Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (21): 3310-3315.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0907
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulation of Smad4 by miRNA-196a-5p influences gastric cancer stem cell characteristics
Guo Rui1, Dai Jian-feng2, Luo Yu-ming1, Zhao Hai-ming1, Tang Peng1
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, the East Branch of Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China; 2College of Forestry and Health, Sichuan Radio and TV University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Revised:2018-05-14Online:2018-07-28Published:2018-07-28 -
Contact:Dai Jian-feng, Master, Lecturer, College of Forestry and Health, Sichuan Radio and TV University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Guo Rui, Master, Attending physician, Department of Gastroenterology, the East Branch of Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of Sichuan Provincial Health and Family Planning Committee in 2017, No. 17PJ041
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Rui, Dai Jian-feng, Luo Yu-ming, Zhao Hai-ming, Tang Peng. Regulation of Smad4 by miRNA-196a-5p influences gastric cancer stem cell characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(21): 3310-3315.
share this article
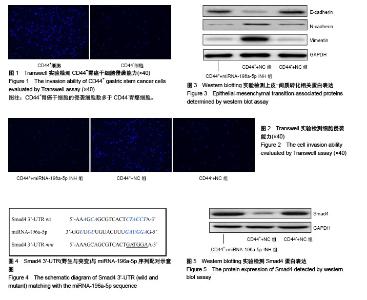
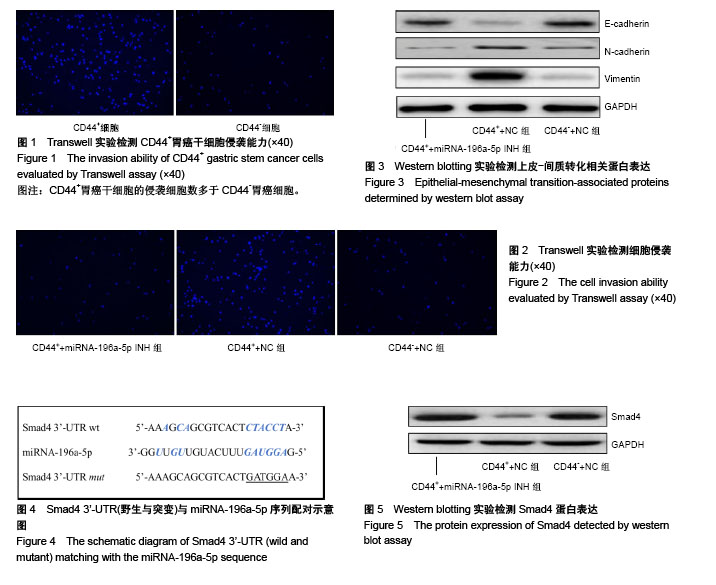
2.1 胃癌干细胞的分选 采用流式细胞术分选胃癌BGC-823细胞系中的肿瘤干细胞,分选前后CD44+细胞百分比分别为(3.58±0.95)%和(94.65±6.47)%,差异有显著性意义(t=-24.121,P=0.000),成功分选得到胃癌干细胞。 2.2 胃癌干细胞的侵袭能力增强 Transwell实验结果显示,CD44+细胞的侵袭细胞数为(169.54±17.24)个,显著高于CD44-细胞(86.49±9.37)个,差异有显著性意义(t=7.331,P=0.001),见图1。 2.3 miRNA-196a-5p调节胃癌干细胞的侵袭能力 Real-time PCR结果显示,CD44+细胞中miRNA-196a-5p相对表达量(4.28±0.59)显著高于CD44-细胞(1.13±0.43),差异有显著性意义(t=7.473,P=0.001)。 Transwell实验结果显示,CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组的侵袭细胞数(75.36±9.24)个,明显低于CD44++NC组(175.64±14.26)个,差异有显著性意义(t=11.385,P=0.000),而CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组与CD44-+NC组[(71.65±6.85)个]之间的侵袭细胞数差异无显著性意义(t=0.559,P=0.303),见图2。 Western blotting实验结果显示,CD44++miRNA- 196a-5p INH组E-cadherin蛋白相对表达量(0.41±0.05)高于CD44++NC细胞(0.11±0.02),差异有显著性意义(t=9.649,P=0.003),CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组与CD44-+NC组(0.43±0.07)之间差异无显著性意义(t=-0.643,P=0.278),见图3;CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组N-cadherin蛋白相对表达量(0.09±0.02)低于CD44++NC组(0.22±0.04),差异有显著性意义(t=-5.422,P=0.003),CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组与CD44-+NC组(0.09± 0.03)之间差异无显著性意义(t=-0.480,P=0.328),见图3;CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组中Vimentin蛋白相对表达量(0.13±0.04)低于CD44++NC组(0.89±0.19),差异有显著性意义(t=-6.780,P=0.001),CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组与CD44-+NC组(0.12±0.03)之间差异无显著性意义(t=0.346,P=0.373),见图3。 2.4 Smad4是miRNA-196a-5p靶基因 生物信息学软件(www.targetscan.org,www.microrna.org)分析结果显示,miRNA-196a-5p与Smad4 mRNA 3’-UTR区域具有潜在结合位点,见图4。Western blotting实验结果显示,CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组Smad4蛋白相对表达量(2.06±0.29)高于CD44++NC组(0.38±0.06),差异有显著性意义(t=9.826,P=0.000),CD44++miRNA-196a-5p INH组与CD44-+NC组(1.98±0.34)之间差异无显著性意义(t=0.310,P=0.386),见图5。 双荧光素酶实验结果显示,miRNA-196a-5p mimics+psicheck-Smad4-wt细胞的相对荧光强度(0.46±0.12)显著低于NC+psicheck-Smad4-wt细胞(1.06±0.14) (t=-5.636,P=0.002),而miRNA-196a-5p mimics+psicheck-Smad4- mut细胞的相对荧光强度(1.02±0.13)与NC+psicheck- Smad4-wt细胞(1.01±0.15)之间差异无显著性意义(t=0.087,P=0.467)。"
| [1] Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, et al. Report of incidence and mortality in China cancer registries, 2009. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013;25(1):10-21.[2] Kim TH, Shivdasani RA. Stomach development, stem cells and disease. Development. 2016;143(4):554-565.[3] Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(4): 271-289.[4] Zhang X, Hua R, Wang X, et al. Identification of stem-like cells and clinical significance of candidate stem cell markers in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(9):9815-9831. [5] Zhang WJ, Zhou ZH, Guo M, et al. High Infiltration of Polarized CD163+ Tumor-Associated Macrophages Correlates with Aberrant Expressions of CSCs Markers, and Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Recurrent Gastric Cancer. J Cancer. 2017;8(3):363-370.[6] Liu S, Clouthier SG, Wicha MS. Role of microRNAs in the regulation of breast cancer stem cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2012;17(1):15-21.[7] Liu N, Zhong L, Zeng J, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-200a associates with tumor proliferation, CSCs phenotype and chemosensitivity in ovarian cancer. Neoplasma. 2015;62(4): 550-559.[8] Lee SJ, Seo JW, Chae YS, et al. Genetic polymorphism of miR-196a as a prognostic biomarker for early breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(6):2943-2949.[9] Gocze K, Gombos K, Juhasz K, et al. Unique microRNA expression profiles in cervical cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013; 33(6):2561-2567.[10] Sun M, Liu XH, Li JH, et al. MiR-196a is upregulated in gastric cancer and promotes cell proliferation by downregulating p27(kip1). Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(4):842-852.[11] Tsai MM, Wang CS, Tsai CY, et al. MicroRNA-196a/-196b promote cell metastasis via negative regulation of radixin in human gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014;351(2):222-231. [12] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(1):7-30.[13] Zhang J, Gan L, Xu MD, et al. The prognostic value of age in non-metastatic gastric cancer after gastrectomy: a retrospective study in the U.S. and China. J Cancer. 2018; 9(7):1188-1199.[14] Yin J, Song JN, Bai ZG, et al. Gastric Cancer Mortality Trends in China (2006-2013) Reveal Increasing Mortality in Young Subjects. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(8):4671-4679.[15] 邹文斌,杨帆,李兆申.中国胃癌诊治关键在于提高早期诊断率[J].浙江大学学报:医学版,2015,44(1):9-14,53. [16] Mitra A, Mishra L, Li S. EMT, CTCs and CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget. 2015;6(13): 10697-10711.[17] Jeong YJ, Oh HK, Park SH, et al. Association between inflammation and cancer stem cell phenotype in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(2):2380-2386.[18] Carmon KS, Gong X, Yi J, et al. LGR5 receptor promotes cell-cell adhesion in stem cells and colon cancer cells via the IQGAP1-Rac1 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(36): 14989-15001. [19] Wang M, Yang F, Qiu R, et al. The role of mmu-miR-155-5p-NF-κB signaling in the education of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by gastric cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2018;7(3):856-868.[20] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, et al. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009;27(5):1006-1020.[21] Han S, Guo J, Liu Y, et al. Knock out CD44 in reprogrammed liver cancer cell C3A increases CSCs stemness and promotes differentiation. Oncotarget. 2015;6(42): 44452-44465.[22] Senel F, Kökenek Unal TD, Karaman H, et al. Prognostic Value of Cancer Stem Cell Markers CD44 and ALDH1/2 in Gastric Cancer Cases. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017;18(9): 2527-2531. [23] Zhang C, Li C, He F, et al. Identification of CD44+CD24+ gastric cancer stem cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011; 137(11):1679-1686.[24] Song Z, Yue W, Wei B, et al. Sonic hedgehog pathway is essential for maintenance of cancer stem-like cells in human gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e17687.[25] Shitara K, Doi T, Nagano O, et al. Dose-escalation study for the targeting of CD44v+ cancer stem cells by sulfasalazine in patients with advanced gastric cancer (EPOC1205). Gastric Cancer. 2017;20(2):341-349.[26] Kulkarni M, Tan TZ, Syed Sulaiman NB, et al. RUNX1 and RUNX3 protect against YAP-mediated EMT, stem-ness and shorter survival outcomes in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2018; 9(18):14175-14192. [27] Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA, et al. EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(2):128-134.[28] Suarez-Carmona M, Lesage J, Cataldo D, et al. EMT and inflammation: inseparable actors of cancer progression. Mol Oncol. 2017;11(7):805-823.[29] Wang J, Wang X, Liu F, et al. microRNA-335 inhibits colorectal cancer HCT116 cells growth and epithelial- mesenchymal transition (EMT) process by targeting Twist1. Pharmazie. 2017;72(8):475-481.[30] Tang CP, Zhou HJ, Qin J, et al. MicroRNA-520c-3p negatively regulates EMT by targeting IL-8 to suppress the invasion and migration of breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(5): 3144-3152.[31] Lu Z, Nian Z, Jingjing Z, et al. MicroRNA-424/E2F6 feedback loop modulates cell invasion, migration and EMT in endometrial carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(69): 114281-114291. [32] Pereira-da-Silva T, Coutinho Cruz M, Carrusca C, et al. Circulating microRNA profiles in different arterial territories of stable atherosclerotic disease: a systematic review. Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;8(1):1-13.[33] Deng Z, He Y, Yang X, et al. MicroRNA-29: A Crucial Player in Fibrotic Disease. Mol Diagn Ther. 2017;21(3):285-294.[34] Ma C, Huang T, Ding YC, et al. MicroRNA-200c overexpression inhibits chemoresistance, invasion and colony formation of human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):6533-6539.[35] Yu D, Shin HS, Lee YS, et al. miR-106b modulates cancer stem cell characteristics through TGF-β/Smad signaling in CD44-positive gastric cancer cells. Lab Invest. 2014;94(12): 1370-1381. [36] Yang JP, Yang JK, Li C, et al. Downregulation of ZMYND11 induced by miR-196a-5p promotes the progression and growth of GBM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;494 (3-4):674-680.[37] Maruyama T, Nishihara K, Umikawa M, et al. MicroRNA-196a-5p is a potential prognostic marker of delayed lymph node metastasis in early-stage tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(2):2349-2363.[38] Zhang W, Li Y. miR-148a downregulates the expression of transforming growth factor-β2 and SMAD2 in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 2016;48(5):1877-1885.[39] Wang XH, Liu MN, Sun X, et al. TGF-β1 pathway affects the protein expression of many signaling pathways, markers of liver cancer stem cells, cytokeratins, and TERT in liver cancer HepG2 cells. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(3):3675-3681.[40] Liu TJ, Guo JL, Wang HK, et al. Semaphorin-7A contributes to growth, migration and invasion of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma through TGF-β-mediated EMT signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(4):1035-1043.[41] Goto M, Osada S, Imagawa M, et al. FAD104, a regulator of adipogenesis, is a novel suppressor of TGF-β-mediated EMT in cervical cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16365.[42] Yang H, Zhan L Yang T, et al. Ski prevents TGF-β-induced EMT and cell invasion by repressing SMAD-dependent signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 2015; 34(1):87-94. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||