Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 138-144.doi: 10.12307/2022.956
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of urine-derived stem cells and their exosomes on kidney diseases
Guo Yujun, Lu Wenjun, Yang Shulong, Li Zhaozhu
- Department of Pediatric Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2021-11-23Accepted:2022-01-19Online:2023-01-08Published:2022-06-14 -
Contact:Li Zhaozhu, MD, Chief physician, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Guo Yujun, Master candidate, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81871837 (to LZZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Yujun, Lu Wenjun, Yang Shulong, Li Zhaozhu. Effect of urine-derived stem cells and their exosomes on kidney diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 138-144.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
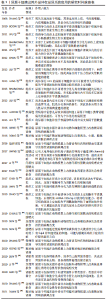
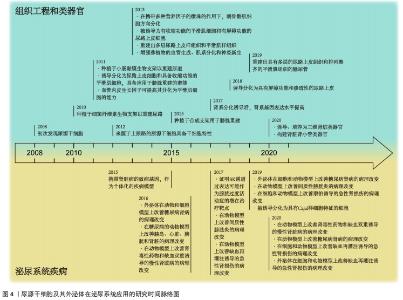
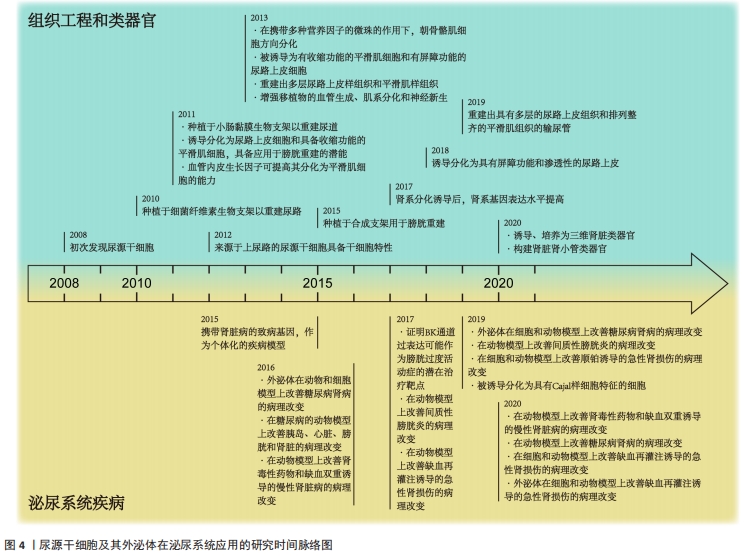
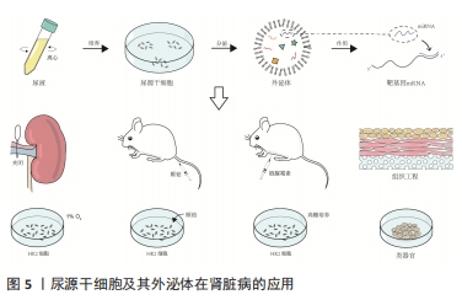
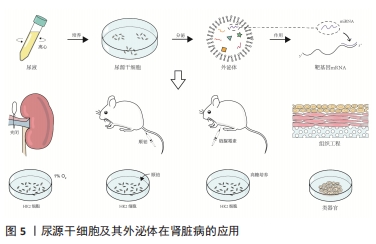
2.1 尿源干细胞及其外泌体的生物学特性 2.1.1 尿源干细胞的生物学特性 近年来,来源于各种成体组织的间充质干细胞不断被发现,并得到广泛研究。ZHANG等[8]于2008年通过离心的方法在尿液中获取了一类在体外具有自我增殖和多向分化潜能的细胞,命名为尿液来源祖细胞,其具有增殖分裂并诱导分化为尿路上皮细胞和平滑肌细胞的潜能。尿源干细胞的提取方法简便,仅需使用离心的方法,配合以适宜的培养基,即可培养出具有增殖活性的细胞克隆[22-23]。稳定传代后,尿源干细胞在光学显微镜下表现出纺锤样或米粒样的外观[24-26]。BHARADWAJ等[9]在体外条件下培养尿源干细胞,发现其在标准培养条件下中具有贴壁生长的能力,并且具有成骨、成脂、成软骨三系分化能力,表达间充质干细胞表面标志物(CD73、CD90、CD105),不表达造血干细胞表面标志物(CD14、CD19、CD34、CD45、HLA-DR),符合国际细胞治疗协会(International Society for Cellular Therapy,ISCT)规定的鉴定多能间充质干细胞的最低标准[27]。随着研究的深入,尿源干细胞的各类表面标志物分子不断被发现。除表达间充质干细胞表面标志物、不表达造血干细胞表面标志物外,尿源干细胞还表达胚胎干细胞标志物(SSEA4、TRA-1-60、TRA-1-81)[9,11,28]、黏附分子(CD29、CD166)[29-32] 、足细胞标志物(CD146)等[22,25,33]。 关于尿源干细胞的来源问题,目前仍未有确切的答案。多数研究者认为,尿源干细胞来源于肾脏[9-11]。一项研究将尿源干细胞的贡献者限定为接受男性供者肾移植的女性受者[9],发现培养出的尿源干细胞均含有人类Y染色体,这一项研究为尿源干细胞来源于肾脏这一假设提供了强有力的证据。基于表面标志物的鉴定,研究者将尿源干细胞的来源更确切地定位在肾小囊壁层细胞或足细胞[9,25,34]。但也有研究者认为尿源干细胞起源于肾小管上皮细胞[35-36]。由于尿源干细胞本身存在于泌尿系统,且很可能来源于肾脏组织,因此,无论是通过直接分化为组织细胞或间接分泌细胞外囊泡发挥作用,尿源干细胞及其细胞外囊泡对于肾脏病的干预作用都更加符合真实的病理生理过程,因此可能具备优于其他间充质干细胞等干预措施的能力。 2.1.2 尿源干细胞来源外泌体的生物学特性 目前,在各类疾病中,关于间充质干细胞发挥作用的形式,绝大多数研究者认为其是通过传递细胞外囊泡发挥作用的[37]。外泌体是各类细胞外囊泡中研究较为深入的一类,它起源于细胞的内体,通过多囊体与细胞膜融合释放至细胞外。外泌体作为细胞间信息交流的运载体,携带核酸、蛋白质等活性物质,可以对多种生物过程产生调节作用[38]。尿源干细胞来源外泌体含有内体蛋白标志物(ALIX、TSG101)、四次跨膜蛋白(CD9、CD63、CD81)[38],此外,还含有肾脏组织特异性蛋白(Nephrin、Wilm’s tumor-1)[39],在缺血再灌注诱导的肾损伤[39-40]、糖尿病肾病[28,41]、骨质疏松[42]、股骨头坏死[43]、椎间盘退变[44]、压力性尿失禁[45]、肢体缺血性损伤等多种疾病的动物、细胞模型中表现出保护作用[46]。 2.2 尿源干细胞及其外泌体在肾脏病的应用 尿源干细胞及其外泌体作为一种干预因素及干细胞来源,已有大量研究探索其在泌尿系统的应用,见表1和图4[8-10,22-24,28,33,39-41,47-66]。文章主要综述尿源干细胞及其外泌体在急性肾损伤、慢性肾脏病(包括糖尿病肾病)以及肾脏组织工程及类器官领域的作用,见图5。 "
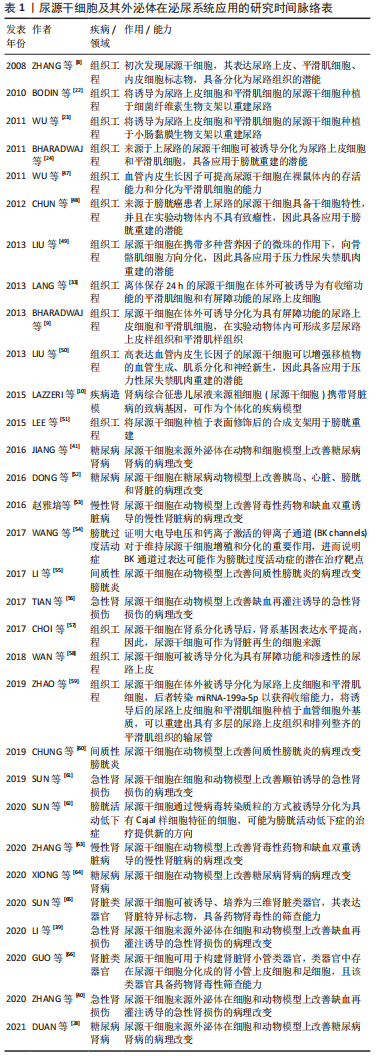
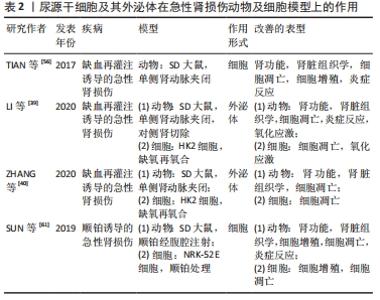
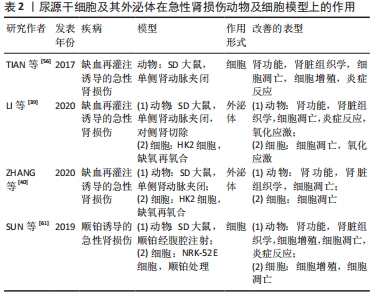
2.2.1 尿源干细胞及其外泌体在急性肾损伤的应用 急性肾损伤是由多种病因引起的,是以短期内血肌酐升高和尿量减少为特征的综合征[67]。在顺铂诱导急性肾损伤的动物和细胞模型上,尿源干细胞被证明具有改善肾功能和组织学改变、促进细胞增殖、调节细胞周期、抑制细胞凋亡和炎症反应的作用[61]。 TIAN等[56]构建肾脏缺血再灌注损伤大鼠模型,将尿源干细胞注射至模型动物肾脏皮质,发现尿源干细胞可以显著降低血肌酐、尿素氮的上升程度,缓解组织学病理学改变,促进肾脏组织细胞增殖,抑制细胞凋亡。在对于尿源干细胞改善急性肾损伤作用机制的探索中,研究者们发现,尿源干细胞干预后炎症因子的表达水平发生明显改变;在转录水平,尿源干细胞处理组较对照组而言促炎细胞因子(干扰素γ、白细胞介素1β)表达明显降低,抗炎细胞因子(白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β1)表达明显上升。 LI等[39]在缺血再灌注诱导的急性肾损伤大鼠及细胞(HK2)模型中,证明了尿源干细胞及其外泌体可以发挥改善肾功能及组织学改变、抑制组织细胞凋亡、降低氧化应激水平、抑制炎症细胞浸润的作用。关于作用机制,研究发现尿源干细胞来源外泌体携带高水平的miR-146a-5p,作用于受体细胞的靶基因IRAK1,通过调控下游信号通路(NF-κB),进而发挥上述作用。 在另外一项缺血再灌注诱导急性肾损伤实验性研究中[40],研究者们发现miR-216a-5p在尿源干细胞来源外泌体中浓集,通过抑制靶基因PTEN的表达,调控下游Akt信号通路,最终改善肾功能和组织学损伤、抑制组织炎症反应和氧化应激,其在缺氧-再氧合的细胞模型中同样可以发挥抑制细胞凋亡和氧化应激水平的作用。 因此,尿源干细胞及其外泌体可以在个体、组织、细胞多个水平上改善多种原因引起的急性肾损伤,见表2[39-40,56,61],且可能是通过转运miRNA发挥作用的。间充质干细胞来源外泌体可能通过其携带的蛋白质、核酸、脂质等各种分子对疾病产生干预作用,当前的研究仅筛选出个别miRNA在尿源干细胞来源外泌体对急性肾损伤的治疗中发挥作用,其他作用机制仍需进一步研究。 "
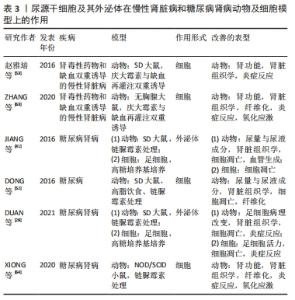
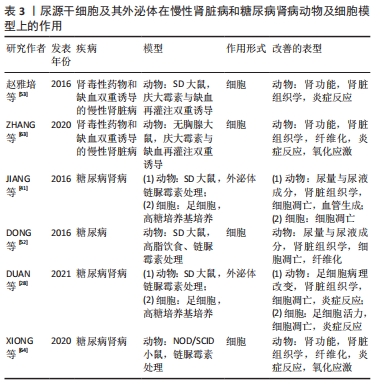
2.2.2 尿源干细胞及其外泌体在慢性肾脏病和糖尿病肾病的应用 慢性肾脏病被定义为存在肾小球滤过率小于60 mL/(min·1.73 m2)的情况或存在肾脏损伤的证据(如白蛋白尿),病程超过3个月[68]。赵雅培等[53]构建缺血再灌注与庆大霉素双重诱导的慢性肾损伤大鼠模型,然后将尿源干细胞注射至肾实质内,结果显示,尿源干细胞干预组相较阳性对照组可以明显降低血肌酐水平、改善肾脏组织学改变、抑制单核细胞浸润。与之相似的另一项研究,ZHANG等[63]构建缺血再灌注与庆大霉素双重诱导的慢性肾损伤裸鼠模型,结果表明,尿源干细胞可以明显降低血肌酐水平、提高远期肾小球滤过率、改善肾脏组织病理学改变(肾小球硬化、肾小管萎缩、胶原沉积、肾间质纤维化)、抑制单核细胞浸润、缓解氧化应激。 作者所在团队正在进行尿源干细胞应用于单侧输尿管梗阻诱导的肾脏损害模型的研究,结果表明尿源干细胞来源外泌体对于肾脏组织纤维化及炎症反应具有明显的改善作用(文章尚未发表)。 糖尿病肾病是糖尿病微血管病变的主要表现之一,是慢性肾脏病的重要类型,是终末期肾脏病的主要原因[69]。关于尿源干细胞及其外泌体对糖尿病肾病干预作用的探索始于JIANG等[41]在链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型上的一项研究。在动物模型上,尿源干细胞可以降低尿蛋白含量、阻止足细胞凋亡、促进肾小球内皮细胞增殖;在高糖培养基诱导足细胞损伤的细胞模型上,尿源干细胞干预可以抑制足细胞凋亡。研究者进一步检测了尿源干细胞条件培养基及外泌体内细胞因子的表达水平,发现血管内皮生长因子、转化生长因子β、血管生成素、骨形态发生蛋白7表达量相较未培养过尿源干细胞的对照组培养基明显升高,这可能是尿源干细胞来源外泌体促进血管内皮增殖的作用机制。 另一项基于链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病小鼠模型上的研究表明[64],尿源干细胞可以改善肾功能和胰岛功能,改善肾脏组织学损伤,抑制组织纤维化和巨噬细胞浸润。相较于阳性对照组,尿源干细胞干预组肾脏组织色素上皮衍生因子的表达水平较高,而色素上皮衍生因子在糖尿病肾病的发生发展中被认为具有抑制炎症和抗氧化应激的保护作用,因此,尿源干细胞对于糖尿病肾病的改善作用可能依赖于色素上皮衍生因子表达水平的上调。 一项关于糖尿病及其各种并发症的研究中[52],尿源干细胞被证明可以在动物模型上显著改善胰岛、肾脏、心室肌、膀胱的结构与功能。对于肾脏而言,尿源干细胞干预后,尿液检查各项指标(红细胞数、24 h尿量、24 h尿蛋白含量、尿肌酐、尿素氮、肌酐清除率)明显优于阳性对照组;组织学检查提示尿源干细胞处理组肾脏组织凋亡细胞数明显低于阳性对照组,且纤维化程度、足细胞损伤程度明显降低。使用荧光标记尿源干细胞的示踪结果显示,仅在肾脏和胰腺检测到荧光标记,心室肌及膀胱组织内并未检测到,说明尿源干细胞不仅通过归巢、分化为受体组织细胞发挥作用,同时也通过旁分泌的形式分泌各种因子发挥作用。 研究表明,糖尿病肾病的发生发展与血管内皮生长因子A诱导的肾脏异常血管生成有关[70-71]。基于这一结果,DUAN等[28]使用在线数据库预测可以调控血管内皮生长因子A的miRNA,选择相关程度最高的miRNA‐16‐5p,并通过慢病毒转染使其在尿源干细胞中高表达。高糖培养基培养的足细胞与高表达miRNA‐16‐5p的尿源干细胞共培养,或转染miRNA‐16‐5p类似物后,足细胞损伤明显改善。动物模型上,尿源干细胞无论是否转染miRNA‐16‐5p,其来源外泌体均可降低肾脏组织足细胞的损伤程度(足细胞形态、数目、足突宽度、系膜区面积、炎症因子水平),但转染miRNA‐16‐5p的尿源干细胞分泌的外泌体表现出更加显著的保护作用。 基于以上研究结果,尿源干细胞及其外泌体对于慢性肾脏病以及糖尿病肾病具有明显的治疗作用,可以延缓慢性肾脏病以及糖尿病肾病的进展,见表3[28,41,52-53,63-64],这对于肾脏病的治疗具有重要意义。关于其分子水平的作用机制,需要在未来进一步研究。由于尿源干细胞表达足细胞标志物(CD146),且其分泌的外泌体具有改善足细胞损伤的作用,进一步增加了尿源干细胞与足细胞同源的可能性。 "

2.2.3 尿源干细胞及其外泌体在肾脏组织工程和类器官领域的应用 肾脏组织工程和再生医学是使用干细胞治疗肾脏病的另外一条具有发展潜力的道路[72]。ZHANG等[8]首次发现尿源干细胞时,因尿路上皮以及平滑肌相关蛋白在尿源干细胞内表达,认为尿源干细胞具有分化为尿路上皮以及尿路平滑肌的潜力,进而猜测尿源干细胞具有应用于泌尿系统组织工程的能力。随着对于尿源干细胞在组织工程领域研究的深入,研究者们成功在体外诱导出具有屏障功能的尿路上皮细胞和具有收缩功能的平滑肌细胞[58-59]。 CHOI等[57]使用肾系分化培养基诱导尿源干细胞,结果提示诱导分化后的尿源干细胞肾系基因表达水平(PAX2、WT1、LIM1、PDGFRA、E-CADHERIN、CD24、ACTB、AQP1、OCLN、NPHS1)随分化程度加深而不断提高,且分化后的尿源干细胞表达更高水平的肾系关键标志物。虽然该研究尚未构建成三维肾脏组织结构,但体现了尿源干细胞在肾脏组织工程和类器官领域的潜力。 肾脏类器官可用于构建三维肾脏疾病模型、研究肾脏病治疗药物、进行肾毒性药物筛检,还可为肾脏再生医学提供可能的供体组织[73]。研究表明,肾脏细胞外基质可以在体外条件下诱导、培养尿源干细胞形成三维肾脏类器官,其与对照组肾脏类器官具有相似的组织形态和肾脏特异标志物表达水平(AQP1、EPO、Podocin、Synaptopodin)。在药物肾毒性筛检方面,尿源干细胞构建的类器官具备与对照组类器官可比的毒性筛查能力[65]。 在另外一项使用肾脏细胞外基质诱导尿源干细胞形成肾脏肾小管类器官的研究中[66],构建的肾小管类器官具有肾小管样组织结构,且表达近端小管上皮细胞标志物(AQP1)和足细胞标志物(Synaptopodin、Nephrin),证明此诱导培养条件可以诱导类器官中的尿源干细胞分化为肾小管上皮细胞和足细胞[64]。在顺铂和丙酮毒性的筛检实验中,肾脏肾小管类器官表达肾损伤标志物(KIM-1、CYP2E1),并产生相应的组织病理学改变。因此,尿源干细胞构建的肾脏肾小管类器官可以作为药物肾毒性的筛检工具。 结合上述研究,尿源干细胞具备干细胞多向分化潜能[35,74-76],相较其他各类间充质干细胞,具备特殊的肾系分化能力,甚至可以诱导、分化为肾脏类器官,进一步证实了尿源干细胞对肾脏病作用的特殊性。关于其来源问题,尿源干细胞可能是具有肾定向分化偏向的间充质细胞,也可能为混合了肾祖细胞与间充质细胞的细胞群。 "

| [1] LEVEY AS, CORESH J. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2012;379(9811):165-180. [2] AL-JAGHBEER M, DEALMEIDA D, BILDERBACK A, et al. Clinical Decision Support for In-Hospital AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(2):654-660. [3] HOSTE EA, BAGSHAW SM, BELLOMO R, et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41(8):1411-1423. [4] CORESH J, SELVIN E, STEVENS LA, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298(17):2038-2047. [5] ZHANG L, WANG F, WANG L, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in China: a cross-sectional survey. Lancet. 2012;379(9818):815-822. [6] LIYANAGE T, NINOMIYA T, JHA V, et al. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet. 2015;385(9981): 1975-1982. [7] KESHTKAR S, AZARPIRA N, GHAHREMANI MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):63. [8] ZHANG Y, MCNEILL E, TIAN H, et al. Urine derived cells are a potential source for urological tissue reconstruction. J Urol. 2008;180(5):2226-2233. [9] BHARADWAJ S, LIU G, SHI Y, et al. Multipotential differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells: potential for therapeutic applications in urology. Stem Cells. 2013;31(9):1840-1856. [10] LAZZERI E, RONCONI E, ANGELOTTI ML, et al. Human Urine-Derived Renal Progenitors for Personalized Modeling of Genetic Kidney Disorders. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26(8):1961-1974. [11] RAHMAN MS, WRUCK W, SPITZHORN LS, et al. The FGF, TGFβ and WNT axis Modulate Self-renewal of Human SIX2+ Urine Derived Renal Progenitor Cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):739. [12] VAN NIEL G, D’ANGELO G, RAPOSO G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213-228. [13] BRUNO S, GRANGE C, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009; 20(5):1053-1067. [14] GATTI S, BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(5):1474-1483. [15] MA J, ZHAO Y, SUN L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59. [16] LU Z, CHEN Y, DUNSTAN C, et al. Priming Adipose Stem Cells with Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Preconditioning Potentiates Their Exosome Efficacy for Bone Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(21-22):1212-1220. [17] CHEW JRJ, CHUAH SJ, TEO KYW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance periodontal ligament cell functions and promote periodontal regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019;89:252-264. [18] HU L, WANG J, ZHOU X, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32993. [19] WANG J, YI Y, ZHU Y, et al. Effects of adipose-derived stem cell released exosomes on wound healing in diabetic mice. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020;34(1):124-131. [20] CAO L, XU H, WANG G, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis by promoting M2 macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;72:264-274. [21] CHEN L, LU FB, CHEN DZ, et al. BMSCs-derived miR-223-containing exosomes contribute to liver protection in experimental autoimmune hepatitis. Mol Immunol. 2018;93:38-46. [22] BODIN A, BHARADWAJ S, WU S, et al. Tissue-engineered conduit using urine-derived stem cells seeded bacterial cellulose polymer in urinary reconstruction and diversion. Biomaterials. 2010;31(34):8889-8901. [23] WU S, LIU Y, BHARADWAJ S, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells seeded in a modified 3D porous small intestinal submucosa scaffold for urethral tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2011;32(5):1317-1326. [24] BHARADWAJ S, LIU G, SHI Y, et al. Characterization of urine-derived stem cells obtained from upper urinary tract for use in cell-based urological tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(15-16):2123-2132. [25] GUAN X, MACK DL, MORENO CM, et al. Dystrophin-deficient cardiomyocytes derived from human urine: new biologic reagents for drug discovery. Stem Cell Res. 2014;12(2):467-480. [26] CHEN AJ, PI JK, HU JG, et al. Identification and characterization of two morphologically distinct stem cell subpopulations from human urine samples. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63(5):712-723. [27] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [28] DUAN YR, CHEN BP, CHEN F, et al. Exosomal microRNA-16-5p from human urine-derived stem cells ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through protection of podocyte. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(23):10798-10813. [29] OUYANG B, SUN X, HAN D, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells alone or genetically-modified with FGF2 Improve type 2 diabetic erectile dysfunction in a rat model. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92825. [30] PEI M, LI J, ZHANG Y, et al. Expansion on a matrix deposited by nonchondrogenic urine stem cells strengthens the chondrogenic capacity of repeated-passage bone marrow stromal cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;356(2):391-403. [31] HE W, ZHU W, CAO Q, et al. Generation of Mesenchymal-Like Stem Cells From Urine in Pediatric Patients. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(6):2181-2185. [32] CHEN L, LI L, XING F, et al. Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells: Potential for Cell-Based Therapy of Cartilage Defects. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:4686259. [33] LANG R, LIU G, SHI Y, et al. Self-renewal and differentiation capacity of urine-derived stem cells after urine preservation for 24 hours. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53980. [34] LIU G, WU R, YANG B, et al. Human Urine-Derived Stem Cell Differentiation to Endothelial Cells with Barrier Function and Nitric Oxide Production. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(9):686-698. [35] KANG HS, CHOI SH, KIM BS, et al. Advanced Properties of Urine Derived Stem Cells Compared to Adipose Tissue Derived Stem Cells in Terms of Cell Proliferation, Immune Modulation and Multi Differentiation. J Korean Med Sci. 2015;30(12):1764-1776. [36] KIM K, GIL M, DAYEM AA, et al. Improved Isolation and Culture of Urine-Derived Stem Cells (USCs) and Enhanced Production of Immune Cells from the USC-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. J Clin Med. 2020;9(3):827. [37] YANG X, XIONG X, ZHOU W, et al. Effects of human urine-derived stem cells on the cementogenic differentiation of indirectly-cocultured periodontal ligament stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(2):361-378. [38] TOH WS, LAI RC, ZHANG B, et al. MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018;46(4):843-853. [39] LI X, LIAO J, SU X, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model via exosomal miR-146a-5p which targets IRAK1. Theranostics. 2020;10(21):9561-9578. [40] ZHANG Y, WANG J, YANG B, et al. Transfer of MicroRNA-216a-5p From Exosomes Secreted by Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Reduces Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:610587. [41] JIANG ZZ, LIU YM, NIU X, et al. Exosomes secreted by human urine-derived stem cells could prevent kidney complications from type I diabetes in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:24. [42] CHEN CY, RAO SS, TAN YJ, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human urine-derived stem cells prevent osteoporosis by transferring CTHRC1 and OPG. Bone Res. 2019;7:18. [43] CHEN CY, DU W, RAO SS, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human urine-derived stem cells inhibit glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by transporting and releasing pro-angiogenic DMBT1 and anti-apoptotic TIMP1. Acta Biomater. 2020;111:208-220. [44] GUO Z, SU W, ZHOU R, et al. Exosomal MATN3 of Urine-Derived Stem Cells Ameliorates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Antisenescence Effects and Promotes NPC Proliferation and ECM Synthesis by Activating TGF-β. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:5542241. [45] WU R, HUANG C, WU Q, et al. Exosomes secreted by urine-derived stem cells improve stress urinary incontinence by promoting repair of pubococcygeus muscle injury in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):80. [46] ZHU Q, LI Q, NIU X, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Promote Ischemia Repair in a Mouse Model of Hind-Limb Ischemia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(3):1181-1192. [47] WU S, WANG Z, BHARADWAJ S, et al. Implantation of autologous urine derived stem cells expressing vascular endothelial growth factor for potential use in genitourinary reconstruction. J Urol. 2011;186(2):640-647. [48] CHUN SY, KIM HT, LEE JS, et al. Characterization of urine-derived cells from upper urinary tract in patients with bladder cancer. Urology. 2012;79(5): 1186.e1-7. [49] LIU G, PARETA RA, WU R, et al. Skeletal myogenic differentiation of urine-derived stem cells and angiogenesis using microbeads loaded with growth factors. Biomaterials. 2013;34(4):1311-1326. [50] LIU G, WANG X, SUN X, et al. The effect of urine-derived stem cells expressing VEGF loaded in collagen hydrogels on myogenesis and innervation following after subcutaneous implantation in nude mice. Biomaterials. 2013;34(34):8617-8629. [51] LEE JN, CHUN SY, LEE HJ, et al. Human Urine-derived Stem Cells Seeded Surface Modified Composite Scaffold Grafts for Bladder Reconstruction in a Rat Model. J Korean Med Sci. 2015;30(12):1754-1763. [52] DONG X, ZHANG T, LIU Q, et al. Beneficial effects of urine-derived stem cells on fibrosis and apoptosis of myocardial, glomerular and bladder cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;427:21-32. [53] 赵雅培,刘翠景,杨翠英,等.人尿源干细胞移植治疗慢性肾病大鼠[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(32):4838-4844. [54] WANG Q, ZHAO J, WU C, et al. Large conductance voltage and Ca2+-activated K+ channels affect the physiological characteristics of human urine-derived stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(4):1876-1885. [55] LI J, LUO H, DONG X, et al. Therapeutic effect of urine-derived stem cells for protamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced interstitial cystitis in a rat model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):107. [56] TIAN SF, JIANG ZZ, LIU YM, et al. Human urine-derived stem cells contribute to the repair of ischemic acute kidney injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16(4):5541-5548. [57] CHOI JY, CHUN SY, HA YS, et al. Potency of Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells for Renal Lineage Differentiation. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;14(6):775-785. [58] WAN Q, XIONG G, LIU G, et al. Urothelium with barrier function differentiated from human urine-derived stem cells for potential use in urinary tract reconstruction. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):304. [59] ZHAO Z, LIU D, CHEN Y, et al. Ureter tissue engineering with vessel extracellular matrix and differentiated urine-derived stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;88:266-279. [60] CHUNG JW, CHUN SY, LEE EH, et al. Verification of mesenchymal stem cell injection therapy for interstitial cystitis in a rat model. PLoS One. 2019; 14(12):e0226390. [61] SUN B, LUO X, YANG C, et al. Therapeutic Effects of Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells in a Rat Model of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury In Vivo and In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:8035076. [62] SUN B, DONG X, ZHAO J, et al. Differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells into interstitial cells of Cajal-like cells by exogenous gene modification: A preliminary study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;523(1):10-17. [63] ZHANG C, GEORGE SK, WU R, et al. Reno-protection of Urine-derived Stem Cells in A Chronic Kidney Disease Rat Model Induced by Renal Ischemia and Nephrotoxicity. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(3):435-446. [64] XIONG G, TAO L, MA WJ, et al. Urine-derived stem cells for the therapy of diabetic nephropathy mouse model. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24(3):1316-1324. [65] SUN G, DING B, WAN M, et al. Formation and optimization of three-dimensional organoids generated from urine-derived stem cells for renal function in vitro. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):309. [66] GUO H, DENG N, DOU L, et al. 3-D Human Renal Tubular Organoids Generated from Urine-Derived Stem Cells for Nephrotoxicity Screening. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(12):6701-6709. [67] KHWAJA A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012;120(4):c179-184. [68] LAMEIRE NH, LEVIN A, KELLUM JA, et al. Harmonizing acute and chronic kidney disease definition and classification: report of a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Consensus Conference. Kidney Int. 2021;100(3):516-526. [69] QI C, MAO X, ZHANG Z, et al. Classification and Differential Diagnosis of Diabetic Nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:8637138. [70] STEVENS M, OLTEAN S. Modulation of VEGF-A Alternative Splicing as a Novel Treatment in Chronic Kidney Disease. Genes (Basel). 2018;9(2):98. [71] NAKAGAWA T, KOSUGI T, HANEDA M, et al. Abnormal angiogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 2009;58(7):1471-1478. [72] MOON KH, KO IK, YOO JJ, et al. Kidney diseases and tissue engineering. Methods. 2016;99:112-119. [73] NISHINAKAMURA R. Human kidney organoids: progress and remaining challenges. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019;15(10):613-624. [74] QIN H, ZHU C, AN Z, et al. Silver nanoparticles promote osteogenic differentiation of human urine-derived stem cells at noncytotoxic concentrations. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:2469-2478. [75] GUAN J, ZHANG J, LI H, et al. Human Urine Derived Stem Cells in Combination with β-TCP Can Be Applied for Bone Regeneration. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0125253. [76] CHUN SY, KIM HT, KWON SY, et al. The efficacy and safety of Collagen-I and hypoxic conditions in urine-derived stem cell ex vivo culture. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;13(4):403-415. |
| [1] | Li Zhen, Liu Hongbao. Influencing factors and mechanism of nanoparticle renal targeting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 453-460. |
| [2] | Lan Qian, Gu Yangcong, Xiao Xin, Bi Xueting, Li Na. Human periodontal ligament stem cells-derived exosomes interfere with the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 54-58. |
| [3] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [4] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| [5] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [6] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [7] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [8] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [9] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [10] | Wang Xue, Liu Yang, Xu Jianfeng, Long Qianfa, Wang Tong, Zhong Jun. Neuroprotective effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on hippocampal neurons in mice with intracerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4928-4934. |
| [11] | Ye Hua, Yang Jiaming, Zhang Jiahong, Niu Yanlong, Wang Maoyuan. Biological role of exosomes in denervated muscle atrophy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5062-5068. |
| [12] | Li Qingru, Zhang Linqi, Chen Xu, Shi Ruoyu, Wang Xixi. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles in the treatment and repair of acute and chronic renal injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5069-5075. |
| [13] | Deng Xiaohui, Zhang Zengzeng, Zhang Zhihua, Zhu Lingyan. Mechanism and application prospects of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes gene-modified microRNA in the treatment of diabetic foot [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5076-5084. |
| [14] | Shen Enpu, Huang Ba, Liu Danping, Qi Hui, Wu Zhiwen, Li Beibei. Exosomes derived from melatonin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4800-4805. |
| [15] | Lin Bo, Chen Xinyu, Jin Qiu, Zhu Zhiman, Zhao Wenhui. Effects of miR-126-3p from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell released exosomes on human umbilical vein endothelial cell glucolipotoxicity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4773-4779. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||