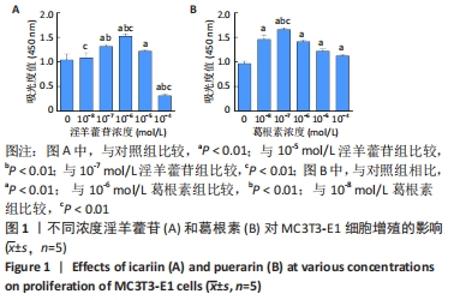
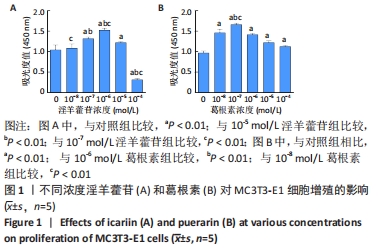
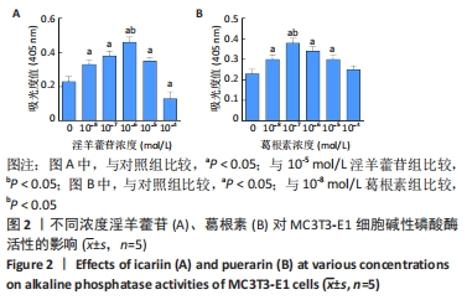
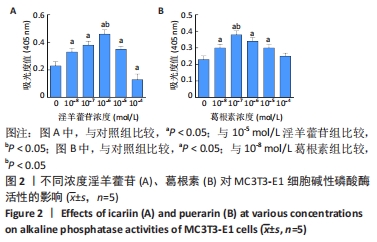
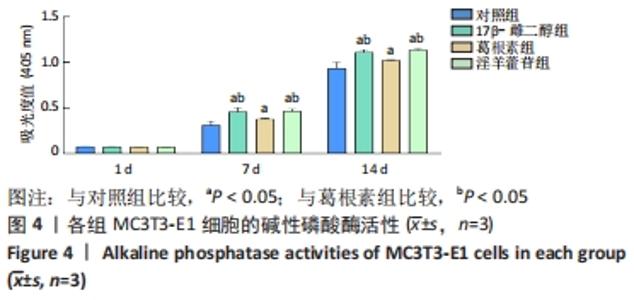
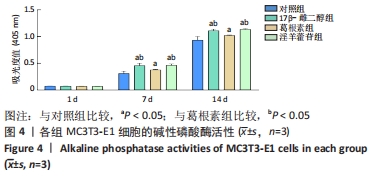
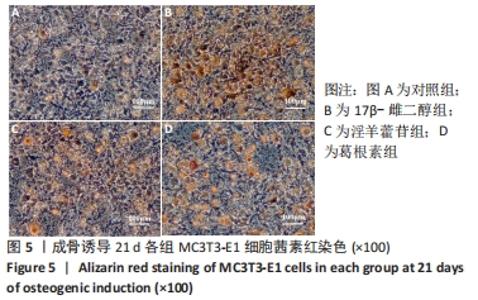
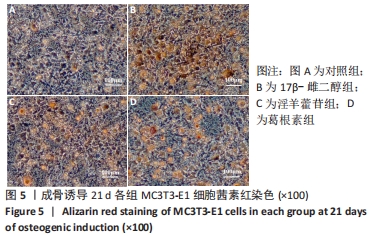
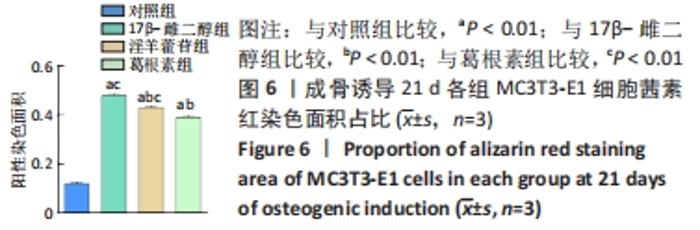
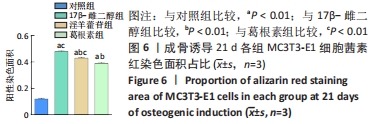
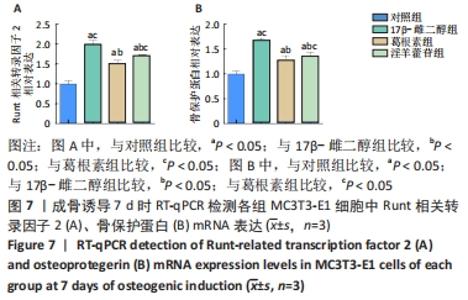
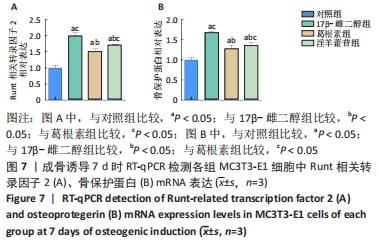
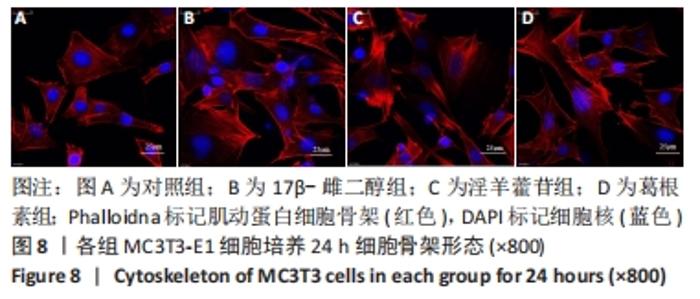
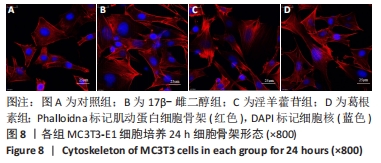
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 872-877.doi: 10.12307/2023.219
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts
Qiao Luhui1, Ma Ziyu2, Guo Haoyu2, Hou Yudong2
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Yantai Stomatological Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264000, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264003, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-04Accepted:2022-02-22Online:2023-02-28Published:2022-08-11 -
Contact:Hou Yudong, Master, Professor, School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264003, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Qiao Luhui, Master, Physician, Department of Prosthodontics, Yantai Stomatological Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] EL-RASHIDY AA, ROETHER JA, HARHAUS L, et al. Regenerating bone with bioactive glass scaffolds: A review of in vivo studies in bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:1-28. [2] 李祖浩,王辰宇,王中汉.骨质疏松性骨缺损的治疗进展:支架植入与局部药物递送[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(18):2939-2945. [3] BUHRMANN C, HONARVAR A, SETAYESHMEHR M, et al. Herbal Remedies as Potential in Cartilage Tissue Engineering: An Overview of New Therapeutic Approaches and Strategies. Molecules. 2020;25(13): 3075. [4] AWALE G, WONG E, RAJPURA K, et al. Engineered Bone Tissue with Naturally-Derived Small Molecules. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(24): 3585-3594. [5] WU Y, XIA L, ZHOU Y, et al. Evaluation of osteogenesis and angiogenesis of icariin loaded on micro/nano hybrid structured hydroxyapatite granules as a local drug delivery system for femoral defect repair. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(24):4871-4883. [6] 刘永庆,李琪佳,甘洪全,等.葛根素联合国产多孔钽对人成骨细胞COL-I、OC、OPN表达和细胞增殖的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2017,23(2):236-243. [7] AN J, YANG H, ZHANG Q, et al. Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation. Life Sci. 2016;147:46-58. [8] XU Y, LI L, TANG Y, et al. Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation by suppressing Notch signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;865:172794. [9] SUZUKI H, TATEI K, OHSHIMA N, et al. Regulation of MC3T3-E1 differentiation by actin cytoskeleton through lipid mediators reflecting the cell differentiation stage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019; 514(2):393-400. [10] ZENG X, FENG Q, ZHAO F, et al. Puerarin inhibits TRPM3/miR-204 to promote MC3T3-E1 cells proliferation, differentiation and mineralization. Phytother Res. 2018;32(6):996-1003. [11] WANG Z, WANG D, YANG D, et al. The effect of icariin on bone metabolism and its potential clinical application. Osteoporos Int. 2018; 29(3):535-544. [12] 何罕亮.雌激素对成骨细胞MC3T3-E1的影响及其相关机制研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2018. [13] CLEMENTINI M, MORLUPI A, AGRESTINI C, et al. Immediate versus delayed positioning of dental implants in guided bone regeneration or onlay graft regenerated areas: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;42(5):643-650. [14] LU J, HAO Y, ZHAO W, et al. Molecular, Cellular and Pharmaceutical Aspects of Autologous Grafts for Peri-implant Hard and Soft Tissue Defects. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2017;18(1):85-94. [15] YAMADA Y, HARA K, NAKAMURA S, et al. Minimally invasive approach with tissue engineering for severe alveolar bone atrophy case. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;42(2):260-263. [16] KŘÍŽOVÁ L, DADÁKOVÁ K, KAŠPAROVSKÁ J, et al. Isoflavones. Molecules. 2019;24(6):1076. [17] SIROTKIN AV, HARRATH AH. Phytoestrogens and their effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;741:230-236. [18] WANG Y, WANG WL, XIE WL, et al. Puerarin stimulates proliferation and differentiation and protects against cell death in human osteoblastic MG-63 cells via ER-dependent MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt activation. Phytomedicine. 2013;20(10):787-796. [19] YANG X, ZHENG H, LIU Y, et al. Puerarin for OVX-Induced Postmenopausal Osteoporosis in Murine Model: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(1):37-42. [20] XIE L, LIU N, XIAO Y, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Osteogenesis Induced by Icariin and Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2: A Dynamic Observation. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1058. [21] HO MX, POON CC, WONG KC, et al. Icariin, but Not Genistein, Exerts Osteogenic and Anti-apoptotic Effects in Osteoblastic Cells by Selective Activation of Non-genomic ERα Signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:474. [22] URASOPON N, HAMADA Y, CHERDSHEWASART W, et al. Preventive effects of Pueraria mirifica on bone loss in ovariectomized rats. Maturitas. 2008;59(2):137-148. [23] TIYASATKULKOVIT W, MALAIVIJITNOND S, CHAROENPHANDHU N, et al. Pueraria mirifica extract and puerarin enhance proliferation and expression of alkaline phosphatase and type I collagen in primary baboon osteoblasts. Phytomedicine. 2014;21(12):1498-1503. [24] HO-SHUI-LING A, BOLANDER J, RUSTOM LE, et al. Bone regeneration strategies: Engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 2018;180:143-162. [25] FENG Q, CHENG SY, YANG R, et al. Puerarin promotes the viability and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by enhancing LC3B-mediated autophagy through downregulation of miR-204. Exp Ther Med. 2020; 19(2):883-890. [26] 吴曦,彭锐.不同浓度淫羊藿苷对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(5):669-674. [27] 张姝江,李颖,白波,等.中药骨康方对体外培养大鼠成骨细胞骨架保护作用的初步实验研究[J].世界中医药,2016,11(5):880-883. [28] WEI Q, WANG B, HU H, et al. Icaritin promotes the osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the regulation of sclerostin expression. Int J Mol Med. 2020;45(3):816-824. [29] YANG A, YU C, LU Q, et al. Mechanism of Action of Icariin in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:5747298. [30] HONG D, CHEN HX, YU HQ, et al. Morphological and proteomic analysis of early stage of osteoblast differentiation in osteoblastic progenitor cells. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(14):2291-2300. [31] SHANBHAG S, PANDIS N, MUSTAFA K, et al. Bone tissue engineering in oral peri-implant defects in preclinical in vivo research: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1): e336-e349. [32] RISTELI L, RISTELI J. Biochemical markers of bone metabolism. Ann Med. 1993;25(4):385-393. [33] ZHAN XQ, ZENG XW, ZHANG YY, et al. Puerarin promotes the viability and differentiation of MC3T3‑E1 cells by miR‑204‑regulated Runx2 upregulation. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):6262-6268. [34] BOYLE WJ, SIMONET WS, LACEY DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337-342. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [3] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [4] | Wu Boyu, Ye Kai, Chen Jiahan, Wang Jianghua, Wurikaixi·Aiyiti, Jiang Houfeng, Teng Yong. Biocompatibility of 3D printed polyetheretherketone/hydroxyapatite composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1932-1937. |
| [5] | Wei Yanzhao, Zheng Xiaohan, Gao Shijun, Huang Ting, Wei Xufang, Chen Xinxu, Zhao Zhenqiang. Expression of autocrine macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its receptors of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 34-41. |
| [6] | Yang Yan, Wang Jingxian, Zhang Ronghong, Li Chen, Fan Anran, Cui Dongbing, Wu Shumei. Effects of conditioned media of different sources on the proliferation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 49-53. |
| [7] | Lan Qian, Gu Yangcong, Xiao Xin, Bi Xueting, Li Na. Human periodontal ligament stem cells-derived exosomes interfere with the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 54-58. |
| [8] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [9] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [10] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [13] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [14] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [15] | Zhou Liang, Chen Xingzhen, Li Zhenyu, Zhang Zekun, Duan Guoqing. The mechanism of lncRNA HOTAIR in interleukin-1beta-mediated osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5607-5613. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||