Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 91-98.doi: 10.12307/2022.977
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neural differentiation and neural biomarker expression of dental pulp stem cells
Xi Hualei, Xue Bing, Xu Wanqiu, Xu Xiaohang, Yao Lihong, Wang Xiumei
- Department of Oral Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-06Accepted:2022-02-16Online:2023-01-08Published:2022-06-06 -
Contact:Wang Xiumei, MD, Chief physician, Department of Oral Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Xi Hualei, Master candidate, Department of Oral Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150000, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, No. ZD2019H002 (to WXM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xi Hualei, Xue Bing, Xu Wanqiu, Xu Xiaohang, Yao Lihong, Wang Xiumei. Neural differentiation and neural biomarker expression of dental pulp stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 91-98.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
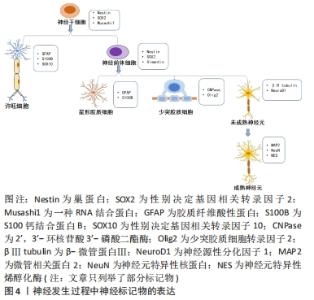
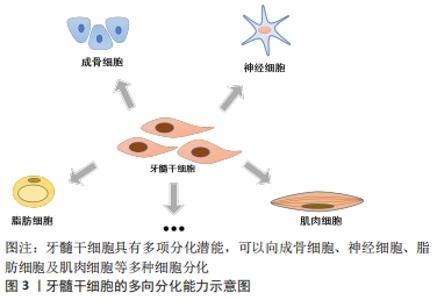
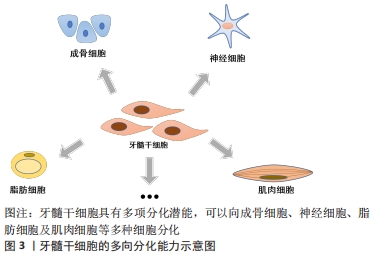
目前已知牙髓干细胞的细胞表面标记物有CD13,CD29,CD44,CD73,CD90,CD105,CD106,CD146,CD166,CD271,Stro-1和Stro-3,而CD3,CD8,CD11b(或CD14),CD15,CD19(或CD79α),CD33,CD34,CD45,CD71,CD117和 HLA-DR均为阴性[6]。并且与间充质干细胞相似,它们都具有分化为神经细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞、成肌细胞和成骨细胞等细胞的能力[7],同时表达相应的标记物。成骨细胞标记物,如骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白4、矮小相关转录因子2和Ⅰ型胶原;成软骨细胞标记物,如Ⅱ型胶原;成脂肪细胞标记物,如瘦素、脂肪蛋白和过氧化物酶体增殖物激活的受体γ;成肌细胞标记物,如结蛋白、肌生成素、肌球蛋白和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白,充分体现了牙髓干细胞的干细胞特性。牙髓干细胞作为一种来源于牙髓的间充质干细胞,取材方便,在拔除的第三磨牙、脱落的乳牙[8]、甚至已证实在不可逆性牙髓炎的牙髓中也含有牙髓干细胞[4],不存在伦理争议,而且免疫原性低。与其他干细胞(骨髓间充质干细胞和脂肪干细胞)相比,牙髓干细胞表现出更强的增殖能力和免疫调节能力[9-10]。同时,牙髓干细胞具有血管化特性,可以加速血液流动,增强组织修复[11]。 由于牙髓干细胞起源于神经嵴,在适当的刺激下,牙髓干细胞能够分化为神经样干细胞并表达典型的神经标记物,如巢蛋白、βⅢ微管蛋白、微管相关蛋白2、神经元特异性烯醇化酶等神经源性标记物等[12]。同时表现出与功能性神经元相同的钠电流,形成了电压依赖性钠离子和钾离子通道[13]。此外,牙髓干细胞在体外可以产生一些具有神经保护作用的神经营养因子,例如神经生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子、神经营养因子3、血管内皮生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子,这些神经营养因子在体外具有神经再生功能及保护作用,如脑源性神经营养因子可以促进发育中和成年脊椎动物神经系统中神经元的存活、分化和维持[14];碱性成纤维细胞生长因子在体外能促进细胞增殖、抑制细胞凋亡、维持骨髓间充质干细胞的干性[15]。此外,它还被证实能促进内源性神经前体细胞的增殖和分化[16]。随着神经营养因子的表达减少,神经元再生的能力和许旺细胞支持再生神经元的能力也有所下降[17]。牙髓干细胞衍生因子也被报道过介导神经再生,研究证明牙髓干细胞来源的趋化因子CXCL12是引导轴突沿着生长轨迹再生的一个重要因素[18]。 牙髓干细胞这种新型干细胞,因其干细胞性、神经源性及来源的广泛性等多种特性使其在多种疾病治疗领域具有重大意义,通过对其更加深入的研究,向其他领域的学者更加全面立体地展现牙髓干细胞的优势,为更多疾病的治疗提供干细胞来源。 2.2 神经源性标记物 随着对牙髓干细胞的研究深入,已经有研究证明牙髓干细胞在适当的微环境下可以分化为功能性神经元[19-20]。 在脑源性神经营养因子、神经营养因子3和胶质细胞源性生长因子等内源性神经营养因子作用下促进牙髓干细胞的神经分化,并且分化的细胞显示出功能性神经细胞活动[21]。YANG等[22]在体外分离鉴定牙髓干细胞,将标记后的干细胞植入脊髓损伤大鼠的脊髓内,发现部分移植细胞存活并分化为成熟神经元和少突胶质细胞并表达神经元特异核蛋白、髓鞘碱性蛋白等神经标记物。ULLAH等[23]将牙髓干细胞移植到大鼠坐骨神经损伤模型中,发现移植的细胞部分分化为神经细胞,轴突纤维和髓鞘的特异性标记物均增加,同时大鼠的行为活动明显改善。以上研究表明牙髓干细胞在神经再生和神经治疗领域具有广阔的应用前景。但其鉴定过程中,对于标记物的选择未有统一的观点。以下总结牙髓干细胞向神经细胞分化表达的标记物及其在文章所查近来发表文献中的使用频次,有助于为未来研究牙髓干细胞向神经细胞分化时标记物的选择及作用机制提供参考,见图4。 "
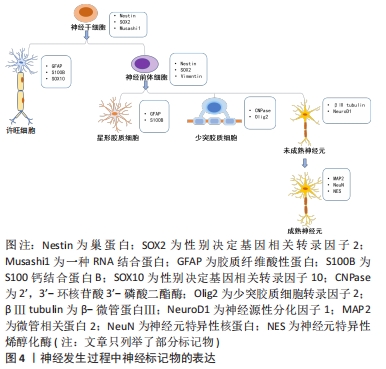

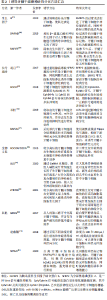
2.2.1 巢蛋白 是一种中间丝蛋白,它与波形蛋白或α-内联蛋白共同组装形成一个异二聚体卷曲复合体形成中间丝[8]。巢蛋白在胚胎发育早期的神经上皮表达,在成年神经干细胞、未成熟的神经前体细胞、各种神经系统肿瘤细胞、移植到神经系统干细胞以及在大脑和脊髓受损时均表达升高[24],在细胞分化时消失[25],常被用作神经干细胞标记物。在神经发生过程中,巢蛋白通过其在星形胶质细胞到神经干细胞的Notch信号中的作用负向调节神经元的分化和存活[26]。当巢蛋白基因敲除后,细胞自我更新能力降低,细胞凋亡增加,表明巢蛋白具有细胞保护作用[27]。在胚胎发育过程中,早期发育阶段的大多数巢蛋白阳性细胞处于活跃的增殖状态,一旦这些细胞停止分裂并参与分化,巢蛋白的表达将被下调[28-29]。通过采用表皮生长因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、肝素等生长因子诱导牙髓干细胞,诱导后的牙髓干细胞对巢蛋白表达明显增强,且细胞形态与神经元相似,并具有增殖分化为神经元的能力[30]。其他研究也报道了牙髓干细胞在体外进行神经预诱导后巢蛋白的表达明显提高,而继续诱导后,胶质细胞和神经元标记物表达升高[31-32],巢蛋白的表达下降[33-35]。以上表明巢蛋白在神经发生过程中可用作神经前体细胞标记物,其他标记物的表达也提示了牙髓干细胞发生了进一步的分化。 2.2.2 性别决定基因相关转录因子2(SRY-related HMGbox-containing transcription factor-2,SOX2) 是SOX转录因子家族的成员,它编码一个高度保守的DNA结合基序,称为HMG(高迁移率组)盒,在哺乳动物发育的不同阶段发挥重要作用。SOX2在胚胎干细胞和发育中的成年神经干细胞中高表达[25],是神经干细胞标记物,被认为是神经干细胞增殖和分化的关键。在成人大脑中,SOX2阳性细胞能够产生分化细胞和相同的SOX2阳性细胞,这表明它们具有多潜能和自我更新的能力[36]。MAURIZIO等[37]研究发现,SOX2缺陷小鼠的神经干细胞产生的成熟神经元数量减少,并表现出明显的分化缺陷。而另一项研究发现,在正常的胚胎神经管中SOX2过表达会阻止这些细胞的分化,并保持它们的自我更新[38]。 实验将牙髓干细胞经脑源性神经营养因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子等生长因子处理后,检测到巢蛋白和SOX2等神经前体标记物的表达上调,并且发现细胞形态发生明显改变[27]。在诱导牙髓干细胞向神经元分化的过程中,SOX2表达也开始下调[39]。因此,SOX2可能在胚胎和成年神经元的成熟和(或)存活过程中发挥作用。 2.2.3 βⅢ微管蛋白(βⅢ tubulin) 被认为是一种神经元特异性标记分子,属于神经元早期标记物,参与细胞骨架的组成,与神经元嵴细胞的迁移有关。该蛋白在神经元前体有丝分裂纺锤体中检测到,在未成熟神经元中呈阳性表达[40]。在研究证明,诱导牙髓干细胞向神经分化,当细胞停止增殖开始分化时,βⅢ tubulin表达增加[35, 41]。除了神经元,已有研究证明在未分化的干细胞,例如在骨髓间充质干细胞、脂肪干细胞和牙髓干细胞中均有表达[42],推测其可能是多数干细胞共有特征,所以将其作为神经元分化的惟一证据使用需进一步评估。但可能牙髓干细胞的神经发生特性可以使其在没有神经诱导的情况下自发分化为神经元样细胞,表达了神经元特异性标记物。另外在某些恶性肿瘤中也检测到[43-44],提示βⅢ tubulin的表达与细胞的有丝分裂有关。 2.2.4 胶质纤维酸性蛋白 是一种维持星形胶质细胞机械强度的中间丝蛋白,表达于神经分化末期的星形胶质细胞,在中枢神经系统损伤后胶质纤维酸性蛋白的表达也明显升高[45],是星形胶质细胞的一个众所周知的标记物[46]。成年后部分区域胶质纤维酸性蛋白的表达升高,与该区域的反应性星形胶质细胞增加相对应,衰老过程中的这种增加是大脑老化最普遍的标志之一[45]。以往的实验也验证缺乏胶质纤维酸性蛋白小鼠的星形胶质细胞间距不规则,半桥粒数量减少且细胞结构紊乱。在诱导牙髓干细胞向神经元分化的过程,多采用此蛋白检测是否有形成星形胶质细胞。在大量实验中也已得到验证,牙髓干细胞经神经诱导后,神经元特异性烯醇化酶、神经元特异性核蛋白和微管相关蛋白2等神经元标记物大量表达,而胶质纤维酸性蛋白的表达呈阴性,表示神经元或神经元样细胞的形成[14, 29, 32, 34]。 2.2.5 S100钙结合蛋白B(S100B) 是一种相对分子质量为21 000的同源二聚体结构蛋白,属于钙介导的多基因蛋白家族,由星形胶质细胞合成,对胶质细胞、神经元和小胶质细胞发挥自分泌和旁分泌作用,特异性地表达于中枢神经系统[47]。S100B主要分布于胶质细胞和许旺细胞中,其含量低但却非常稳定[48]。因其是一种钙结合蛋白,参与了多种细胞内功能的钙依赖性调节,如蛋白磷酸化、酶活性、细胞增殖和分化、细胞骨架成分的动态变化、膜的结构组织、细胞内Ca2+稳态、炎症和保护细胞免受氧化损伤[45]。临床研究表明,生理浓度下的S100B参与神经元和胶质细胞的生长、增殖和激活;浓度过量时会引起细胞凋亡,从而促进其作为炎症和退行性神经疾病研究的标记物的潜在作用[49]。有人将在体外预处理的牙髓干细胞移植到坐骨神经缺损处,检测到大量有髓轴突,同时移植的细胞S100B表达升高,形态发生改变[50],提示可能形成许旺细胞。 2.2.6 微管相关蛋白2 是微管相关蛋白家族的成员,是一种与成熟中枢神经系统中的神经细胞骨架相连的蛋白,标记于突触前和突触后的两侧,被认为与微管组装有关,而微管组装是神经发生的必要步骤[51]。胶质细胞在分化早期表达微管相关蛋白2,但成熟脑中微管相关蛋白2的主要来源是神经元,微管相关蛋白2对于神经元的树突发育是必不可少的,因此被用作神经元标记物[52]。同时,微管相关蛋白2的免疫反应性可以作为一种敏感的IHC标记物来表征阿尔茨海默病脑组织中淀粉样斑块的类型[53]。研究表明,预诱导期微管相关蛋白2的表达较低,提示细胞在这一阶段没有完全分化,并且是未成熟的。而在诱导阶段,大多数神经元在分化和成熟过程中巢蛋白的表达减少,而神经元标记物微管相关蛋白2表达增加[33, 39, 41]。 2.2.7 神经元特异性核蛋白 是一种神经元特异性核蛋白,在大多数神经元细胞核中表达的标记物,但它只在有丝分裂后神经元中表达[54]。神经元特异性核蛋白蛋白在整个个体发育过程中的表达仅与神经组织有关,除神经组织外,在其他组织中尚未检测到该标记物。此外,该蛋白从未在胶质细胞中被检测到,这表明它是一种特殊的神经元标记物[55]。但在一些小脑细胞、视网膜内核层细胞、脊髓中的γ运动神经元和交感神经链的神经节细胞未见神经元特异性核蛋白表达。并且在某些疾病和特定的生理状态下,神经元特异性核蛋白染色是可变的,甚至会消失[56],所以建议在某些疾病和特定生理状态下应用神经元特异性核蛋白免疫反应作为成熟神经元的明确标记物时应慎重。研究发现,将分化的牙髓干细胞注射到大鼠的脑脊液中,它们整合到受损的脑实质中并存活了4周,并检测到神经元特异性核蛋白等神经元标记物的表达,提示可能形成神经元[33]。 2.2.8 神经元特异性烯醇化酶 是糖酵解酶烯醇化酶的细胞特异性同工酶,它是神经元和神经内分泌细胞内的一种糖酵解酶[49]。在脊椎动物中,存在3种不同基因表达的烯醇化酶同工酶:烯醇化酶α是普遍存在;烯醇化酶β是肌肉特异性的;而烯醇化酶γ是神经元特异性的。烯醇化酶γγ和αγ-二聚体的表达是神经分化的晚期事件,因此它是神经成熟的指标。神经元特异性烯醇化酶是神经元和外周神经内分泌细胞高度特异的标记物[57], 但星形胶质细胞对神经元特异性烯醇化酶也呈阳性免疫细胞化学反应。神经元特异性烯醇化酶活性的变化与许多由神经损伤引起的神经系统疾病密切相关[14]。 文章总结了神经标记物在牙髓干细胞中的表达及临床意义,见表1。 "

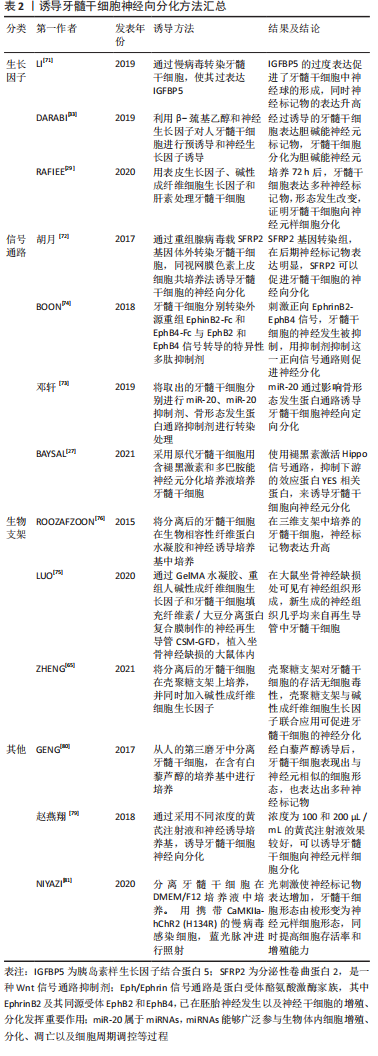
2.3 牙髓干细胞的神经分化方法 研究证实,牙髓干细胞在无神经诱导条件下培养时,在显微镜下可观察到一些神经样细胞;而在基础培养基中单纯培养时,也能观察到一些神经样细胞[17],这一现象表明牙髓干细胞具有强烈的神经分化倾向。近年来,在对牙髓干细胞的功能特征和机制研究的基础上,牙髓干细胞向神经方向分化做了大量的研究,已有了显著的成果,多数采用以下几类方法: 2.3.1 生长因子诱导 采用神经生长因子诱导牙髓干细胞向神经细胞分化。有研究先利用β-巯基乙醇对牙髓干细胞进行预诱导,再使用神经生长因子对牙髓干细胞进行神经诱导,使其分化为胆碱能神经元,结果显示,预诱导使细胞成为神经母细胞,在这一阶段细胞没有完全分化,并且是未成熟的;经神经生长因子的神经诱导后,牙髓干细胞明显表达巢蛋白、神经丝蛋白160、微管相关蛋白2a和Cha T,表明胆碱能神经元的形成[33]。还有研究表明将转化生长因子β3联合牙髓干细胞可促进实验兔面神经再生,同时检测到兔的S100蛋白和巢蛋白的高表达,证实了牙髓干细胞可定向分化为神经细胞[69]。RAFIEE等[29]将牙髓干细胞经表皮生长因子/碱性成纤维细胞生长因子处理后,巢蛋白、微管相关蛋白2、神经元素1等神经元标记物也出现了高表达。但MEHRI等[39]证明,在脑源性神经营养因子的作用下,这些神经球的形成速度比表皮生长因子/碱性成纤维细胞生长因子更快;此外,在脑源性神经营养因子处理的细胞中观察到更大的集落。近几年发现神经因子相关载体蛋白也能促进牙髓干细胞神经向分化。胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白5 (Insulin‐like growth factor‐binding protein 5,IGFBP5)是胰岛素样生长因子的载体蛋白,可调节胰岛素样生长因子的活性[70]。使用慢病毒感染的方式使IGFBP5在牙髓干细胞内过表达可上调神经源性标记物(巢蛋白、βⅢ-tubulin等)的表达,促进了牙髓干细胞中巢蛋白和βⅢ-tubulin阳性神经球的百分比。并且在大小和数量上都增强了牙髓干细胞的神经球形成[71]。在神经分化培养基中加入神经营养因子改变了细胞骨架的动力学,促进了神经元的成熟[35]。 2.3.2 调节信号通路 通过一些信号分子影响神经发育过程的信号通路,从而促进牙髓干细胞的神经分化,例如分泌性卷曲蛋白2(secreted frizzled related protein 2,SFRP2)通过抑制Notch及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促使牙髓干细胞向神经样细胞分化[72]。同时也有文献证明,阻断Notch信号可能会促进神经元基因的表达,并促进神经前体细胞向神经元分化。Notch信号可以通过抑制包括神经母细胞特异性转录因子1在内的神经元转录因子来调节神经前体的维持和抑制神经元的分化[26]。另据研究表明,miR-20能够通过激活骨形态发生蛋白信号通路,从而诱导乳牙牙髓干细胞向神经元样细胞定向分化[73]。研究证实,Eph/Ephrin信号通路是蛋白受体酪氨酸激酶家族,其中EphrinB2及其同源受体EphB2和EphB4,已在胚胎神经发生以及神经干细胞的增殖、分化发挥重要作用。有研究通过刺激正向EphrinB2-EphB4信号,发现牙髓干细胞的神经发生明显被抑制,而用抑制剂抑制这一正向信号通路则促进神经分化[74]。BAYSAL等[27]使用褪黑素激活Hippo信号通路,抑制下游的效应蛋白YES相关蛋白,YES相关蛋白是细胞增殖主要调节因子,从而诱导牙髓干细胞向神经元分化。 2.3.3 生物支架 对牙髓干细胞进行预支架可以更好地发挥其向神经分化的潜能,也是目前一种很有前途的组织工程方法。使用GelMA水凝胶、重组人碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和牙髓干细胞填充纤维素/大豆分离蛋白复合膜制作的神经再生导管CSM-GFD,治疗大鼠坐骨神经缺损,能够使神经的功能得以恢复,并观察到几乎所有缺损部位新形成的神经组织都来源于CSM-GFD中外源性牙髓干细胞的直接分化[75]。将牙髓干细胞与壳聚糖支架和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子共培养也可促进牙髓干细胞的神经分化[65]。当碱性成纤维细胞生长因子2和牙髓干细胞接种于三维纤维蛋白水凝胶上时,牙髓干细胞显示出向视网膜神经节细胞分化的表型迹象,包括视网膜神经节细胞相关基因或蛋白的表达,如Brn3b;但不能确定是否是具有功能的视网膜神经节细胞[76]。所以对细胞的预支架可以促进细胞附着、迁移、增殖、分化和功能。除此之外,如水凝胶材料,因其具有的三维多孔结构成为了输送生长因子的极佳载体,使它具有缓释特性[77-78]。 2.3.4 其他方法 除了以上所述的方法外,使用某些中药,化学物质(例如黄芪、白藜芦醇等)均可诱导牙髓干细胞向神经分化[79-80]。研究还发现,通过光可以控制转基因干细胞的活性。NIYAZI等[81]研究结果表明,通过去极化牙髓干细胞进行光遗传学刺激可提高细胞存活率和(或)提升增殖能力,并能促进其向神经元样细胞分化。而KOGO等[62]使用高K+ BSS-Ca2+缓冲液对牙髓干细胞进行神经分化,发现此方法可以激活K+通道,提高牙髓干细胞向神经元样细胞分化的速度。可能由于细胞内K+浓度变化调节跨膜电位,进而控制细胞周期,诱导牙髓干细胞的分化[82]。促使牙髓干细胞向神经分化是干细胞替代治疗的关键环节,所以使牙髓干细胞稳定而安全的分化为神经细胞是未来研究的重要方向。 文章对诱导牙髓干细胞神经向分化方法进行了汇总,见表2。 "
| [1] DARABI S, TIRAIHI T, BOJNORDI MN, et al. Nerve growth factor and the trans-differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into cholinergic-like neurons. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2019;10(6):609-618. [2] BOJNORDI MN. Improvement of neuroglial cells differentiation from human dental pulp stem cells using CSF. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 2016. [3] MOHAN SP, RAMALINGAM M. Dental pulp stem cells in neuroregeneration. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2020;12(5):60. [4] WANG D, WANG Y, TIAN W, et al. Advances of tooth-derived stem cells in neural diseases treatments and nerve tissue regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(3):e12572. [5] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630. [6] SHI X, MAO J, LIU Y. Pulp stem cells derived from human permanent and deciduous teeth: Biological characteristics and therapeutic applications. Stem Cell Transl Med. 2020;9(4):445-464. [7] LUKE A M, PATNAIK R, KURIADOM S, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells differentiation to neural cells, osteocytes and adipocytes-An in vitro study. Heliyon. 2020;6(1):e03054. [8] SHETTY H, KAKADE A, SHETTY S, et al. Immunohistochemical characterization of stem cell and differentiation markers of the dental pulp of human natal teeth. Future Sci OA. 2018;4(6):FSO342. [9] KUNIMATSU R, NAKAJIMA K, AWADA T, et al. Comparative characterization of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth, dental pulp, and bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;501(1):193-198. [10] Sanen K, Martens W, Georgiou M, et al. Engineered neural tissue with Schwann cell differentiated human dental pulp stem cells: potential for peripheral nerve repair? J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(12):3362-3372. [11] Pisciotta A, Bertoni L, Vallarola A, et al. Neural crest derived stem cells from dental pulp and tooth-associated stem cells for peripheral nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(3):373-381. [12] MORTADA I, MORTADA R, BAZZAL MA. Dental pulp stem cells and neurogenesis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1083:63-75. [13] MORTADA I, MORTADA R, BAZZAL MA. Dental pulp stem cells and the management of neurological diseases: an update. J Neurosci Res. 2018;96(2):265-272. [14] HAN Q, WANG Q, WU J, et al. Nell-1 promotes the neural-like differentiation of dental pulp cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513(2):515-521. [15] ALBASHARI A, HE Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Thermosensitive bFGF-modified hydrogel with dental pulp stem cells on neuroinflammation of spinal cord injury. ACS Omega. 2020;5(26):16064-16075. [16] ZHANG JJ, ZHU JJ, HU YB, et al. Transplantation of bFGF-expressing neural stem cells promotes cell migration and functional recovery in rat brain after transient ischemic stroke. Oncotarget. 2017;8(60):102067-102077. [17] WANG DR, WANG YH, PAN J, et al. Neurotrophic effects of dental pulp stem cells in repair of peripheral nerve after crush injury. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(10):1196-1213. [18] MEAD B, LOGAN A, BERRY M, et al. Concise review: dental pulp stem cells: a novel cell therapy for retinal and central nervous system repair. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):61-67. [19] YOUNG CS, SHAY S, YU-JIN J, et al. Differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into dopaminergic neuron-like cells in vitro. J Korean Med Sci. 2016;31(2):171-177. [20] GNANASEGARAN N, GOVINDASAMY V, KATHIRVALOO P, et al. Effects of cell cycle phases on the induction of dental pulp stem cells toward dopaminergic-like cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2): e881-e893. [21] GONMANEE T, THONABULSOMBAT C, VONGSAVAN K, et al. Differentiation of stem cells from human deciduous and permanent teeth into spiral ganglion neuron-like cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;88:34-41. [22] YANG C, LI X, SUN L, et al. Potential of human dental stem cells in repairing the complete transection of rat spinal cord. J Neural Eng. 2017;14(2):026005.1-026005.14. [23] ULLAH I, PARK JM, KANG YH, et al. Transplantation of human dental pulp-derived stem cells (hDPSCs) or differentiated neuronal cells from hDPSCs identically enhances regeneration of the injured peripheral nerve. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26(17):1247-1257. [24] GILYAROV AV. Nestin in central nervous system cells. Neurosci Behav Physiol. 2008;38(2):165-169. [25] ZHANG J, JIAO J. Molecular biomarkers for embryonic and adult neural stem cell and neurogenesis. BioMed Res Int. 2015;2015:727542. [26] NIAPOUR A, HAMIDABADI HG, NIAPOUR N, et al. Pharmacological Notch pathway inhibition leads to cell cycle arrest and stimulates ascl1 and neurogenin2 genes expression in dental pulp stem cells-derived neurospheres. Biotechnol Lett. 2019;41(6-7):873-887. [27] BAYSAL E, ZRH EB, BUBER E, et al. The effect of melatonin on hippo signaling pathway in dental pulp stem cells. Neurochem Int. 2021;148: 105079. [28] ZHANG X, ZHOU Y, LI H, et al. Transplanted dental pulp stem cells migrate to injured area and express neural markers in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(1):258-266. [29] RAFIEE F, POURTEYMOURFARD-TABRIZI Z, MAHMOUDIAN-SANI MR, et al. Differentiation of dental pulp stem cells into neuron-like cells. Int J Neurosci. 2020;130(2):107-116. [30] ZHANG J, MIN L, CAO P, et al. Effects of nerve growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor promote human dental pulp stem cells to neural differentiation. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(4):1015-1025. [31] MOAYERI A, NAZM BOJNORDI M, HARATIZADEH S, et al. Transdifferentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into oligoprogenitor cells. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2017;8(5):387-394. [32] LI D, ZOU XY, EL-AYACHI I, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells and gingival mesenchymal stem cells display action potential capacity in vitro after neuronogenic differentiation. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2019; 15(1):67-81. [33] DARABI S, TIRAIHI T, NAZM BOJNORDI M, et al. Trans-differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into cholinergic-like neurons via nerve growth factor. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2019;10(6):609-617. [34] CHO YA, KIM DS, SONG M, et al. Protein interacting with never in mitosis A-1 induces glutamatergic and GABAergic neuronal differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells. J Endod. 2016;42(7):1055-1061. [35] GONMANEE T, ARAYAPISIT T, VONGSAVAN K, et al. Optimal culture conditions for neurosphere formation and neuronal differentiation from human dental pulp stem cells. J Appl Oral Sci. 2021;29: e20210296. [36] CAVALLARO M, MARIANI J, LANCINI C, et al. Impaired generation of mature neurons by neural stem cells from hypomorphic Sox2 mutants. Development. 2008;135(3):541-557. [37] MERCURIO S, SERRA L, NICOLIS SK. More than just stem cells: functional roles of the transcription factor sox2 in differentiated glia and neurons. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4540. [38] WAKAMATSU Y, UCHIKAWA M. The many faces of Sox2 function in the neural crest development. Dev Growth Differ. 2021;63(1):93-99. [39] MEHRI A, JAMI S, CHALESHTORI M H. Upregulation of Neuroprogenitor and Neural Markers via Enforced miR-124 and Growth Factor Treatment. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2020;9(1):62-70. [40] CHACON J, ROGERS C D. Early expression of Tubulin Beta-III in avian cranial neural crest cells. Gene Expr Patterns. 2019;34:119067. [41] BOJNORDI MN, HARATIZADEH S, DARABI S, et al. Neural derivation of human dental pulp stem cells via neurosphere technique. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2018;119(9):550-553. [42] FOUDAH D, MONFRINI M, DONZELLI E, et al. Expression of neural markers by undifferentiated mesenchymal-like stem cells from different sources. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:987678. [43] KAMAL MA, AL-ZAHRANI MH, KHAN SH, et al. Tubulin proteins in cancer resistance: a review. Curr Drug Metab. 2020;21(3):178-185. [44] ARUN KANAKKANTHARA AB, JOHN H, MILLER C. βIII-tubulin overexpression in cancer: Causes, consequences, and potential therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1876(2):188607. [45] BRAMANTI V, TOMASSONI D, AVITABILE M, et al. Biomarkers of glial cell proliferation and differentiation in culture. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2010;2:558-570. [46] MACHADO CV, PASSOS ST, CAMPOS TMC, et al. The dental pulp stem cell niche based on aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 expression. Int Endod J. 2016;49(8):755-763. [47] DU W, LI H, SUN J, et al. The prognostic value of serum neuron specific enolase (nse) and s100b level in patients of acute spinal cord injury. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:4510-4515. [48] 王国卿,封丽芳,夏作理.S100B蛋白生物学功能及在神经系统疾病中的应用[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(28):6166-6167. [49] CATA J P, ABDELMALAK B, FARAG E. Neurological biomarkers in the perioperative period. Br J Anaesth. 2011;107(6):844-858. [50] CARNEVALE G, PISCIOTTA A, RICCIO M, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells expressing STRO-1, c-kit and CD34 markers in peripheral nerve regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):e774-e785. [51] S BODA KU NTLA, JIJUMON A S, VILLABLANCA C, et al. Microtubule-associated proteins: structuring the cytoskeleton. Trends Cell Biol. 2019;29(10):804-819. [52] BLÜMCKE I, BECKER AJ, NORMANN S, et al. Distinct expression pattern of microtubule-associated protein-2 in human oligodendrogliomas and glial precursor cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2001;60(10):984-993. [53] D’ANDREA M, HOWANSKI R, SALLER C. MAP2 IHC detection: a marker of antigenicity in CNS tissues. Biotech Histochem. 2017;92(5):363-373. [54] HOCHULI A, SENEGAGLIA AC, SELENKO AH, et al. Dental pulp from human exfoliated deciduous teeth-derived stromal cells demonstrated neuronal potential: in vivo and in vitro studies. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(5):495-506. [55] GUSELNIKOVA VV, KORZHEVSKIY DE. NeuN as a neuronal nuclear antigen and neuron differentiation marker. Acta Naturae. 2015;7(2):42-47. [56] Duan W, Zhang YP, Hou Z, et al. Novel insights into NeuN: from neuronal marker to splicing regulator. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(3):1637-1647. [57] ISGRÒ MA, BOTTONI P, SCATENA R. Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: biochemical and clinical aspects. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015; 867:125-143. [58] GONMANEE T, SRITANAUDOMCHAI H, VONGSAVAN K, et al. Neuronal differentiation of dental pulp stem cells from human permanent and deciduous teeth following coculture with rat auditory brainstem slices. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2020;303(11):2931-2946. [59] DARVISHI M, HAMIDABADI HG, BOJNORDI MN, et al. Differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into functional motor neuron; in vitro and ex vivo study. Tissue Cell. 2021;72:101542. [60] OSCAR O, SOLIS-CASTRO, BOISSONADE FM, et al. Establishment and neural differentiation of neural crest-derived stem cells (NCSCs) from human dental pulp in serum‐free conditions. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(11):1462-1476. [61] LUKE AM, PATNAIK R, KURIADOM S, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells differentiation to neural cells, osteocytes and adipocytes-An in vitro study. Heliyon. 2020;6(1):e03054. [62] KOGO Y, SETO C, TOTANI Y, et al. Rapid differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells to neuron-like cells by high K+ stimulation. Biophys Physicobiol. 2020;17:132-139. [63] HSIAO D, HSU SH, CHEN RS, et al. Characterization of designed directional polylactic acid 3D scaffolds for neural differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Formos Med Assoc. 2020;119(1 Pt 2): 268-275. [64] GANAPATHY K, DATTA I, BHONDE R. Astrocyte-like cells differentiated from dental pulp stem cells protect dopaminergic neurons against 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(6):4395-4413. [65] ZHENG K, FENG G, ZHANG J, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes human dental pulp stem cells cultured in 3D porous chitosan scaffolds to neural differentiation. Int J Neurosci. 2021;131(7):625-633. [66] CARNEVALE G, PISCIOTTA A, RICCIO M, et al. Human dental pulp stem cells expressing STRO-1, c-kit and CD34 markers in peripheral nerve regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):e774-e785. [67] GOUDARZI G, HAMIDABADI HG, BOJNORDI MN, et al. Role of cerebrospinal fluid in differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into neuron-like cells. Anat Cell Biol. 2020;53(3):292-300. [68] HENG BC, JIANG S, YI B, et al. Small molecules enhance neurogenic differentiation of dental-derived adult stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2019; 102:26-38. [69] 陈彪,张睿,张文娟,等.牙髓干细胞对兔面神经损伤的修复作用及其机制[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2018,44(3):7. [70] HAN N, ZHANG F, LI G, et al. Local application of IGFBP5 protein enhanced periodontal tissue regeneration via increasing the migration, cell proliferation and osteo/dentinogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in an inflammatory niche. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):210. [71] LI J, DIAO S, YANG H, et al. IGFBP5 promotes angiogenic and neurogenic differentiation potential of dental pulp stem cells. Dev Growth Differ. 2019;61(9):457-465. [72] 胡月.SFRP2在调控人牙髓干细胞神经向分化中的作用研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2017. [73] 邓轩,阳芳,唐西清,等.miR-20调控人乳牙牙髓干细胞向神经元样细胞的定向分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(21):7. [74] BOON H, TING G, JIANGUANG X, et al. EphrinB2 signalling modulates the neural differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. Biomed Rep. 2018;9(2):161-168. [75] LUO L, HE Y, JIN L, et al. Application of bioactive hydrogels combined with dental pulp stem cells for the repair of large gap peripheral nerve injuries. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):638-654. [76] ROOZAFZOON R, LASHAY A, VASEI M, et al. Dental pulp stem cells differentiation into retinal ganglion-like cells in a three dimensional network. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457(2):154-160. [77] LOU J, STOWERS R, NAM S, et al. Stress relaxing hyaluronic acid-collagen hydrogels promote cell spreading, fiber remodeling, and focal adhesion formation in 3D cell culture. Biomaterials. 2018;154:213-222. [78] LUO L, HE Y, WANG X, et al. Potential roles of dental pulp stem cells in neural regeneration and repair. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:1731289. [79] 赵燕翔,王劲松,王松灵.黄芪注射液对人牙髓干细胞神经分化的影响[J].北京口腔医学,2018,26(3):4. [80] GENG YW, ZHANG Z, LIU MY, et al. Differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells into neuronal by resveratrol. Cell Biol Int. 2017;41(12):1391-1398. [81] NIYAZI M, ZIBAII M I, DARGAHI L, et al. Neurogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells by optogenetics stimulation. J Chem Neuroanat. 2020;109:101821. [82] URREGO D, TOMCZAK AP, ZAHED F, et al. Potassium channels in cell cycle and cell proliferation. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014; 369(1638):20130094. [83] CASEIRO AR, PEREIRA T, IVANOVA G, et al. Neuromuscular regeneration: perspective on the application of mesenchymal stem cells and their secretion products. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:9756973. [84] LI YH, LI JE, LIU WW. Comparing the effect of neurotrophic factor induced mscs (BMSC and DPSC) on the expression of myelin proteins Nogo-A and OMgp in a glaucoma rat model. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017; 10(3):4705. [85] SINGH M, KAKKAR A, SHARMA R, et al. Synergistic effect of BDNF and FGF2 in efficient generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10378. |
| [1] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [2] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [3] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [4] | Yang Yan, Wang Jingxian, Zhang Ronghong, Li Chen, Fan Anran, Cui Dongbing, Wu Shumei. Effects of conditioned media of different sources on the proliferation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 49-53. |
| [5] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [6] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| [7] | Liu Yunling, He Ruya, Nie Minhai, Li Tengyan, Liu Xuqian. Application of concentrated growth factor and epidermal growth factor in the field of oral and maxillofacial soft and hard tissue injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 105-113. |
| [8] | Shi Xu, Li Ruiyu, Zhang Bing, Chen Qi, Zuo Hua. Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 121-129. |
| [9] | Guo Yujun, Lu Wenjun, Yang Shulong, Li Zhaozhu. Effect of urine-derived stem cells and their exosomes on kidney diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 138-144. |
| [10] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [11] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [12] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [13] | Kong Yamin, Yan Juntao, Ma Bingxiang, Li Huawei. Massage vibration intervenes with MyoD expression and proliferation and differentiation of muscle satellite cells in rats with sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1160-1166. |
| [14] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [15] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||