Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (31): 5076-5084.doi: 10.12307/2022.726
Mechanism and application prospects of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes gene-modified microRNA in the treatment of diabetic foot
Deng Xiaohui1, Zhang Zengzeng2, Zhang Zhihua3, Zhu Lingyan1
- 1Department of Endocrinology, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi Province Endocrine and Metabolic Disease Clinical Medicine Research Center, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Department of Joint Surgery, Huangshi Central Hospital, Huangshi 435000, Hubei Province, China; 3Queen Mary College of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-10-25Accepted:2021-11-13Online:2022-11-08Published:2022-04-25 -
Contact:Zhu Lingyan, MD, Associate professor, Department of Endocrinology, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi Province Endocrine and Metabolic Disease Clinical Medicine Research Center, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Deng Xiaohui, Master candidate, Department of Endocrinology, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi Province Endocrine and Metabolic Disease Clinical Medicine Research Center, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160155, No. 81860153 (to ZLY); China Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Committee Hehuang Scientific Research Fund, No. 2019005 (to ZLY); Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, No. 20202ACBL216007 (to ZLY); Education and Teaching Program of Nanchang University, No. NCUYJSJG-2021-068, 20190054 (to ZLY); Science and Technology Plan of Health Commission of Jiangxi Province, No. 20203106 (to ZLY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Deng Xiaohui, Zhang Zengzeng, Zhang Zhihua, Zhu Lingyan. Mechanism and application prospects of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes gene-modified microRNA in the treatment of diabetic foot[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5076-5084.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
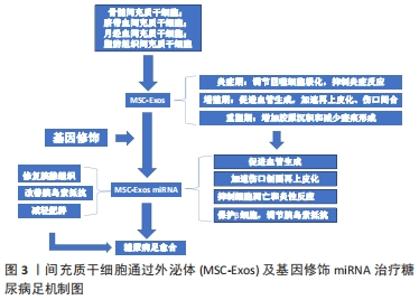
2.1 间充质干细胞外泌体的来源、成分及外泌体 miRNA的特性 外泌体的概念在1980年研究正常细胞和肿瘤细胞脱落小体时首次被提出。随后,在研究绵羊网织红细胞成熟过程中首次被从上清液中分离提纯出来,并称之为“exosome”。外泌体一度被认为是细胞排泄废物的一种方式,如今却在各个领域发挥着至关重要的功能[9]。在生理或病理条件下,间充质干细胞分泌外泌体是直径为30-150 nm、密度为1.10-1.18 g/mL的带有膜的囊泡[10]。间充质干细胞外泌体作为胞内囊泡结构内涵miRNAs、胞质蛋白及mRNA,通过与细胞膜融合后以胞吐形式释放到细胞外,形成间充质干细胞外泌体[11]。同时,各种体液例如唾液、精液、血液、羊水、乳汁均存在其特定的外泌体,外泌体存在广泛、易于获取,且特异性强。 间充质干细胞外泌体主要是由选择性的3种组分组成,包括蛋白质、mRNA和miRNA。鉴于小尺寸、无毒性、靶点转移的特点,间充质干细胞外泌体主要功能是作为一种载体而存在,通过介导其内富含的miRNAs以及蛋白质,通过明确的靶向作用于临近细胞进而介导细胞间的信息交流,参与机体遗传信息交换、血管生成、炎症调节和免疫应答等多个病理生理过程[12]。miRNA是21-23个核苷酸的非蛋白编码RNA分子,在转录后水平作为基因表达的调节因子[13]。在目前的研究中,外泌体蛋白多作为一些癌症的诊断标志物,而miRNA更多地是作为细胞间通讯工具参与调节靶细胞的信息转录调控发挥重要功能。且在间充质干细胞外泌体包含的这些分子中,关于 miRNAs作用的研究最多,间充质干细胞根据所处微环境特异性地调整外泌体 miRNAs的生成与分泌,例如在糖尿病前期受试者和葡萄糖不耐受小鼠中,miR-192 和 miR-193b的丰度均显著增加[14]。外泌体 miRNAs的这种特性,赋予了其作为治疗靶点和生物标志物来提高对诊断和治疗的反应及效果,也使得其广泛应用于各种疾病的治疗成为了可能。 miRNAs在外泌体发挥作用中占有举足轻重的地位,因此该综述着重探讨miRNA的功能[15]。外泌体可包裹miRNA并保持其完整性,miRNA稳定地在细胞之间完成转移,并在受体细胞释放发挥功能,外泌体通过 miRNA的转运实现细胞间的信息交流,介导细胞微环境,调节特异靶细胞的生物学活性以及表型[16],诱导靶细胞功能发生改变,导致一系列生物反应,从而发挥多种生物学功能[17-18],进而发挥治疗作用。 2.2 间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA成为治疗糖尿病足的新策略 糖尿病足的发生主要是由于高糖和炎性环境造成血管生成受损[19],如何控制炎症以及解决患肢血液循环不足、血供差和血运重建在糖尿病足的治疗中尤为重要。间充质干细胞是一类临床上常见的具有多向分化潜能的组织干细胞,它来源于发育早期的中胚层,主要从从骨髓、脐带血、脂肪组织中获取,并且可以方便地实现体外培养、扩增。间充质干细胞具有巨大自我更新能力、免疫调节特性和多系分化潜能而成为组织工程学界的研究热点,可应用于各种疾病引起的损伤的修复,可促进局部受损组织的缺血修复和血管生成[20]。但研究发现间充质干细胞可促进肿瘤形成[21],这极大地限制了间充质干细胞的临床应用。与此同时,从间充质干细胞培养基中分离出的外泌体具有类似于间充质干细胞的修复功能,且无肿瘤形成风险[22],并且间充质干细胞外泌体比间充质干细胞免疫原性低、稳定性高、易于储存[23]。因此间充质干细胞外泌体作为间充质干细胞的替代品更加安全有效,目前已成为促进组织再生的更佳选择。间充质干细胞外泌体包含各种功能蛋白和miRNA分子,而由外泌体运载和转移的miRNA是在细胞与细胞之间联系起最重要作用的分子,同时,miRNA也是在各种疾病治疗中通过抑制炎症、凋亡以及促进血管生成介导愈合发挥最重要功能的活性分子[24]。近年来的研究发现,对间充质干细胞进行特定基因修饰可以改变间充质干细胞外泌体miRNA 组成并改变其生物学特性,间充质干细胞外泌体通过基因修饰miRNA与受体结合,充当细胞间信号转导者,是细胞信号传导中近程和远程中高度保守的细胞因子,能够游离在细胞间隙有效传输多种信号分子[25],进而调节靶细胞中的转录调控,诱导靶细胞功能发生改变,从而达到治疗糖尿病足的效果。间充质干细胞外泌体及其基因修饰miRNA已成为治疗糖尿病足的新策略。接下来,文章将系统阐述间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA治疗糖尿病足的原因、修饰方法以及修饰后的外泌体临床应用面临的问题和挑战,深入探讨间充质干细胞外泌体和外泌体 miRNA基因修饰治疗糖尿病足的研究进展和治疗机制,治疗机制见图3。 "
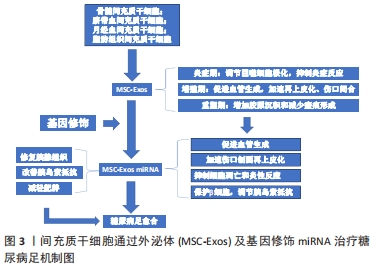
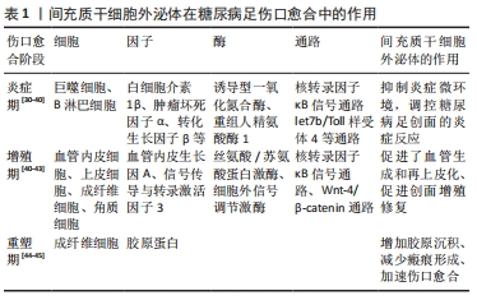
2.2.1 外泌体基因修饰miRNA治疗糖尿病足的原因 随着基因修饰技术的日新月异,其在各种疾病中的应用也越来越广泛。有研究发现通过基因修饰过表达外泌体 miR-214可以直接抑制季戊四醇四硝酸酯、b淋巴细胞瘤-2细胞死亡的相互作用介质(Bim)和促细胞凋亡蛋白(Bax)的抗凋亡作用,改善炎症、促进神经和血管新生,导致对深低温循环停止诱导的大鼠脑损伤的神经保护作用进一步增强[26]。外泌体基因修饰miRNA在其他组织系统疾病取得良好治疗效果,而且如何改善炎症、抗凋亡、促进神经和血管新生正是糖尿病足需要的治疗机制,这不禁引发研究者的思考。糖尿病足的长期不愈合溃疡导致反复感染的难治性创面是否也能使用外泌体基因修饰miRNA来改变糖尿病足正面对的困顿局面。 研究发现,糖尿病足病变组织中各种效应miRNA分子有过表达或者表达降低的情况。有研究发现与正常小鼠相比,糖尿病足小鼠真皮伤口中 miR-497 的表达显著降低,但以调节炎症反应而闻名的 miR-497 会促进糖尿病足伤口愈合[27]。有研究发现与健康对照组相比,糖尿病足患者和大鼠血清miR-217水平显著上调,而抑制miR-217可上调大鼠低氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮细胞生长因子通路,促进糖尿病足大鼠血管新生,改善炎症反应,有效促进溃疡愈合[28]。这些数据反过来揭示了miRNA序列的改变或修正,可以通过抑制致病性或破坏损害型miRNA的功能或恢复基本基因的功能来治疗糖尿病足。这更加确定了文章的想法的正确性。 同时,由于现有治疗措施不仅无法治愈糖尿病足,甚至未能大幅度改善患者的截肢率,这些突出表明迫切需要制定个体化治疗方案。那是否能够通过对各个疾病阶段的患者病变组织进行详细miRNA测序提供有关导致疾病的突变以及特定基因变化(基因型)和疾病严重程度之间相关性的详细信息,进而制定个体化基因修饰miRNA投入糖尿病足的治疗。这是一个诱人的目标,具有改善和拯救糖尿病足患者生命的巨大潜力,最终甚至可能根除许多其他疾病。 2.2.2 间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA基因修饰技术、机制及载体 经典的体内基因靶向修饰方法涉及正常的同源重组,效率低、耗时费力,随着科学的进步,基因组修饰新工具的问世克服了这一难题。迄今为止,有转录激活因子(TALEN)、锌指核酸酶(ZFN)、规律成簇的间隔短回文重复和Cas9 (CRISPR-Cas9)3种技术可用于基因组的靶向编辑。 利用锌指核酸酶和转录激活因子进行基因组修饰,在靶向基因修饰中发挥了重要作用。但是,它们的复杂性、难度和昂贵性限制了使用。随后,研究人员开发出了一种可靠、简单、快速、经济、高效的方法来进行精确的基因组修饰,即规律成簇的间隔短回文重复和Cas9系统,它的问世使得可以在几乎任何生物体和细胞类型中实现熟练的基因组修饰。大量杂交规律成簇的间隔短回文重复和Cas9系统能够修改表观基因组,调节转录,纠正DNA和RNA的突变,具有安全高效稳定的巨大优势[29]。 基因修饰技术需要载体工具的介导来发挥作用。目前,应用较多的载体系统分为3种:病毒、纳米粒子、RNA 纳米粒子(RNP),每一种载体系统都有不同的优点和局限性。病毒载体中腺相关病毒(AAV)在临床最常用,有广泛的组织靶向可能性、高效的优点,但免疫原性高、价格昂贵且持续表达可能导致脱靶效应。纳米粒子价格低廉,免疫原性低但组织靶向能力有限。RNA 纳米粒子(RNP)无基因组整合或长期表达,脱靶效应更少,但在体内具有潜在的免疫原性,无保护的RNA 纳米粒子有降解的可能性[30]。 因此,在未来的动物实验和临床研究中,应该选择一种安全有效的最优化的基因修饰技术和载体工具来实现治疗效果。 2.2.3 间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA的优势、面临的问题和挑战 间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA是一种无细胞疗法,摆脱了间充质干细胞需要面对的很多生物活性问题。首先,可以对外泌体进行过滤灭菌;其次,外泌体的稳定性会延长,对冷冻储存条件的需求会降低;此外,它们可以作为现成产品进行冻干,同时保留其功能[21]。总之,与细胞疗法相比,这些方法不仅可以降低制造成本,而且使用起来更加安全有效。 但是,间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA的应用也面临着很多问题和挑战。首先是如何通过改变细胞培养微环境和基因修饰来操纵间充质干细胞分泌足量的外泌体来满足治疗需求。同时,要实现临床转化,改进的外泌体表征和可大规模使用的分离方法,以及不受培养基污染的成分是至关重要的。其次,开发和选择一种安全高效的给药方式也是面对的一大挑战,外泌体输送组织修复最常见的方式是直接向损伤部位局部注射外泌体,但通过批量注射的外泌体可被机体迅速隔离和清除[31],大量组织工程研究发现壳聚糖水凝胶创面敷料具有止血、抗菌、生物降解和生物相容性,可以提供外泌体的可控释放,是缓释材料的良好载体[32];而壳聚糖创面敷料也可以提供外泌体的持续释放[33],因此,在未来的研究中,利用组织工程技术,将间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA与具有控释功能的生物材料结合更加准确稳定地掌控miRNA的靶向释放和传输可能是一种有前景的伤口愈合新疗法。再者,基因修饰有可能引起miRNA靶点的改变,从而改变下游信号,因此需要强调量化的复杂性和考虑绝对编辑水平的重要性。外泌体中的其他各种生物活性因子可能会产生意想不到的副反应,需要寻找一种纯化外泌体组分的技术,以达到治疗效果的同时尽量避免副反应。此外,最近的一项研究表明,基因修饰后,可能会因罕见易位导致癌症,编辑的miRNA分子可能发挥与野生型miRNA相同的作用,它们的失调可能赋予致癌特性[34],虽然这些事件发生的频率极低,但它们对投入临床治疗却极其重要,因此,外泌体对肿瘤发生的潜在副反应应进行长期监测评估。但在最终开发安全有效的间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA在糖尿病足的临床应用方面,相信随着技术的提升以及动物实验、临床试验的深入,没有不可逾越的障碍。 2.3 间充质干细胞外泌体在治疗糖尿病足方面的研究进展 伤口愈合是一个多阶段的、复杂的生物学过程,包括3个不同且相互重叠的阶段:炎症期、增殖期和重塑期[35]。有许多因素可以破坏愈合过程,例如糖尿病足可通过不同的病理生理机制干扰创面愈合过程,如延长炎症和缺氧、细胞功能障碍、血管生成和新生血管受损以及神经病变。与此同时,许多不同类型的细胞和生物活性分子有助于协调糖尿病足伤口损伤修复。研究发现,在各种动物模型中,间充质干细胞外泌体对糖尿病足组织再生和伤口愈合有显著作用[36]。间充质干细胞外泌体参与多种生理病理过程,如炎症微环境调节、机体免疫调节、组织损伤与修复、参与细胞内信号传导和细胞间通讯等[37]。间充质干细胞外泌体促进糖尿病足创面愈合的具体作用[30-45],见表1。 "
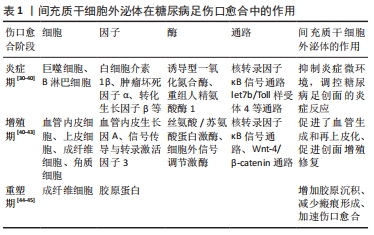
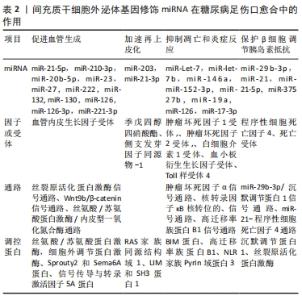
2.3.1 炎症期 炎症是一种普遍存在于多种疾病的基本机制,并驱动各种伤口愈合事件发生[38]。严重和长期的炎症与糖尿病足慢性和不可愈合的伤口有关[39]。巨噬细胞是重要的免疫细胞,参与组织止血、肉芽组织形成和伤口愈合等免疫反应。巨噬细胞被分为2个主要亚组:M1或促炎巨噬细胞、M2或抗炎巨噬细胞。研究表明M1巨噬细胞可产生白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎细胞因子,M2巨噬细胞可产生转化生长因子β、血管内皮生长因子等抗炎细胞因子[40-41]。因此,在调节糖尿病足炎症反应中巨噬细胞极化起着不可或缺的作用[42]。在糖尿病足中,M1到M2的转化受损,M2巨噬细胞相关基因如重组人精氨酸酶1的表达在糖尿病足创面中显著下调[43-44]。研究表明,脂肪来源的间充质干细胞外泌体可以促进体外M1-M2巨噬细胞极化[45]。核转录因子κB信号通路是巨噬细胞激活和极化调节的重要信号通路,有研究发现,人脐带来源的间充质干细胞外泌体通过下调与巨噬细胞极化和炎症分解相关的Toll样受体4和核转录因子κB/P65等基因激活M2巨噬细胞[46]。脂多糖预处理的间充质干细胞外泌体通过let7b/Toll样受体4途径促进巨噬细胞极化,这是巨噬细胞极化的一个公认途径[47]。间充质干细胞外泌体抑制激活磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶通路和削弱蛋白激酶的磷酸化,通过促进表达季戊四醇四硝酸酯进而调节 M1/M 2极化率。这抑制了糖尿病足伤口的炎症反应,加速了从炎症阶段到组织再生阶段的快速过渡[48-49]。研究证明,经血来源的间充质干细胞外泌体可以通过降低诱导型一氧化氮合酶活性诱导巨噬细胞从M1型向M2型极化,调节B 淋巴细胞的活化、分化和增殖,抑制炎症微环境,调控糖尿病足创面的炎症反应[50]。 2.3.2 增殖期 增殖期主要包含血管、成纤维细胞和角质细胞的增殖。创面的愈合速度和重塑程度由创面血管化程度决定。血管生成不足是糖尿病足创面的一个特点,它产生较少的血管内皮生长因A,导致愈合速度缓慢。在糖尿病足缺血组织的促血管生成过程中间充质干细胞外泌体起着核心作用。研究发现,经血来源的间充质干细胞外泌体通过上调血管内皮生长因A促进新血管生成、增加了新生血管的数量[50]。有研究发现,人脐带来源的间充质干细胞外泌体通过Wnt-4介导的β-catenin通路激活诱导创面血管生成[51]。此外,脂肪来源的间充质干细胞外泌体可增加内皮细胞增殖和血管生成[52]。有研究指出,骨髓源性间充质干细胞外泌体,可由丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶、细胞外信号调节激酶和信号传导与转录激活因子3等伤口愈合的重要信号通路介导增强促血管生成活性[53]。同时,也有研究证实,人脐带来源的间充质干细胞外泌体通过wnt-4介导的β-catenin激活正调控上皮细胞的增殖和迁移。间充质干细胞外泌体通过刺激角质形成细胞和成纤维细胞的增殖和迁移,并能促进弹性蛋白和胶原蛋白的合成[51]。研究发现,经血来源的间充质干细胞外泌体通过核转录因子κB p65亚基的上调和核转录因子κB信号通路的激活,增加角质细胞增殖介导皮肤创伤修复,促进了再上皮化、伤口闭合和血管生成,促进创面增殖[50]。 2.3.3 重塑期 瘢痕形成是糖尿病足皮肤损害组织重塑期的一部分,也是整个创面愈合的最终阶段。成纤维细胞和毛细血管增殖形成的肉芽组织的主要组成部分是Ⅰ型和Ⅲ型胶原。然而,Ⅰ型胶原蛋白在成人伤口中占主导地位。在早期肉芽组织中Ⅲ型胶原蛋白增加,当胶原蛋白合成转向Ⅰ型胶原蛋白时,伤口收缩。经血来源的间充质干细胞外泌体通过Ⅰ型胶原mRNA上调导致再上皮化和伤口闭合率增加,Ⅰ型/Ⅲ型胶原比值下降,减少瘢痕形成,使得糖尿病足的不愈合创面得到有效改善[54]。此外,人脐带来源的间充质干细胞外泌体通过增加胶原沉积和减少瘢痕形成来加速伤口愈合[55]。 2.4 间充质干细胞外泌体的基因修饰miRNA与糖尿病足治疗 2.4.1 间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA 作为糖尿病足信息性生物标志物和治疗靶点 miRNA具有很多功能,例如miR-21,miR-27b等用于调节转录后通过与靶标mRNA的结合来表达基因,从而导致mRNA降解,达到翻译抑制甚至基因抑制或激活的效果。研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA治疗能够诱导生理效应[56-57]。间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA 可作为信息性生物标志物和治疗靶点。由于它可以使用相对较少的样本量通过易于获得的技术轻松测量,因此大多数研究都集中在循环 miRNA上,优先分析血液中存在的 miRNA群体。报告支持循环 miRNA作为糖尿病足生物标志物的价值,含有miR-155和miR-142-3p、miR-142-5p的间充质干细胞外泌体,可以以活性形式转移到有利于细胞凋亡的β细胞中。受体β细胞中这些miRNA的失活可避免间充质干细胞外泌体介导的细胞凋亡并防止糖尿病小鼠糖尿病足的发展[58]。葡萄糖耐受时可检测到miR-148a,miR-146,miR-126,miR-34a,miR-30d和miR-24有不同程度的增加,miR-122,miR-133,miR-210与糖尿病足疾病进展呈现相关性,miR-375与β细胞损伤有关[59-60]。细胞外 miRNA,例如miR-126减少或miR-193b和miR-192增加[61-62],表明处于糖尿病前期,从而可以早期识别有风险的受试者,把握预防性治疗的有效时机,进而防止糖尿病足的发生和发展。与此同时,糖尿病足患者对治疗的反应也可通过循环 miRNA进行动态测评。糖尿病足患者也可以在药物治疗或运动干预后通过改善血糖控制使miRNA趋于正常化[63]。间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA在作为糖尿病足治疗靶标和早期诊断、疗效评估和预后判定诊断生物标志物中显示出巨大的潜力[64-65]。 2.4.2 间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA治疗糖尿病足的优势 虽然间充质干细胞外泌体对糖尿病足创面的损伤修复有正性调控作用,但限制性太大,可操作空间太小,缺乏一种可调控的技术使其发挥更丰富高效的功能。而基因修饰技术与间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA结合的方法完美地弥补了这个缺陷,给糖尿病足的治疗翻开了新的篇章。基因修饰不仅改善了外泌体的功能,而且可以根据治疗需要对间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA进行个体化的精确编辑,进而改变间充质干细胞外泌体 miRNA 组成并改变其生物学特性,miRNA通过参与转录调控基因表达,以达到安全高效的糖尿病足治疗作用。间充质干细胞外泌体的基因修饰miRNA是治疗糖尿病足的后起之秀。近年来,随着间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA广泛应用于各种糖尿病并发症治疗,并在器官与组织再生修复领域取得显著效果,其在糖尿病足的修复中也引起越来越多研究者的重视。 2.4.3 间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰 miRNA在糖尿病足伤口愈合中的功能及作用 间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰 miRNA可以通过参与转录调控基因表达并通过促进血管生成、加速伤口创面再上皮化、抑制凋亡和炎症反应、调节细胞再生、保护β细胞调节胰岛素抵抗,在糖尿病足伤口愈合中起重要康复作用[66]。使用间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA来治疗糖尿病足及其他糖尿病并发症已经取得了许多进展,其在糖尿病足伤口愈合中的作用见表2。"
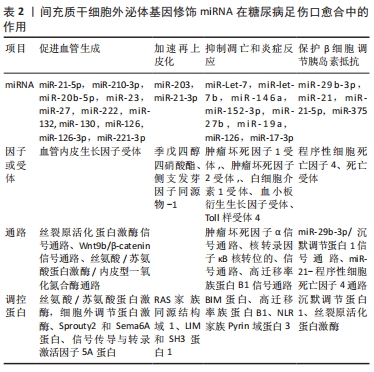
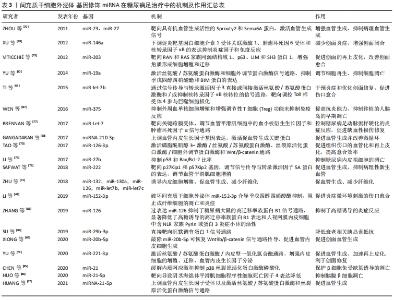
促进血管生成:缺氧是组织损伤最普遍的因素之一,血管的生成对于创面组织的营养和氧供应至关重要,研究显示脐带源间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-21-5p通过上调血管内皮生长因子受体以及激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路促进血管生成,促进糖尿病足缺血组织修复[67]。miR-210-3p也可通过上调血管内皮生长因子基因表达并激活促血管生成关键蛋白(如SRC,丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,细胞外调节蛋白激酶)来促进血管生成并改善微循环[68]。敲除miR-20b-5p可恢复 Wnt9b/β-catenin 信号通路传导,促进血管内皮细胞生成促进创面血管生成,显著促进创面愈合[69]。miR-23和miR-27通过靶向具有抗血管生成活性的Sprouty2和Sema6A蛋白,激活血管生成信号,增强血管生成。同时还可以抑制体外血管生成和出生后视网膜血管在体内的发育,抑制病理血管生成[70]。脂肪源间充质干细胞外泌体穿梭miR-222通过靶向p27Kip1和p57Kip2基因,在调节血管平滑肌细胞增殖中发挥关键作用,同时可以通过调节信号传导与转录激活因子5A蛋白的表达,抑制DR晚期可能发生的病理性新生血管。在视网膜组织修复中的重要作用[71]。脂肪源间充质干细胞外泌体含有一些促血管生成(miR-132,miR-130a和miR-126)的miRNA和一个抗纤维化的miRNA家族(miR-let7b和miR-let7c)。在体外可以促进血管生成,并减少纤维化,诱导内皮细胞增殖,恢复糖尿病大鼠体内勃起功能[72]。滑膜间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-126-3p过表达可以激活磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶/丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/细胞外调节蛋白激酶,以及与血管形成密切相关的Wnt/β-catenin 通路,可以激活血管生成,增加肉芽组织的形成,加速再上皮化,并促进体内胶原的成熟,加快组织愈合修复[73]。阿托伐他汀预处理的间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-221-3p上调通过激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶/内皮型一氧化氮合酶通路增强内皮细胞的增殖、迁移、血管内皮生长因子分泌等生物学功能,促进血管生成和肉芽组织形成生成,加速再上皮化和伤口再生,从而加速糖尿病创面修复。不仅增加了新生血管的数量,而且提高了它们的成熟度[74]。 加速伤口创面再上皮化:损伤部位的内源性细胞迁移和增殖是组织愈合级联过程中不可分割的步骤。表皮源间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-203下调可以通过靶向RAN和RAS家族同源结构域1、p63、LIM和SH3蛋白1,从而增强角质形成细胞增殖和迁移来积极促进皮肤创面的再上皮化,改善创面愈合[75]。脐带源间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-21-3p能够抑制季戊四醇四硝酸酯和侧支发芽因子同源物1,改善成纤维细胞功能和促进血管生成,有助于加速再上皮化、减少瘢痕宽度,加速皮肤伤口愈合[76]。 抑制凋亡和炎症反应、调节细胞再生:细胞凋亡在缺血等损伤后的组织损伤中发挥作用,炎症的消除对于组织的愈合至关重要,过表达miR-Let-7可以靶向关键跨膜受体(肿瘤坏死因子1受体,肿瘤坏死因子2受体,白细胞介素1受体,血小板衍生生长因子受体),以防止与炎症、血管粘连和纤维化有关的关键蛋白的上调。在调节血管平滑肌细胞中的血小板衍生生长因子和肿瘤坏死因子α信号通路中发挥重要作用,直接影响平滑肌细胞的增殖、迁移、单核细胞黏附和核转录因子κB激活,控制糖尿病足动脉粥样硬化的炎症反应,促进缺血性损伤修复[77]。脂多糖预处理的间充质干细胞外泌体穿梭的miR-let-7b通过信号传导与转录激活因子3直接或间接激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶和/或抑制核转录因子κB核转位的信号通路,靶向调控Toll样受体4参与巨噬细胞极化,以更好地干预炎症反应和维持组织稳态,优化创面修复,促进糖尿病足皮肤伤口愈合[47]。间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-146a可以下调促炎靶基因白细胞介素1受体关联激酶1、肿瘤坏死因子6受体和核转录因子κB的表达抑制炎症因子和免疫反应,减少创面炎症,增强创面闭合[78]。破坏间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-152-3p介导的季戊四醇四硝酸酯抑制,从而阻止成纤维细胞的凋亡和炎症,促进糖尿病足炎症微环境刺激的伤口愈合[48]。miR-27b可以通过抑制 p53 和 Bax/Bcl-2 比率抑制糖尿病内皮祖细胞的凋亡[79]。miR-19a可以激活丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶和细胞外调节蛋白激酶信号通路、抑制季戊四醇四硝酸酯和BIM蛋白的表达、调节细胞再生、抑制细胞凋亡[80]。间充质干细胞外泌体过表达miR-126成功地抑制了糖尿病大鼠的高迁移率族蛋白B1信号通路,显著降低了高糖诱导的高迁移率族蛋白B1表达和人视网膜内皮细胞中含NLR家族Pyrin域蛋白3炎症小体的活性,抑制了炎症反应,改善高血糖诱导的视网膜炎症[81]。脐带间充质干细胞外泌体 miR -17-3p通过靶向信号转导与转录激活因子1可降低糖尿病视网膜病变小鼠血糖和糖化血红蛋白,增加体质量、血红蛋白含量和血糖水平,降低炎症因子和血管内皮生长因子含量,减轻氧化损伤,通过抑制信号转导与转录激活因子1抑制视网膜细胞凋亡。改善糖尿病视网膜病变小鼠的炎症反应和抗氧化损伤[39]。 保护β细胞、修复胰腺组织、改善肥胖及胰岛素抵抗:1,2型糖尿病患者均伴有不同程度的胰岛损伤。通过促进胰岛再生和提高胰岛素靶组织的敏感性,可以延缓糖尿病及其并发症的进展,从源头避免糖尿病足的发生,这是一种糖尿病患者的潜在新治疗方法[82-83]。骨髓源间充质干细胞外泌体 miR-29b-3p下调直接靶向沉默调节蛋白1,miR-29b-3p/沉默调节蛋白1信号通路通过与靶miRNA的3’ un翻译区(3’ UTR)或蛋白编码序列相互作用发挥其功能,可以显著降低衰老相关胰岛素抵抗[84]。间充质干细胞外泌体通过miR-21缓解内质网应激和抑制p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶磷酸化来保护β细胞免受缺氧诱导的凋亡,使糖尿病足患者受益[85]。间充质干细胞外泌体递送miR-21-5p靶向导致阴茎海绵体平滑肌细胞程序性细胞死亡因子4表达降低,刺激海绵体平滑肌增殖,抑制凋亡,从而减轻糖尿病大鼠勃起功能障碍。同时作为一种具有促炎作用的选择性蛋白翻译抑制剂,沉默程序性细胞死亡因子4在饮食诱导的肥胖、白色脂肪组织炎症和胰岛素抵抗中发挥抑制作用miR-21-程序性细胞死亡因子4轴通过抑制胰腺β细胞死亡对1型糖尿病的保护作用[86]。过表达干扰死亡受体和抗-miR-375的骨髓源间充质干细胞外泌体,可以沉默人胰岛的死亡受体和miR-375,抑制外周血单核细胞增殖和增强调节性T细胞(Treg)功能来抑制免疫反应,并提高它们的活力和抗炎症细胞因子的功能,可抑制移植的人胰岛的早期凋亡,改善胰岛移植[87]。间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰miRNA在糖尿病足治疗中的机制及作用汇总表,见表3。 "
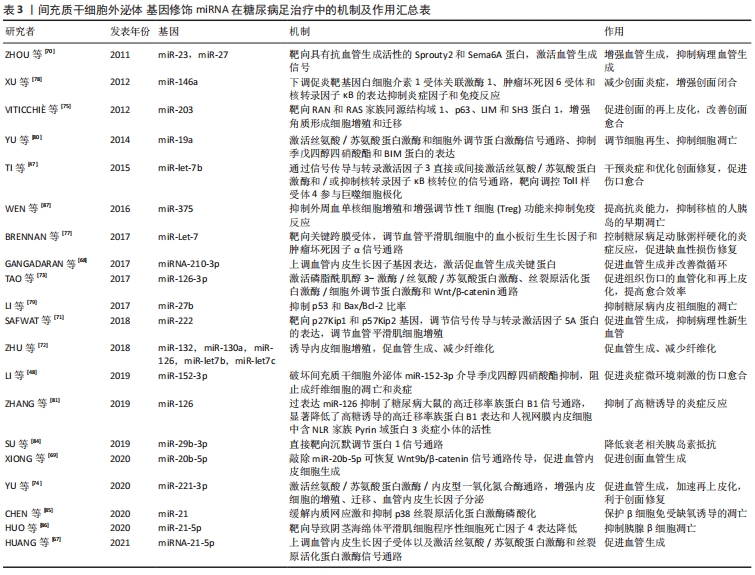
| [1] MENDIS S, DAVIS S, NORRVING B. Organizational update: the world health organization global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2014; one more landmark step in the combat against stroke and vascular disease. Stroke. 2015; 46(5):e121-e122. [2] HUANG Y, KARURANGA S, MALANDA B. Call for data contribution to the IDF Diabetes Atlas 9th Edition 2019. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;140:351-352. [3] WU A, CHEN B, LIANG Z. Mesenchymal stem cells as a prospective therapy for the diabetic foot. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:4612167. [4] MUHS BE, GAGNE P, SHEEHAN P. Peripheral arterial disease: clinical assessment and indications for revascularization in the patient with diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2005;5(1):24-29. [5] CHEN Y, YU B, XUE G. Effects of storage solutions on the viability of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2013; 22(6):1075-1086. [6] SAYED N, WU JC. Translation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells: from clinical trial in a dish to precision medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;67(18):2161-2176. [7] GYORGY B, SZABO TG, PASZTOI M. Membrane vesicles, current state-of-the-art: emerging role of extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(16):2667-2688. [8] HUANG YZ, GOU M, DA LC. Mesenchymal stem cells for chronic wound healing: current status of preclinical and clinical studies. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(6): 555-570. [9] JOHNSTONE RM. Exosomes biological significance: A concise review. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2006;36(2):315-321. [10] KOMAKI M, NUMATA Y, MORIOKA C. Exosomes of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells stimulate angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1): 219. [11] MATHIEU M, MARTIN,JAULAR L, LAVIEU G. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):9-17. [12] LIU J, LI W, WANG Y. Islet-1 overexpression in human mesenchymal stem cells promotes vascularization through monocyte chemoattractant protein-3. Stem Cells. 2014;32(7):1843-854. [13] KIM VN, HAN J, SIOMI MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(2):126-139. [14] PARRIZAS M, BRUGNARA L, ESTEBAN L. Circulating miR-192 and miR-193b are markers of prediabetes and are modulated by an exercise intervention. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E407-E415. [15] DENG F, MILLER J. A review on protein markers of exosome from different bio-resources and the antibodies used for characterization. J Histotechnol. 2019; 42(4):226-239. [16] FERGUSON SW, WANG J, LEE CJ. The microRNA regulatory landscape of MSC-derived exosomes: a systems view. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):1419. [17] KOUREMBANAS S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13-27. [18] PHINNEY DG, DI GIUSEPPE M, NIAH J. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun. 2015;6: 8472. [19] MATHIYALAGAN P, LIANG Y, KIM D. Angiogenic mechanisms of human CD34+ stem cell exosomes in the repair of ischemic hindlimb. Circ Res. 2017;120(9):1466-1476. [20] MENDELSON A, FRENETTE PS. Hematopoietic stem cell niche maintenance during homeostasis and regeneration. Nat Med. 2014;20(8):833-846. [21] Yu JM, JUN ES, BAE YC. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissues favor tumor cell growth in vivo. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(3):463-473. [22] COSENZA S, TOUPET K, MAUMUS M. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics. 2018;8(5):1399-1410. [23] ZHANG ZG, BULLER B, CHOPP M. Exosomes -beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(4):193-203. [24] BRENNAN MA, LAYROLLE P, MOONEY DJ. Biomaterials functionalized with MSC secreted extracellular vesicles and soluble factors for tissue regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(37):1909125. [25] THUMA F, ZOLLER M. Outsmart tumor exosomes to steal the cancer initiating cell its niche. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;28:39-50. [26] SHI J, JIANG X, GAO S. Gene-modified exosomes protect the brain against prolonged deep hypothermic circulatory arrest. Ann Thorac Surg. 2021;111(2): 576-585. [27] BAN E, JEONG S, PARK M. Accelerated wound healing in diabetic mice by miRNA-497 and its anti-inflammatory activity. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121: 109613. [28] LIN CJ, LAN YM, QU MQ. Expression of miR-217 and HIF-1α/VEGF pathway in patients with diabetic foot ulcer and its effect on angiogenesis of diabetic foot ulcer rats. J Endocrinol Invest. 2019;42(11):1307-1317. [29] GUPTA D, BHATTACHARJEE Q, MANDAL D. CRISPR-Cas9 system: A new-fangled dawn in gene editing. Life Sci. 2019;232:116636. [30] DOUDNA JA. The promise and challenge of therapeutic genome editing. Nature. 2020;578(779214):229-236. [31] ZHANG S, CHU WC, LAI RC. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(12):2135-2140. [32] Wang C, Wang M, Xu T, et al. Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(1):65-76. [33] Tao SC, Guo SC, Li M. Chitosan wound dressings incorporating exosomes derived from microRNA-126-overexpressing synovium mesenchymal stem cells provide sustained release of exosomes and heal full-thickness skin defects in a diabetic rat model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):736-747. [34] MADDALO D, MANCHADO E, CONCEPCION CP. In vivo engineering of oncogenic chromosomal rearrangements with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Nature. 2014;516 (7531):423-427. [35] GURTNER GC, WERNER S, BARRANDON Y, Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321. [36] ZHANG J, GUAN J, NIU X. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J Transl Med. 2015;13:49. [37] COLOMBO M, RAPOSO G, THERY C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255-289. [38] ALLER MA, ARIAS JL, NAVA MP. Posttraumatic inflammation is a complex response based on the pathological expression of the nervous, immune, and endocrine functional systems. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2004;229(2):170-181. [39] LANDEN NX, LI D, STAHLE M. Transition from inflammation to proliferation: a critical step during wound healing. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(20):3861-3885. [40] VERRECK FA, DEBOER T, LANGENBERG DM. Human IL-23-producing type 1 macrophages promote but IL-10-producing type 2 macrophages subvert immunity to (myco) bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(13):4560-4565. [41] GORDON S, MARTINEZ FO. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity. 2010;32(5):593-604. [42] MANTOVANI A, SOZZANI S, LOCATI M. Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002 Nov;23(11):549-555. [43] YANEZ-MO M, SILJANDER PR, ANDREU Z. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27066. [44] FINLEY PJ, DECLUE CE, SELL SA. Diabetic wounds exhibit decreased Ym1 and arginase expression with increased expression of IL-17 and IL-20. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2016;5(11):486-494. [45] LO SICCO C, REVERBERI D, BALBI C. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as mediators of anti-inflammatory effects: endorsement of macrophage polarization. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):1018-1028. [46] LI X, LIU L, YANG J. Exosome derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell mediates miR-181c attenuating burn-induced excessive inflammation. EBioMedicine. 2016;8:72-82. [47] TI D, HAO H, TONG C. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med. 2015;13:308. [48] LI B, LUAN S, CHEN J. The MSC-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 promotes wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers by upregulating PTEN via microRNA-152-3p. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:814-826. [49] LIU W, YU M, XIE D. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):259. [50] DALIRFARDOUEI R, JAMIALAHMADI K, JAFARIAN AH. Promising effects of exosomes isolated from menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell on wound-healing process in diabetic mouse model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019; 13(4):555-568. [51] ZHANG B, WANG M, GONG A. HucMSC-exosome mediated-wnt4 signaling is required for cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells. 2015;33(7):2158-2168. [52] LIANG X, ZHANG L, WANG S. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stem cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis by transferring miR-125a. J Cell Sci. 2016; 129(11):2182-2189. [53] SHABBIR A, COX A, RODRIGUEZ-MENOCAL L. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes induce proliferation and migration of normal and chronic wound fibroblasts, and enhance angiogenesis in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(14):1635-1647. [54] VOLK SW, WANG Y, MAULDIN EA. Diminished type III collagen promotes myofibroblast differentiation and increases scar deposition in cutaneous wound healing. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;194(1):25-37. [55] ZHANG J, CHEN C, HU B. Exosomes derived from human endothelial progenitor cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing by promoting angiogenesis through Erk1/2 signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 2016;12(12):1472-1487. [56] THOMOU T, MORI MA, DREYFUSS JM. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature. 2017;542(7642):450-455. [57] JIANG N, XIANG L, HE L. Exosomes mediate epithelium-mesenchyme crosstalk in organ development. ACS Nano. 2017;11(8):7736-7746. [58] GUAY C, KRUIT JK, ROME S. Lymphocyte-derived exosomal microRNAs promote pancreatic β cell death and may contribute to Type 1 diabetes development. Cell Metab. 2019;29(2):348-361.e6. [59] DDLIC D, EISELE C, SCHMID R. Characterization of micro-RNA changes during the progression of type 2 diabetes in zucker diabetic fatty rats. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17(5):665. [60] SEYHAN AA, NUNEZ LOPEZ YO. Pancreas-enriched miRNAs are altered in the circulation of subjects with diabetes: a pilot cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:31479. [61] ZAMPETAKI A, KIECHL S, DROZDOV L. Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res. 2010; 107(6):810-817. [62] PARRIZAS M, BRUGNARA L, ESTEBAN Y. Circulating miR-192 and miR-193b are markers of prediabetes and are modulated by an exercise intervention. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E407-E415. [63] SANTOVITO D, DE NARDIS V, MARCANTONIO P. Plasma exosome microRNA profiling unravels a new potential modulator of adiponectin pathway in diabetes: effect of glycemic control. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(9):E1681-E1685. [64] SCHNEIDER MR. MicroRNAs as novel players in skin development, homeostasis and disease. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166(1):22-28. [65] MOURA J, BORSHEIM E, CARVALHO E. The role of microRNAs in diabetic complications-special emphasis on wound healing. Genes (Basel). 2014;5(4):926-956. [66] NING MS, ANDL T. Control by a hair’s breadth: the role of microRNAs in the skin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(7):1149-1169. [67] HUANG C, LUO W, WANG Q. Human mesenchymal stem cells promote ischemic repairment and angiogenesis of diabetic foot through exosome miRNA-21-5p. Stem Cell Res. 2021;52:102235. [68] GANGADARAN P, RAJENDRAN RL, LEE HW. Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells activates VEGF receptors and accelerates recovery of hindlimb ischemia. J Control Release. 2017;264:112-126. [69] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN, C. Circulating exosomal miR-20b-5p inhibition restores wnt9b signaling and reverses diabetes-associated impaired wound healing. Small. 2020;16(3):e1904044. [70] ZHOU Q, GALLAGHER R, UFRET-VINCENTY R. Regulation of angiogenesis and choroidal neovascularization by members of microRNA-23~27~24 clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(20):8287-8292. [71] SAFWAT A, SABRY D, RAGIAE A. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuate retina degeneration of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rabbits. J Circ Biomark. 2018;7:1849454418807827. [72] ZHU LL, HUANG X, YU W. Transplantation of adipose tissue-derived stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorates erectile function in diabetic rats. Andrologia. 2018. doi: 10.1111/and.12871. [73] TAO SC, GUO SC, LI M. Chitosan wound dressings incorporating exosomes derived from microrna-126-overexpressing synovium mesenchymal stem cells provide sustained release of exosomes and heal full-thickness skin defects in a diabetic rat model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):736-747. [74] YU M, LIU W, LI J. Exosomes derived from atorvastatin-pretreated MSC accelerate diabetic wound repair by enhancing angiogenesis via AKT/eNOS pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):350. [75] VITICCHIE G, LENA AM, CIANFARANI F. MicroRNA-203 contributes to skin re-epithelialization. Cell Death Dis. 2012;3(11):e435. [76] HU Y, RAO SS, WANG ZX. Exosomes from human umbilical cord blood accelerate cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Theranostics. 2018;8(1):169-184. [77] BRENNAN E, WANG B, MCCLELLAND A. Protective effect of let-7 miRNA family in regulating inflammation in diabetes-associated atherosclerosis. Diabetes. 2017;66(8):2266-2277. [78] XU J, WU W, ZHANG L. The role of microRNA-146a in the pathogenesis of the diabetic wound-healing impairment: correction with mesenchymal stem cell treatment. Diabetes. 2012;61(11):2906-2912. [79] LI H ,LIU J, WANG Y. MiR-27b augments bone marrow progenitor cell survival via suppressing the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in Type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2017;313(4):E391-E401. [80] YU B, KIM HW, GONG M. Exosomes secreted from GATA-4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells serve as a reservoir of anti-apoptotic microRNAs for cardioprotection. Int J Cardiol. 2015;182:349-360. [81] ZHANG W, WANG Y, KONG Y. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells modulate miR-126 to ameliorate hyperglycemia-induced retinal inflammation via targeting HMGB1. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60(1):294-303. [82] GUAY C, REGAZZI R. Exosomes as new players in metabolic organ cross-talk. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;19 Suppl 1:137-146. [83] MAHDIPOUR E, SALMASI Z, SABETI N. Potential of stem cell-derived exosomes to regenerate β islets through Pdx-1 dependent mechanism in a rat model of type 1 diabetes. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):20310-20321. [84] SU T, Su T, XIAO Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal miR-29b-3p regulates aging-associated insulin resistance. ACS Nano. 2019;13(2): 2450-2462. [85] CHEN J, CHEN J, CHENG Y. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect beta cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis via miR-21 by alleviating ER stress and inhibiting p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):97. [86] HUO W, LI Y, ZHANG Y. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-21-5p downregulates PDCD4 and ameliorates erectile dysfunction in a rat model of diabetes mellitus. FASEB J. 2020;34(10):13345-13360. [87] WEN D, PENG Y, LIU D. Mesenchymal stem cell and derived exosome as small RNA carrier and Immunomodulator to improve islet transplantation. J Control Release. 2016;238:166-175. [88] XIONG J, HU H, GUO R. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes as a new strategy for the treatment of diabetes complications. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12: 646233. [89] AN T, CHEN Y, TU Y. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: application and challenges. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(2):369-378. |
| [1] | LIU Danni, SUN Guanghua, ZHOU Guijuan, LIU Hongya, ZHOU Jun, TAN Jinqu, HUANG Xiarong, PENG Ting, FENG Wei-bin, LUO Fu. Effect of electroacupuncture on apoptosis of neurons in cerebral cortex of rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury at "Shuigou" and "Baihui" points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [3] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [4] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [8] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [9] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [10] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [11] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [12] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [13] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [14] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [15] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||