Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 293-299.doi: 10.12307/2022.920
Previous Articles Next Articles
Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation
Chen Feng1, Ren Guowu1, Zhang Xiaoyun2, Chen Yueping2, Shi Rusheng1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-11-23Accepted:2021-12-29Online:2023-01-18Published:2022-06-20 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaoyun, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Feng, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81960803 and 81760796 (both to CYP); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Youth Fund), No. 2020GXNSFBA159053 (to ZXY); Guangxi University Young Teachers’ Basic Ability Improvement Project, No. 2019KY0352 (to ZXY); Jin Tiange Young and Middle-aged Fund Project (Project 61) (to ZXY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
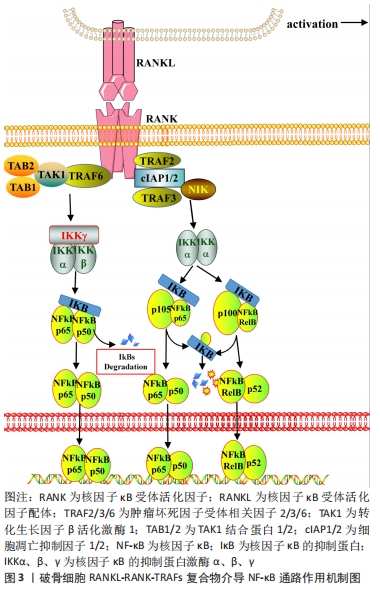
2.1 RANK信号的激活与募集 破骨细胞分化所需的趋化因子和细胞因子,以巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和RANKL较为关键。研究表明巨噬细胞集落刺激因子与RANKL可由成骨细胞、激活后的巨噬细胞、B细胞、T细胞等分泌表达[6]。而恰巧破骨细胞与巨噬细胞、B细胞、T细胞等免疫细胞共同在血液中循环,并具有共享髓系谱系。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子经上述免疫细胞分泌后,率先促进骨髓祖细胞表达RANK,使骨髓祖细胞能够效应RANKL。此后,巨噬细胞集落刺激因子与破骨细胞表面的巨噬细胞集落刺激因子受体结合,吸引磷酸化DNAX激活蛋白12和非受体酪氨酸激酶Syk组成的信号复合物,这些复合物介入了破骨细胞增殖、分化和存活等生命过程[7-8]。因此,作者认为巨噬细胞集落刺激因子与RANKL激活RANK信号在破骨细胞活化中发挥着重要的作用。 RANK属于肿瘤坏死因子受体超家族的成员,与肿瘤坏死因子受体类似。RANK自身结构缺乏磷酸化的蛋白激酶和激活下游信号分子的内在激酶活性,因此,RANK需要通过募集肿瘤坏死因子受体激活因子(tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors,TRAFs)来启动下游信号级联的反应[9]。TRAFs由多个亚型组成,在破骨细胞分化的研究中以TRAF2、TRAF3和TRAF6研究较为广泛。TRAF2、TRAF3和细胞凋亡抑制因子1/2(cellular inhibitors of apoptosis 1 and 2,cIAP1/2)可形成一个复合物,独立于TRAF6的诱导作用,TRAF3作为桥接因子使cIAP1/2介导核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)诱导激酶的K48链接泛素化,以降解NF-κB诱导激酶来激活非经典NF-κB信号[10-11]。TRAF6是介导破骨细胞RANKL-RANK激活的信号级联反应的主要衔接蛋白,可使与其相互作用的蛋白存在相同基序,这些基序为激活寡聚化,将TRAF6直接连接到跨膜受体的细胞内结构域,如RANK、肿瘤坏死因子超家族受体、白细胞介素1受体等;或者通过细胞质中连接蛋白间接向受体发出信号,如Casitas B家系淋巴瘤(c-casitas B-lineage lymphoma,c-Cbl)、活化C激酶1(receptor for activated c kinase 1,RACK1)、Src蛋白酪氨酸激酶(Src protein-tyrosine kinase,Src)等[12-14]。此外,TRAF6的激活依赖于TRAF6环指结构域与多种泛素结合酶催化合成独特泛素链的作用,这条独特泛素链通过泛素的赖氨酸63接链相关激酶,以此介导下游信号的激活,如募集和激活转化生长因子β活化激酶1(TGF-beta-activated kinase 1,TAK1)导致经典的IκB激酶(inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase,IKK)/NF-κB和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)的下游激活[15-16]。基于RANKL-RANK-TRAFs复合物特殊募集作用与激活方式,目前至少发现8个信号通路被RANKL-RANK-TRAFs复合物介导的蛋白激酶信号激活,分别为经典与非经典的NF-κB、3条MAPK [c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)、受体酪氨酸激酶p38激酶(p38 kinase,p38)及细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase,ERK)]、Src、磷酸肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositde-3 kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,AKT)、钙/钙调蛋白依赖性蛋白激酶(Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase,CaMK)/活化T细胞核因子1(nuclear factor of activated T cells 1,NFATc1)、GTP结合蛋白(GTP binding protein,Ras)/大鼠肉瘤关联因子1(Ras-associated factor-1,Raf1) /ERK等信号通路。 2.2 NF-κB信号通路 NF-κB转录因子约在30年前被发现,此后随着研究的深入,发现NF-κB是炎症和免疫稳态的主要调节因子,其通过转录控制下的大量促炎因子和抗炎因子的表达,参与慢性炎症骨病和自身免疫骨病的发生[17-18]。NF-κB是对Rel转录因子家族的总称,包括NF-kappaB1(p50)、NF-kappa2(p52)、RelA(p65)、RelB和c-Rel(Rel),除Rel转录因子家族还有NF-kappaB1 (P105)和NF-kappaB2(P100)。NF-κB蛋白以异源和同源二聚体结构将上述Rel转录因子结合,如p50/RelA、p50/c-Rel、p52/c-Rel、p65/c-Rel、RelA/RelA等[17]。NF-κB1(p50)和NF-κB2(p52)双基因敲除小鼠会表现出严重的骨硬化,破骨细胞分化需要激活NF-κB信号介导[19]。NF-κB二聚体通常与抑制剂蛋白I-KappaB以非共价相互作用存在于细胞质,该复合物受到IKKα、β、γ磷酸化并发生裂解,使游离NF-κB复合物能够从细胞质转移到细胞核中触发靶基因反式激活[20]。在破骨细胞非经典NF-κB信号通路中,TRAF2/TRAF3/cIAP1/2复合物泛素化降解的NF-κB诱导激酶会激活IKKα,IKKα进而介导NF-κB p105/p65和NF-κB p100/RelB二聚体加工裂解为NF-κB p50/p65、p52/RelB并向细胞核易位,最终促进破骨细胞分化[21-23]。在破骨细胞经典NF-κB信号通路中,TRAF6通过TAK1与TAK1结合蛋白1(TGF-beta activated kinase 1 binding protein 1,TAB1)以及接头蛋白TAK1结合蛋白2(TGF-beta activated kinase 1 binding protein 2,TAB2)形成复合物,活化的TAK1会激活IKKα、β、γ三聚体加工裂解NF-κB RelA/p50向细胞核易位,且在破骨细胞中NF-κB RelA/p50除了影响上游RANK信号外,也响应肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素1信号的诱导[23-24]。NF-κB既被RANK信号和多种炎症因子激活,且存在多个亚型的效应,见图3。因此,探寻NF-κB对骨病的影响以及相应的抑制炎症、抑制破骨形成的生物材料时,应当注重NF-κB具体亚型的表达机制。 "
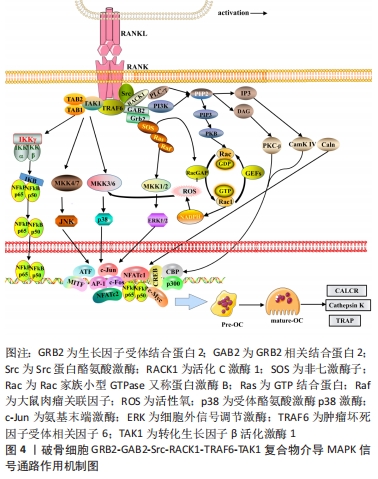
2.3 TRAF6、Src与MAPK信号通路 Src是骨代谢中的关键信号分子,在调节生长、存活、增殖、黏附和运动中发挥重要作用[25]。研究表明,成熟破骨细胞表达高水平的c-Src,敲除Src的成熟破骨细胞则无法形成肌动蛋白环和密封区,而抑制c-Src激酶活性会减少破骨前体细胞迁移和之后的皱褶边缘、再吸收坑的形成[26-27]。此外,Src家族激酶作为破骨细胞分泌盐酸和骨降解酶所必需的信号,还存在于囊泡膜中。RANK-TRAF6-TAK1复合物结构缺乏内在酪氨酸激酶活性的受体,需要通过结合适配器、支架蛋白、对接蛋白等因子来完成对下游信号的激活。研究表明,活化C激酶1(receptor for activated c kinase 1,RACK1)作为蛋白激酶C(protein kinase C,PKC)的支架,将TRAF6-TAK1复合物与MKK6、c-Src 连接,来促进破骨细胞中的细胞骨架重组[28-29]。而生长因子受体结合蛋白2(growth factor receptor bound protein 2,GRB2)与其受体相关的结合剂2(GRB2 associated binding protein 2,GAB2)形成一种对接蛋白,GAB2结构中含有GRB2-Src同源SH2结构域的结合位点,GRB2-GAB2复合物会与Src发生相互作用。此外,GAB2会被TRAF6募集到RANK的细胞质尾部并发生结合[30-31]。由此,GRB2-GAB2-Src-RACK1-TRAF6-TAK1形成了相互交叉结合的复合物,进而调控Rho家族小G蛋白Ras/Raf1/ERK信号通路和PI3K/AKT信号通路[29-30]。 MAPK本质上是一种进化保守的信号,MAPKs以MAPKKK/MAPKK/MAPK 3层激酶级联方式进行信号传导。在破骨细胞的相关研究中发现3种不同的RANK介导的MAPKs信号,分别为受体p38、JNK、ERK。3种不同MAPKs均是上文所述的GRB2-GAB2-Src-RACK1-TRAF6-TAK1复合物的下游效应信号。①RANK-TRAF6-TAK1复合物能够激活MEK4/7、MEK3/6磷酸化,活化后的MEK4/7、MEK3/6分别介导JNK、p38表达。JNK易位到细胞核内磷酸化多个转录因子,如c-Jun、c-Fos、NFAT1,p38易位到细胞核内磷酸化p53、ATF、CREB等转录因子[32-33];②GRB2-GAB2-Src复合物分别从p38、ERK信号介入破骨细胞生命过程。GRB2-GAB2从细胞质中募集非七激酶子(son of sevenless,SOS),并通过SOS的 C端富含脯氨酸的序列相互结合;而SOS作为小GTPase Ras的关键激活剂,SOS与Ras-GDP结合启动 Ras GTPase激活蛋白以促进GTP形成,在GDP与GTP交换的过程中会形成Rac1和活化Raf,Rac1结合相关蛋白以增加还原型辅酶Ⅱ氧化酶产生活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)以激活MKK6/p38信号;而活化Raf可在相关位点活化MEK1、MEK2,以磷酸化ERK1/2信号,ERK1/2易位到细胞核,会激活NFATc1、c-Myc、MITF转录因子[34-35],见图4。由于RANK的特殊结构需要募集多种酶组成复合物来完成对下游信号的激活,相关的骨再生纳米纤维的研究表明,纳米纤维支架对RANKL、MAPK-P38和Wnt 信号之间的信号传导产生串扰作用,起到促进骨再生作用[36]。因此,在探寻破骨的病理生理作用乃至干预措施的研究时应当注重RANKL与多个信号的交叉影响机制。 "
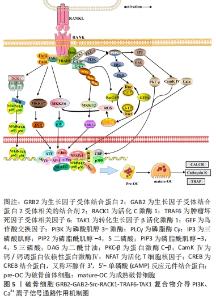
2.4 Src与PI3K、Ca2+信号通路 GRB2-GAB2-Src复合物除了募集SOS以调控Ras/Raf1/ERK信号外,其自身的活化依赖PI3K、磷脂酶Cγ(phospholipase C γ,PLCγ)的催化激活,由此RANK复合物也介导了PI3K/AKT信号和PLCγ/Ca2+信号。IA类PI3K是在3′位磷酸化磷脂酰肌醇的脂类激酶,PI3K由异二聚体催化亚基p110和调节亚基p85组成,静息情况下催化亚基p110以高亲和力与p85调节亚基结合,以阻止PI3K的激活。当p85调节亚基的SH2结构域与RANK信号的Src结合时,减弱了p85对p110的抑制作用,把胞质内的底物磷脂酰肌醇-4,5二磷酸转化为磷脂酰肌醇-3,4,5三磷酸,磷脂酰肌醇-3,4,5三磷酸作为第二信使进一步与蛋白激酶B的N端PH结构域结合,使AKT从细胞质转移到细胞膜上[37]。AKT通过多种途径激活或抑制下游一系列底物,如凋亡相关蛋白Bad、Caspase9,细胞增殖分化基因c-Myc、FoxO、p27、GSK-3,进而发挥抗凋亡、促进增殖分化的作用[37-39]。在破骨细胞形成的中、晚期,磷酸化的PLC-γ发挥分解酶活性,使底物磷脂酰肌醇-4,5二磷酸水解成三磷酸肌醇和二酰甘油2个成分,三磷酸肌醇、二酰甘油从膜内侧向胞质溶胶中扩散;三磷酸肌醇与内质网上的三磷酸肌醇受体促使内质网中储存的Ca2+流入胞内,此后二酰甘油和钙离子分别激活蛋白激酶-C-β和调钙素,蛋白激酶-C-β进一步激活DNA靶点CREB,而调钙素进一步诱导钙调神经磷酸酶、钙/钙调蛋白依赖性激酶Ⅳ来激活转录因子NFAT,NFATc1的自动扩增诱导破骨细胞特异性基因表达,如抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、降钙素受体和组织蛋白酶K等[39-40],见图5。在破骨形成的过程中,除了酶与炎症因子的相互作用关系外,还涉及GRB2-GAB2-Src复合物对磷脂类、Ca2+的激活,多种物质的综合作用最终调控破骨细胞增殖、分化、骨吸收以及抗凋亡等生命过程。"
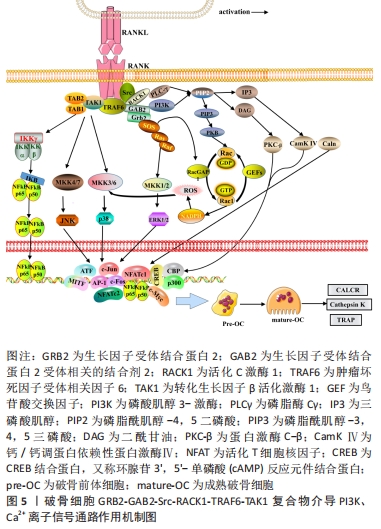
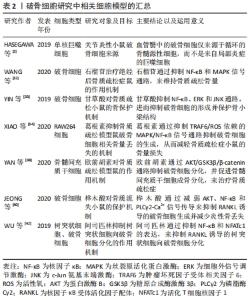
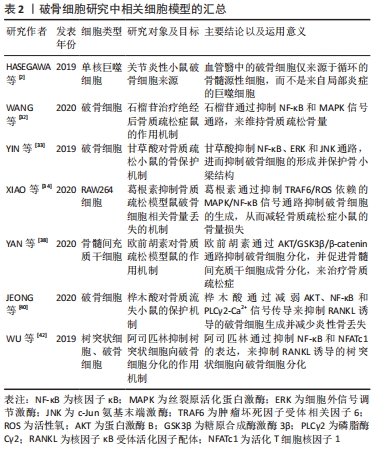
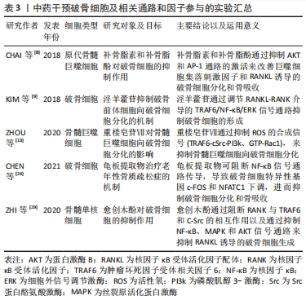
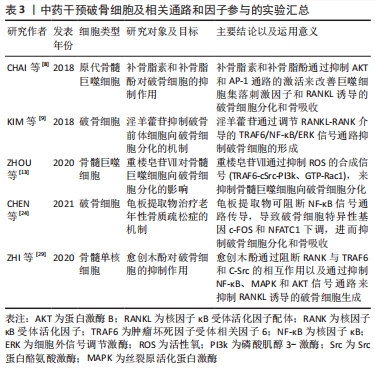
2.5 NFAT与RANK下游的转录位点 活化T细胞核因子(nuclear factor of activated T cells,NFAT)结构、功能、应答在T细胞中研究最为广泛,NFAT家族由5个成员组成,包括NFAT1(也称为NFATp或NFATc2)、NFAT2(也称为NFATc或NFATc1)、NFAT3(也称为NFATc4)、NFAT4(也称为NFATx或NFATc3)和NFAT5[41]。研究表明,除NFAT5外,NFATc1-c4均可在骨细胞中表达,且这4种NFAT亚型均受到Ca2+信号的调控。关于破骨细胞的NFAT家族研究中以NFAT1、NFAT2较多,NFATc1缺陷小鼠表现出严重的骨硬化症,而NFATc2缺陷小鼠骨骼则可正常发育[42]。由于NFATc1和NFATc2的DNA结合域的相似性且密切相关,NFATc2被募集到NFATc1启动子,与NF-κB协同促进NFATc1的扩增。因此,不能单纯的认为NFATc2不参与破骨细胞分化的调控过程。研究发现,尽管在RANKL刺激下NFATc2 mRNA水平降低,但NFATc2蛋白水平在破骨细胞生成过程中适度增加,因此,NFATc2表达可能存在翻译后调节的作用;通过诱导基序缺陷的NFATc2破骨细胞,破骨细胞吸收表现出较小的封闭区,且Acp5、Ctsk和Calcr mRNA等破骨细胞分化标志物水平表达下降,证实了NFATc2在破骨细胞成熟和骨吸收中具有直接作用[43]。值得注意的是,NFATc2和NFATc1的结构决定了两者的启动子存在共同的NFAT乙酰化结合位点;但在破骨细胞分化中,环腺苷3’,5’-单磷酸(cAMP)反应元件结合蛋白-结合蛋白和p300/CBP相关因子(PCAF)等乙酰化酶调节因子均会被招募到NFATc1启动子,但不招募到NFATc2启动子中,由此认为NFATc1是破骨细胞分化的关键作用因子[44]。 此外,目前已发现在破骨细胞生成过程中有RANK下游的多种转录因子与NFATc1启动子结合:如NF-κB、ERK1/2下游的MITF、c-Myc,p38、JNK下游的c-Fos/AP-1和c-Myc。c-Fos是AP-1家族的成员,调控破骨细胞分化过程,受到p38、JNK激活后c-Fos、c-Jun、ATF、MITF蛋白在胞核中形成二聚体复合物AP-1,敲除c-Fos或c-Jun基因的小鼠会发生骨硬化症[44]。NFATc1的自动扩增也需要AP-1的激活,以实现NFATc1对破骨细胞分化特异性基因的稳健诱导[45-46]。在破骨细胞吸收功能方面,PANG等[47-48]研究表明,AP-1、MITF和NFATc1能够独立刺激组织蛋白酶K启动子活性,但任何两者的组合均会进一步增强组织蛋白酶K启动子的活性,其中AP-1(c-fos/c-jun)和NFATc1的组合诱导的活性增加最大。因此,NFAT与RANK多个下游靶点发生组蛋白修饰,协同参与了调控破骨细胞分化、增殖、骨吸收等生命过程。 2.6 破骨细胞研究实验分类信息汇总 见表1-3。 "
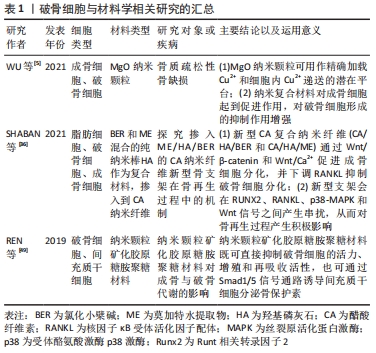
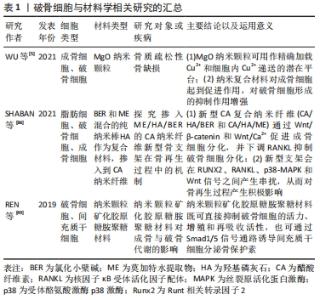
| [1] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2073. [2] HASEGAWA T, KIKUTA J, SUDO T, et al. Identification of a novel arthritis-associated osteoclast precursor macrophage regulated by FoxM1. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(12):1631-1643. [3] AMIN N, BOCCARDI V, TAGHIZADEH M, et al. Probiotics and bone disorders: the role of RANKL/RANK/OPG pathway. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(3):363-371. [4] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39(1):19-26. [5] WU H, YANG S, XIAO J, et al. Facile synthesis of multi-functional nano-composites by precise loading of Cu2+ onto MgO nano-particles for enhanced osteoblast differentiation, inhibited osteoclast formation and effective bacterial killing. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 130:112442. [6] LI ZH, SI Y, XU G, et al. High-dose PMA with RANKL and MCSF induces THP‑1 cell differentiation into human functional osteoclasts in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(6):8380-8384. [7] MUN SH, PARK PSU, PARK-MIN KH. The M-CSF receptor in osteoclasts and beyond. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(8):1239-1254. [8] CHAI L, ZHOU K, WANG S, et al. Psoralen and Bakuchiol Ameliorate M-CSF Plus RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Resorption Via Inhibition of AKT and AP-1 Pathways in Vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):2123-2133. [9] KIM B, LEE KY, PARK B. Icariin abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264.7 cells. Phytomedicine. 2018;51:181-190. [10] AVNET S, CHANO T, MASSA A, et al. Acid microenvironment promotes cell survival of human bone sarcoma through the activation of cIAP proteins and NF-κB pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 2019;9(6):1127-1144. [11] YAO Z, LEI W, DUAN R, et al. RANKL cytokine enhances TNF-induced osteoclastogenesis independently of TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) 6 by degrading TRAF3 in osteoclast precursors. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(24):10169-10179. [12] DOU Y, TIAN X, ZHANG J, et al. Roles of TRAF6 in Central Nervous System. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(9):1306-1313. [13] ZHOU L, SONG H, ZHANG Y, et al. Polyphyllin VII attenuated RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation via inhibiting of TRAF6/c-Src/PI3K pathway and ROS production. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1): 112-121. [14] SCHIMMACK G, SCHORPP K, KUTZNER K, et al. YOD1/TRAF6 association balances p62-dependent IL-1 signaling to NF-κB. Elife. 2017;6:e22416. [15] SWARNKAR G, CHEN TH, ARRA M, et al. NUMBL Interacts with TAK1, TRAF6 and NEMO to Negatively Regulate NF-κB Signaling During Osteoclastogenesis. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12600. [16] AN Y, ZHANG H, WANG C, et al. Activation of ROS/MAPKs/NF-κB/NLRP3 and inhibition of efferocytosis in osteoclast-mediated diabetic osteoporosis. FASEB J. 2019;33(11):12515-12527. [17] MITCHELL JP, CARMODY RJ. NF-κB and the Transcriptional Control of Inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2018;335:41-84. [18] LEE WS, YASUDA S, KONO M, et al. MicroRNA-9 ameliorates destructive arthritis through down-regulation of NF-κB1-RANKL pathway in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Clin Immunol. 2020;212:108348. [19] JIMI E, TAKAKURA N, HIURA F, et al. The Role of NF-κB in Physiological Bone Development and Inflammatory Bone Diseases: Is NF-κB Inhibition “Killing Two Birds with One Stone”?. Cells. 2019;8(12):1636. [20] BAK SU, KIM S, HWANG HJ, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)/carbon monoxide (CO) axis suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation by inhibiting redox-sensitive NF-κB activation. BMB Rep. 2017;50(2):103-108. [21] KIM I, KIM JH, KIM K, et al. The IRF2BP2-KLF2 axis regulates osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation. BMB Rep. 2019;52(7):469-474. [22] TAKAKURA N, MATSUDA M, KHAN M, et al. A novel inhibitor of NF-κB-inducing kinase prevents bone loss by inhibiting osteoclastic bone resorption in ovariectomized mice. Bone. 2020;135:115316. [23] PARK JH, LEE NK, LEE SY. Current Understanding of RANK Signaling in Osteoclast Differentiation and Maturation. Mol Cells. 2017;40(10):706-713. [24] CHEN H, SHEN G, SHANG Q, et al. Plastrum testudinis extract suppresses osteoclast differentiation via the NF-κB signaling pathway and ameliorates senile osteoporosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;276: 114195. [25] ANGATA T. Siglecs that Associate with DAP12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020; 1204:215-230. [26] MATSUBARA T, ADDISON WN, KOKABU S, et al. Characterization of unique functionalities in c-Src domains required for osteoclast podosome belt formation. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100790. [27] GYŐRI DS, MÓCSAI A. Osteoclast Signal Transduction During Bone Metastasis Formation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:507-522. [28] PARK JH, JEONG E, LIN J, et al. RACK1 interaction with c-Src is essential for osteoclast function. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(7):1-9. [29] ZHI X, FANG C, GU Y, et al. Guaiacol suppresses osteoclastogenesis by blocking interactions of RANK with TRAF6 and C-Src and inhibiting NF-κB, MAPK and AKT pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):5122-5134. [30] JEONG E, CHOI HK, PARK JH, et al.STAC2 negatively regulates osteoclast formation by targeting the RANK signaling complex. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(8):1364-1374. [31] WANG D, GU JH, FENG LL, et al. 1-α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 potentiates avian osteoclast activation by increasing the formation of zipper-like structure via Src/Rac1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;501(2):576-583. [32] WANG W, BAI J, ZHANG W, et al. Protective Effects of Punicalagin on Osteoporosis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and Inflammation via the NF-κB and MAPK Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:696. [33] YIN Z, ZHU W, WU Q, et al. Glycyrrhizic acid suppresses osteoclast differentiation and postmenopausal osteoporosis by modulating the NF-κB, ERK, and JNK signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;859: 172550. [34] XIAO L, ZHONG M, HUANG Y, et al. Puerarin alleviates osteoporosis in the ovariectomy-induced mice by suppressing osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of TRAF6/ROS-dependent MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(21):21706-21729. [35] JEEVARATNAM K, SALVAGE SC, LI M, et al. Regulatory actions of 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate on osteoclast function: possible roles of Epac-mediated signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1433(1):18-28. [36] SHABAN NZ, KENAWY MY, TAHA NA, et al. Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers: Incorporating Hydroxyapatite (HA), HA/Berberine or HA/Moghat Composites, as Scaffolds to Enhance In Vitro Osteoporotic Bone Regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(23):4140. [37] LOU Z, PENG Z, WANG B, et al. miR-142-5p promotes the osteoclast differentiation of bone marrow-derived macrophages via PTEN/PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(5):815-824. [38] YAN DY, TANG J, CHEN L, et al. Imperatorin promotes osteogenesis and suppresses osteoclast by activating AKT/GSK3 β/β-catenin pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(3):2330-2341. [39] KIM JM, LEE K, JEONG D. Selective regulation of osteoclast adhesion and spreading by PLCγ/PKCα-PKCδ/RhoA-Rac1 signaling. BMB Rep. 2018;51(5):230-235. [40] JEONG DH, KWAK SC, LEE MS, et al. Betulinic Acid Inhibits RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis via Attenuating AKT, NF-κB, and PLCγ2-Ca2+ Signaling and Prevents Inflammatory Bone Loss. J Nat Prod. 2020; 83(4):1174-1182. [41] KAMANO Y, WATANABE J, IIDA T, et al. Binding of PICK1 PDZ domain with calcineurin B regulates osteoclast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496(1):83-88. [42] WU L, LUO Z, LIU Y, et al. Aspirin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation in dendritic cells by suppressing NF-κB and NFATc1 activation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):375. [43] YU J, ZANOTTI S, SCHILLING L, et al. Nuclear factor of activated T cells 2 is required for osteoclast differentiation and function in vitro but not in vivo. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(11):9334-9345. [44] BAEK K, PARK HJ, BAEK JH, et al. Isoproterenol Increases RANKL Expression in a ATF4/NFATc1-Dependent Manner in Mouse Osteoblastic Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2204. [45] MOGNOL GP, GONZÁLEZ-AVALOS E, GHOSH S, et al. Targeting the NFAT:AP-1 transcriptional complex on DNA with a small-molecule inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(20):9959-9968. [46] KATAGIRI T, KAMEDA H, NAKANO H, et al. Regulation of T cell differentiation by the AP-1 transcription factor JunB. Immunol Med. 2021;44(3):197-203. [47] PANG M, RODRÍGUEZ-GONZALEZ M, HERNANDEZ M, et al. AP-1 and MITF interact with NFATc1 to stimulate cathepsin K promoter activity in osteoclast precursors. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(8):12382-12392. [48] JANG JS, KANG IS, CHA YN, et al. Vav1 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. BMB Rep. 2019;52(11):659-664. [49] REN X, ZHOU Q, FOULAD D, et al. Nanoparticulate mineralized collagen glycosaminoglycan materials directly and indirectly inhibit osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast activation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(5):823-834. [50] CAI X, XING J, LONG CL, et al. DOK3 Modulates Bone Remodeling by Negatively Regulating Osteoclastogenesis and Positively Regulating Osteoblastogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(11):2207-2218. [51] KUROTAKI D, YOSHIDA H, TAMURA T. Epigenetic and transcriptional regulation of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 2020;138:115471. [52] KIM KT, LEE YS, HAN I. The Role of Epigenomics in Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9455. |
| [1] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [2] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [3] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [4] | Lin Shi, Yuan Jiayao, Lin Xiancan, Yang Binbin, Wu Jianjun, Dongzhi Zhuoma, Tang Zijia, Yang Zhijie, Wan Lei, Huang Hongxing. Diagnostic value of peripheral blood interferon-gamma and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 165-170. |
| [5] | Wei Tengfei, He Xiaoming, Wei Yurou, Zhan Zhiwei, He Mincong, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Differential expression of Piezo1 in osseous tissue of steroid- and alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 270-275. |
| [6] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [7] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [8] | Zhang Jie, Tian Ai. Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 314-321. |
| [9] | Zhu Miaomiao, Kong Fanming, Zhao Qian. Exercise regulates lactic acid metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 322-328. |
| [10] | Feng Hao, Zhang Bin, Wang Jianping. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can improve bone metabolism in osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 72-75. |
| [11] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [12] | Xi Hualei, Xue Bing, Xu Wanqiu, Xu Xiaohang, Yao Lihong, Wang Xiumei. Neural differentiation and neural biomarker expression of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 91-98. |
| [13] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| [14] | Shi Xu, Li Ruiyu, Zhang Bing, Chen Qi, Zuo Hua. Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 121-129. |
| [15] | Guo Yujun, Lu Wenjun, Yang Shulong, Li Zhaozhu. Effect of urine-derived stem cells and their exosomes on kidney diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 138-144. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||