Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (6): 903-908.doi: 10.12307/2023.262
Previous Articles Next Articles
Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children
Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong
- Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100105, China
-
Received:2022-02-23Accepted:2022-05-11Online:2023-02-28Published:2022-08-11 -
Contact:Mu Xiaohong, MD, Chief physician, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100105, China -
About author:Zhang Houjun, Doctoral candidate, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100105, China -
Supported by:Frontier Project of Beijing Natural Science Foundation-Haidian Original Innovation Joint Fund, No. 19L2059 (to MXH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 903-908.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
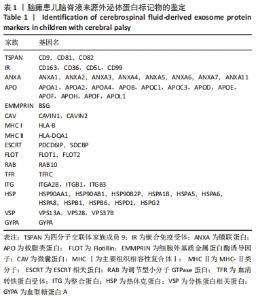
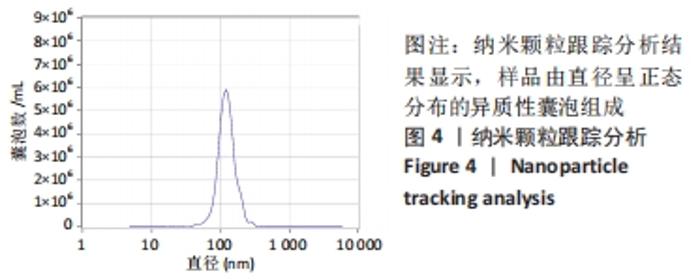
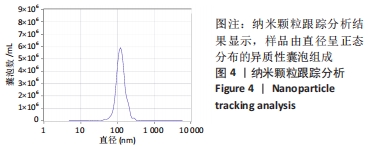
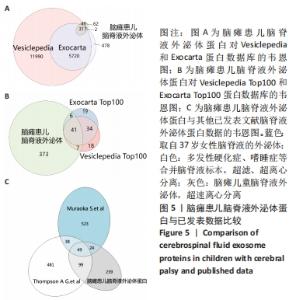
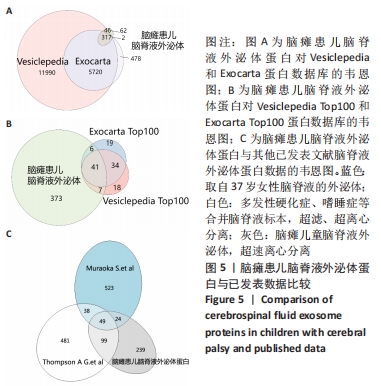
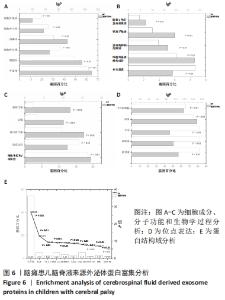
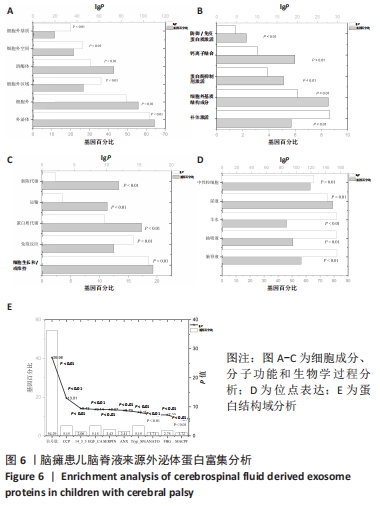
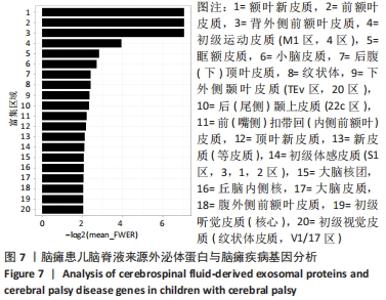
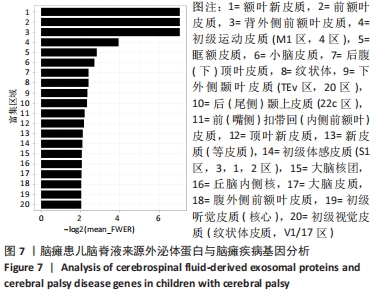
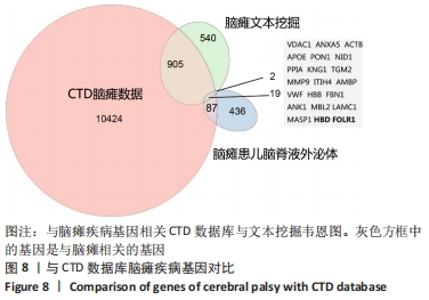
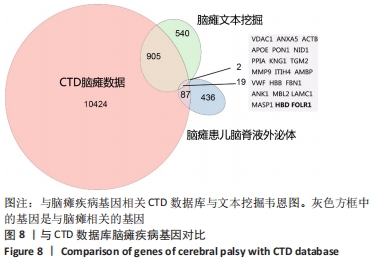
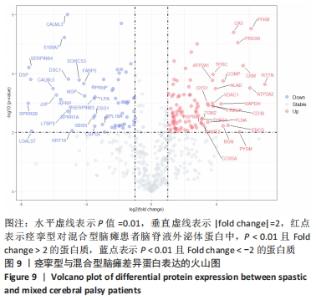
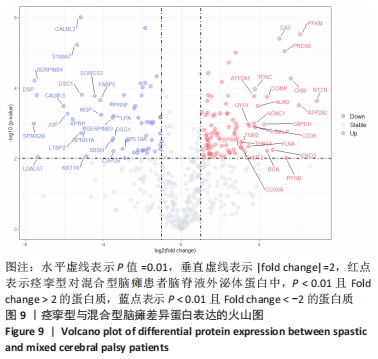
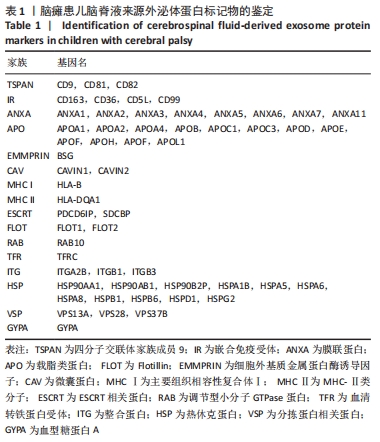
2.2 脑瘫患儿脑脊液外泌体蛋白图谱生成 使用无标记质谱分析外泌体中的蛋白,生成脑瘫患儿脑脊液外泌体蛋白图谱。混合型和痉挛型样本各3个重复中共鉴定出551个蛋白质,其中427个蛋白被鉴定出至少有2个唯一的肽段,这些蛋白中有大量外泌体特异表达的蛋白,见表1。与Vesiclepedia和ExoCarta protein Databases中的数据进行比较[19-20],发现Vesiclepedia TOP100和ExoCarta TOP100中分别鉴定出48个和47个蛋白,见图5A,B,这些数据表明外泌体的分离和蛋白质分析是可靠的。与已发表的其他脑脊液外泌体的蛋白质组数据进行比较[21-22],此研究鉴定的蛋白质中有148个(36%)或73个(17.8%)与其他数据组相同,见图5C。这3组数据集中相同的蛋白质有49种,且这些蛋白大多为外泌体特异表达蛋白。"
| [1] GLADSTONE M. A review of the incidence and prevalence, types and aetiology of childhood cerebral palsy in resource-poor settings. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2010;30(3):181-196. [2] GRAHAM HK, ROSENBAUM P, PANETH N, et al. Cerebral palsy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:15082. [3] MACLENNAN AH, THOMPSON SC, GECZ J. Cerebral palsy: causes, pathways, and the role of genetic variants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;213(6):779-788. [4] BANGASH AS, HANAFI MZ, IDREES R, et al. Risk factors and types of cerebral palsy. J Pak Med Assoc. 2014;64(1):103-107. [5] ERKIN G, DELIALIOGLU SU, OZEL S, et al. Risk factors and clinical profiles in Turkish children with cerebral palsy: analysis of 625 cases. Int J Rehabil Res. 2008;31(1):89-91. [6] TAKEUCHI H, INAGAKI S, MOROZUMI W, et al. VGF nerve growth factor inducible is involved in retinal ganglion cells death induced by optic nerve crush. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16443. [7] NOVAK I, MORGAN C, ADDE L, et al. Early, Accurate Diagnosis and Early Intervention in Cerebral Palsy: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(9):897-907. [8] THÉRY C, AMIGORENA S, RAPOSO G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22. [9] SKOG J, WÜRDINGER T, VAN RIJN S, et al. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(12):1470-1476. [10] URBANELLI L, BURATTA S, SAGINI K, et al. Exosome-based strategies for Diagnosis and Therapy. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 2015;10(1):10-27. [11] CHIASSERINI D, VAN WEERING JR, PIERSMA SR, et al. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid extracellular vesicles: a comprehensive dataset. J Proteomics. 2014;106:191-204. [12] YAGI Y, OHKUBO T, KAWAJI H, et al. Next-generation sequencing-based small RNA profiling of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes. Neurosci Lett. 2017;636:48-57. [13] MANEK R, MOGHIEB A, YANG Z, et al. Protein Biomarkers and Neuroproteomics Characterization of Microvesicles/Exosomes from Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Following Traumatic Brain Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2018; 55(7):6112-6128. [14] MEHDIANI A, MAIER A, PINTO A, et al. An innovative method for exosome quantification and size measurement. J Vis Exp. 2015;(95):50974. [15] PATHAN M, KEERTHIKUMAR S, CHISANGA D, et al. A novel community driven software for functional enrichment analysis of extracellular vesicles data. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017;6(1):1321455. [16] DAVIS AP, GRONDIN CJ, JOHNSON RJ, et al. Comparative Toxicogenomics Database (CTD): update 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D1138-D1143. [17] PLETSCHER-FRANKILD S, PALLEJÀ A, TSAFOU K, et al. DISEASES: text mining and data integration of disease-gene associations. Methods. 2015;74:83-89. [18] GROTE S, PRÜFER K, KELSO J, et al. ABAEnrichment: an R package to test for gene set expression enrichment in the adult and developing human brain. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(20):3201-3203. [19] KEERTHIKUMAR S, CHISANGA D, ARIYARATNE D, et al. ExoCarta: A Web-Based Compendium of Exosomal Cargo. J Mol Biol. 2016;428(4):688-692. [20] KALRA H, SIMPSON RJ, JI H, et al. Vesiclepedia: a compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012;10(12):e1001450. [21] THOMPSON AG, GRAY E, MAGER I, et al. UFLC-Derived CSF Extracellular Vesicle Origin and Proteome. Proteomics. 2018;18(24):e1800257. [22] MURAOKA S, LIN W, CHEN M, et al. Assessment of separation methods for extracellular vesicles from human and mouse brain tissues and human cerebrospinal fluids. Methods. 2020;177:35-49. [23] STREET JM, BARRAN PE, MACKAY CL, et al. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Transl Med. 2012;10:5. [24] BAIETTI MF, ZHANG Z, MORTIER E, et al. Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(7):677-685. [25] THÉRY C, OSTROWSKI M, SEGURA E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9(8):581-593. [26] FILIPE V, HAWE A, JISKOOT W. Critical evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the measurement of nanoparticles and protein aggregates. Pharm Res. 2010;27(5):796-810. [27] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [28] SURKAR SM, HOFFMAN RM, WILLETT S, et al. Hand-Arm Bimanual Intensive Therapy Improves Prefrontal Cortex Activation in Children With Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2018;30(2):93-100. [29] SURKAR SM, HOFFMAN RM, HARBOURNE R, et al. Cognitive-Motor Interference Heightens the Prefrontal Cortical Activation and Deteriorates the Task Performance in Children With Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(2):225-232. [30] AMUNTS K, SCHLEICHER A, ZILLES K. Persistence of layer IV in the primary motor cortex (area 4) of children with cerebral palsy. J Hirnforsch. 1997; 38(2):247-260. [31] PARK HJ, KIM CH, PARK ES, et al. Increased GABA-A receptor binding and reduced connectivity at the motor cortex in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy: a multimodal investigation using 18F-fluoroflumazenil PET, immunohistochemistry, and MR imaging. J Nucl Med. 2013;54(8):1263-1269. [32] KHAN B, TIAN F, BEHBEHANI K, et al. Identification of abnormal motor cortex activation patterns in children with cerebral palsy by functional near-infrared spectroscopy. J Biomed Opt. 2010;15(3):036008. [33] MUKHOPADHYAY R, MAHADEVAPPA M, LENKA PK, et al. Therapeutic effects of functional electrical stimulation on motor cortex in children with spastic Cerebral Palsy. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015;2015:3432-3435. [34] GÜMÜŞ E, ARAS BD, ÇILINGIR O, et al. Apolipoprotein E allelic variants and cerebral palsy. Turk J Pediatr. 2018;60(4):361-371. [35] LIEN E, ANDERSEN GL, BAO Y, et al. Gene sequences regulating the production of apoE and cerebral palsy of variable severity. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2014;18(5):591-596. [36] SAVARD A, BROCHU ME, CHEVIN M, et al. Neuronal self-injury mediated by IL-1β and MMP-9 in a cerebral palsy model of severe neonatal encephalopathy induced by immune activation plus hypoxia-ischemia. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:111. [37] LI H, WANG XL, WU YQ, et al. Correlation of the predisposition of Chinese children to cerebral palsy with nucleotide variation in pri-miR-124 that alters the non-canonical apoptosis pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(9): 1453-1462. |
| [1] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [2] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [3] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [4] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [5] | Gao Ting, Ma Xiaohong, Li Xiaorong. Extraction and identification of exosomes from three different sources of ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| [6] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [7] | Xu Qijing, Yang Yichun, Lei Wei, Yang Ying, Yu Jiang, Xia Tingting, Zhang Meng, Zhang Tao, Zhang Qian. Advances and problems in cell-free treatment of diabetic skin chronic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [8] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| [9] | Zhang Weiye, Zhan Jiawen, Zhu Liguo, Wang Shangquan, Chen Ming, Wei Xu, Feng Minshan, Yu Jie, Han Tao, Cai Chuhao, Zhou Shuaiqi, Shao Chenchen. Effect of nucleus pulposus cells-derived exosomes under cyclic mechanical tension on endplate chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(2): 223-229. |
| [10] | Ling Huajun, Cui Ruiwen, Wang Qiyou. 3D extracellular matrix hydrogel loaded with exosomes promotes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1900-1905. |
| [11] | Lan Qian, Gu Yangcong, Xiao Xin, Bi Xueting, Li Na. Human periodontal ligament stem cells-derived exosomes interfere with the proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 54-58. |
| [12] | Liu Runyuan, Dong Ming, Han Wenqing, Dong Juhong, Niu Weidong. Application and progress of small extracellular vesicles in periodontal and pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 83-90. |
| [13] | Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Extracellular vesicles in chronic periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 99-104. |
| [14] | Guo Yujun, Lu Wenjun, Yang Shulong, Li Zhaozhu. Effect of urine-derived stem cells and their exosomes on kidney diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 138-144. |
| [15] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||