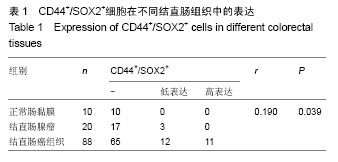
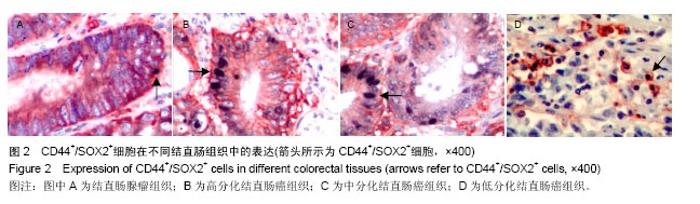
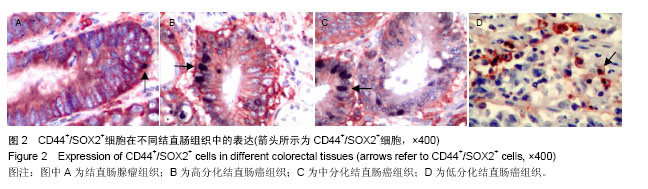
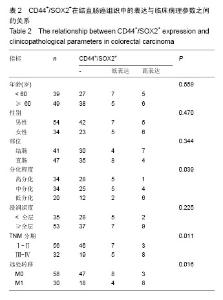
| [1] Alison MR, Islam S, Wright NA. Stem cells in cancer: instigators and propagators. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 14):2357-2368.[2] Todaro M, Francipane MG, Medema JP, et al. Colon cancer stem cells: promise of targeted therapy. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(6):2151-2162.[3] Deng S, Yang X, Lassus H, et al. Distinct expression levels and patterns of stem cell marker, aldehyde dehydrogenase isoform 1 (ALDH1), in human epithelial cancers. PLoS One. 2010;5(4):e10277.[4] Saigusa S, Tanaka K, Toiyama Y, et al. Correlation of CD133, OCT4, and SOX2 in rectal cancer and their association with distant recurrence after chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(12):3488-3498.[5] Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105-111.[6] Dalerba P, Cho RW, Clarke MF. Cancer stem cells: models and concepts. Annu Rev Med. 2007;58:267-284.[7] Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(10):755-768.[8] Han X, Fang X, Lou X, et al. Silencing SOX2 induced mesenchymal-epithelial transition and its expression predicts liver and lymph node metastasis of CRC patients. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41335.[9] Kuzmichev AN, Kim SK, D'Alessio AC, et al. Sox2 acts through Sox21 to regulate transcription in pluripotent and differentiated cells. Curr Biol. 2012;22(18):1705-1710.[10] Fang X, Yu W, Li L, et al. ChIP-seq and functional analysis of the SOX2 gene in colorectal cancers. OMICS. 2010;14(4): 369-384.[11] Hütz K, Mejías-Luque R, Farsakova K, et al. The stem cell factor SOX2 regulates the tumorigenic potential in human gastric cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(4):942-950.[12] Jia X, Li X, Xu Y, et al. SOX2 promotes tumorigenesis and increases the anti-apoptotic property of human prostate cancer cell. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011;3(4):230-238.[13] Herreros-Villanueva M, Zhang JS, Koenig A, et al. SOX2 promotes dedifferentiation and imparts stem cell-like features to pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogenesis. 2013;2:e61.[14] Alonso MM, Diez-Valle R, Manterola L, et al. Genetic and epigenetic modifications of Sox2 contribute to the invasive phenotype of malignant gliomas. PLoS One. 2011;6(11): e26740.[15] 张登才,刘斌,张丽华,等.一种简便实用的组织芯片制作方法[J]. 诊断病理学杂志,2013,20(11):722-724.[16] Kosinski C, Li VS, Chan AS, et al. Gene expression patterns of human colon tops and basal crypts and BMP antagonists as intestinal stem cell niche factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(39):15418-15423.[17] Moossavi S, Ansari R. Intestinal stem cell imaging in colorectal cancer screening. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2013; 9(2):37-39.[18] Yeung TM, Gandhi SC, Wilding JL, et al. Cancer stem cells from colorectal cancer-derived cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(8):3722-3727.[19] Clevers H. The cancer stem cell: premises, promises and challenges. Nat Med. 2011;17(3):313-319.[20] Gires O. Lessons from common markers of tumor-initiating cells in solid cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(24): 4009-4022.[21] Catalano V, Gaggianesi M, Spina V, et al. Colorectal cancer stem cells and cell death. Cancers (Basel). 2011;3(2): 1929-1946.[22] 王欢,马法库,刘斌,等.结直肠癌组织中DCLK1+/Ki67-肿瘤干细胞样细胞的形态和分布[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(10): 1575-1579.[23] 马法库,王欢,刘斌,等. CD44+/C-myc+癌干细胞在结直肠肿瘤中表达及与预后的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(14): 2161-2166.[24] Voutsadakis IA. Pluripotency transcription factors in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer and implications for prognosis. Biomark Med. 2015;9(4):349-361.[25] Masui S, Nakatake Y, Toyooka Y, et al. Pluripotency governed by Sox2 via regulation of Oct3/4 expression in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):625-635.[26] Fong H, Hohenstein KA, Donovan PJ. Regulation of self-renewal and pluripotency by Sox2 in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(8):1931-1938.[27] Alonso MM, Diez-Valle R, Manterola L, et al. Genetic and epigenetic modifications of Sox2 contribute to the invasive phenotype of malignant gliomas. PLoS One. 2011;6(11): e26740.[28] Lu YX, Yuan L, Xue XL, et al. Regulation of colorectal carcinoma stemness, growth, and metastasis by an miR-200c-Sox2-negative feedback loop mechanism. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(10):2631-2642.[29] Han X, Fang X, Lou X, et al. Silencing SOX2 induced mesenchymal-epithelial transition and its expression predicts liver and lymph node metastasis of CRC patients. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41335.[30] 陈尚忠,周自华,邹媚,等.SOX2蛋白在结直肠癌中的表达及临床意义[J].临床肿瘤学杂志,2011,16(11):991-994.[31] Lundberg IV, Edin S, Eklöf V, et al. SOX2 expression is associated with a cancer stem cell state and down-regulation of CDX2 in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:471. [32] Du XM, Wang LH, Chen XW, et al. Prognostic value of Sox2 expression in digestive tract cancers: A meta-analysis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2016;36(3):305-312.[33] Jin Y, Jiang Z, Guan X, et al. miR-450b-5p Suppresses Stemness and the Development of Chemoresistance by Targeting SOX2 in Colorectal Cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2016; 35(5):249-256. [34] Zhou M, Lu Y, Yuan L, et al. Preliminary screening of downstream proteins of Sox2 and role of Sox2 in colonic cancer cell migration and invasion. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014;34(11):1594-1600. |