Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 230-236.doi: 10.12307/2022.934
Previous Articles Next Articles
miR-132-3p targets and modulates Ptch1 to reduce neuropathic pain in mice with chronic constriction injury
Zhao Feng1, Fan Shaoqing1, Cheng Xiaoyan1, Li Xiaona1, Li Changsheng2, Ma Haojie1
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Henan Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Henan Cancer Hospital, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-13Accepted:2021-10-28Online:2023-01-18Published:2022-06-20 -
Contact:Zhao Feng, Department of Anesthesiology, Henan Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhao Feng, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Henan Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Medical Science and Technology Project of Henan Province, No. 201702242 (to LCS); the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program in Henan Province, No. 182102410015 (to LCS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Feng, Fan Shaoqing, Cheng Xiaoyan, Li Xiaona, Li Changsheng, Ma Haojie. miR-132-3p targets and modulates Ptch1 to reduce neuropathic pain in mice with chronic constriction injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 230-236.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
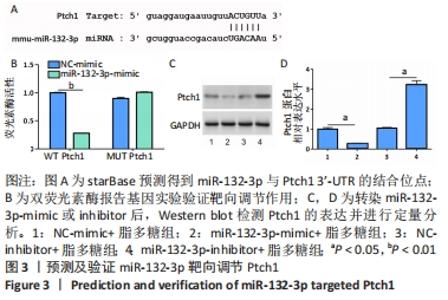
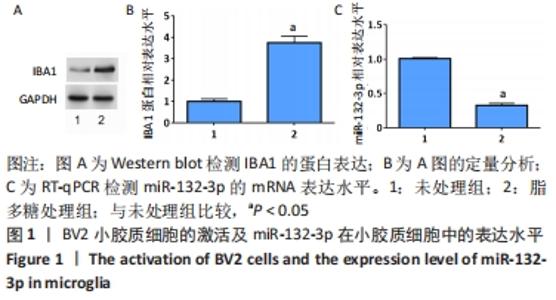
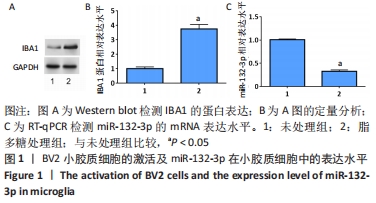
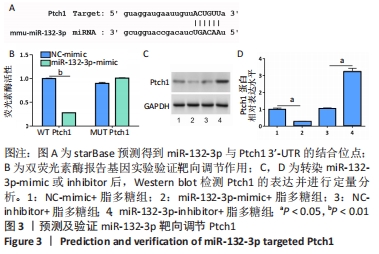
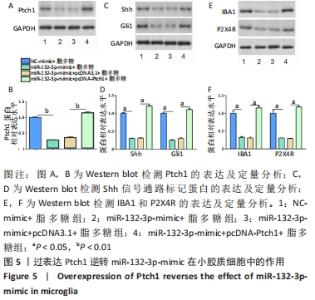
2.3 预测及验证miR-132-3p通过与Ptch1的3'-UTR结合靶向调节Ptch1的表达 通过在线数据库starBase预测得到miR-132-3p与Ptch1的3'-UTR相结合,结合位点见图3A。随后通过双荧光素酶报告基因实验进一步验证其靶向调节作用,结果发现miR-132-3p-mimic降低野生型(WT)Ptch1 3'-UTR报告载体的荧光素酶活性,而对突变型(MUT)没有影响,见图3B。转染miR-132-3p-mimic或inhibitor进入BV2细胞24 h后用脂多糖刺激培养24 h,通过Western blot检测Ptch1的表达,结果显示过表达miR-132-3p后抑制了BV2细胞中Ptch1的表达(P < 0.05),见图3C,D。"
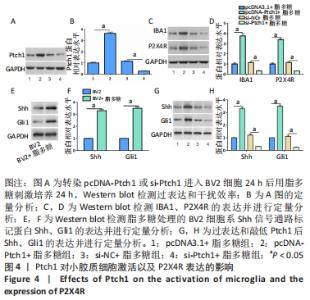
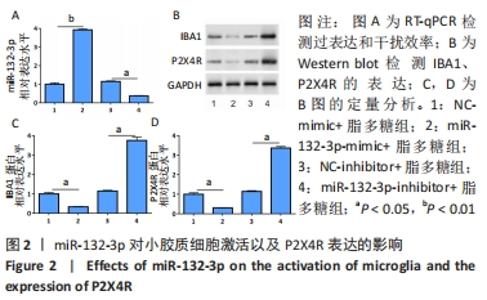
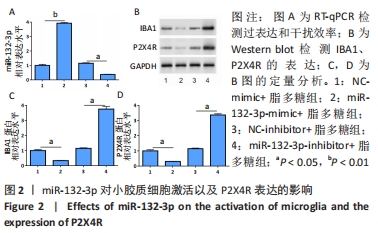
2.4 Ptch1对小胶质细胞的激活以及P2X4R表达的影响 将Ptch1表达载体pcDNA-Ptch1或siRNA(si-Ptch1)转染BV2细胞24 h后用脂多糖刺激培养24 h,通过Western blot检测过表达和干扰效率,见图4A,B。然后检测小胶质细胞激活标记物IBA1以及P2X4R的表达,结果显示敲低Ptch1抑制了小胶质细胞的激活以及P2X4R的表达(P < 0.05),见图4C,D。研究发现Shh信号通路在慢性压迫性神经损伤疼痛模型中被激活,慢性压迫性神经损伤大鼠脊髓腰骶膨大部位Shh信号通路蛋白Shh、Gli表达增加,而Ptch1受Shh信号通路调节且能对Shh信号通路起调控作用[19]。因此,该研究通过Western blot进一步检测Shh信号通路标记蛋白的表达来观察该通路是否在小胶质细胞激活过程中发挥作用,结果显示激活的小胶质细胞中Shh通路标记蛋白表达上调,而敲低Ptch1则抑制该通路的激活(P < 0.05),见图4E-H。"
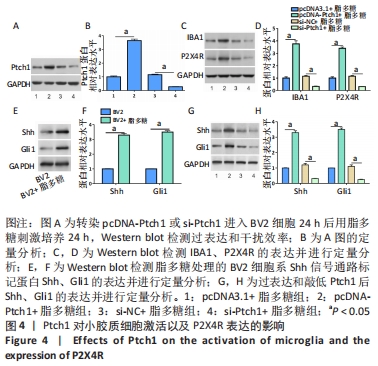
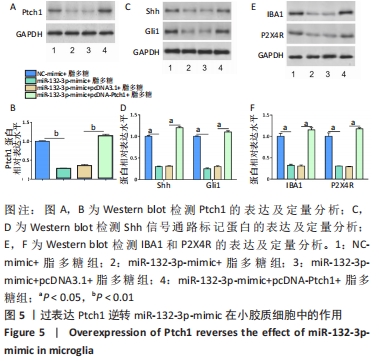
2.5 过表达Ptch1逆转miR-132-3p-mimic在小胶质细胞中的作用 单独转染miR-132-3p-mimic或者与pcDNA-Ptch1共同转染BV2细胞24 h后用脂多糖刺激培养24 h,通过Western blot检测Ptch1的表达,结果发现pcDNA-Ptch1逆转miR-132-3p-mimic对其表达的影响,见图5A,B。然后通过Western blot检测Shh信号通路标记蛋白、IBA1以及P2X4R的表达,结果表明过表达Ptch1逆转了miR-132-3p-mimic对Shh信号通路以及对小胶质细胞激活的抑制作用,上调P2X4R的表达(P < 0.05),见图5C-F。"
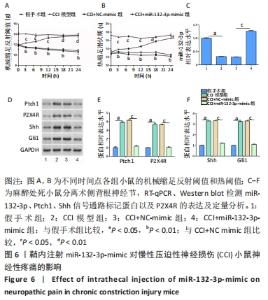
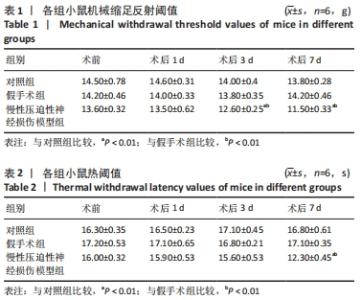
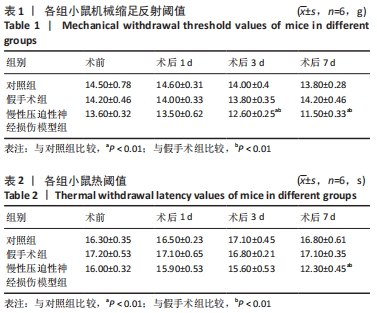
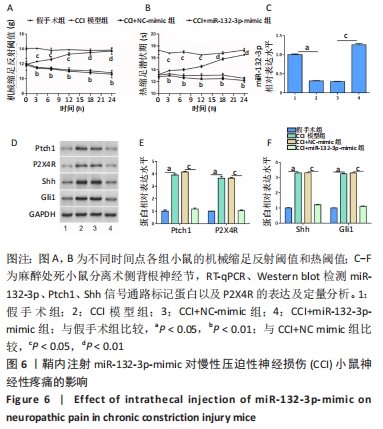
为观察miR-132-3p对慢性压迫性神经损伤小鼠神经性疼痛的影响,于术后第7天鞘内注射miR-132-3p-mimic,在不同时间点监测动物行为指标,结果发现鞘内注射miR-132-3p-mimic明显提高慢性压迫性神经损伤小鼠的机械缩足反射阈值和热阈值,减轻小鼠的机械和热痛觉过敏,见图6A,B。随后各组选取3只小鼠麻醉处死,分离术侧背根神经节,采用RT-qPCR、Western blot检测miR-132-3p、Ptch1、Shh信号通路标记蛋白以及P2X4R的表达,结果显示慢性压迫性神经损伤小鼠背根神经节中miR-132-3p表达下调(P < 0.05),见图6C,Ptch1表达上调(P < 0.05),见图6D,E,Shh信号通路处于激活状态(P < 0.05),见图6D,F,P2X4R表达上调(P < 0.05),见图6D,E,鞘内注射miR-132-3p-mimic可以下调Ptch1的表达,抑制Shh信号通路的激活发挥镇痛作用,减轻慢性压迫性神经损伤小鼠的神经性疼痛,见图6C-F。 "
| [1] BICKER S, LACKINGER M, WEIß K, et al. MicroRNA-132, -134, and -138: a microRNA troika rules in neuronal dendrites. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(20):3987-4005. [2] CHEN D, HU S, WU Z, et al. The Role of MiR-132 in Regulating Neural Stem Cell Proliferation, Differentiation and Neuronal Maturation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(6):2319-2330. [3] ATEN S, PAGE CE, KALIDINDI A, et al. miR-132/212 is induced by stress and its dysregulation triggers anxiety-related behavior. Neuropharmacology. 2019;144:256-270. [4] LIU G, YIN F, ZHANG C, et al. Effects of regulating miR-132 mediated GSK-3β on learning and memory function in mice. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):1191-1197. [5] ARAI M, GENDA Y, ISHIKAWA M, et al. The miRNA and mRNA changes in rat hippocampi after chronic constriction injury. Pain Med. 2013;14(5): 720-729. [6] 施燕渲,朱涛.微RNA-132在神经病理性疼痛中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2017,23(16):3170-3173. [7] 施燕渲,朱涛.miR-132在神经病理性疼痛传导通路中的表达[J].实用医学杂志,2017,33(19):3189-3192. [8] ZHANG R, HUANG M, CAO Z, et al. MeCP2 plays an analgesic role in pain transmission through regulating CREB / miR-132 pathway. Mol Pain. 2015;11:19. [9] WU B, LI J, WANG H, et al. MiR-132-3p serves as a tumor suppressor in mantle cell lymphoma via directly targeting SOX11. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(11):2197-2208. [10] GE Y, SONG X, LIU J, et al. The Combined Therapy of Berberine Treatment with lncRNA BACE1-AS Depletion Attenuates Aβ25-35 Induced Neuronal Injury Through Regulating the Expression of miR-132-3p in Neuronal Cells. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(4):741-751. [11] 杨秀方,褚凯丽,李媛,等.miR-132调节非小细胞肺癌hedgehog信号通路受体基因PTCH1及细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭[J].复旦学报(医学版),2015,42(3):291-299,306. [12] YANG Z, GAO L, JIA H, et al. The Expression of Shh, Ptch1, and Gli1 in the Developing Caudal Spinal Cord of Fetal Rats With Anorectal Malformations. J Surg Res. 2019;233:173-182. [13] TUKACHINSKY H, PETROV K, WATANABE M, et al. Mechanism of inhibition of the tumor suppressor Patched by Sonic Hedgehog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(40):E5866-E5875. [14] MOREAU N, MAUBORGNE A, BOURGOIN S, et al. Early alterations of Hedgehog signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells after peripheral nerve injury elicit blood-nerve barrier disruption, nerve inflammation, and neuropathic pain development. Pain. 2016;157(4):827-839. [15] MOREAU N, BOUCHER Y. Hedging against Neuropathic Pain: Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Pathological Nerve Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(23):9115. [16] FURUBE E, KAWAI S, INAGAKI H, et al. Brain Region-dependent Heterogeneity and Dose-dependent Difference in Transient Microglia Population Increase during Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2203. [17] LV R, DU L, ZHANG L, et al. Polydatin attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and microglia apoptosis via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2019;217:119-127. [18] 李永丰,任维,刘一辉.CB1受体通过钾离子通道介导外周镇痛作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(4):92-98. [19] 刘宇临.Sonic hedgehog信号通路在神经病理性疼痛模型大鼠中的表达及其意义的研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2017. [20] COLLOCA L, LUDMAN T, BOUHASSIRA D, et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17002. [21] BARON R, MAIER C, ATTAL N, et al. Peripheral neuropathic pain: a mechanism-related organizing principle based on sensory profiles. Pain. 2017;158(2):261-272. [22] NI HD, YAO M, HUANG B, et al. Glial activation in the periaqueductal gray promotes descending facilitation of neuropathic pain through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J Neurosci Res. 2016;94(1):50-61. [23] KUAN YH, SHYU BC. Nociceptive transmission and modulation via P2X receptors in central pain syndrome. Mol Brain. 2016;9(1):58. [24] CHEN L, LIU YW, YUE K, et al. Differential expression of ATP-gated P2X receptors in DRG between chronic neuropathic pain and visceralgia rat models. Purinergic Signal. 2016;12(1):79-87. [25] ZHANG WJ, LUO HL, ZHU ZM. The role of P2X4 receptors in chronic pain: A potential pharmacological target. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 129:110447. [26] INOUE K, TSUDA M. Nociceptive signaling mediated by P2X3, P2X4 and P2X7 receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;187:114309. [27] 陈桂玲,张加强.右美托咪定对神经病理性痛大鼠脊髓P2X3和P2X4受体表达的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(6):27-31. [28] TRANG M, SCHMALZING G, MÜLLER CE, et al. Dissection of P2X4 and P2X7 Receptor Current Components in BV-2 Microglia. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8489. [29] INOUE K. Role of the P2X4 receptor in neuropathic pain. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2019;47:33-39. [30] ZHANG WJ, ZHU ZM, LIU ZX. The role of P2X4 receptor in neuropathic pain and its pharmacological properties. Pharmacol Res. 2020;158:104875. [31] HALIEVSKI K, GHAZISAEIDI S, SALTER MW. Sex-Dependent Mechanisms of Chronic Pain: A Focus on Microglia and P2X4R. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2020;375(1):202-209. [32] XU R, YANG F, LI L, et al. CB2/miR-124 signaling down-regulate the expression of purinergic P2X4 and P2X7 receptor in dorsal spinal cord of CCI rats. 2020. [33] GONG X, HUANG MY, CHEN L. Mechanism of miR-132-3p Promoting Neuroinflammation and Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. eNeuro. 2022;9(1):ENEURO.0393-21.2021. [34] WANG X, WANG H, ZHANG T, et al. Inhibition of MicroRNA-195 Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Targeting Patched1 and Inhibiting SHH Signaling Pathway Activation. Neurochem Res. 2019;44(7):1690-1702. [35] COHEN M, KICHEVA A, RIBEIRO A, et al. Ptch1 and Gli regulate Shh signalling dynamics via multiple mechanisms. Nat Commun. 2015;6: 6709. [36] 孙艳.2,5-己二酮致人卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡及Sonichedgehog信号通路调控机制的研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2012. [37] CHOUDHRY Z, RIKANI AA, CHOUDHRY AM, et al. Sonic hedgehog signalling pathway: a complex network. Ann Neurosci. 2014;21(1):28-31. [38] 牛小莉.丁苯酞对血管性痴呆大鼠认知功能及Shh/Ptch1信号通路和内质网应激相关蛋白表达的影响[D].石家庄:河北医科大学, 2019. [39] BELGACEM YH, HAMILTON AM, SHIM S, et al. The Many Hats of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Nervous System Development and Disease. J Dev Biol. 2016;4(4):35. [40] HE W, CUI L, ZHANG C, et al. Sonic Hedgehog Promotes Neurite Outgrowth of Primary Cortical Neurons Through Up-Regulating BDNF Expression. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(4):687-695. [41] LI X, LI Y, LI S, et al. The role of Shh signalling pathway in central nervous system development and related diseases. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021;39(2):180-189. [42] 刘宇临,刘丹彦.Sonic hedgehog信号通路在神经病理性疼痛模型大鼠中的表达及其意义[J].重庆医科大学学报,2016,41(1):61-65. [43] 冯晓雪,蔡孟,杨晓秋,等.大鼠神经病理性痛时脊髓Sonic hedgehog信号通路与炎症反应的关系[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2018, 38(11):1347-1350. [44] 冯晓雪,杨晓秋,刘丹彦. 环巴明抑制SHH信号通路缓解大鼠神经病理性疼痛[J].基础医学与临床,2016,36(5):661-665. |
| [1] | Shi Xu, Li Ruiyu, Zhang Bing, Chen Qi, Zuo Hua. Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 121-129. |
| [2] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1286-1292. |
| [3] | Dong Miaomiao, Lai Han, Li Manling, Xu Xiuhong, Luo Meng, Wang Wenhao, Zhou Guoping. Effect of electroacupuncture on expression of nucleotide binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3/cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase 1 in rats with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 749-755. |
| [4] | Mao Ke, Gao Yuhua, Zhou Songlin, Zhao Yanfen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Du Silong, Li Xilong. MiR-204-5p alleviates neuropathic pain in rats with chronic constriction injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4680-4686. |
| [5] | Zeng Chunrong, Liu Menglan, Xie Yang, Li Zuoxiao. Preventive and therapeutic effects of naringin on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4127-4135. |
| [6] | Wang Yuyin, Wei Wenyue, Guo Minfang, Li Hongxia, Zhang Jing, Gu Qingfang, Liu Xiaoqin, Guo Xiaoping, Song Lijuan, Chai Zhi, Ma Cungen, Wei Jiezhong. Bushen Yizhi Anti-aging Prescription improves cognitive function of APP/PS1 mice by regulating microglia and macrophage polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(26): 4166-4172. |
| [7] | Sun Xinzheng, Chen Xiaoke, Wang Chenghao, He Hui. Exercise improves pain induced by sciatic nerve injury in animal models: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 321-328. |
| [8] | Li Chuanhong, Yu Xing, Yang Yongdong, Zhao He. Microglia in spinal cord injury: M1/M2 phenotypic polarization and neurotoxic/neuroprotective effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2265-2272. |
| [9] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [10] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [11] | Du Yihong, Sun Yan, Yang Ruoyu, Wang Liyan, Cai Ming. Mechanisms of neuroinflammation in mild cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4743-4749. |
| [12] | Zhi Yibo, Zhang Jie, Liu Jian, Li Weiyan. Chemokine CCL21 in anterior cingulate cortex is involved in chronic neuropathic pain in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 242-246. |
| [13] | Luan Shuangyu, Zeng Liang, Chen Bin, Tian Wei, Yan Nan, Chen Xi, Zhang Shuo, Wang Zhengdong. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on microglial activation after optic nerve injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3937-3942. |
| [14] | Sun Fen, Liu Mingyan, Liu Ming, Sun Xinyi, Feng Yunxia. Effect of microRNA-132-3p overexpression on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 59-64. |
| [15] | Pan Weibin, Lin Xiaomin, Fan Xiao. Electroacupuncture regulates activation of astrocytes and microglia after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4675-4680. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||