Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (3): 434-440.doi: 10.12307/2023.027
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings
Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing
- Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-03Accepted:2022-01-19Online:2023-01-28Published:2022-06-01 -
Contact:Wan Qianbing, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhou Jie, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Project), No. 81970984 (to WQB); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Project), No. 82071164 (to PXB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
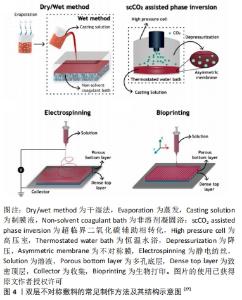
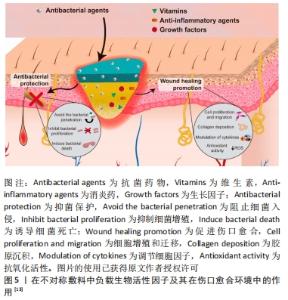
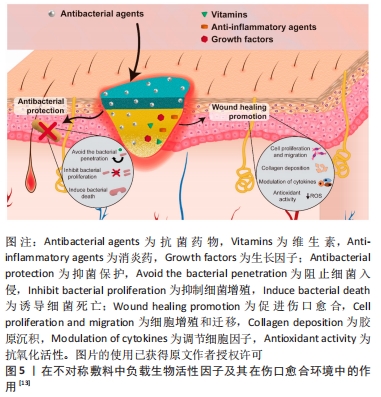
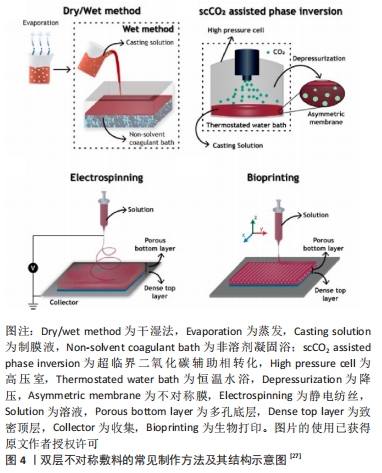
2.1 不对称敷料的物理性能 理想的伤口敷料应该具有与天然皮肤组织相近的物理性能,保证在使用时不发生破损,有一定的透气性、保湿性等,参考的数据指标主要包括力学性能、孔隙率、水汽透过率等[17]。人体皮肤的杨氏模量为4.6-20.0 MPa,拉伸强度为5.00-30.00 MPa,断裂拉伸率为35.00%-115.00%[18],理想敷料的孔隙率应在60%-90%[19],水汽透过率值应该在2 000-2 500 mL/(m2·d)[20]。MIGUEL等[20]通过静电纺丝技术制备出一种以丝素和聚已内酯为表层、以丝素蛋白和透明质酸为内层的不对称敷料,在干、湿条件下对其进行物理性能测试,结果显示在两种条件下该敷料各方面物理性能均与理想敷料的要求相近。利用静电纺丝制作的致密表层,能在不显著影响敷料透气性、孔隙率的情况下,为敷料提供一定的机械支持作用,提升敷料的整体机械强度[19]。POONGUZHALI等[21]通过硬脂酸改性壳聚糖/聚乙烯基吡咯烷酮/纳米纤维素膜,并研究该膜在改性前后的性能差异,结果显示该敷料改性前后的力学性能表现出相似性,但其水汽透过率和溶胀率均有小幅度下降,这是因为多孔层孔隙率大、亲水性强,而致密疏水层的存在降低了敷料的总孔隙率和对水分子的亲和力。可见,不对称敷料的不对称特性并不会对其物理性能产生显著影响,其物理性能主要取决于组成材料的相关性能及制作方法[22]。通过不对称敷料致密层和多孔层的复合材料在物理性能上的差异互补,能够得到比单层敷料更理想的敷料性能。 2.2 不对称敷料的结构 2.2.1 单层改性不对称敷料 单层改性不对称敷料在制作过程中首先通过静电纺丝或冷冻干燥等方法,制作出一均匀对称的单层膜,再对膜的一侧使用疏水或亲水材料进行改性,最终获得亲-疏水性、抗菌性等性能不对称的敷料。XIA等[23]在经冷冻干燥法制作的季铵盐壳聚糖纳米颗粒/壳聚糖复合海绵表面,利用硬脂酸修饰获得了具有不对称润湿性复合敷料,该敷料的疏水改性面表现出较好的抗细菌浸润能力,而原有的多孔亲水结构能够广泛地吸收渗出液,抑制细菌的生长,当该不对称结构与敷料负载药物的抗菌性相结合时,能够加速创面愈合。WANG等[24] 将添加了纳米银颗粒的壳聚糖/丝素蛋白液经冷冻干燥作为支架,并对一侧进行硬脂酸改性,然后将富血小板血浆加载到支架上,当使用该敷料时,疏水侧能避免水分过度流失,保持创面湿润,同时隔离空气中的微生物,降低了伤口继发感染的可能;而亲水侧在体液的作用下促进了敷料中纳米银颗粒和富血小板血浆的释放,保证了创面的局部抗菌作用,并促进了创面愈合。通过简单的涂布、喷洒等涂层法能够快速实现敷料的不对称改性,是目前对均匀敷料实现不对称改性的常用方法。 除了上述的涂层改性法,一些学者通过对敷料一侧进行化学交联修饰得到不对称敷料。RIBBA等[25]通过光接枝法,用聚乙烯醇对聚乳酸静电纺丝膜的一面进行了稳定的化学共价改性,改性侧的水接触角由122°变为44°,实现了敷料亲水性的不对称转变。不论是使用涂层还是化学交联法,均采用了相对成本较低、简单快速易行的方式实现了敷料的不对称改性,能够增强敷料的抗菌、止血、载药、保湿等性能,有较好的应用前景。 2.2.2 双层不对称敷料 双层敷料在不对称敷料中最为常见,常用的制作方法包括相转法、静电纺丝、3D生物打印等[26-27],见图4,其中以静电纺丝法运用最为广泛。ARAGON等[28]通过静电纺丝合成了负载单萜香芹酚的聚己内酯/聚醋酸乙烯酯不对称膜,膜顶层能防止伤口快速脱水和细菌渗透,底层多孔结构利于药物负载,且具有高吸水性和杀菌性。LI等[29]在聚多巴胺处理的聚乙烯醇纳米纤维膜表面,经二次纺丝制成聚己内酯/丝素蛋白疏水纳米纤维膜,形成具有单向导湿性的不对称双层复合膜,该敷料能对过多的渗出物进行高效转出,使创口处的内源性凝血因子和血小板相对增加,起到促止血、促愈合的作用。静电纺丝技术生成的敷料具有较高的孔隙率和比表面积[30],能相对轻松地将生物活性物质包裹在其中,提高敷料的抗菌性能和/或促愈合功能[13],现已被广泛运用于多功能敷料的研究。 "
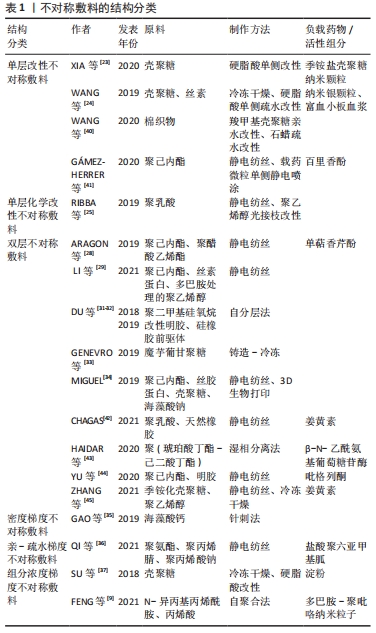
除上述方法外,有学者致力于用更简单的方法制出性能优良的不对称敷料。DU等[31-32]用端环氧聚二甲基硅氧烷改性明胶与硅橡胶前驱体共混,通过表面张力梯度驱动的自分层作用形成具有不对称双层结构的膜,该敷料表现出较好的物理性能,生物降解性符合正常皮肤伤口愈合过程。GENEVRO等[33]通过铸造-冷冻工艺生产成本低廉、生物相容性良好的魔芋葡甘聚糖不对称膜。这些方法不依靠特殊仪器,不引入多余溶剂,所制得的膜具有生物相容性良好、成本低廉等优势,同时也能满足作为伤口敷料的要求,提供利于愈合的环境。 在制作敷料时,不同的技术有其独特优势。MIGUEL等[34]通过静电纺丝制备了聚己内酯/丝胶纳米纤维膜作为表皮模拟层,再利用3D生物打印技术层层打印壳聚糖/海藻酸钠水凝胶模拟真皮层,制作了三维皮肤不对称敷料。使用多种方法联合,对不同的层面使用不同的制作技术,利于得到有关性能更理想的敷料。 2.2.3 梯度不对称敷料 不同于传统的双层不对称敷料,梯度敷料通常由3层或更多层组成,通过敷料内结构、组成等形成具有梯度表现的敷料,其梯度效应可表现在敷料的密度组成上。GAO等[35]采用针刺法制备了具有纤维密度梯度的海藻酸钙纤维敷料,液体在敷料内扩散时表现为尖向高密度面的三角形,溶液从高密度面向低密度面扩散时的速率比从低密度面到高密度面扩散的速率快,说明该敷料的纤维密度梯度影响了渗出液在敷料中的扩散。纤维的密度梯度和排列方向改变了渗出液在敷料中的扩散和分布,利用该特性制备的取向性纤维敷料能够实现对液体的定向导出,有利于创面愈合。 亲-疏水梯度在影响液体于材料内部的定向输送过程中有重要意义,使用亲水性不同的材料制备多层次的敷料可以获得具有亲水性梯度的敷料。QI等[36]利用静电纺丝技术将抗菌剂包埋在具有亲-疏水梯度结构的敷料中,该敷料自内向外由疏水聚氨酯层、亲水聚氨酯/聚丙烯腈-聚丙烯酸钠和高亲水的聚丙烯腈-聚丙烯酸钠三层纳米纤维组成,孔径依次减小,根据不同层次之间的亲水性及孔径差异产生的毛细管压差,实现由内到外单向排水的自泵效应;当液滴接触该敷料疏水面时,水分可以穿过疏水层,使亲水层迅速湿润,并防止液体的反向渗透。通过亲-疏水性梯度实现渗出物在敷料内的高效转运,并防止液体反渗、避免伤口处渗出液累积,对于渗出增多的感染伤口等有较大的临床运用意义。 敷料内不均匀分布的组分可以形成有组分浓度梯度的敷料,产生相关的不对称性能。SU等[37]在壳聚糖中加入淀粉,通过调节淀粉的量可获得有亲-疏水梯度的复合海绵,在硬脂酸改性后,海绵两侧均表现为疏水,随着淀粉量的增加,敷料底层亲水性增加,而顶层仍保持疏水性。这种不对称的亲水性归因于淀粉的梯度分布、粗糙的三维骨架结构以及亲疏水基团表面分布不均三因素的协同作用。利用敷料内不对称分布的组分的特性,在近伤口侧和表面表现出不同的湿润性、粘接性等,还能实现敷料性能的可调控性,得到多功能的智能敷料,有利于解决传统敷料在临床运用中的许多问题。 不对称敷料的结构分类,见表1。 "

2.3.1 单层改性不对称敷料的生物应用 通过对均匀敷料的一侧或双侧进行涂层或化学改性,能够方便地在原始敷料的基础上获得新的性能或是使部分原有性能得到提升,有助于该敷料的应用。WANG等[40]通过简单快速的喷雾涂层法在常用的棉织物敷料两侧喷涂不同的材料,制作了不对称改性棉织物,该棉织物的一侧喷洒止血性能优良的羧甲基壳聚糖溶液以实现该侧的亲水改性,而另一侧使用石蜡构建起超疏水表面,改性后棉织物的亲水侧能快速吸收血液,促进止血;疏水面防止血液过度吸收,较原敷料具有更好的止血效果,在需要紧急止血的伤口表面能够取得较好的应用效果。GáMEZ-HERRERA等[41]通过在静电纺丝形成的聚己内酯纳米纤维膜一侧,利用静电喷涂的方式负载含有百里香酚的聚乳酸/羟基乙酸微粒,获得了不对称的静电纺丝敷料;当载药的聚乳酸/羟基乙酸微粒与体液相接触时,由于聚乳酸/羟基乙酸具有一定的水解性,其中负载的百里香酚就能在敷料运用的局部实现持续释放,从而起到消炎抗菌的作用。由于聚己内酯降解缓慢,直接利用静电纺丝聚己内酯膜负载百里香酚的药物释放行为较差,利用这种单侧修饰改性的方法能优化敷料在药物负载与释放方面的性能,有利于药物发挥其相关作用,共同促进伤口愈合。使用单侧改性法能在已经成形的敷料上方便地进行改进,赋予敷料更好的抗菌、止血作用,还能进行药物负载,使原有敷料的性能更佳,有更好的运用背景。 2.3.2 双层不对称敷料的生物应用 双层不对称敷料的表层通过其致密的孔隙和疏水性对气、液、细菌等起到限制作用,能对底层负载的活性药物起到保护作用,或与负载药物相协同共同促进伤口愈合。CHAGAS等[42]在含有姜黄素的聚乳酸/天然橡胶微纤维层表面制作了聚乳酸纳米纤维阻水表层,该敷料的阻水层在使用10 d内能起到限制外界细菌渗透的作用,通过这种不对称的结构还能保护底层易受光降解的姜黄素,使其能够充分发挥抗炎抗菌作用。HAIDAR等[43]设计了一种针对生物膜给药的不对称敷料,能够抑制生物膜形成和/或在生物膜形成后进行破坏,该敷料致密疏水层的孔径较小,能够起到一定的“筛选效应”,限制部分营养物质和氧气的自由穿过,在一定程度上起到了抑制伤口生物膜形成(约20%)的作用;当加入β-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶时,能显著抑制生物膜形成(约84%),对慢性感染伤口起到较好的抗菌、促愈合作用。YU等[44]采用静电纺丝法制备以聚己内酯为疏水外层、聚吡咯列酮-明胶为亲水性内层的双层不对称敷料,该敷料能对吡格列酮进行缓释,改善局部高糖环境,不对称结构能抗细菌侵袭、减少创面感染,使伤口愈合微环境向有利方向进展。 除了与负载药物相协同,不对称敷料的亲-疏水结构特性还赋予了敷料一定的单向导湿性。ZHANG等[45]使用静电纺丝加冷冻干燥法制作季铵化壳聚糖/聚乙烯醇纤维纳米气凝胶,随后在气凝胶表面利用静电纺丝形成聚己内酯/姜黄素纳米纤维膜得到双层不对称敷料,该敷料能够自主地将渗出液从创面快速引流出来,并防止渗出液的反向渗透;通过在敷料中加入姜黄素使之具有抗菌、抗氧化性能,缩短伤口愈合的炎症期。此类敷料能够在一些高渗出环境,如糖尿病伤口、烧伤伤口、感染伤口等起到较好的作用。糖尿病小鼠模型实验表明,相较于其他对照组,使用该敷料处理后部位再生的皮肤具有更高的血管密度、更多的胶原沉积和更成熟的分层结构,证明该敷料能加速糖尿病创面愈合。 双层不对称敷料作为最为经典的一类不对称敷料,其在不同伤口愈合环境包括慢性糖尿病伤口[23]、压疮[7]、感染伤口[46]、难治性感染伤口等均取得较好的应用效果[47],其自身不对称结构对感染和气液交换的控制作用,协同负载药物的相关作用,使其能在伤口愈合的不同阶段均起到促进愈合的作用[48]。 2.3.3 梯度不对称敷料的生物应用 利用敷料的梯度结构,能够带来除经典不对称敷料性能之外的智能特性,或较单层、双层不对称敷料更为精细的梯度性能。FENG等[9]利用了聚吡咯的导电性、聚多巴胺的附着力和光热性能、N-异丙基丙烯酰胺的热响应性等,制作了由近红外触发的具有可调节黏附、自变形、抗菌等多功能的不对称敷料。聚吡咯-聚多巴胺纳米颗粒在水凝胶内由于惯性沉降而呈梯度分布,当进行近红外辐照时,不均匀的升温引起敷料内部的水分子转移,引起敷料自变形并减少敷料与创面之间的黏附面积和黏附力。因此,使用该敷料进行换药时,能实现敷料的无痛更换,减轻换药给患者带来的痛苦。此外,使用该敷料对感染创面进行近红外诱导的光热疗法时,相较于聚吡咯-聚多巴胺纳米颗粒均匀分布的敷料,该梯度敷料可达到更高的温度、获得更高的光热抗菌效率,其导电性还能促进电信号传导,有效缩短感染创口愈合过程。除此之外,梯度不对称敷料还能在双层不对称敷料单向导水性的基础上获得更精细的亲-疏水梯度,实现更为高效的导液性能[38],对于高渗出环境有更好的处理能力。梯度不对称敷料的研究目前仍较少,但对敷料的梯度组分、密度、亲-疏水性等的研究,带来了具有更多益于不同愈合环境的伤口的智能、多功能敷料。关于智能梯度不对称敷料的应用及研究应该是未来的研究方向之一,也是解决目前临床上难以处理的愈合问题的一剂潜在良药,需要进一步的研究与开发。 "

| [1] GUERRA A, BELINHA J, JORGE RN. Modelling skin wound healing angiogenesis: A review. J Theor Biol. 2018;459:1-17. [2] CHEN KY, LIAO WJ, KUO SM, et al. Asymmetric chitosan membrane containing collagen I nanospheres for skin tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(6):1642-1649. [3] SIMÕES D, MIGUEL SP, RIBEIRO MP, et al. Recent advances on antimicrobial wound dressing: A review. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018; 127:130-141. [4] LIANG Y, HE J, GUO B. Functional hydrogels as wound dressing to enhance wound healing. ACS Nano. 2021;15(8):12687-12722. [5] XUE J, WANG X, WANG E, et al. Bioinspired multifunctional biomaterials with hierarchical microstructure for wound dressing. Acta Biomater. 2019;100:270-279. [6] OP’T VELD RC, WALBOOMERS XF, JANSEN JA, et al. Design considerations for hydrogel wound dressings: strategic and molecular advances. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020;26(3):230-248. [7] GÓRSKA A, DOROŻYŃSKI P, WĘGLARZ WP, et al. Spatiotemporal characterization of hydration process of asymmetric polymeric wound dressings for decubitus ulcers. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(2):843-853. [8] DUOLIKUN T, GHAZALI N, LEO BF, et al. Asymmetric Cellulosic Membranes: Current and Future Aspects. Symmetry. 2020;12(7):1160. [9] FENG L, SHI W, CHEN Q, et al. Smart Asymmetric Hydrogel with Integrated Multi‐Functions of NIR‐Triggered Tunable Adhesion, Self‐Deformation, and Bacterial Eradication. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021; 2100784. [10] WU J, QIU Q, WANG Y, et al. Asymmetric water affinity on antibacterial electrospun sub-micro cellulose acetate Janus membrane. Materials Letters. 2019;256:126607. [11] MI FL, SHYU SS, WU YB, et al. Fabrication and characterization of a sponge-like asymmetric chitosan membrane as a wound dressing. Biomaterials. 2001;22(2):165-173. [12] LEI M, QU X, LIU H, et al. Programmable electrofabrication of porous janus films with tunable janus balance for anisotropic cell guidance and tissue regeneration. Advanced Functional Materials. 2019;29(18): 1900065. [13] GRAÇA MFP, DE MELO-DIOGO D, CORREIA IJ, et al. Electrospun Asymmetric Membranes as Promising Wound Dressings: A Review. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(2):183. [14] 唐川,关怡新,姚善泾,等.超临界溶液浸渍法制备负载磺胺嘧啶银不对称壳聚糖膜伤口敷料研究[J].高分子学报,2014(6):774-781. [15] FEDERICO S, PITARRESI G, PALUMBO FS, et al. An asymmetric electrospun membrane for the controlled release of ciprofloxacin and FGF-2: Evaluation of antimicrobial and chemoattractant properties. Mat Sci Eng C. 2021;123:112001. [16] LI Y, ZHU C, FAN D, et al. Construction of porous sponge-like PVA-CMC-PEG hydrogels with pH-sensitivity via phase separation for wound dressing. Int J Polym Mater Po. 2020;69(8):505-515. [17] MIGUEL SP, MOREIRA AF, CORREIA IJ. Chitosan based-asymmetric membranes for wound healing: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019; 127:460-475. [18] MIGUEL SP, RIBEIRO MP, COUTINHO P, et al. Electrospun polycaprolactone/aloe vera_chitosan nanofibrous asymmetric membranes aimed for wound healing applications. Polymers. 2017;9(5):183. [19] YIN X, WEN Y, LI Y, et al. Facile fabrication of sandwich structural membrane with a hydrogel nanofibrous mat as inner layer for wound dressing application. Front Chem. 2018;6:490. [20] MIGUEL SP, SIMÕES D, MOREIRA AF, et al. Production and characterization of electrospun silk fibroin based asymmetric membranes for wound dressing applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;121:524-535. [21] POONGUZHALI R, BASHA SK, KUMARI VS. Novel asymmetric chitosan/PVP/nanocellulose wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;112:1300-1309. [22] FEIZ S, NAVARCHIAN AH, JAZANI OM. Poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes in wound-dressing application: microstructure, physical properties, and drug release behavior. Iran Polym J. 2018;27(3):193-205. [23] XIA G, ZHAI D, SUN Y, et al. Preparation of a novel asymmetric wettable chitosan-based sponge and its role in promoting chronic wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;227:115296. [24] WANG Q, QIAN Z, LIU B, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of new PRP antibacterial moisturizing dressings for infectious wound repair. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2019;30(6):462-485. [25] RIBBA L, TAMAYO L, FLORES M, et al. Asymmetric biphasic hydrophobic/hydrophilic poly (lactic acid)–polyvinyl alcohol meshes with moisture control and noncytotoxic effects for wound dressing applications. J Appl Polym Sci. 2019;136(17):47369. [26] NAPAVICHAYANUN S, BONANI W, YANG Y, et al. Fibroin and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel wound dressing containing silk sericin prepared using high-pressure carbon dioxide. Adv Wound Care. 2019;(9):452-462. [27] MOUSAVI S M, ZAREI M, HASHEMI S A, et al. Asymmetric membranes: a potential scaffold for wound healing applications. Symmetry. 2020; 12(7):1100. [28] ARAGON J, COSTA C, COELHOSO I, et al. Electrospun asymmetric membranes for wound dressing applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;103:109822. [29] LI TT, ZHONG Y, PENG HK, et al. Multiscale composite nanofiber membranes with asymmetric wetability: preparation, characterization, and applications in wound dressings. J Mater Sci. 2021;56(6):4407-4419. [30] REIS TC, CASTLEBERRY S, REGO AMB, et al. Three-dimensional multilayered fibrous constructs for wound healing applications. Biomater Sci. 2016;4(2) 319-330. [31] DU W, ZHANG Z, FAN W, et al. Fabrication and evaluation of polydimethylsiloxane modified gelatin/silicone rubber asymmetric bilayer membrane with porous structure. Mater Design. 2018;158:28-38. [32] DU W, ZHANG Z, LI Z. Influence of the weight ratio of polydimethylsiloxane modified gelatin to silicone rubber on the potential performance of asymmetric bilayer membranes as wound dressings. Polym Int. 2019;68(10):1739-1747. [33] GENEVRO GM, NETO RJG, DE ALMEIDA PAULO L, et al. Glucomannan asymmetric membranes for wound dressing. J Mater Res. 2019;34(4): 481-489. [34] MIGUEL SP, CABRAL CSD, MOREIRA AF, et al. Production and characterization of a novel asymmetric 3D printed construct aimed for skin tissue regeneration. Colloid Surface B. 2019;181:994-1003. [35] GAO Y, JIN X. Needle-punched three-dimensional nonwoven wound dressings with density gradient from biocompatible calcium alginate fiber. Text Res J. 2019;89(14):2776-2788. [36] QI L, OU K, HOU Y, et al. Unidirectional water-transport antibacterial trilayered nanofiber-based wound dressings induced by hydrophilic-hydrophobic gradient and self-pumping effects. Mater Design. 2021; 201:109461. [37] SU C, ZHAO H, YANG H, et al. Stearic acid-modified starch/chitosan composite sponge with asymmetric and gradient wettability for wound dressing. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2018;2(1):171-181. [38] XU Q, SIGEN A, GAO Y, et al. A hybrid injectable hydrogel from hyperbranched PEG macromer as a stem cell delivery and retention platform for diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2018;75:63-74. [39] MARCANO A, BOU HAIDAR N, MARAIS S, et al. Designing biodegradable PHA-based 3D scaffolds with antibiofilm properties for wound dressings: optimization of the microstructure/nanostructure. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2017;3(12):3654-3661. [40] WANG Y, XIAO D, ZHONG Y, et al. Facile fabrication of carboxymethyl chitosan/paraffin coated carboxymethylated cotton fabric with asymmetric wettability for hemostatic wound dressing. Cellulose. 2020; 27(6):3443-3453. [41] GÁMEZ-HERRERA E, GARCÍA-SALINAS S, SALIDO S, et al. Drug-eluting wound dressings having sustained release of antimicrobial compounds. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;152:327-339. [42] CHAGAS PAM, SCHNEIDER R, DOS SANTOS DM, et al. Bilayered electrospun membranes composed of poly (lactic-acid)/natural rubber: A strategy against curcumin photodegradation for wound dressing application. React Funct Polym. 2021;163:104889. [43] HAIDAR N B, MARAIS S, DÉ E, et al. Chronic wound healing: A specific antibiofilm protein-asymmetric release system. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;106:110130. [44] YU B, HE C, WANG W, et al. Asymmetric wettable composite wound dressing prepared by electrospinning with bioinspired micropatterning enhances diabetic wound healing. ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2020; 3(8):5383-5394. [45] ZHANG K, JIAO X, ZHOU L, et al. Nanofibrous composite aerogel with multi-bioactive and fluid gating characteristics for promoting diabetic wound healing. Biomaterials. 2021;276:121040. [46] LIANG D, LU Z, YANG H, et al. Novel asymmetric wettable AgNPs/chitosan wound dressing: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(6):3958-3968. [47] QIAN Z, BAI Y, ZHOU J, et al. A moisturizing chitosan-silk fibroin dressing with silver nanoparticles-adsorbed exosomes for repairing infected wounds. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(32):7197-7212. [48] LIU M, WANG Y, HU X, et al. Janus N, N-dimethylformamide as a solvent for a gradient porous wound dressing of poly (vinylidene fluoride) and as a reducer for in situ nano-silver production: anti-permeation, antibacterial and antifouling activities against multi-drug-resistant bacteria both in vitro and in vivo. RSC Adv. 2018;8(47):26626-26639. [49] LIANG Y, ZHAO X, HU T, et al. Adhesive hemostatic conducting injectable composite hydrogels with sustained drug release and photothermal antibacterial activity to promote full‐thickness skin regeneration during wound healing. Small. 2019;15(12):1900046. [50] PILEHVAR-SOLTANAHMADI Y, DADASHPOUR M, MOHAJERI A, et al. An overview on application of natural substances incorporated with electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds to development of innovative wound dressings. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(5):414-427. [51] ASHFAQ M, VERMA N, KHAN S. Highly effective Cu/Zn-carbon micro/nanofiber-polymer nanocomposite-based wound dressing biomaterial against the P. aeruginosa multi-and extensively drug-resistant strains. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77:630-641. [52] WANG H, NIU H, ZHOU H, et al. Multifunctional directional water transport fabrics with moisture sensing capability. ACS applied materials & interfaces. 2019;11(25):22878-22884. [53] GU J, GU H, ZHANG Q, et al. Sandwich-structured composite fibrous membranes with tunable porous structure for waterproof, breathable, and oil-water separation applications. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018;514: 386-395. |
| [1] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [2] | Lin Zeyu, Xu Lin. Research progress in gout-induced bone destruction mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [3] | Liu Hanfeng, Wang Jingjing, Yu Yunsheng. Artificial exosomes in treatment of myocardial infarction: current status and prospects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1118-1123. |
| [4] | Ma Shuwei, He Sheng, Han Bing, Zhang Liaoyun. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of animals with acute liver failure: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1137-1142. |
| [5] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [6] | Xu Rong, Wang Haojie, Geng Mengxiang, Meng Kai, Wang Hui, Zhang Keqin, Zhao Huijing. Research advance in preparation and functional modification of porous polytetrafluoroethylene artificial blood vessels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [7] | Yin Tong, Yang Jilei, Li Yourui, Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming. Application of core-shell structured nanofibers in oral tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [8] | Chen Xiaofang, Zheng Guoshuang, Li Maoyuan, Yu Weiting. Preparation and application of injectable sodium alginate hydrogels [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [9] | Liu Chuang, Shan Shuo, Yu Tengbo, Zhou Huan, Yang Lei. Advantages, discomfort and challenges of clinical application of orthopedic hemostatic materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 795-803. |
| [10] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [11] | Tian Xin, Liu Tao, Yang Huilin, He Fan. In vitro evaluation of sustained release Kartogenin by gelatin methacryloyl microspheres for repairing nucleus pulposus degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 724-730. |
| [12] | Li Jiaqi, Huang Yuanli, Li Yan, Wang Chunren, Han Qianqian. Mechanism and influencing factors in molecular weight degradation of non-cross-linked hyaluronic acid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 747-752. |
| [13] | Zhang Ming, Wang Bin, Jia Fan, Chen Jie, Tang Wei. Application of brain-computer interface technology based on electroencephalogram in upper limb motor function rehabilitation of stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
| [14] | He Yuanjie, Chen Yuheng, Zhao Yongchao, Wang Zhenglong. Progress in epigenetic regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell remodeling in the occurrence and development of aortic aneurysms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 602-608. |
| [15] | Ma Sicong, Chen Jing, Li Yunqing. Functions and roles of connective tissue growth factor in nervous systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 615-620. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||