Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (7): 1075-1080.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2175
Previous Articles Next Articles
Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis
Wang Zhengdong1, Huang Na2, Chen Jingxian2, Zheng Zuobing2, Hu Xinyu2, Li Mei2, Su Xiao2, Su Xuesen2, Yan Nan3
- 1Basic Medical College, 2School of Public Health, 3College of Applied Technology, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-16Revised:2020-04-21Accepted:2020-05-16Online:2021-03-08Published:2020-12-08 -
Contact:Yan Nan, MD, Associate professor, College of Applied Technology, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wang Zhengdong, MD, Associate professor, Basic Medical College, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81803200; the Social Development and Industrialization Guidance Plan of Liaoning Province, No. 2019JH8/10300047
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080.
share this article
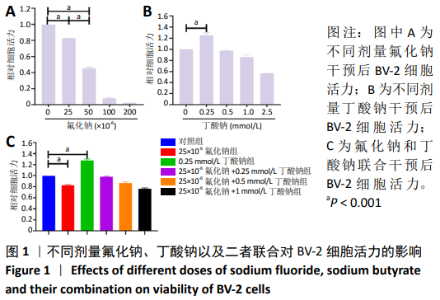
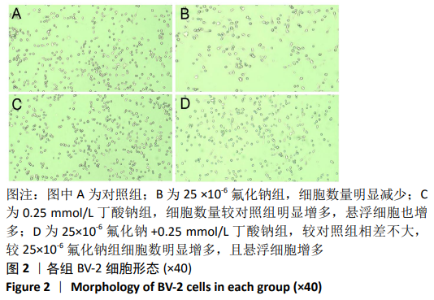
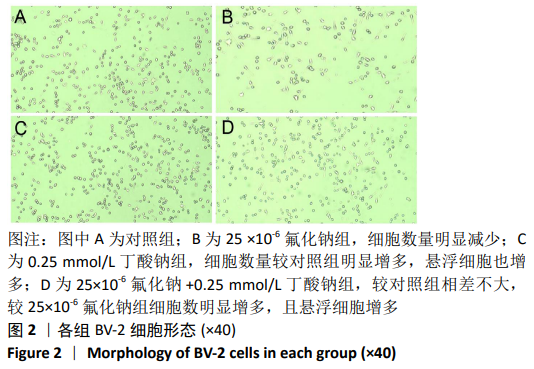
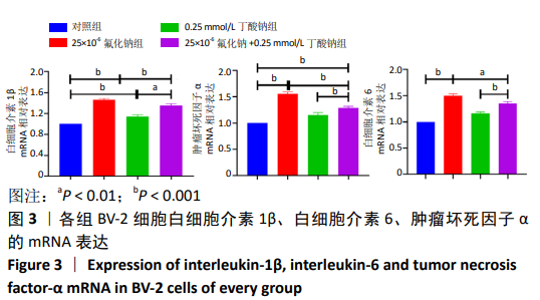
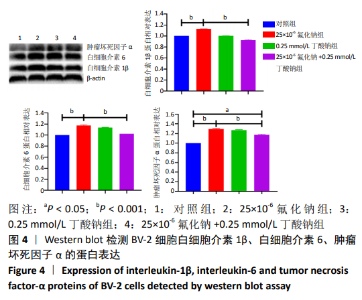
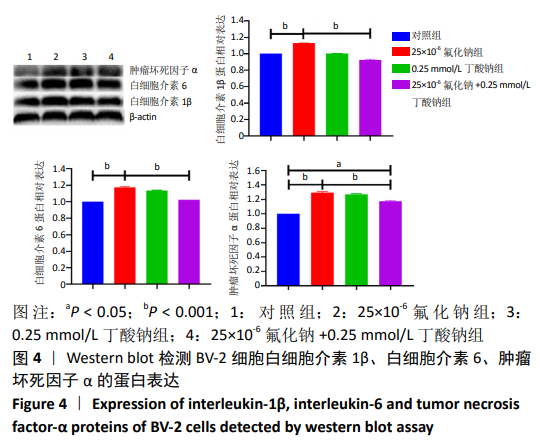
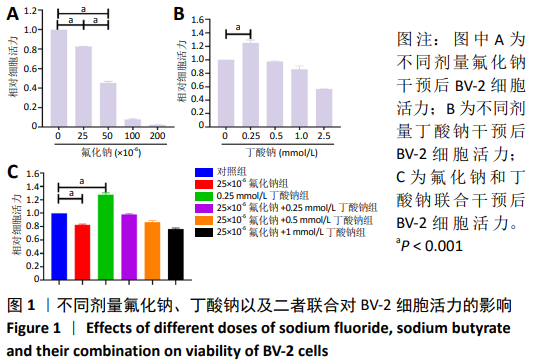
2.1 CCK-8检测各组BV-2小胶质细胞活力 随着氟化钠浓度的增加, BV-2细胞活力逐渐降低,均低于对照组,当氟化钠浓度为25×10-6时,BV-2细胞活力与对照组差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001),可作为BV-2细胞染毒的最佳浓度,见图1A。0.25 mmol/L丁酸钠能升高BV-2细胞活力,随着丁酸钠浓度的增加,BV-2细胞活力也明显降低,当作用浓度达到 1 mmol/L时,细胞活力降低至75%左右,见图1B。0.25,0.5,1 mmol/L丁酸钠和25×10-6氟化钠联合作用能降低BV-2细胞活力,0.25 mmol/L丁酸钠能够逆转25×10-6氟化钠下降的细胞活力,使细胞活力恢复到与对照组大致水平,见图1C。"
| [1] QUADRI JA, ALAM MM, SARWAR S, et al. Multiple Myeloma-Like Spinal MRI Findings in Skeletal Fluorosis: An Unusual Presentation of Fluoride Toxicity in Human. Front Oncol. 2016;6:245. [2] 孙殿军,沈雁峰,赵新华,等.中国大陆地方性氟中毒病情动态与现状分析[J].中国地方病学杂志, 2001, 20(6): 429-433. [3] 赵丽军,孙玉富,于光前,等.评价地方性氟中毒防控效果的唯一标准——地方性氟中毒病区控制标准(GB17017-2010)解读[J].中国卫生标准管理, 2011, 2(2): 37-40. [4] 颜南. 氟通过激活MAPK和NF-κB信号通路促进小胶质细胞炎性因子分泌的研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2018. [5] 刘艳洁,高勤,龙义国,等.慢性氟中毒对大鼠脑组织Phospho-Elk-1表达的影响[J].贵阳医学院学报, 2011, 30(3): 251-255. [6] 孙增荣,刘风贞,杨海贤,等.饮高氟水小鼠脑海马回组织超微结构观察[J].中国地方病学杂志, 2000, 19(5):333-334. [7] CHOI AL, SUN G, ZHANG Y, et al. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Health Perspect. 2012; 120(10):1362-1368. [8] GRANDJEAN P. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: an updated review. Environ Health. 2019;18(1):110. [9] SABOUR S, GHORBANI Z. Developmental fluoride neurotoxicity: clinical importance versus statistical significance. Environ Health Perspect. 2013;121(3):A70. [10] CHEN J, NIU Q, XIA T, et al. ERK1/2-mediated disruption of BDNF-TrkB signaling causes synaptic impairment contributing to fluoride-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Toxicology. 2018;410:222-230. [11] SÄEMANN MD, BÖHMIG GA, OSTERREICHER CH, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of sodium butyrate on human monocytes: potent inhibition of IL-12 and up-regulation of IL-10 production. FASEB J. 2000; 14(15):2380-2382. [12] QIU Z, LU P, WANG K, et al. Dexmedetomidine Inhibits Neuroinflammation by Altering Microglial M1/M2 Polarization Through MAPK/ERK Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(2):345-353. [13] LIU B, HUANG B, HU G, et al. Corrigendum: Isovitexin-Mediated Regulation of Microglial Polarization in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation via Activation of the CaMKKβ/AMPK-PGC-1α Signaling Axis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:41. [14] AL MAMUN A, CHAUHAN A, QI S, et al. Microglial IRF5-IRF4 regulatory axis regulates neuroinflammation after cerebral ischemia and impacts stroke outcomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(3):1742-1752. [15] GAO G, LI C, ZHU J, et al. Glutaminase 1 Regulates Neuroinflammation After Cerebral Ischemia Through Enhancing Microglial Activation and Pro-Inflammatory Exosome Release. Front Immunol. 2020;11:161. [16] SERHAN A, AERTS JL, BODDEKE EWGM, et al. Neuroprotection by Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in Rats with Ischemic Stroke is Associated with Microglial Changes and a Reduction in Neuroinflammation. Neuroscience. 2020;426:101-114. [17] KATO T, TAKAHASHI M, FUKUDA NN, et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature. 2013;504(7480):446-450. [18] JAWORSKA J, ZIEMKA-NALECZ M, SYPECKA J, et al. The potential neuroprotective role of a histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate, after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. J Neuroinflammation. 2017; 14(1):34. [19] HU X, ZHANG K, XU C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of sodium butyrate preconditioning during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Exp Ther Med. 2014;8(1):229-232. [20] PATNALA R, ARUMUGAM TV, GUPTA N, et al. HDAC Inhibitor Sodium Butyrate-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation Enhances Neuroprotective Function of Microglia During Ischemic Stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 54(8):6391-6411. [21] KIM JA, KIM SH, KIM IS, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Mixture of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Sodium Butyrate in Atopic Dermatitis Murine Model. J Med Food. 2018;21(7):716-725. [22] ROY AC, CHANG G, MA N, et al. Sodium butyrate suppresses NOD1-mediated inflammatory molecules expressed in bovine hepatocytes during iE-DAP and LPS treatment. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11): 19602-19620. [23] WANG CC, WU H, LIN FH, et al. Sodium butyrate enhances intestinal integrity, inhibits mast cell activation, inflammatory mediator production and JNK signaling pathway in weaned pigs. Innate Immun. 2018;24(1):40-46. [24] SILVA LG, FERGUSON BS, AVILA AS, et al. Sodium propionate and sodium butyrate effects on histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity, histone acetylation, and inflammatory gene expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J Anim Sci. 2018;96(12):5244-5252. [25] GUO J, WANG Y, JIANG P, et al. Sodium butyrate alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced endometritis in mice through inhibiting inflammatory response. Microb Pathog. 2019;137:103792. [26] LI Y, SHEN R, WEN G, et al. Effects of Ketamine on Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the Hippocampus of Mice Following Acute or Chronic Administration. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:139. [27] NAKANISHI H. Microglial cathepsin B as a key driver of inflammatory brain diseases and brain aging. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(1):25-29. [28] YAN N, LIU Y, LIU S, et al. Fluoride-Induced Neuron Apoptosis and Expressions of Inflammatory Factors by Activating Microglia in Rat Brain. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(7):4449-4460. [29] VALVASSORI SS, DAL-PONT GC, STECKERT AV, et al. Sodium butyrate has an antimanic effect and protects the brain against oxidative stress in an animal model of mania induced by ouabain. Psychiatry Res. 2016; 235:154-159. [30] LEE HJ, SON Y, LEE M, et al. Sodium butyrate prevents radiation-induced cognitive impairment by restoring pCREB/BDNF expression. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(9):1530-1535. [31] LI H, SUN J, WANG F, et al. Sodium butyrate exerts neuroprotective effects by restoring the blood-brain barrier in traumatic brain injury mice. Brain Res. 2016;1642:70-78. [32] GUBERN C, CAMÓS S, HURTADO O, et al. Characterization of Gcf2/Lrrfip1 in experimental cerebral ischemia and its role as a modulator of Akt, mTOR and β-catenin signaling pathways. Neuroscience. 2014; 268:48-65. [33] VAL-LAILLET D, GUÉRIN S, COQUERY N, et al. Oral sodium butyrate impacts brain metabolism and hippocampal neurogenesis, with limited effects on gut anatomy and function in pigs. FASEB J. 2018;32(4): 2160-2171. [34] SANTA-CECÍLIA FV, SOCIAS B, OUIDJA MO, et al. Doxycycline Suppresses Microglial Activation by Inhibiting the p38 MAPK and NF-kB Signaling Pathways. Neurotox Res. 2016;29(4):447-459. [35] OH WJ, JUNG U, EOM HS, et al. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory responses by Buddleja officinalis extract in BV-2 microglial cells via negative regulation of NF-kB and ERK1/2 signaling. Molecules. 2013;18(8):9195-9206. [36] HAN MH, LEE WS, NAGAPPAN A, et al. Flavonoids Isolated from Flowers of Lonicera japonica Thunb. Inhibit Inflammatory Responses in BV2 Microglial Cells by Suppressing TNF-α and IL-β Through PI3K/Akt/NF-kb Signaling Pathways. Phytother Res. 2016;30(11):1824-1832. [37] CHEN R, ZHAO LD, LIU H, et al. Fluoride Induces Neuroinflammation and Alters Wnt Signaling Pathway in BV2 Microglial Cells. Inflammation. 2017;40(4):1123-1130. [38] FERNANDO WMADB, MARTINS IJ, MORICI M, et al. Sodium Butyrate Reduces Brain Amyloid-β Levels and Improves Cognitive Memory Performance in an Alzheimer’s Disease Transgenic Mouse Model at an Early Disease Stage. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;74(1):91-99. [39] KINAWY AA. Synergistic oxidative impact of aluminum chloride and sodium fluoride exposure during early stages of brain development in the rat. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26(11):10951-10960. [40] 高博. NLRP1炎症小体在慢性应激诱导的小鼠抑郁样行为中的作用[D].合肥:安徽医科大学, 2018. [41] CHEN G, RAN X, LI B, et al. Sodium Butyrate Inhibits Inflammation and Maintains Epithelium Barrier Integrity in a TNBS-induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease Mice Model. EBioMedicine. 2018;30:317-325. |
| [1] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [2] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [3] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [4] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [5] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [6] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [7] | Chai Le, Lü Jianlan, Hu Jintao, Hu Huahui, Xu Qingjun, Yu Jinwei, Quan Renfu. Signal pathway variation after induction of inflammatory response in rats with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [8] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [9] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [10] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [11] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [12] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [13] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [14] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [15] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||