Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 237-245.doi: 10.12307/2022.1023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of ligustrazine and overexpression of miR-20b-5p on synovial, cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in rats with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: a histological observation
Xie Pingjin1, Luo Zhen2, 3, Lu Qigui1, Guo Yanxing1, 4, Chen Qunqun2, 3, Li Feilong2, 3
- 1Shenzhen Hospital, Shanghai University of Chinese Medicine/Shenzhen Luohu District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000; 2Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006; 3Guangdong Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Orthopedics and Traumatology, Guangzhou 510378; 4Luoyang Orthopedic-Traumatological Hospital of Henan Province/Henan Provincial Orthopedic Hospital, Luoyang 471000
-
Received:2022-01-12Accepted:2022-03-07Online:2023-01-18Published:2022-06-18 -
Contact:Lu Qigui, Chief physician, Shenzhen Hospital, Shanghai University of Chinese Medicine/Shenzhen Luohu District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Xie Pingjin, Master, Physician, Shenzhen Hospital, Shanghai University of Chinese Medicine/Shenzhen Luohu District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Fundamental Research Project of Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee in 2020, No. JCYJ20190812170815559 (to LQG); Top Three Medical and Health Project of Shenzhen, No. SZZYSM202101005 (to XPJ [project participant]); Scientific Research Project of Guangdong Province Administration Bureau of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 20202085 (to LFL); Doctors Startup Vertical Collaboration Project of Guangdong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, No. 2018A030310606 (to CQQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Lu Qigui, Guo Yanxing, Chen Qunqun, Li Feilong. Effect of ligustrazine and overexpression of miR-20b-5p on synovial, cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in rats with early-stage knee osteoarthritis: a histological observation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 237-245.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
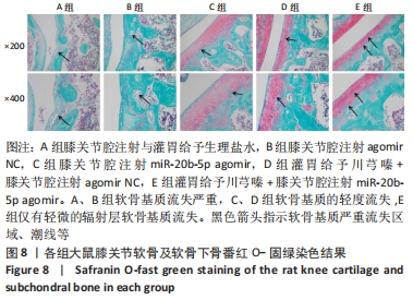
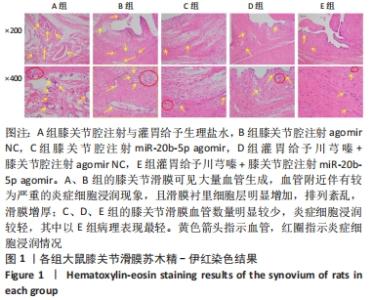
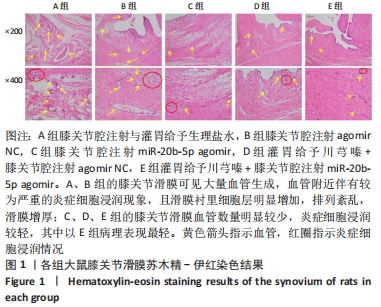
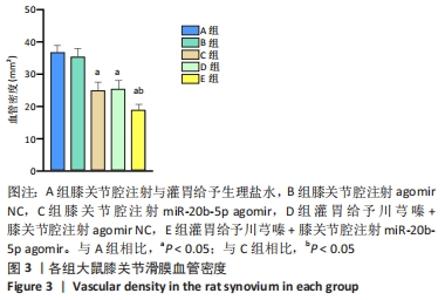
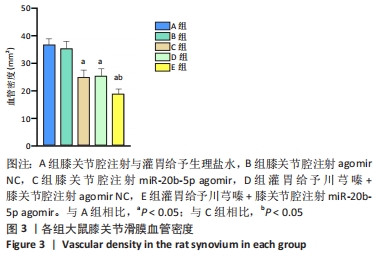
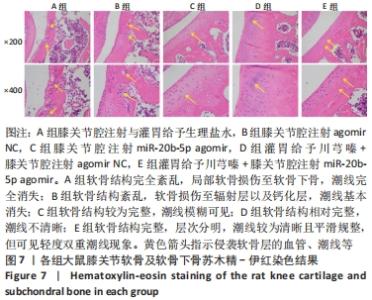
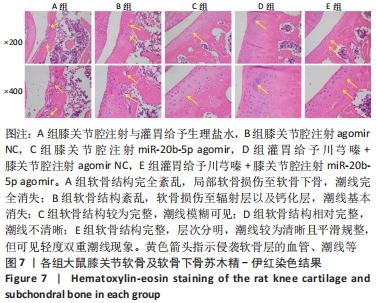
A组大鼠软骨结构完全紊乱,局部软骨损伤至软骨下骨,软骨细胞形态异常,软骨和软骨下骨交界区明显可见多处血管生成,潮线完全消失。B组大鼠软骨结构紊乱,软骨损伤至辐射层以及钙化层,潮线不可见,软骨和软骨下骨交界区可见血管生成,严重侵袭并破坏软骨结构,潮线基本消失。C组大鼠软骨表面局部表现粗糙,软骨结构较为完整,细胞形态较为正常,软骨及软骨下骨交界区未见明显血管侵袭,潮线模糊可见,但整体相对上移且局部向上突出,移行层和辐射层部分软骨基质的伊红染色较淡,提示可能有轻度软骨基质流失。D组大鼠软骨表面略为粗糙,软骨结构相对完整,细胞形态相对正常,局部辐射层细胞数量减少,软骨及软骨下骨交界区未见血管侵袭,潮线不清晰。E组大鼠软骨表面略为粗糙,软骨结构完整,层次分明,软骨细胞形态较为正常,软骨及软骨下骨交界区未见明显血管侵袭,潮线较为清晰且平滑规整,但可见轻度双重潮线现象。 2.3.2 番红O-固绿染色结果 见图8。 "

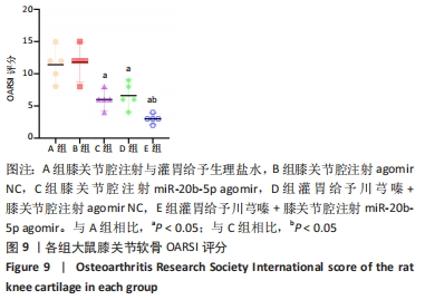
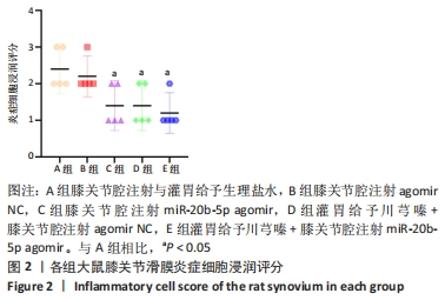
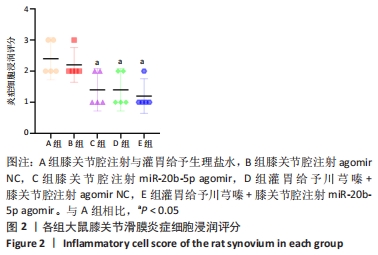
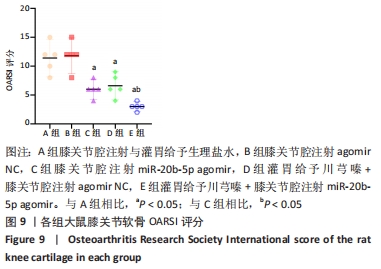
A组大鼠软骨番红O几乎未见着色,且软骨组织出现空洞,提示软骨基质流失严重;B组大鼠软骨番红O同样未见着色,且软骨及软骨下骨交界区域血管侵袭部位可见空洞,该组大鼠软骨基质流失情况与模型组类似。C组大鼠软骨番红O染色优于A、B组,但移行层和辐射层染色稍淡,潮线整体上移且局部向上突出,表现与苏木精-伊红染色结果一致,提示该组软骨基质的轻度流失。D组大鼠软骨番红O染色较C组略深,但潮线不规整,提示钙化层向非钙化层的侵袭。相较于其他组,E组大鼠软骨番红O染色整体最深,潮线最为清晰平滑,但能清晰地看到轻度双重潮线现象,表现与苏木精-伊红染色结果一致,提示可能具有轻微的辐射层软骨基质流失。 2.3.3 OARSI评分 见图9。 "
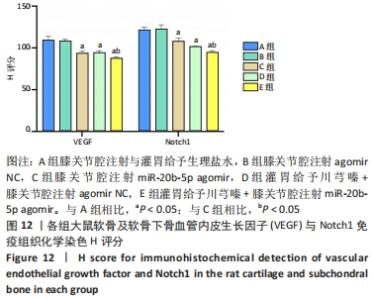
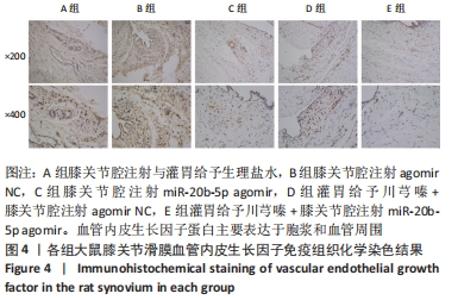
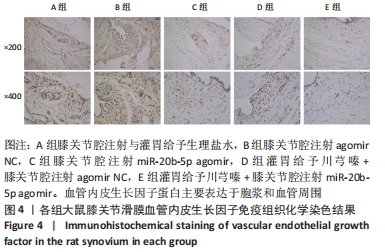
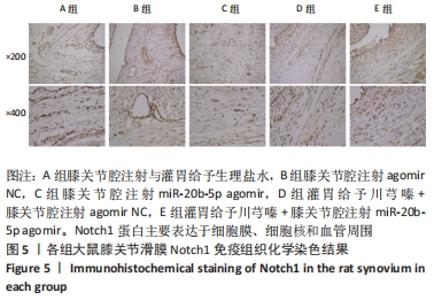
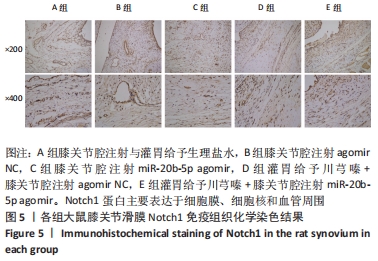
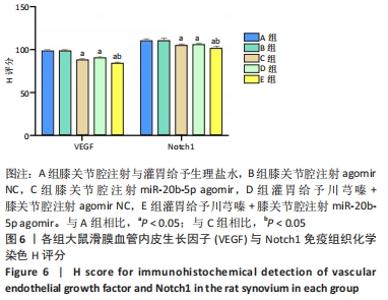
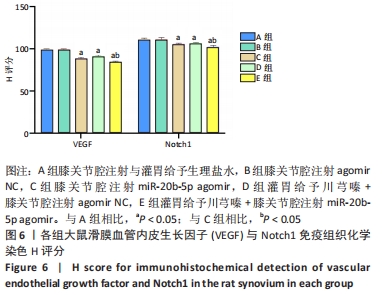
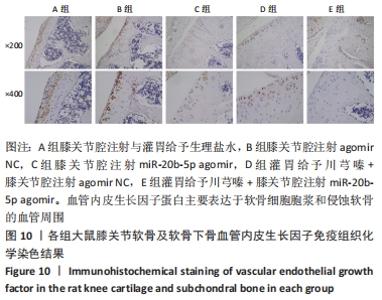
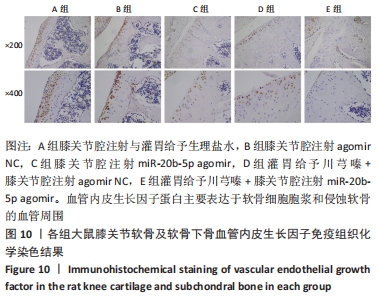
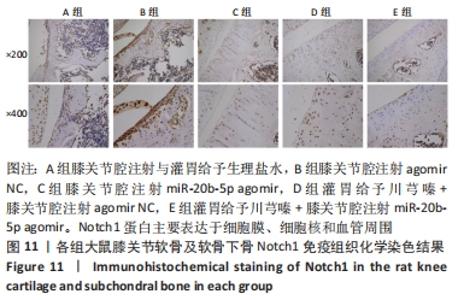
多重比较显示,C、D、E组软骨及软骨下骨切片中的血管内皮生长因子、Notch1蛋白阳性表达评分均低于A组(血管内皮生长因子:P均< 0.001;Notch1:P=0.002,P=0.001,P < 0.001)、B组(血管内皮生长因子:P均< 0.001;Notch1:P=0.009,P=0.004,P < 0.001);C、D组的血管内皮生长因子、Notch1阳性表达评分均高于E组(血管内皮生长因子:P=0.004,P=0.002;Notch1:P=0.002,P=0.006);C组和D组之间的血管内皮生长因子、Notch1蛋白阳性表达评分表差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图12。 "

| [1] LU KH, LU PW, LU EW, et al. The potential remedy of melatonin on osteoarthritis. J Pineal Res. 2021;71(3):e12762. [2] WALSH DA, BONNET CS, TUMER EL, et al. Angiogenesis in the synovium and at the osteochondral junction in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(7):743-751. [3] HENROTIN Y, PESESSE L, LAMBERT C. Targeting the synovial angiogenesis as a novel treatment approach to osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2014;6(1):20-34. [4] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436. [5] BARRANCO C. Osteoarthritis: Animal data show VEGF blocker inhibits post-traumatic OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(11):638. [6] GORDON WR, ARNETT KL, BLACKLOW SC. The molecular logic of Notch signaling--a structural and biochemical perspective. J Cell Sci. 2008; 121(Pt 19):3109-3119. [7] SAHARA M, HANSSON EM, WERNET O, et al. Manipulation of a VEGF-Notch signaling circuit drives formation of functional vascular endothelial progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Res. 2014;24(7):820-841. [8] 谢平金,余翔,柴生颋,等.川芎嗪干预早期膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨Ⅱ型胶原纤维α1基因与血管内皮生长因子mRNA及miR20b的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(12):1846-1851. [9] 李飞龙,谢平金,柴生颋,等.川芎嗪对膝骨性关节炎大鼠软骨VEGF表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(7):904-909. [10] 梁桂洪,梁祖建,谢平金,等.川芎嗪对膝骨性关节炎大鼠软骨下骨中miR-20b/VEGF和BMP2/Smad1通路的影响[J].中国药房, 2019,30(4):448-453. [11] MAISTO R, TROTTA MC, PETRILLO F, et al. Resolvin D1 Modulates the Intracellular VEGF-Related miRNAs of Retinal Photoreceptors Challenged With High Glucose. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:235. [12] LAZZARA F, TROTTA MC, PLATANIA CBM, et al. Stabilization of HIF-1α in Human Retinal Endothelial Cells Modulates Expression of miRNAs and Proangiogenic Growth Factors. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1063. [13] 罗臻,李宏栩,卢启贵,等.红姜提取物保护早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠的关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(32):5155-5161. [14] PRITZKER KP, GAY S, JIMENEZ SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(1):13-29. [15] MOULD AW, TONKS ID, CAHILL MM, et al. Vegfb gene knockout mice display reduced pathology and synovial angiogenesis in both antigen-induced and collagen-induced models of arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(9):2660-2669. [16] 陈永,邱富娟,朱兴旺,等.血管翳并非类风湿关节炎的专利——膝骨关节炎血管翳病理形态观察[J].南方医科大学学报,2019,39(6): 747-750. [17] VARGHESE F, BUKHARI AB, MALHOTRA R, et al. IHC Profiler: an open source plugin for the quantitative evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of human tissue samples. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96801. [18] WALSH DA. Angiogenesis and arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38(2):103-112. [19] SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(11):625-635. [20] BENITO MJ, VEALE DJ, FITZGERALD O, et al. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(9):1263-1267. [21] WANG W, WANG L, GULKO PS, et al. Computational deconvolution of synovial tissue cellular composition: presence of adipocytes in synovial tissue decreased during arthritis pathogenesis and progression. Physiol Genomics. 2019;51(6):241-253. [22] MIMPEN JY, BALDWIN MJ, CRIBBS AP, et al. Interleukin-17A Causes Osteoarthritis-Like Transcriptional Changes in Human Osteoarthritis-Derived Chondrocytes and Synovial Fibroblasts In Vitro. Front Immunol. 2021;12:676173. [23] CHEN Y, JIANG W, YONG H, et al. Macrophages in osteoarthritis: pathophysiology and therapeutics. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(1):261-268. [24] FENG Y, HU S, LIU L, et al. HMGB1 contributes to osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint by inducing synovial angiogenesis. J Oral Rehabil. 2021;48(5):551-559. [25] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446. [26] MAPP PI, WALSH DA. Mechanisms and targets of angiogenesis and nerve growth in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(7):390-398. [27] PESESSE L, SANCHEZ C, HENROTIN Y. Osteochondral plate angiogenesis: A new treatment target in osteoarthritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2011;78(2):144-149. [28] HU Y, CHEN X, WANG S, et al. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):20. [29] YAJUN W, JIN C, ZHENGRONG G, et al. Betaine Attenuates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and Angiogenesis in Subchondral Bone. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:723988. [30] 梁桂洪,曾令烽,潘建科,等.川芎嗪干预骨性关节炎的机制研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(12):6228-6232. [31] MAISTO R, TROTTA MC, PETRILLO F, et al. Resolvin D1 Modulates the Intracellular VEGF-Related miRNAs of Retinal Photoreceptors Challenged With High Glucose. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:235. [32] LUO Y, HE J, TAO X, et al. miR‑20b negatively regulates VEGF expression by targeting STAT3 in H22 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(5):2806-2813. [33] CASCIO S, D’ANDREA A, FERLA R, et al. miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 2010;224(1):242-249. [34] 陶象男,汪忆梦,宋传旺.miR-20b直接靶向3’-UTR负性调节VEGF的表达[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2016,45(1):22-26. [35] Borgonio Cuadra VM, Gonzalez-Huerta NC, Romero-Cordoba S, et al. Altered expression of circulating microRNA in plasma of patients with primary osteoarthritis and in silico analysis of their pathways. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e97690. [36] CHEN Y, ZHANG L, LI E, et al. Long-chain non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes the progression of osteoarthritis via sponging miR-20b/PTEN axis. Life Sci. 2020;253:117685. [37] SAETAN N, HONSAWEK S, TANAVALEE A, et al. Relationship of plasma and synovial fluid vascular endothelial growth factor with radiographic severity in primary knee osteoarthritis. Int Orthop.2014;38(5):1099. [38] CARLEVARO MF, CERMELLI S, CANCEDDA R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in cartilage neovascularization and chondrocyte differentiation: auto-paracrine role during endochondral bone formation. J Cell Sci. 2000;113(Pt 1):59. [39] LU J, ZHANG H, CAI D, et al. Positive-Feedback Regulation of Subchondral H-Type Vessel Formation by Chondrocyte Promotes Osteoarthritis Development in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5): 909-920. [40] ROMEO SG, ALAWI KM, RODRIGUES J, et al. Endothelial proteolytic activity and interaction with non-resorbing osteoclasts mediate bone elongation. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(4):430-441. [41] QIN H, ZHAO X, HU YJ, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis to Alleviate Abnormal Bone Formation and Angiogenesis Could Improve the Subchondral Bone Microenvironment in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8852574. [42] TSAI CH, LIU SC, CHUNG WH, et al. Visfatin Increases VEGF-dependent Angiogenesis of Endothelial Progenitor Cells during Osteoarthritis Progression. Cells. 2020;9(5):1315. [43] LI B, CHEN K, QIAN N, et al. Baicalein alleviates osteoarthritis by protecting subchondral bone, inhibiting angiogenesis and synovial proliferation. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(11):5283-5294. [44] WANG YH, KUO SJ, LIU SC, et al. Apelin Affects the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating VEGF-Dependent Angiogenesis and miR-150-5p Expression in Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells. 2020;9(3):594. [45] LI W, LIN J, WANG Z, et al. Bevacizumab tested for treatment of knee osteoarthritis via inhibition of synovial vascular hyperplasia in rabbits. J Orthop Translat. 2019;19:38-46. [46] PEREZ-FIDALGO JA, ORTEGA B, SIMON S, et al. NOTCH signalling in ovarian cancer angiogenesis. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(24):1705. [47] Sassi N, Laadhar L, Driss M, et al. The role of the Notch pathway in healthy and osteoarthritic articular cartilage: from experimental models to ex vivo studies. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(2):208. [48] CHIGURUPATI S, ARUMUGAM TV, SON TG, et al. Involvement of notch signaling in wound healing. PLoS One. 2007;2(11):e1167. [49] EBRAHIM N, DESSOUKY AA, MOSTAFA O, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells combined with platelet-rich plasma accelerate diabetic wound healing by modulating the Notch pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):392. [50] SUCHTING S, FREITAS C, LE NOBLE F, et al. The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 negatively regulates endothelial tip cell formation and vessel branching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(9):3225-3230. [51] LUO Z, SHANG X, ZHANG H, et al. Notch Signaling in Osteogenesis, Osteoclastogenesis, and Angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2019;189(8):1495-1500. [52] AKIL A, GUTIÉRREZ-GARCÍA AK, GUENTER R, et al. Notch Signaling in Vascular Endothelial Cells, Angiogenesis, and Tumor Progression: An Update and Prospective. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:642352. [53] 黄敏玲,卢赵琦,申震,等.骨碎补总黄酮干预Notch信号通路影响骨重建过程中成血管-成骨耦联[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(32):5116-5122. [54] GAO W, SWEENEY C, WALSH C, et al. Notch signalling pathways mediate synovial angiogenesis in response to vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin 2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(6):1080-1088. [55] LIAO J, WEI Q, ZOU Y, et al. Notch Signaling Augments BMP9-Induced Bone Formation by Promoting the Osteogenesis-Angiogenesis Coupling Process in Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(5):1905-1923. [56] WANG H, HUANG X, ZHANG J, et al. The expression of VEGF and Dll4/Notch pathway molecules in ovarian cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2014;436: 243-248. |
| [1] | Niu Zihan, Yu Yang, Ai Jiang, Bu Panpan, Li Wenbo, Suriye·Reheman, Ma Shaolin. Total flavonoids of Hippophae rhamnoides L. interfere with the regression of hypertrophic scar tissue blocks in a rabbit ear model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 258-263. |
| [2] | Liu Gang, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Xu Lin, Fan Xiao, Tao Jingwei, Zhang Houjun, He Feng, Zhao Yi, Mu Xiaohong. Tetramethylpyrazine improves hemorheological indexes in rats with complete spinal cord transection: a dynamic observation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 282-286. |
| [3] | Liu Yinghong, Yi Yating. Mechanism and implication of angiogenesis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 307-313. |
| [4] | Shi Xu, Li Ruiyu, Zhang Bing, Chen Qi, Zuo Hua. Effect of inflammatory reaction mediated by microglia polarization in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 121-129. |
| [5] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [6] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [7] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [8] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [9] | Lyu Zichen, Tu Zhenxing, Xu Ao, Cheng Kang, Wang Hongtao, Wang Bin. Mechanism of bone healing and angiogenesis during distraction osteogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5881-5888. |
| [10] | Long Zhisheng, Xiong Long, Gong Feipeng, Li Jingtang, Zeng Jianhua, Deng Ying, Lan Min, Kong Weihao, Chen Gang. Effect of artificial bone with multi-scale hydroxyapatite/chitosan microtubule structure on rabbit bone defect repair and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5436-5441. |
| [11] | Yu Yunbao, Chen Lin, Wu Xiya, Yan Lerong, Miao Zhang, Man Yang, Jing Renyi, Lei Zhen, Chu Zhiqiang, Zhang Hongwei. Vascular endothelial growth factor-Notch signaling pathways in endothelial precursor cells in promoting the transformation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 4946-4953. |
| [12] | Deng Xiaohui, Zhang Zengzeng, Zhang Zhihua, Zhu Lingyan. Mechanism and application prospects of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes gene-modified microRNA in the treatment of diabetic foot [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5076-5084. |
| [13] | Zhao Xinxin, Yang Xiaoqing, Zhang Yuquan. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve pregnancy outcomes of spontaneous abortion mouse models by promoting vascular endothelial growth factor expression in decidua [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4793-4799. |
| [14] | Zhu Boheng, Peng Ying, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of sterol regulatory element binding protein in wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4729-4734. |
| [15] | Zhao Dun, Fang Bin, Yi Chunzhi, He Mincong, Zheng Jiaqian, Li Yue. Effects of total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae on bone remodeling and expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2, vascular endothelial growth factor and CD31 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4638-4642. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||