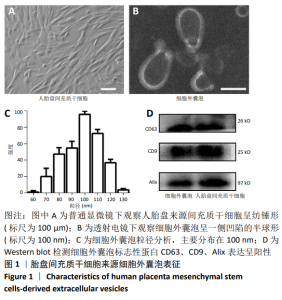
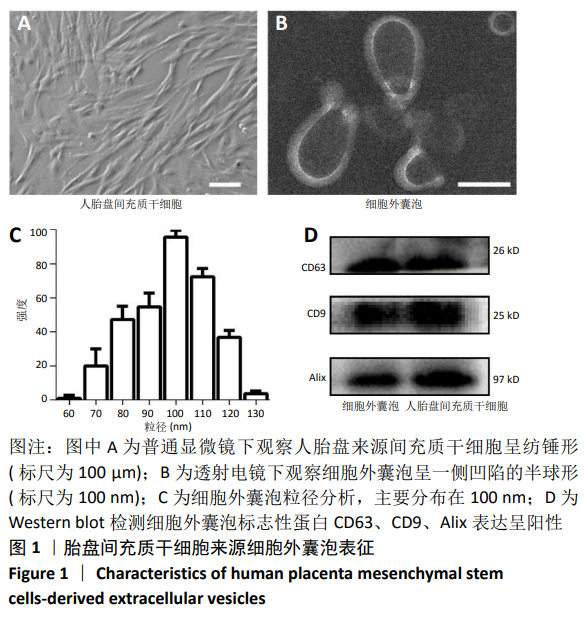
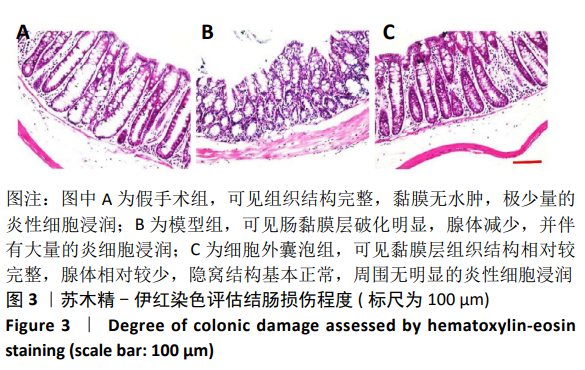
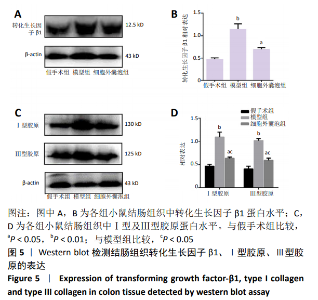
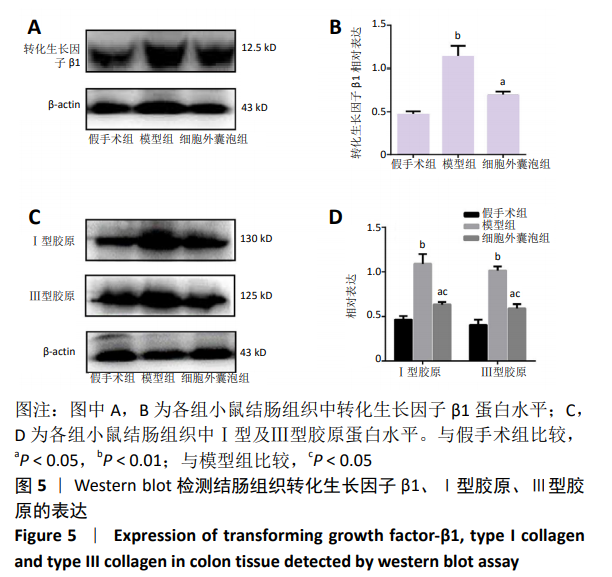
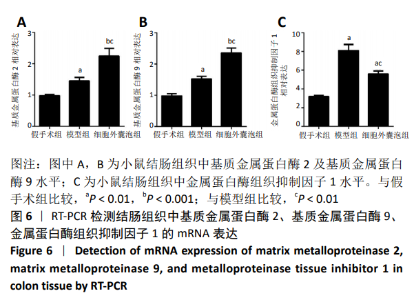
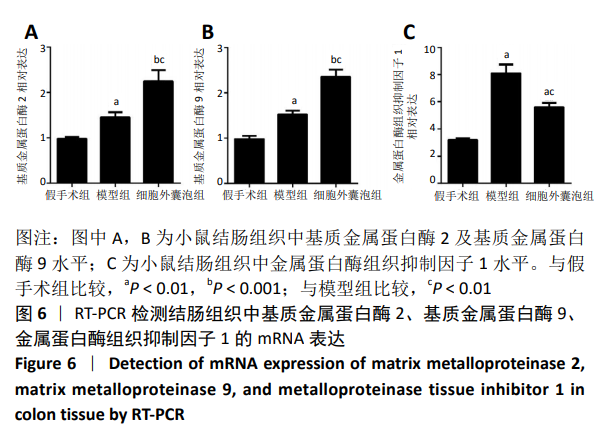
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 1026-1031.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2167
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis
Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang
- Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300052, China
-
Received:2020-01-06Revised:2020-01-14Accepted:2020-03-13Online:2021-03-08Published:2020-12-08 -
About author:Duan Liyun, Master candidate, Department of Gastroenterology, General Hospital, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300052, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031.
share this article
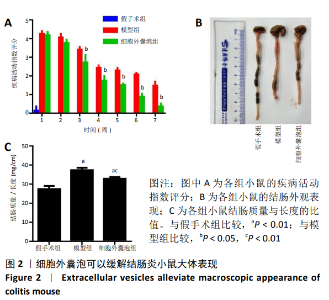
2.2 实验动物数量分析 实验选用24只BALB/c雄性小鼠,分为3组,实验过程中无脱落,全部进入实验结果分析阶段。 2.3 各组小鼠大体表现 各组小鼠进行疾病活动指数评分,见图2A。与模型组相比,细胞外囊泡组小鼠疾病活动指数评分降低(P < 0.05)。各组小鼠结肠外观:假手术组小鼠肠壁完整光滑,无粘连;模型组小鼠肠壁变硬,肠道充血水肿,周围有粘连,结肠长度缩短;细胞外囊泡组小鼠肠道无明显充血水肿,部分周围有粘连,结肠长度较模型组明显增长,见图2B。各组小鼠结肠质量/长度的比值:假手术组小鼠结肠质量/长度比值最低,细胞外囊泡组小鼠结肠质量/长度比值较模型组明显下降,差异有显著性意义 (P < 0.05),见图2C。"

| [1] WEIMERS P, MUNKHOLM P. The Natural History of IBD: Lessons Learned. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2018;16(1):101-111. [2] FIOCCHI C, LUND PK. Themes in fibrosis and gastrointestinal inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;300(5):G677-683. [3] PALLONE F, MONTELEONE G. Mechanisms of tissue damage in inflammatory bowel disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2001;17(4):307-312. [4] ZORZI F, CALABRESE E, MONTELEONE G. Pathogenic aspects and therapeutic avenues of intestinal fibrosis in Crohn’s disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;129(12):1107-1113. [5] LATELLA G, DI GREGORIO J, FLATI V, et al. Mechanisms of initiation and progression of intestinal fibrosis in IBD. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(1): 53-65. [6] LI J, MAO R, KURADA S, et al. Pathogenesis of fibrostenosing Crohn’s disease. Transl Res. 2019;209:39-54. [7] RIEDER F, FIOCCHI C, ROGLER G. Mechanisms, Management, and Treatment of Fibrosis in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(2): 340-350.e6. [8] LOEUILLARD E, BERTRAND J, HERRANEN A, et al. 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced chronic colitis with fibrosis and modulation of TGF-β1 signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(48):18207-18215. [9] DI SABATINO A, JACKSON CL, PICKARD KM, et al. Transforming growth factor beta signalling and matrix metalloproteinases in the mucosa overlying Crohn’s disease strictures. Gut. 2009;58(6):777-789. [10] BETTENWORTH D, RIEDER F. Pathogenesis of Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Perspectives for Therapeutic Implication. Dig Dis. 2017;35(1-2):25-31. [11] MEIJER MJ, MIEREMET-OOMS MA, VAN DER ZON AM, et al. Increased mucosal matrix metalloproteinase-1, -2, -3 and -9 activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and the relation with Crohn’s disease phenotype. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39(8):733-739. [12] EL AGHA E, KRAMANN R, SCHNEIDER RK, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Fibrotic Disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(2):166-177. [13] VOSWINKEL J, FRANCOIS S, SIMON JM, et al. Use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) in chronic inflammatory fistulizing and fibrotic diseases: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2013;45(2):180-192. [14] CAMUSSI G, DEREGIBUS MC, CANTALUPPI V. Role of stem-cell-derived microvesicles in the paracrine action of stem cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013; 41(1):283-287. [15] VAN NIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228. [16] SHOJAATI G, KHANDAKER I, FUNDERBURGH ML, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Corneal Fibrosis and Inflammation via Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Delivery of miRNA. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(11):1192-1201. [17] LAWRANCE IC, WU F, LEITE AZ, et al. A murine model of chronic inflammation-induced intestinal fibrosis down-regulated by antisense NF-kappa B. Gastroenterology. 2003;125(6):1750-1761. [18] MURTHY SN, COOPER HS, SHIM H, et al. Treatment of dextran sulfate sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin. Dig Dis Sci. 1993; 38(9):1722-1734. [19] CHOI YJ, KOO JB, KIM HY, et al. Umbilical cord/placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit fibrogenic activation in human intestinal myofibroblasts via inhibition of myocardin-related transcription factor A. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):291. [20] LI T, YAN Y, WANG B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6): 845-854. [21] BIANCONE L, BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(8): 3037-3042. [22] BURRELLO J, MONTICONE S, GAI C, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Immune-Modulation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:83. [23] WANG B, YAO K, HUUSKES BM, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Deliver Exogenous MicroRNA-let7c via Exosomes to Attenuate Renal Fibrosis. Mol Ther. 2016;24(7):1290-1301. [24] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346. [25] MARDPOUR S, GHANIAN MH, SADEGHI-ABANDANSARI H, et al. Hydrogel-Mediated Sustained Systemic Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improves Hepatic Regeneration in Chronic Liver Failure. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(41):37421-37433. [26] FANG S, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10): 1425-1439. [27] BIER A, BERENSTEIN P, KRONFELD N, et al. Placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells and their exosomes exert therapeutic effects in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Biomaterials. 2018;174:67-78. [28] DOEPPNER TR, HERZ J, GÖRGENS A, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(10):1131-1143. [29] QI X, ZHANG J, YUAN H, et al. Exosomes Secreted by Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Critical-Sized Bone Defects through Enhanced Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(7):836-849. [30] GARCÍA-OLMO D, GARCÍA-ARRANZ M, GARCÍA LG, et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for treatment of rectovaginal fistula in perianal Crohn’s disease: a new cell-based therapy. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2003;18(5):451-454. [31] CARVELLO M, LIGHTNER A, YAMAMOTO T, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Perianal Crohn’s Disease. Cells. 2019;8(7). pii: E764. [32] PHINNEY DG, PITTENGER MF. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells. 2017;35(4):851-858. [33] QIU G, ZHENG G, GE M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles affect disease outcomes via transfer of microRNAs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):320. [34] KESHTKAR S, AZARPIRA N, GHAHREMANI MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):63. [35] HONG P, YANG H, WU Y, et al. The functions and clinical application potential of exosomes derived from adipose mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive review. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):242. [36] TKACH M, THÉRY C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226-1232. [37] RIEDER F, FIOCCHI C. Mechanisms of tissue remodeling in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis. 2013;31(2):186-193. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [5] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [6] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [7] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [8] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [9] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [10] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [11] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [12] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [13] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [14] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [15] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||