Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 314-321.doi: 10.12307/2022.1006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration
Zhang Jie1, Tian Ai1, 2
- 1School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Restoration and Implant, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-10Accepted:2022-03-03Online:2023-01-18Published:2022-06-20 -
Contact:Tian Ai, MD, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China; Department of Restoration and Implant, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jie, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760192 (to TA); Joint Fund of Guiyang Science and Technology Bureau, No. [2018]1-82 (to TA); Guizhou Medical University Doctoral Start-up Fund, No. YJ2016-16 (to TA)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jie, Tian Ai. Advances in the signaling pathway of M2 macrophages involved in bone regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 314-321.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
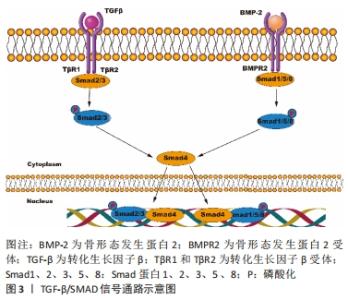
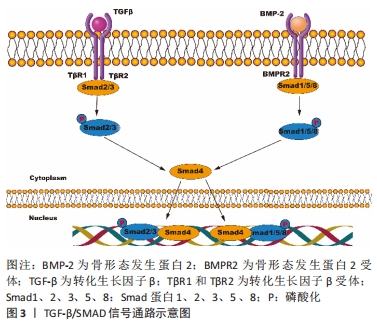
2.1 TGF-β/Smad通路 TGF-β具有调节成骨细胞的迁移、增殖和早期分化等功能。哺乳动物包括TGF-β1、TGF-β2和TGF-β3亚型。已有研究报道巨噬细胞可能产生TGF-β诱导损伤后的异位骨化[8]。骨形态发生蛋白是一类多功能生长因子,属于TGF-β超家族中的一员,在成骨诱导因子的所有亚型中,骨形态发生蛋白2的效能最强,能够大幅提升骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化,加速骨愈合[9]。TGF-β信号经一个复合体介导,该复合体具有3种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性的跨膜受体(Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型受体;TβR1,2和3)。TβR2磷酸化TβR1,而TβR1通过Smad蛋白复合物将信号从细胞膜转到细胞核[10],见图3。"
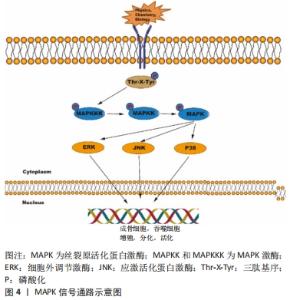
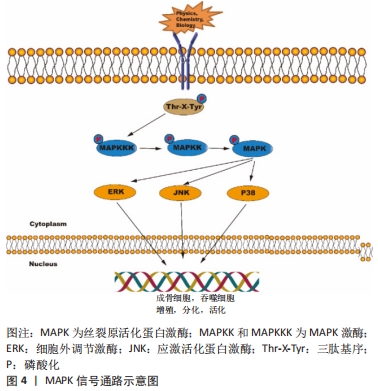
众多研究表明TGF-β/Smad信号通路参与调节巨噬细胞的M2型极化,使TGF-β的分泌增加,并激活Smad信号,从而提高RUNX2等成骨标记基因的表达以促进成骨细胞的增殖和早期分化。最近,具有生理功能的生物支架通过与免疫微环境反应从而介导的巨噬细胞极化得到了广泛关注,其可促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,从而有效推动骨缺损修复。ZHANG等[11]研究表明白细胞介素4掺入富钙结冷胶(Ca-GG)水凝胶微球中可促进巨噬细胞向M2极化,减少细胞凋亡。Ca-GG+白细胞介素4组能显著提高TGF-β1R、p-Smad2和p-Smad3蛋白表达,同时使用siRNA抑制TGF-β1R的表达,碱性磷酸酶染色结果显示siRNA组的成骨能力显著降低以及Runx2的表达被逆转;此外,体内研究显示在术后12周,Ca-GG+白细胞介素4组与正常对照组相比,新生骨体积明显增加,骨钙素和Runx2的表达也增加。最新研究发现,将含TGF-β1的明胶-肝素微球(MS/TGF-β1)负载到可注射的锂-肝素水凝胶中,其中锂-肝素水凝胶不仅作为MS/TGF-β1的传递载体,而且作为促进成骨的锂离子释放基质,而TGF-β1则通过TGF-β/Smad2/3/Snail途径将促炎的M1巨噬细胞转变为促进愈合的M2表型,从而提高TGF-β、骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子的表达,早期的骨免疫调节和锂诱导的骨形成相结合,促进了成骨和血管生成,进而引导骨再生[12]。 骨形态发生蛋白/Smad信号通路在成骨细胞分化调控中起重要作用,同时该信号通路可受微环境中金属离子和炎症因子的调节影响巨噬细胞的功能活化。骨形态发生蛋白2通过pSmad1/5/8依赖的途径激活巨噬细胞,并增加血管内皮生长因子的表达产生正反馈回路[13]。例如,微量的镁离子(100 mg/L)可通过抑制TLR-核因子κB(nuclear factor-κB,NF-κB)信号通路,导致M2表型活化,使血管内皮生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2的分泌增加,进而上调Smad4和BMPR1A蛋白水平,激活骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad信号,使骨髓间充质干细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性与成骨基因大幅提升[14]。不仅如此,骨形态发生蛋白/Smad信号途径可与NF-κB、MAPK信号串扰以介导白细胞介素1β对牙周韧带干细胞的双重效应。MAO等[15]首次表明低浓度的白细胞介素1β可显著增加牙周韧带干细胞中骨形态发生蛋白2的表达,促进骨形态发生蛋白/Smad信号通路的激活,导致成骨细胞特异性转录因子、骨桥蛋白和碱性磷酸酶基因的表达增加。但是高剂量的白细胞介素1β处理可通过NF-κB、p38和JNK通路的逐渐磷酸化以剂量依赖方式下调pSmad1/5的水平,从而抑制成骨。同时,牙周韧带干细胞的成骨功能受损导致更多的CCL2和CCL5等趋化因子和炎症细胞因子释放,最终诱导巨噬细胞的趋化。 2.2 MAPK信号通路 受到广泛刺激后,MAPK将信号自细胞表面向胞核传递,再对诸多生理活动施以调节,包括成骨和巨噬细胞的增殖、分化与活化等。传统的MAPK包括细胞外调节激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK)1/2、ERK5、JNK与p38MAPK这4条途径[16]。JNK和p38MAPK在细胞暴露于各种物理、化学和生物应激刺激后被激活,而ERK1/2级联信号通路主要处理细胞生长因子刺激的信号[17]。MAPK家族的成员共享相关的结构和生化特性,特别是当它们被位于激酶激活环(T-loop)中的三肽基序(Thr-X-Tyr)上的双重磷酸化激活时,通过一个由(MAPKKK或MAP3K)-(MAPKK或MAP2K)-MAPK组成的级联系统来激活,依次活化将信号转入细胞核内,进而改变基因和蛋白的表达、产生相应的生物学效应[18],见图4。 "
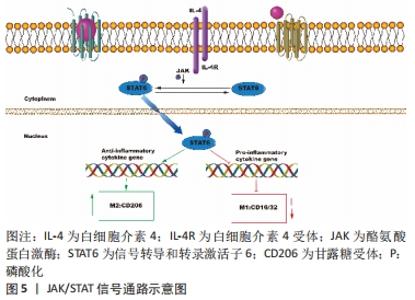
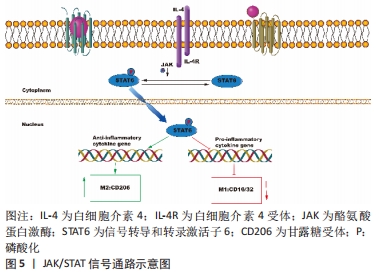
JNK信号通路是巨噬细胞极化和炎症细胞因子生成的一个重要调节器,其主要通过增加p-JNK和下游转录因子c-Myc的表达改变巨噬细胞的极化类型[19];同时,该信号通路在M2巨噬细胞调节骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化中对骨代谢和骨重建起关键作用。LI等[20]在巨噬细胞与牙周韧带干细胞共培养体系中发现,使用CM-M2(白细胞介素4诱导巨噬细胞的条件培养基)处理的牙周韧带干细胞能显著上调p-Akt、p-JNK和c-Jun的表达,并提高牙周韧带干细胞中牙骨质蛋白1、骨唾液蛋白和骨钙素的表达,这表明M2巨噬细胞可以通过Akt和JNK通路促进牙周韧带干细胞的成牙骨质分化。 p38与ERK信号通路经调控细胞周期调节器的表达与Runx2的活性,对成骨细胞的增殖、分化与凋亡施以调节[21]。XU等[22]通过粗糙微米钛表面(SLA)与掺锶微纳米表面(Sr-SLA)在体内外实验的成骨效应对比发现,伴随愈合时间延长,M1细胞数目不断下降,M2细胞数目不断增多,掺锶微纳米表面的促炎因子(白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β)的分泌显著降低,抗炎因子(白细胞介素10、骨形态发生蛋白2和血小板衍生生长因子)的分泌明显增加;同时掺锶微纳米表面上ERK的磷酸化蛋白水平、成骨基因表达增加,这说明掺锶微纳米表面可能通过ERK信号调节巨噬细胞向M2型,从而影响成骨分化。钛颗粒诱导的体内骨质溶解和骨丢失主要通过激活MAPK信号通路驱动巨噬细胞进入M1炎性状态。研究发现哈尔明碱、氯化锂和西红花苷均可下调MAPK信号从而减轻钛颗粒诱导的骨溶解和增强骨组织的免疫调节作用。其中哈尔明碱通过抑制p-JNK的活化,而氯化锂则通过下调p-ERK和p-p38水平诱导M2分化,减少M1巨噬细胞的数量,并增加抗炎和骨相关细胞因子的释放从而提高大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力[23-24]。ZHU等[25]研究发现使用西红花苷能显著减弱钛颗粒诱导后CCR7、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的表达,有效增加CD206、白细胞介素10的分泌和精氨酸1以及成骨细胞因子表达,具有抑制炎症和促进骨整合的作用,并且能降低p38和JNK的活化以抑制骨细胞凋亡。以上结果表明MAPK信号通路的抑制可能是治疗钛颗粒引起的炎性骨溶解的潜在机制。 2.3 JAK/STAT信号通路 JAK/STAT 信号通路是多种细胞因子、激素和生长因子的重要下游介质,其对骨骼发育、愈合与新陈代谢发挥关键作用[26]。此信号通路的构成为细胞酪氨酸受体、STAT蛋白与K蛋白,主要涉及4类JAK亚型(JAK1、JAK2、JAK3和酪氨酸激酶2)和7个STAT转录因子(STAT1,STAT2,STAT3,STAT4,STAT5a,STAT5b和STAT6)。JAK与受体结合后被激活,导致STATs的磷酸化,随后磷酸化的STATs二聚化,然后通过核膜运输到细胞核,以调节下游特定靶基因的转录[27]。 JAK/STAT信号的激活与多种细胞因子、生长因子以及内外环境相关,促使一系列免疫反应的发生,从而引起相应的细胞或骨组织的改变[28-30]。研究证实,白细胞介素4经由白细胞介素4受体(IL-4R1与IL-4R2)来激活STAT6,对巨噬细胞向M2极化施以调节[28],并分泌CD206、白细胞介素10和白细胞介素6等抗炎因子以促进成骨[5],见图5。然而JAK/STAT的抑制剂AG490可以明显抑制巨噬细胞的M2型极化[30],这为颌骨缺损的治疗提供了一个新方向。 "
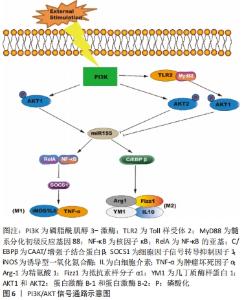
除此之外,JAK/STAT通路是骨再生材料促进成骨的正向调节因子。YU等[29]指出脱细胞甲床支架的植入会增加p-JAK2和p-STAT3的表达,使巨噬细胞极化向M2表型,同时增加了骨形态发生蛋白2和RUNX2的表达,从而促进大鼠颅骨临界缺损的骨形成以及成骨分化。另一项关于Exendin-4(GLP-1受体激动剂)对骨质疏松大鼠骨形成影响的研究指出,Exendin-4通过促进巨噬细胞M2极化来预防骨丢失和促进骨形成,其通过GLP-1R信号和Stat3信号之间的信号交叉,诱导骨髓巨噬细胞极化为M2亚型,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向吸收部位迁移,M2巨噬细胞又分泌TGF-β1来促进成骨[31]。 2.4 PI3K/Akt信号通路 PI3K/Akt信号通路是细胞代谢过程的经典信号通路,对骨生长与骨形成具一定调节作用。此外该通路对巨噬细胞的存活起着至关重要的作用[32]。外界刺激可以激活PI3K并不同程度地调节Akt1和Akt2的激活。AKT1上调miR-155 mRNA表达,从而激活RelA/NF-κB通路,下调细胞因子信号转导抑制因子1基因的转录,导致促炎巨噬细胞基因的表达增加。但是,Akt2抑制miR-155,导致CAAT/增强子结合蛋白β(C/EBPβ)上调,并导致M2基因的表达。其中Toll 样受体2(Toll-like Receptors2,TLR2)、髓系分化初级反应基因88(MyD88)能激活Akt1,抑制miR-155[33],见图6。 "
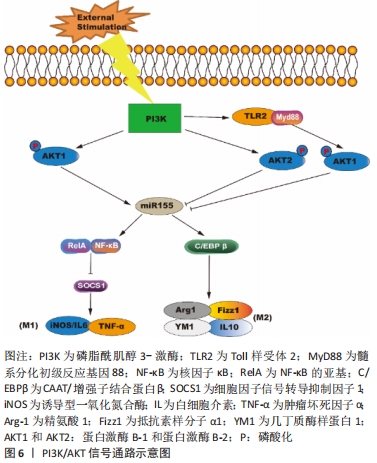
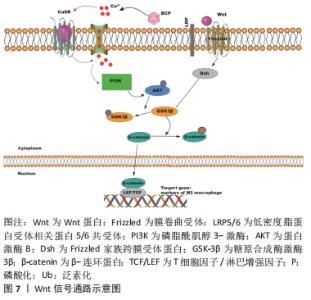
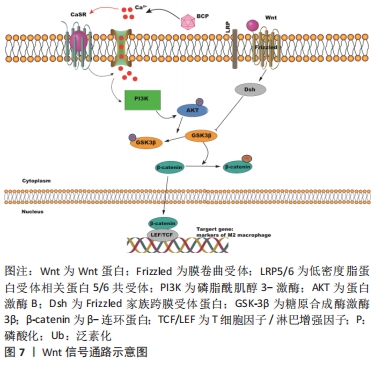
有学者提出,在具有亚微米表面形貌的磷酸三钙陶瓷上培养4 d的RAW264.7细胞的整合素β1水平以及PI3K和Akt的磷酸化水平明显升高,并且磷酸三钙陶瓷上M2分泌的细胞因子呈高表达。总之,这表明磷酸三钙陶瓷可能通过PI3K/Akt途径与整合素β1结合,驱动巨噬细胞进入促愈合状态,从而在早期形成有利于异位骨再生的免疫环境[34]。此外,ZHAO等[35]发现PI3K/AKT信号通路还可与糖原合成酶激酶3β(glycogen synthase kinase-3β,GSK-3β)/β-连环蛋白(β-catenin)信号通路相互交联从而参与免疫调节影响膜内成骨。他们的实验结果显示,巨噬细胞清道夫受体1(macrophage scavenger receptor1,MSR1) 会抑制GSK-3β的磷酸化,增强β-catenin的核转位,使PI3K/Akt通路活化,经提升M2巨噬细胞的PGC1 mRNA的表达,对线粒体的生物发生和氧合酶(OXPHOS)的表达施以促进作用,由此增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。同时,动物实验结果揭示MSR1 KO小鼠在术后7 d的M2标记物的mRNA表达下降,导致膜内骨修复延迟。有趣的是,将WT小鼠的骨髓移植至KO小鼠体内后,M2标记物的表达和成骨效应发生逆转。但是由于巨噬细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞之间的相互作用是复杂的,MSR1是否参与了骨髓间充质干细胞对M1或M2巨噬细胞的免疫调节功能,以及M1和M2极化巨噬细胞所涉及的具体机制有待进一步分析。 2.5 Wnt信号通路 在胚胎发育过程中,Wnt信号在各种功能中发挥关键调节作用,包括参与骨骼和软骨的形成[36]。该信号通路以Wnt/β-catenin传导通路、非对称细胞分裂的细胞内通路、Wnt细胞平面极化通路与调控纺锤体方向、Wnt/Ca2 +通路为主[37]。Wnt/β-catenin属经典传导通路,该信号通路激活的核心分子是β-catenin[38]。Wnt配体是巨噬细胞用来调节炎症、伤口愈合和再生微环境的关键信号分子,可通过生化和物理线索激活此配体来修饰巨噬细胞的表型,从而改变巨噬细胞中的Wnt信号[39],这表明Wnt信号传导可以差异性调节巨噬细胞极化。为此,有学者研究表明Wnt/β-catenin在巨噬细胞的M2极化过程中被激活并转移到细胞核,进而结合TCF/LEF转录因子,然后转录下游的目的基因。在这个过程中,GSK-3β作为Wnt/β-catenin信号轴的重要抑制剂,可促进β-catenin的泛素化和降解,降低它的蛋白稳定性,并降低其核进入[40]。此外,该信号的丢失不仅减弱了巨噬细胞的极化,而且减少了间充质干细胞和CD4+T细胞等对骨愈合至关重要的细胞类型的募集[39]。近年来,生物材料的骨免疫调节受到广泛关注。β-磷酸三钙作为一种合成陶瓷生物材料,可诱导巨噬细胞极化转变为M2型,同时通过上调Wnt信号通路中WNT6和下调WIF1的表达水平来促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[41]。ZHANG等[42]提出在成骨过程中,含有羟基磷灰石和β-磷酸三钙的双相磷酸钙能持续释放Ca2+,从而维持M2巨噬细胞极化的长期诱导,促进间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化。该结果的具体机制是由于细胞内Ca2+浓度的增加激活了PI3K/AKT信号通路,并诱导了GSK-3β的磷酸化增加而降低下游活性,导致更多的β-catenin转移,并通过钙传感受体(CaSR)激活巨噬细胞中Arg1和白细胞介素10 (M2标记基因)的转录。在钙传感受体抑制剂的作用下,阻断钙传感受体活性可减少巨噬细胞促进Ca2+的内流,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路和M2极化基因的表达,并减弱上清液刺激的间充质干细胞矿化,见图7。虽然巨噬细胞和Wnt信号长期以来被认为在骨整合中扮演着独立的关键角色,但是目前国内外关于Wnt信号在骨形成和代谢中如何介导巨噬细胞极化的报道较少,有待进一步研究。 "

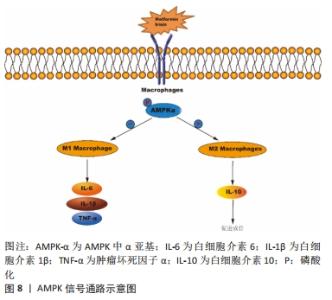
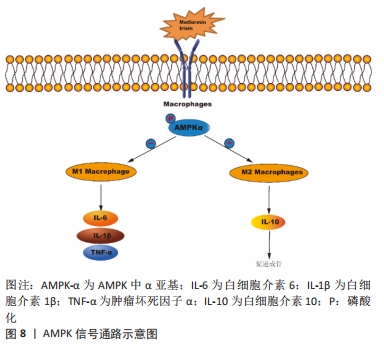
二甲双胍作为一种降血糖药物,可增强成骨细胞的矿化和分化,并在破骨细胞分化过程中负向调节核因子κB受体活化因子配体(RANKL)的表达[46]。YAN等[47]发现二甲双胍可减轻颗粒诱导的小鼠颅骨溶解、炎症严重程度和破骨细胞数量,深入研究后发现二甲双胍不仅能抑制白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的产生,而且能促进抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的释放,并呈剂量依赖性地向M2型转变,并显著促进AMPK的磷酸化,有利于成骨细胞分化。但在使用AMPK抑制剂后,小鼠颅骨的成骨效应显著减弱,促炎因子分泌降低,进一步的揭示AMPK信号传导在二甲双胍抑制超高分子量聚乙烯颗粒诱导的体内溶骨作用的重要作用。另一项关于成骨细胞体外培养研究报道显示鸢尾素诱导的M2巨噬细胞极化明显促进了成骨,并形成矿化颗粒[48],这可能是通过激活AMPK信号通路实现的,表现为AMPK表达水平增高,促炎细胞因子的分泌增加和基质矿化增加。相反,在应用AMPK-αsiRNA敲除后引起鸢尾素的AMPK表达水平降低,同样,鸢尾素介导的CD206-APC、精氨酸1和TGF-β1的表达降低,而肿瘤坏死因子α的表达上调,成骨能力降低[48]。以上研究提示AMPK信号可能通过调节巨噬细胞向M2表型极化中在骨代谢中起重要作用。 2.7 HIF信号通路 HIF信号复杂地参与了骨骼发育和修复过程中血管生成和成骨的耦合。在缺氧的骨微环境下,HIFs的激活刺激了多个基因的转录,对间充质干细胞的招募、分化和血管生成产生影响[49]。HIF是一种αβ异源二聚体转录因子,包含1个HIF-1β亚基和3个α亚基(HIF-1α、HIF-2α和HIF-3α)。然而β亚基经常过量存在,而α亚基依赖氧含量进行功能表达[50]。在低氧条件下,脯氨酸羟化酶结构域的酶活性受到抑制,导致细胞质中HIF-α的积累,随后转位到细胞核,最后与β亚单位二聚化。在招募各类其他转录共激活因子时,此复合体结合缺氧调节基因启动子处的缺氧反应元件,从而对转录进行诱导[49]。 除了缺氧,生物力学刺激、生长因子与促炎症细胞因子同样对HIF通路具调节作用,进而影响M1/M2比例。LIU等[51]提出将地塞米松包埋于重组人骨形态发生蛋白的多孔介孔生物玻璃支架中,通过控制地塞米松的负载量和快速释放,调节巨噬细胞募集和促进M2/M1比值在第4天因B6D/M(重组人骨形态发生蛋白2与地塞米松的质量比为1∶6)激发而升高,进而激活间充质干细胞中的HIF-3α及其下游的叉头盒O信号通路和转录因子SOX-5,促进SOX-9和随后的Ⅱ型胶原的表达,最终有利于种植体整合、间充质干细胞的招募和凝聚以及软骨生成的平衡。此外HIF信号还可与PI3K/AKT信号相互传递影响巨噬细胞表型转化促进2型糖尿病大鼠的骨再生。DAI等[52]在仿生电微环境下通过调节巨噬细胞极化观察糖尿病大鼠的骨再生效果,体外实验发现高血糖条件下电微环境下减弱M1巨噬细胞极化,上调M2极化能力,伴随干扰素调节因子5、p-AKT2 和 HIF-1α的抑制,使高糖极化膜组的碱性磷酸酶活性和成骨相关mRNA的表达水平上调;体内研究结果显示,在炎症早期M1巨噬细胞比例较低,但在伤口愈合阶段M2极化增强;在纳米复合膜植入术后的第4周和第8周,极化组的骨密度、厚度和小梁数量显著增加,且有更多成熟的类骨质组织和新骨生成。 2.8 RhoA/ROCK信号通路 RhoA 是一种鸟苷三磷酸酶(guanosine triphosphatases,GTPase),它不仅参与调节 F-actin 应力纤维的形成、细胞形态、迁移、增殖和各类细胞的分化,还参与RhoA、Rac1和CDC42的组成[53]。RhoA/ROCK通路在M2型巨噬细胞转换中的作用已被明确。例如,最近的一项研究发现,抑制RhoA/ROCK信号通路可以导致M2表型转换为M1表型[54]。这与ZHU等[55]的研究结果一致,即RhoA、Rac1和CDC42的上调可以激活蜂窝状TiO2鳞片上培养的巨噬细胞M2极化相关的信号通路,导致GTPase蛋白和两种特异性磷酸化ROCK底物,即磷酸化肌球蛋白轻链(p-MLC)和肌球蛋白磷酸酶靶标1(p-MYPT1)的表达显著上调;相反,RhoA、Rac1和CDC42的下调导致巨噬细胞的M1活化。此外,他们的结果不仅证实Rho家族GTPase蛋白的上调激活了RhoA/ROCK信号通路,最终诱导M2巨噬细胞活化,而且证实钛表面蜂窝状TiO2结构鳞片的缩小不但能在体外促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化,而且在体内也能促进骨-种植体的骨整合。此项新发现有利于钛种植体的优化与设计,为今后引导性骨再生的免疫疗法开辟了新路径。 "

| [1] SCHENK RK, BUSER D, HARDWICK WR, et al. Healing pattern of bone regeneration in membrane-protected defects: a histologic study in the canine mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1994;9(1):13-29. [2] FUNES SC, RIOS M, ESCOBAR-VERA J, et al. Implications of macrophage polarization in autoimmunity. Immunology. 2018;154(2):186-195. [3] MURRAY PJ. Macrophage Polarization. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017;79:541-566. [4] LASSUS J, SALO J, JIRANEK WA, et al. Macrophage activation results in bone resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;(352):7-15. [5] ZHENG ZW, CHEN YH, WU DY, et al. Development of an Accurate and Proactive Immunomodulatory Strategy to Improve Bone Substitute Material-Mediated Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2018; 8(19):5482-5500. [6] GONG L, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. The Macrophage Polarization Regulates MSC Osteoblast Differentiation in vitro. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46(1):65-71. [7] LIU YC, ZOU XB, CHAI YF, et al. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2014;10(5):520-529. [8] WANG X, LI F, XIE L, et al. Inhibition of overactive TGF-beta attenuates progression of heterotopic ossification in mice. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):551. [9] NIU H, MA Y, WU G, et al. Multicellularity-interweaved bone regeneration of BMP-2-loaded scaffold with orchestrated kinetics of resorption and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2019;216:119216. [10] LIU X, LI X, TAO Y, et al. TCDD inhibited the osteogenic differentiation of human fetal palatal mesenchymal cells through AhR and BMP-2/TGF-β/Smad signaling. Toxicology. 2020;431:152353. [11] ZHANG J, SHI H, ZHANG N, et al. Interleukin-4-loaded hydrogel scaffold regulates macrophages polarization to promote bone mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation via TGF-beta1/Smad pathway for repair of bone defect. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(10):e12907. [12] LI D, YANG Z, ZHAO X, et al. Osteoimmunomodulatory injectable Lithium-Heparin hydrogel with Microspheres/TGF-β1 delivery promotes M2 macrophage polarization and osteogenesis for guided bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2022;435:134991. [13] WEI F, ZHOU Y, WANG J, et al. The Immunomodulatory Role of BMP-2 on Macrophages to Accelerate Osteogenesis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(7-8): 584-594. [14] ZHANG X, CHEN Q, MAO X. Magnesium Enhances Osteogenesis of BMSCs by Tuning Osteoimmunomodulation. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:7908205. [15] MAO CY, WANG YG, ZHANG X, et al. Double-edged-sword effect of IL-1β on the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells via crosstalk between the NF-κB, MAPK and BMP/Smad signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7(7):e2296. [16] KHOLODENKO BN, BIRTWISTLE MR. Four-dimensional dynamics of MAPK information processing systems. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009; 1(1):28-44. [17] YUE J, LóPEZ JM. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21 (7):2346. [18] 武明云 , 虞坚尔 , 薛征 , 等. 基于 MAPK 信号通路的中药治疗支气管哮喘的实验研究进展[J]. 海中医药大学学报 ,2019,33(2):86-91. [19] HAO J, HU Y, LI Y, et al. Involvement of JNK signaling in IL4-induced M2 macrophage polarization. Exp Cell Res. 2017;357(2):155-162. [20] LI X, HE X T, KONG DQ, et al. M2 Macrophages Enhance the Cementoblastic Differentiation of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells via the Akt and JNK Pathways. Stem Cells. 2019;37(12):1567-1580. [21] GE C, XIAO G, JIANG D, et al. Critical role of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-MAPK pathway in osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development. J Cell Biol. 2007;176(5):709-718. [22] XU AT, XIE YW, XU JG, et al. Effects of strontium-incorporated micro/nano rough titanium surfaces on osseointegration via modulating polarization of macrophages. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;207:111992. [23] WANG L, WANG Q, WANG W, et al. Harmine Alleviates Titanium Particle-Induced Inflammatory Bone Destruction by Immunomodulatory Effect on the Macrophage Polarization and Subsequent Osteogenic Differentiation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:657687. [24] YANG C, WANG W, ZHU K, et al. Lithium chloride with immunomodulatory function for regulating titanium nanoparticle-stimulated inflammatory response and accelerating osteogenesis through suppression of MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:7475-7488. [25] ZHU K, YANG C, DAI H, et al. Crocin inhibits titanium particle-induced inflammation and promotes osteogenesis by regulating macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;76:105865. [26] DAMERAU A, GABER T, OHRNDORF S, et al. JAK/STAT Activation: A General Mechanism for Bone Development, Homeostasis, and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(23):9004. [27] XIN P, XU X, DENG C, et al. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;80:106210. [28] KOH YC, YANG G, LAI CS, et al. Chemopreventive Effects of Phytochemicals and Medicines on M1/M2 Polarized Macrophage Role in Inflammation-Related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2208. [29] YU Y, CUI H, ZHANG C, et al. Human nail bed extracellular matrix facilitates bone regeneration via macrophage polarization mediated by the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(18):4067-4079. [30] HE Y, GAO Y, ZHANG Q, et al. IL-4 Switches Microglia/macrophage M1/M2 Polarization and Alleviates Neurological Damage by Modulating the JAK1/STAT6 Pathway Following ICH. Neuroscience. 2020;437:161-171. [31] WANG N, GAO J, JIA M, et al. Exendin-4 Induces Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Migration Through Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages Polarization via PKA-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):1696-1714. [32] VERGADI E, IERONYMAKI E, LYRONI K, et al. Akt Signaling Pathway in Macrophage Activation and M1/M2 Polarization. J Immunol. 2017;198(3): 1006-1014. [33] ZHOU D, HUANG C, LIN Z, et al. Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2014;26(2):192-197. [34] LI M, GUO X, QI W, et al. Macrophage polarization plays roles in bone formation instructed by calcium phosphate ceramics. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(9):1863-1877. [35] ZHAO SJ, KONG FQ, JIE J, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):17-35. [36] HOUSCHYAR KS, TAPKING C, BORRELLI MR, et al. Wnt Pathway in Bone Repair and Regeneration - What Do We Know So Far. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:170. [37] TETSU O, MCCORMICK F. Beta-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature. 1999;398(6726):422-426. [38] 新岗,李永刚,包倪荣,等.骨代谢主要信号通路及信号分子的研究进展[J].基础医学与临床 ,2018,38(12):1799-1803. [39] ABARICIA JO, SHAH AH, CHAUBAL M, et al. Wnt signaling modulates macrophage polarization and is regulated by biomaterial surface properties. Biomaterials. 2020;243:119920. [40] YANG Y, YE YC, CHEN Y, et al. Crosstalk between hepatic tumor cells and macrophages via Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes M2-like macrophage polarization and reinforces tumor malignant behaviors. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(8):793. [41] ZHENG M, WENG M, ZHANG X, et al. Beta-tricalcium phosphate promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through macrophages. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(2):025005. [42] ZHANG J, WU Q, YIN C, et al. Sustained calcium ion release from bioceramics promotes CaSR-mediated M2 macrophage polarization for osteoinduction. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110(3):485-496. [43] PARIHAR A, EUBANK TD, DOSEFF AI. Monocytes and macrophages regulate immunity through dynamic networks of survival and cell death. J Innate Immun. 2010;2(3):204-215. [44] HORWOOD NJ. Macrophage Polarization and Bone Formation: A review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;51(1):79-86. [45] QING L, FU J, WU P, et al. Metformin induces the M2 macrophage polarization to accelerate the wound healing via regulating AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 inflammasome singling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(2):655-668. [46] LA FONTAINE J, CHEN C, HUNT N, et al. Type 2 Diabetes and Metformin Influence on Fracture Healing in an Experimental Rat Model. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016;55(5):955-960. [47] YAN Z, TIAN X, ZHU J, et al. Metformin suppresses UHMWPE particle-induced osteolysis in the mouse calvaria by promoting polarization of macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Mol Med. 2018;24(1):20. [48] YE W, WANG J, LIN D, et al. The immunomodulatory role of irisin on osteogenesis via AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;146:25-35. [49] DRAGER J, HARVEY E J, BARRALET J. Hypoxia signalling manipulation for bone regeneration. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015;17:e6. [50] WAN C, SHAO J, GILBERT SR, et al. Role of HIF-1alpha in skeletal development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192:322-326. [51] LIU Y, YANG Z, WANG L, et al. Spatiotemporal Immunomodulation Using Biomimetic Scaffold Promotes Endochondral Ossification-Mediated Bone Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(11):e2100143. [52] DAI X, HENG BC, BAI Y, et al. Restoration of electrical microenvironment enhances bone regeneration under diabetic conditions by modulating macrophage polarization. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(7):2029-2038. [53] HALL A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279(5350): 509-514. [54] XU Y, CUI K, LI J, et al. Melatonin attenuates choroidal neovascularization by regulating macrophage/microglia polarization via inhibition of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. J Pineal Res. 2020;69(1):e12660. [55] ZHU Y, LIANG H, LIU X, et al. Regulation of macrophage polarization through surface topography design to facilitate implant-to-bone osteointegration. Sci Adv. 2021;7(14):eabf6654. |
| [1] | Liu Huan, Li Han, Ma Yunhao, Zhong Weijian, Ma Guowu. Osteogenic capacity of partially demineralized dentin particles in the maxillary sinus lift [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 354-359. |
| [2] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [3] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [4] | Zong Mingrui, Liu Haiyan, Li Bing, Wu Xiuping. Application of carboxymethyl chitosan in tissue engineering of stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 447-452. |
| [5] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [6] | Zhang Lichen, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Inorganic ion bionic periosteum regulates immune microenvironment to promote bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [7] | Luo Di, Liang Xuezhen, Yan Bozhao, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanism of Bushen Huoxue Capsule in repair of bone defects due to steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 184-191. |
| [8] | Wei Tengfei, He Xiaoming, Wei Yurou, Zhan Zhiwei, He Mincong, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Differential expression of Piezo1 in osseous tissue of steroid- and alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 270-275. |
| [9] | Zhao Feng, Fan Shaoqing, Cheng Xiaoyan, Li Xiaona, Li Changsheng, Ma Haojie. miR-132-3p targets and modulates Ptch1 to reduce neuropathic pain in mice with chronic constriction injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 230-236. |
| [10] | Zhong Jinglin, Cao Huimin, Pan Yaru, Jian Wenxuan, Wang Qi. Ginsenoside Rg3 protects PC12 cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 177-183. |
| [11] | Chen Feng, Ren Guowu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Shi Rusheng. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand signal transduction mechanism and osteoclast activation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 293-299. |
| [12] | Li Mingxiu, Wang Xuan, Yang Jie, Li Yi. An osteoarthritis model in vitro: characteristics and new design idea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 300-306. |
| [13] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [14] | Zhu Miaomiao, Kong Fanming, Zhao Qian. Exercise regulates lactic acid metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 322-328. |
| [15] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||