Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (29): 4743-4749.doi: 10.12307/2021.178
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanisms of neuroinflammation in mild cognitive impairment
Du Yihong1, Sun Yan1, Yang Ruoyu2, Wang Liyan2, Cai Ming2
- 1Sports and Health College, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China; 2College of Rehabilitation Sciences, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China
-
Received:2020-07-21Revised:2020-07-22Accepted:2020-08-13Online:2021-10-18Published:2021-07-22 -
Contact:Cai Ming, MD, Lecturer, College of Rehabilitation Sciences, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China -
About author:Du Yihong, Master candidate, Sports and Health College, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China; College of Rehabilitation Sciences, Shanghai University of Medicine & Health Sciences, Shanghai 201318, China Sun Yan, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Sports and Health College, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330013, Jiangxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Youth Fund Project of Research Planning Foundation on Humanities and Social Sciences of the Ministry of Education, No. 20YJCZH001 (to CM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Du Yihong, Sun Yan, Yang Ruoyu, Wang Liyan, Cai Ming. Mechanisms of neuroinflammation in mild cognitive impairment[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4743-4749.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
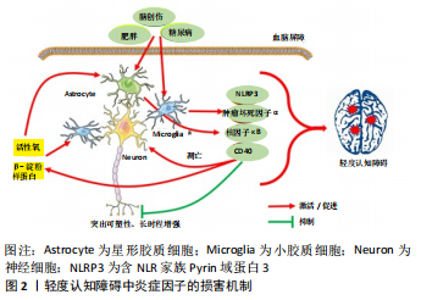
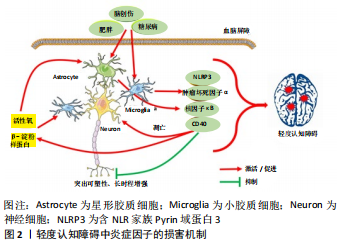
2.1 MCI病理改变 MCI最早的病理变化通常发生在内侧颞叶结构中,各类脑部病理生理变化削弱了对学习记忆功能至关重要的神经网络,包括自由回忆、识别、配对学习等功能。MCI患者在对象命名和语义分类的测试上也受到损害,当神经病理病变包括体积减少、突触可塑性下降、神经元结构发生异变等遍及颞叶、额叶和顶叶皮质以及海马体时,会破坏对特定项目或概念的理解以及它们之间的关联功能[7]。MCI的认知功能减退与神经退行性变有关,其生理特征在于细胞凋亡、突触损伤以及神经元结构异变等。这些神经退行性变性与中枢神经系统炎症引发的促炎性级联反应、β-淀粉样蛋白沉积形成的老年斑和由高磷酸化tau蛋白组成的细胞内神经原纤维缠结等有密切的关系[8]。 研究表明,神经炎症很可能早于痴呆而发生[9]。促炎细胞因子在老年斑附近过表达,并且二者的共同作用减少了患者海马的神经发生,导致海马突触可塑性和重塑神经网络的能力受损[10]。同时有研究报道,在脑脊液和血浆中的促炎细胞因子水平与t-tau和p-tau水平高度相关,他们共同作用于患者的大脑病理变化[11]。这些研究表明神经炎症、β-淀粉样蛋白沉积、tau蛋白缠结之间的相互作用可能是导致MCI神经退行性病变的关键机制,若能抑制上述任何一个过程,就有可能延缓或改善MCI与阿尔茨海默症脑部退行性病变的进程。 2.2 神经炎症在MCI中的作用 除了阿尔茨海默症与MCI中的经典病理学特征外,近年来神经炎症逐渐被认为是疾病进展的主要驱动力[12]。越来越多的证据表明,外周炎症是引起脑内神经炎症的主要因素之一,促炎细胞因子已被证明可通过血脑屏障,进而触发中枢炎症反应。血脑屏障的损害也可加剧中枢性炎症,使得外周免疫细胞进入大脑,促进脑内炎症的发生。肥胖是外周全身性炎症的关键因素,一些研究表明,肥胖症患者体内过多的饱和脂肪酸可穿越血脑屏障直接影响大脑中的神经胶质细胞活化,并且肥胖所引起的2型糖尿病会加速阿尔茨海默症小鼠模型的记忆功能障碍和神经炎症[13]。同时,创伤性脑损伤是MCI发展的危险因素之一,实验表明,创伤性脑损伤加重了认知障碍小鼠模型中的神经炎症[14]。 另外,β-淀粉样蛋白沉积、能量代谢障碍、衰老等脑内因素也能引起中枢神经炎症。神经炎症与β-淀粉样蛋白沉积互为因果,甚至神经炎症决定了β-淀粉样蛋白的病理生理过程。脑内β-淀粉样蛋白沉积可以引起并导致胶质细胞的持续活化,以释放出大量神经炎症因子,引起炎症反应。而脑内的能量代谢障碍也同样可以诱发神经炎症,神经元具有很高的能量需求,并且主要由线粒体提供动力。而线粒体功能障碍会产生高水平的活性氧,导致小胶质细胞激活。同时,星形胶质细胞的功能依赖于功能性线粒体提供能量,线粒体功能障碍可能会对星形胶质细胞的神经保护功能产生负面影响[15-16]。同时,衰老也是引起神经炎症的重要因素,神经元和小胶质细胞衰老不仅会导致突触的丧失、纤维束完整性改变以及氧化应激的增加,并且由于神经胶质相互作用的改变,从而引起其余小胶质细胞活化。有研究表明,在小鼠、大鼠和灵长类动物的中枢神经系统衰老中,小胶质细胞对炎性刺激的敏感性明显增强[17]。 2.3 炎性细胞 越来越多的证据表明,神经毒性是由神经炎症过程介导的。小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞是中枢神经系统炎症的主要介质,这些细胞在响应神经病理反应后被激活,导致包括含NLR家族Pyrin域蛋白3(recombinant NLR family,Pyrin domain containing protein 3,NLRP3)炎性小体、肿瘤坏死因子α、核因子κB、CD40等促炎细胞因子的释放。这些促炎细胞因子介导的神经毒性过程可能直接导致神经元死亡、抑制长时程增强和海马神经发生、降低突触功能[18]。小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞已成为研究疾病期间神经炎症过程的主要候选对象。转位蛋白是跨膜结构域蛋白[19],小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞激活后,转位蛋白水平显著增加,目前已被公认为脑内神经炎症的生物标志物,可以利用转位蛋白的放射性配体通过正电子发射断层扫描对神经炎症进行无创性监测追踪,定量分析神经炎症事件[20]。MCI早期的炎症高峰可能反映了胶质细胞对神经炎症的抗炎反应,然而持续的炎症反应会在MCI后期进一步加重神经退行性病变,包括神经元突触丢失、tau蛋白过度磷酸化等,从而加重患者的记忆功能进一步衰退[21-22]。 2.3.1 小胶质细胞 小胶质细胞作为中枢神经系统的固有免疫细胞,是高度活动的细胞,其活化被认为是中枢神经系统促炎和抗炎环境的主要来源[23-24]。在大脑发育过程中,小胶质细胞被认为可以清除在重塑过程中死亡的细胞,小胶质细胞以2种基本状态存在,即静止状态和活化状态[25]。活化后的小胶质细胞主要分为M1型和M2型。M1型小胶质细胞通过分泌肿瘤坏死因子α以及各种趋化因子和炎症因子来发挥免疫效应,但过多的释放炎症递质如一氧化氮、氧自由基等也会引起神经毒性,损伤正常神经细胞,加重神经损伤。M2型小胶质细胞可分泌一些神经营养因子如神经生长因子及胶质细胞源性神经营养因子等促进损伤神经的修复与再生,从而减轻或抑制炎症反应[26]。现有证据表明,神经炎症的第一个迹象是小胶质细胞的活化[27]。在MCI患者的大脑中,小胶质细胞可以被诸如聚集的β-淀粉样蛋白和外周系统性炎症的持续刺激等激活为M1型活化状态,活化的小胶质细胞将抗原呈递给T细胞,激活各种基因、蛋白质和促炎细胞因子,以介导在MCI中的神经毒性[18]。而在海马体中活化的小胶质细胞会导致空间记忆的缺乏,在MCI患者大脑中的某些区域(包括额叶、尾叶皮质、内嗅皮质以及海马体)均发现了活化的小胶质细胞[28]。虽然小胶质细胞对于健康大脑中的突触和神经元功能至关重要,但小胶质细胞的过度活化可能会在突触修剪过程中起到负面作用。小胶质细胞的持续活化可能会导致抑制性突触的突触前和突触后成分之间的物理隔断,从而引起突触修剪功能障碍和突触丧失,而突触修剪功能障碍可能是导致认知障碍的重要病因。在MCI早期,活化的小胶质细胞有助于清除β-淀粉样蛋白,并通过释放神经生长因子来支持突触重塑[29]。但当小胶质细胞持续活化后,会进一步增加β-淀粉样蛋白的沉积并释放炎性因子,从而加重神经炎症过程。 总而言之,过度活化的小胶质细胞不仅通过释放促炎因子来介导神经毒性,导致神经元变性以至功能丧失,而且还可以进一步增加β-淀粉样蛋白的沉积,导致脑内老年斑的生成,损害认知功能。 2.3.2 星形胶质细胞 星形胶质细胞是脑内数量最多的胶质细胞,其对神经元除了起结构和营养支持的作用外,也负责介导突触前后神经元的双向通讯[30]。星形胶质细胞被认为是神经元-星形胶质细胞通讯的主动驱动器,负责调节突触功能和神经回路整合[31]。同时,星形胶质细胞也是长时程增强和神经胶质递质释放的必不可少的元素。 星形胶质细胞通常被认为对神经元有益,因为它们会产生神经生长因子和神经营养蛋白[32]。但星形胶质细胞也会发生形态和功能变化,以回应大脑疾病和病理状况,这些变化导致星形胶质细胞的激活,最初的目的是消除在初始疾病条件下对大脑的损害,但随着疾病的进展,活化的星形胶质细胞获得毒性功能并逐渐丧失神经营养功能[33]。星形胶质细胞通过充当免疫细胞、持续释放细胞因子和趋化因子来影响效应细胞,调节血脑屏障和塑造神经胶质瘢痕,从而加重中枢神经系统炎症[34]。活化的星形胶质细胞包围β-淀粉样蛋白斑块,导致MCI大脑中的细胞因子和炎症递质释放增加、神经变性、谷氨酸摄取减少、神经营养不良、神经元突触丧失,最终导致认知功能受损[31-32]。 2.4 神经炎症因子 神经炎症的特征是免疫细胞长期活化,随后持续释放促炎细胞因子。细胞因子是一种小的信号蛋白,在炎症过程和免疫系统调节中具有广泛的功能[35]。在神经炎症中,小胶质细胞与星形胶质细胞的激活分泌了大量的促炎细胞因子,这些细胞因子通过不同的信号通路对患者的认知功能产生损害,见图2。 2.4.1 肿瘤坏死因子α 肿瘤坏死因子α是一种多效性细胞因子,参与多种生物学活动,包括炎症、细胞存活、细胞增殖以及细胞死亡[36],肿瘤坏死因子信号传导与多种炎症发病机制有关。肿瘤坏死因子α及其跨膜受体肿瘤坏死因子受体1是有效的促炎细胞因子,在引发和维持炎症反应中起着核心作用。肿瘤坏死因子受体1不仅可以通过激活caspase-3凋亡通路引起神经元的快速凋亡[27],而且还参与淀粉样前体蛋白的加工和β-淀粉样蛋白斑块的形成。肿瘤坏死因子信号已被证明在中枢神经系统中具有若干重要功能,包括调节小胶质细胞活化,调节谷氨酸能传递和控制突触强度[37]。在MCI患者的脑脊液中发现了高水平的肿瘤坏死因子α受体,这些患者多数在随访时发展为阿尔茨海默症[11]。 记忆的形成主要发生在海马区,并通过长时程增强的过程来实现。虽然在中枢神经系统的各种突触下诱导和维护长时程增强的机制非常复杂,而且有些争议,但长时程增强过程依赖于海马神经突触活化产生的谷氨酸。肿瘤坏死因子α的存在不仅会对海马神经递质信号的调节产生不良影响,而且会直接影响谷氨酸的传递,肿瘤坏死因子α已被证明可以增加α-氨基羟甲基恶唑丙酸受体的表达[38]。据研究报道,α-氨基羟甲基恶唑丙酸受体的运输是突触传递效能和蛋白质合成变化的基础[39]。在慢性神经炎症期间,长时间被肿瘤坏死因子α诱导增强的α-氨基羟甲基恶唑丙酸受体会导致长时程增强过程中断,从而导致突触稳态的失调,以至于短期识别和长期空间记忆不足,最终引起认知障碍[40-41]。同时,即早基因Arc/Arg3.1在持久突触可塑性和学习中起关键作用[42],而参与持久突触可塑性过程的必需蛋白质是Arc蛋白,后者是记忆巩固的基础。由于Arc转录受α-氨基羟甲基恶唑丙酸受体调控,所以肿瘤坏死因子α会通过谷氨酸信号稳态的失调而导致Arc蛋白的表达受到破坏。肿瘤坏死因子α也会负调节海马中的脑源性神经营养因子表达并影响海马CA1锥体神经元的突触连接[43]。有研究表明,肿瘤坏死因子α可以引起核因子κB的进一步活化,从而导致环氧合酶2同工酶上调[44]。环氧合酶2是在免疫细胞激活、神经炎症和大脑认知功能中起关键作用的蛋白质,环氧合酶2在锥体神经元中高度表达,能调节学习和记忆功能,所以通过减少肿瘤坏死因子α抑制环氧合酶2的上调可以保护脆弱的锥体神经元。 总之,肿瘤坏死因子α在MCI患者的脑脊液中含量较高,其不仅能引起大脑神经元的快速凋亡、参与β-淀粉样蛋白的形成,而且还可能阻断长时程增强的进程、影响海马神经突触连接,最终导致MCI患者出现识别与记忆障碍。降低MCI患者体内的肿瘤坏死因子α水平有助于改善患者的学习记忆功能,开发出有效的肿瘤坏死因子α阻断剂可能成为治疗MCI与阿尔茨海默症的重要策略。 2.4.2 NLRP3炎性小体 NLRP3炎性小体由NLRP3蛋白、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白和半胱氨酸蛋白酶caspase-1组成[45]。NLRP3的N末端吡啶结构域允许与二聚体衔接凋亡相关斑点样蛋白进行同型相互作用,后者随后通过CARD-CARD相互作用募集procaspase-1。Procaspase-1募集导致邻近诱导的caspase-1寡聚和自催化,导致活性caspase-1片段释放白细胞介素1β。白细胞介素1β以一种无生物学活性的形式由caspase-1分泌与激活,而caspase-1的活性受NLRP3信号控制。β-淀粉样蛋白的增加会导致溶酶体去稳定化,溶酶体破裂是NLRP3激活的内源信号。β-淀粉样蛋白激活的NLRP3炎性小体会产生白细胞介素1β,这进一步促进了“下游”小胶质细胞的活化以及炎症和潜在的神经毒性因子的聚集[46]。有研究表明,NLRP3复合物诱导小胶质细胞的M1样活化,并导致MCI小鼠模型中β-淀粉样蛋白沉积增加和认知障碍[47]。 有研究证明,MCI和阿尔茨海默症的大脑中活性caspase-1的表达明显增强,表明炎症小体在这种神经退行性疾病中发挥了作用,缺少caspase-1和白细胞介素1β基因片段的小鼠在很大程度上避免了空间记忆丧失和与神经退行性病变,该模型证明了当脑内caspase-1和白细胞介素1β的激活减少时,β-淀粉样蛋白的清除增强[48]。NLRP3炎性体中caspase-1活化最明显的结果是促炎细胞因子的分泌,最重要的是白细胞介素1β的分泌,它可能介导多种局部和全身免疫应答。作为先天免疫的主要介质,caspase-1还启动了一种新型的促炎性细胞死亡模式,称为细胞焦亡。这种细胞焦亡在形态上与凋亡有所不同,焦亡发生时细胞会不断胀大直至细胞膜破裂,最终导致具有强烈促炎性的细胞内容物被释放[49]。NLRP3/caspase-1介导的炎症在MCI患者的行为和认知功能障碍中发挥重要作用,由于β-淀粉样蛋白和白细胞介素1β都参与了长时程增强的抑制,因此它们的减少能共同促进长时程增强的保护,NLRP3或caspase-1缺乏症完全阻止了海马体中长时程增强的抑制并改善了认知障碍小鼠的空间记忆[50]。此外,有研究证明,白细胞介素1β会破坏血脑屏障的完整性,从而导致外周免疫细胞浸润到中枢神经系统,白细胞介素1β也会刺激小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的活化,进而诱导促炎因子白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α生成并诱导一氧化氮合酶合成[45],伴随产生一氧化氮,一氧化氮作为特殊的神经递质,在中枢神经系统中参与调控学习记忆和行为等生理机制,并被证实与神经元的损伤和死亡有关。 总之,NLRP3炎性小体在MCI疾病进程中起到重要作用,减少脑内的NLRP3炎性小体能显著改善MCI患者记忆功能、减缓小胶质细胞与星形胶质细胞的活化并且抑制MCI患者向阿尔茨海默症转化,开发合理有效的NLRP3炎性小体抑制剂是MCI治疗的新方向。 2.4.3 核因子κB 核因子κB家族由结构同源物组成,在哺乳动物中包括核因子κB1(p50)、NFκB2(p52)、RelA(p65)、RelB和c-Rel。有的核因子κB蛋白都包含一个称为Rel同源结构域的DNA结合和二聚结构域,该结构域负责DNA结合、二聚化、核易位以及与IκB蛋白的相互作用。在免疫细胞中,核因子κB通常以p65/p65同型二聚体或p65/p50的异聚复合物形式存在[27,43]。在中枢神经系统中,核因子κB与树突的生长和发育、神经元存活、突触可塑性的形成以及长期记忆有关。在神经元核因子κB缺陷型小鼠中,核因子κB信号缺失会削弱突触传递、空间记忆形成和神经元可塑性。同时,许多激酶途径均与激活神经元核因子κB信号传导有关[52]。而在神经胶质细胞中的核因子κB信号在涉及先天免疫、细胞存活和炎症的基因调控中起着重要作用[53],是神经炎症反应中的重要核转录因子。在神经炎症通路TLR/髓样分化因子88/核因子κB中,核因子κB是先天免疫系统和炎症反应中重要的信号转导膜蛋白,在多种疾病中起重要作用。Toll样受体是抵御病原体的第一道防线,Toll样受体通过髓样分化因子88激活Toll样受体4,β-淀粉样蛋白与Toll样受体4的结合可启动核因子κB p65的核易位并增加促炎性递质的表达。有研究表示,在邻近β-淀粉样蛋白斑块区域的神经胶质细胞中发现了活化的核因子κB [54-55]。 有研究结果表明,β-淀粉样蛋白和肿瘤坏死因子α都是通过经典IKK/核因子κB信号通路的激活来抑制长时程增强,IKK/核因子κB途径的激活对于β-淀粉样蛋白介导的长时程增强抑制至关重要[56]。核因子κB激活会激活多种促炎细胞因子,包括肿瘤坏死因子α,而肿瘤坏死因子α可以反向通过IKK调节核因子κB的活化,诱导淀粉样前体蛋白的过表达,从而导致β-淀粉样蛋白产生增加和神经元损伤。同时有研究报道,核因子κB的过度激活可能会导致发作性记忆缺陷的MCI患者的颞叶神经元功能异常[57]。 炎症信号增加的一个主要结果是诱导型转录因子核因子κB的上调,随之而来的是难以控制的脑内传播和炎症恶性循环,从而驱动神经变性过程。因此,通过靶向控制核因子κB信号通路不仅能抑制MCI患者脑内β-淀粉样蛋白的聚集,也可以保护长时程增强、减少体内的炎症反应、保护患者脑内神经元功能,是目前神经退行性病变的一种有效治疗策略。 但是,在开发和评估MCI和阿尔茨海默症的潜在核因子κB抑制剂时应谨慎行事,因为神经元中的活性核因子κB对神经元的生长和存活也起着关键作用。总之,开发有效的核因子κB信号通路抑制剂是目前MCI治疗中值得研究的新方向。 2.4.4 CD40 CD40是一种跨膜受体,是肿瘤坏死因子受体家族的成员,CD40配体和CD40之间的相互作用通过肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子家族成员激活各种信号传导级联[58]。临床研究发现,与认知正常的成年人相比,MCI和阿尔茨海默症患者血液中可溶性CD40及CD40配体的水平较高,这与MCI发病风险增加和认知能力快速下降高度相关[59]。CD40–CD40配体途径与多种炎性反应有关,CD40主要由免疫细胞表达,当小胶质细胞暴露于促炎递质时,CD40的表达迅速上调。此外CD40和CD40配体之间的相互作用会引起胶质细胞的活化、分化和增殖,以及共刺激分子和细胞因子的上调。当神经元存在时,将培养的小胶质细胞与β-淀粉样蛋白和CD40配体并用,小胶质细胞会分泌高水平的肿瘤坏死因子α,从而导致神经元损伤。CD40途径在小胶质细胞表型转化中起着重要作用,通过刺激CD40途径,β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的小胶质细胞活化显著提高。有研究表明,CD40–CD40配体途径的激活可调节β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的小胶质细胞固有免疫反应,包括减少外源β-淀粉样蛋白1-42的小胶质细胞吞噬作用[60]。在携带突变淀粉样前体蛋白基因的小鼠中破坏CD40-CD40配体信号,会导致这些小鼠的小胶质细胞活化和tau过度磷酸化明显减少[61]。 总而言之,上述研究表明,CD40-CD40配体相互作用对于神经炎症反应,尤其是小胶质细胞激活是必不可少的,抑制CD40-CD40配体途径可能极大地延缓MCI进展及其向阿尔茨海默症转化。 "
| [1] 赵梦琦,廖红.神经炎症与疾病中的认知功能障碍的关系研究进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2019,50(4):497-504. [2] PETERSEN RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med. 2004;256(3):183-194. [3] CARRO E, BARTOLOME F, BERMEJO-PAREJA F, et al. Early diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease based on salivary lactoferrin. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2017;8:131-138. [4] PETERSEN R. How early can we diagnose Alzheimer disease (and is it sufficient)?The 2017 Wartenberg lecture. Neurology. 2018;91(9): 395-402. [5] YANG QQ, ZhOU JW. Neuroinflammation in the central nervous system: Symphony of glial cells. Glia. 2019;67(6):1017-1035. [6] FAN Z, BROOKS DJ, OKELLO A, et al. An early and late peak in microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease trajectory. Brain. 2017;140(3):792-803. [7] SIUDA J, PATALONG-OGIEWA M, ŻMUDA W, et al. Cognitive impairment and BDNF serum levels. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2017;51(1):24-32. [8] SHEN XN, NIU LD, WANG YJ, et al. Inflammatory markers in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis and systematic review of 170 studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019;90(5):590-598. [9] MAGAKI S, MUELLER C, DICKSON C, et al. Increased production of inflammatory cytokines in mild cognitive impairment. Experimental Gerontology. 2007;42(3):233-240. [10] TUPPO EE, ARIAS HR. The role of infammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(2):289-305. [11] PILLAI JA, MAXWELL S, BENA J, et al. Key inflammatory pathway activations in the MCI stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2019;6(7):1248-1262. [12] HENEKA MT, CARSON MJ, EL KHOURY J, et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(4):388-405. [13] PUGAZHENTHI S, QIN L, REDDY PH. Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(5):1037-1045. [14] SIVANANDAM TM, THAKUR MK. Traumatic brain injury: a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012;36(5):1376-1381. [15] HUNTER R, OJHA U, BHURTEL S, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-induced functional and structural injury of the mitochondria in the nigrostriatal pathway. Neurosci Res. 2017;114:62-69. [16] GARABADU D, AGRAWAL N, SHARMA A, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism: a common link between neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Behav Pharmacol. 2019;30(8):642-652. [17] PERRY VH, TEELING J. Microglia and macrophages of the central nervous system: the contribution of microglia priming and systemic inflammation to chronic neurodegeneration. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(5):601-612. [18] ROSENBERG PB. Clinical aspects of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int Rev Psychiatry. 2005;17(6):503-514. [19] 刘娜,郑玉敏,罗晓光,等.转位蛋白与神经系统变性疾病[J].中华神经科杂志,2016,49(11):887-891. [20] LAVISSE S, GUILLERMIER M, HÉRARD AS, et al. Reactive astrocytes overexpress TSPO and are detected by TSPO positron emission tomography imaging. J Neurosci. 2012;32(32):10809-10818. [21] SARLUS H, HENEKA M. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3240-3249. [22] YE X, ZHOU WJ, ZHANG J. Association of CSF CD40 levels and synaptic degeneration across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Neurosci Lett. 2019;694:41-45. [23] SUBRAMANIYAN S, TERRANDO N. Neuroinflammation and Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders. Anesth Analg. 2019;128(4):781-788. [24] SUBHRAMANYAM CS, WANG C, HU Q, et al. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;94:112-120. [25] HICKMAN S, IZZY S, SEN P, et al. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21(10):1359-1369. [26] 邓佳丽.小胶质细胞活化抑制与中枢炎症反应关系的研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2020,40(5):1286-1290. [27] SHABAB T, KHANABDALI R, MOGHADAMTOUSI SZ, et al. Neuroinflammation pathways: a general review. Int J Neurosci. 2017; 127(7):624-633 [28] SCHUITEMAKER A, VAN DER DOEF TF, BOELLAARD R, et al. Microglial activation in healthy aging. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(6):1067-1072. [29] YIN Z, RAJ D, SAIEPOUR N, et al. Immune hyperreactivity of Aβ plaque-associated microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2017;55:115-122. [30] ARRANZ AM, DE STROOPER B. The role of astroglia in Alzheimer’s disease: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(4):406-414. [31] KAUR D, SHARMA V, DESHMUKH R. Activation of microglia and astrocytes: a roadway to neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Inflammopharmacology. 2019;27(4):663-677. [32] MCGEER EG, MCGEER PL. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a field in its infancy. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;19(1):355-361. [33] GONZÁLEZ-REYES RE, NAVA-MESA MO, VARGAS-SÁNCHEZ K, et al. Involvement of astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease from a neuroinflammatory and oxidative stress perspective. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:427. [34] LIN L, ZHENG LJ, ZHANG LJ. Neuroinflammation,Gut Microbiome,and Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(11):8243-8250. [35] FURMAN JL, SAMA DM, GANT JC, et al. Targeting astrocytes ameliorates neurologic changes in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci. 2012;32(46):16129-16140. [36] AGGARWAL BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3(9):745-756. [37] MCCOY MK, TANSEY MG. TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2008;5:45. [38] STELLWAGEN D, BEATTIE EC, SEO JY, et al. Differential regulation of AMPA receptor and GABA receptor trafficking by tumor necrosis factor-alpha . J Neurosci. 2005;25(12):3219-3228. [39] SANTOS SD, CARVALHO AL, CALDEIRA MV, et al. Regulation of AMPA receptors and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience. 2009;158(1):105-125. [40] RIAZI K, GALIC MA, KENTNER AC, et al. Microglia-dependent alteration of glutamatergic synaptic transmission and plasticity in the hippocampus during peripheral inflammation. J Neurosci. 2015;35(12): 4942-4952. [41] SAFAVYNIA SA, GOLDSTEIN PA. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction:Moving From Hypothesis to Treatment. Front Psychiatry. 2019;9:752. [42] CHOWDHURY S, SHEPHERD JD, OKUNO H, et al. Arc/Arg3.1 interacts with the endocytic machinery to regulate AMPA receptor trafficking. Neuron. 2006;52(3):445-459. [43] LIU Y, ZHOU LJ, WANG J, et al. TNF-α Differentially Regulates Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus and Spinal Cord by Microglia-Dependent Mechanisms after Peripheral Nerve Injury. J Neurosci. 2017;37(4): 871-881. [44] SAXENA S, MAZE M. Impact on the brain of the inflammatory response to surgery. Presse Med. 2018;47(4 Pt 2):e73-e81. [45] KANNEGANTI TD, LAMKANFI M, NUNEZ G. Intracellular NODlike receptors in host defense and disease. Immunity. 2007;27(4):549-559. [46] HALLE A, HORNUNG V, PETZOLD GC, et al. The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(8):857-865. [47] LUČIŪNAITĖ A, MCMANUS RM, JANKUNEC M, et al. Soluble Aβ oligomers and protofibrils induce NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia. J Neurochem. 2020;155(6):650-661. [48] HENEKA MT, KUMMER MP, STUTZ A, et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature. 2013;493(7434):674-678. [49] LAMKANFI M. Emerging inflammasome effector mechanisms. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(3):213-220. [50] HENEKA MT, KUMMER MP, STUTZ A, et al. NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature. 2013;493(7434):674-678. [51] MITCHELL JP, CARMODY RJ. NF-κB and the Transcriptional Control of Inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2018;335:41-84. [52] SRINIVASAN M, LAHIRI DK. Significance of NF-κB as a pivotal therapeutic target in the neurodegenerative pathologies of Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015;19(4):471-487. [53] ZHANG Q, LENARDO MJ, BALTIMORE D. 30 Years of NF-κB: A Blossoming of Relevance to Human Pathobiology. Cell. 2017;168(1-2): 37-57. [54] LI H, YOON JH, WON HJ, et al. Isotrifoliol inhibits pro-inflammatory mediators by suppression of TLR/NF-κB and TLR/MAPK signaling in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;45:110-119. [55] SEO EJ, FISCHER N, EFFERTH T. Phytochemicals as inhibitors of NF-κB for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Res. 2018;129: 262-273. [56] SAMIDURAI M, RAMASAMY VS, JO J. β-amyloid inhibits hippocampal LTP through TNFR/IKK/NF-κB pathway. Neurol Res. 2018;40(4):268-276. [57] ZHAO Y, DENG H, LI K, et al. Trans-cinnamaldehyde improves neuroinflammation-mediated NMDA receptor dysfunction and memory deficits through blocking NF-κB pathway in presenilin1/2 conditional double knockout mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2019;82:45-62. [58] CHAKRABARTI S, RIZVI M, PATHAK D, et al. Hypoxia influences CD40-CD40L mediated inflammation in endothelial and monocytic cells. Immunol Lett. 2009;122(2):170-184. [59] YE X, ZHOU W, ZHANG J. For Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of CSF CD40 levels and synaptic degeneration across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Neurosci Lett. 2019;694: 41-45. [60] MICHELS M, DANIESLKI LG, VIEIRA A, et al. CD40-CD40 Ligand Pathway is a Major Component of Acute Neuroinflammation and Contributes to Long-term Cognitive Dysfunction after Sepsis. Mol Med. 2015;21(1):219-226. [61] GIUNTA B, REZAI-ZADEH K, TAN J. Impact of the CD40-CD40L dyad in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010;9(2): 149-155. (责任编辑:GD,ZN,TXY) |
| [1] | An Yang, Liao Yinan, Xie Chengxin, Li Qinglong, Huang Ge, Jin Xin, Yin Dong. Mechanism of Inulae flos in the treatment of osteoporosis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [3] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [4] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [5] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [6] | An Yang, Liao Yinan, Xie Chengxin, Li Qinglong, Huang Ge, Jin Xin, Yin Dong. Mechanism of Inulae flos in the treatment of osteoporosis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5662-5669. |
| [7] | Shi Shujuan, Li Cheng, Qiao Lingyan, Yang Binyi, Li Tang. Construction of human SMARCAL11 gene over-expressed lentiviral vector and its effect on proliferation of embryonic kidney cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5682-5687. |
| [8] | Zhang Qunhui, Li Yimei, Zhang Dejun. Hypoxia-inducible factor and coronary heart disease: antagonism and protection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5729-5734. |
| [9] | Huang Minling, Lu Zhaoqi, Shen Zhen, Lin Haixiong, Feng Junjie, Huang Feng, Jiang Ziwei, Cai Qunbin. Effects of total flavone of Rhizoma Drynariae on the coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone remodeling through notch signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5116-5122. |
| [10] | Zou Kun, Guo Wanshou, Deng Yawen, Zhang Qidong, Liu Pei, Wang Weiguo. Molecular mechanism of curcumin in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics and network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5132-5140. |
| [11] | Wang Ding, Lin Tianye, Chen Weijian, Chen Jianfeng, Ou Huizhi, Li Hongzhu, Yang Peng, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Feng Zongquan. Medication rules and mechanism of femoral head necrosis: an analysis based on data mining and network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5148-5154. |
| [12] | Qiu Wandi, Cui Caiyun, Li Yanjun. Effects of resolvin on vital pulp conservation and regeneration during the inflammatory environment of dental pulp, periapical and periodontal tissues [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5191-5196. |
| [13] |
Li Yinglian, Chang Qiong.
Changes in serum tumor necrosis factor alpha, transforming growth factor beta 1, and interleukin-6 levels in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease combined with osteoporosis#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5085-5090.
|
| [14] | Tan Xiaowu, Yu Xiaofan, Jiang Huijiao, Xing Zhikun, Zhao Xueyuan, Gao Fengyi, Wu Xiangwei, Chen Xueling. Effect of xanthohumol on proliferation, migration, tube formation and apoptosis of endothelial progenitor cells and its mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4988-4994. |
| [15] | Guo Minfang, Zhang Huiyu, Zhang Peijun, Bai Zhenjun, Yu Jingwen, Wang Yuyin, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Chai Zhi, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Fasudil inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced astrocytic injury by regulating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 5012-5017. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||