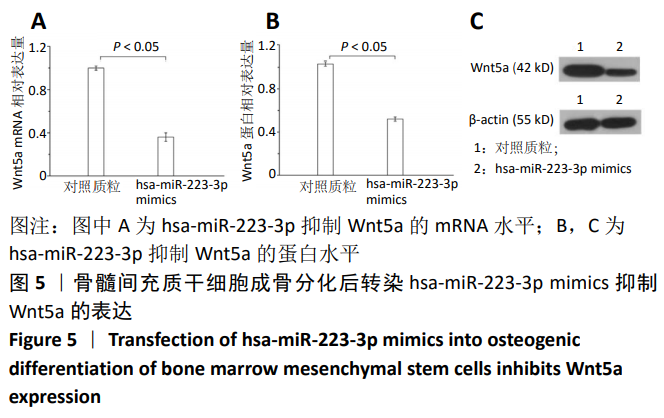
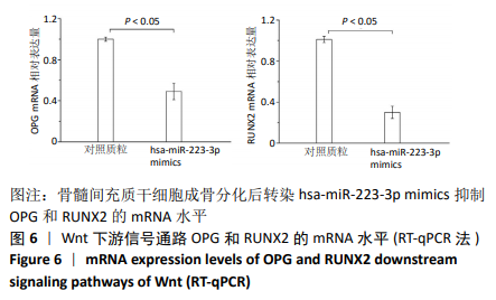
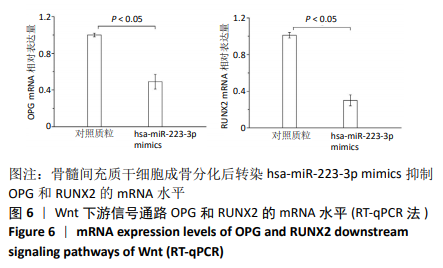
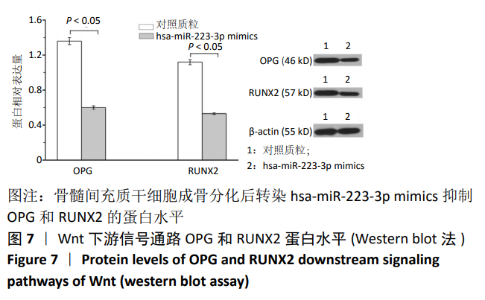
[1] 马远征,王以朋,刘强,等.中国老年骨质疏松诊疗指南(2018)[J].中国老年学杂志, 2019, 39(11):2557-2575.
[2] RALSTON SH, UITTERLINDEN AG. Genetics of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 2010;31(5):629-662.
[3] 张亚楼,邓强,周杨俊杰,等.构建TRAF6基因3’非编码区荧光素酶报告质粒验证及与潜在靶基因TRAF6的靶向关系[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(27):4397-4401.
[4] WANG J, LIU S, LI J, et al. Roles for miRNAs in osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019; 10(1):197.
[5] HRDLICKA HC, LEE SK, DELANY AM. MicroRNAs are Critical Regulators of Osteoclast Differentiation. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2019;5(1):65-74.
[6] BELLAVIA D, DE LUCA A, CARINA V, et al. Deregulated miRNAs in bone health: Epigenetic roles in osteoporosis. Bone. 2019;122:52-75.
[7] JI Q, XU X, SONG Q, et al. miR-223-3p Inhibits Human Osteosarcoma Metastasis and Progression by Directly Targeting CDH6. Mol Ther. 2018; 26(5):1299-1312.
[8] QIN S, SHI X, WANG C, et al. Transcription Factor and miRNA Interplays Can Manifest the Survival of ccRCC Patients. Cancers (Basel). 2019; 11(11). pii: E1668.
[9] LIU P, CHEN Y, WANG B, et al. Expression of microRNAs in the plasma of patients with acute gouty arthritis and the effects of colchicine and etoricoxib on the differential expression of microRNAs. Arch Med Sci. 2019;15(4):1047-1055.
[10] DANTHAM S, SRIVASTAVA AK, GULATI S, et al. Differentially Regulated Cell-Free MicroRNAs in the Plasma of Friedreich’s Ataxia Patients and Their Association with Disease Pathology. Neuropediatrics. 2018;49(1): 35-43.
[11] MANCUSO R, AGOSTINI S, HERNIS A, et al. Circulatory miR-223-3p Discriminates Between Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Patients. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):9393.
[12] DE-UGARTE L, YOSKOVITZ G, BALCELLS S, et al. MiRNA profiling of whole trabecular bone: identification of osteoporosis-related changes in MiRNAs in human hip bones. BMC Med Genomics. 2015;8:75.
[13] 张遥,任秀智,韩金祥,等.Wnt信号通路与人类疾病相关性的研究进展[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2018,31(1):81-86.
[14] 王爱飞,王亮,徐又佳.MicroRNAs对骨质疏松症发病机制的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(1):135-140.
[15] KÜHL M. The WNT/calcium pathway: biochemical mediators, tools and future requirements. Front Biosci. 2004;9:967-974.
[16] 肖启程,严光文,田一男,等. Wnt信号配体种类及其在骨代谢中的作用[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2019, 11(6):613-619.
[17] KRAMER I, HALLEUX C, KELLER H, et al. Osteocyte Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for normal bone homeostasis. Mol Cell Biol. 2010; 30(12):3071-3085.
[18] OKAMOTO M, UDAGAWA N, UEHARA S, et al. Noncanonical Wnt5a enhances Wnt/β-catenin signaling during osteoblastogenesis. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4493.
[19] TAKADA I, MIHARA M, SUZAWA M, et al. A histone lysine methyltransferase activated by non-canonical Wnt signalling suppresses PPAR-gamma transactivation. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(11):1273-1285.
[20] KOOK SH, HEO JS, LEE JC. Crucial roles of canonical Runx2-dependent pathway on Wnt1-induced osteoblastic differentiation of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;402(1-2): 213-223. |