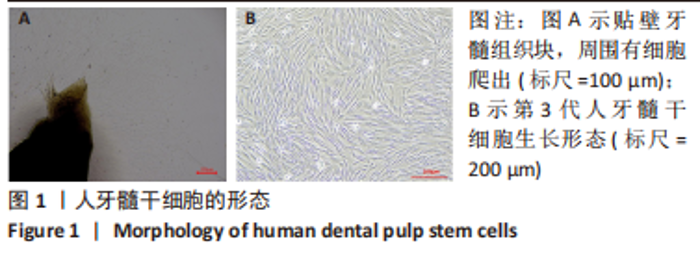
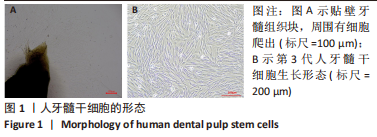
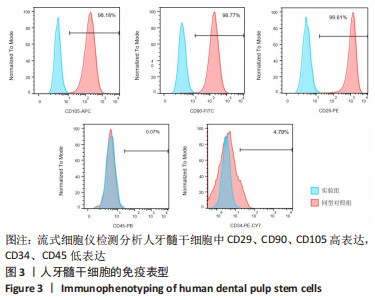
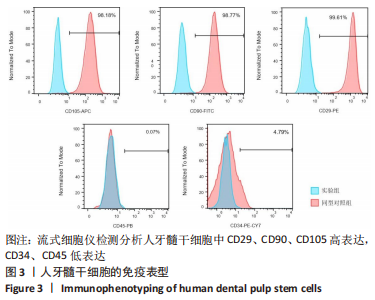
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 56-61.doi: 10.12307/2024.103
Previous Articles Next Articles
Recombinant human growth hormone promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells
Sun Jing1, Liao Jian1, Sun Jiangling2, Cheng Ping2, Feng Hongchao1, 2
- 1School of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Guiyang Stomatology Hospital, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-01-30Accepted:2023-03-04Online:2024-01-08Published:2023-06-28 -
Contact:Feng Hongchao, MD, Professor, Chief physician, School of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; Guiyang Stomatology Hospital, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Sun Jing, Master candidate, School of Stomatology of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission, No. gzwkj2022-431 (to FHC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Jing, Liao Jian, Sun Jiangling, Cheng Ping, Feng Hongchao. Recombinant human growth hormone promotes osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 56-61.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
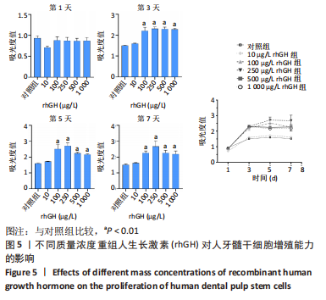
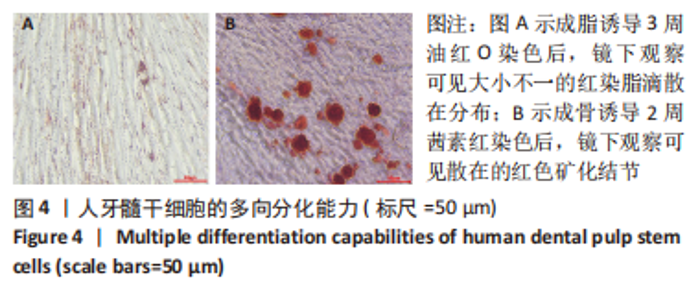
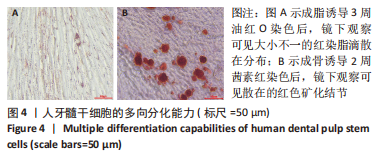
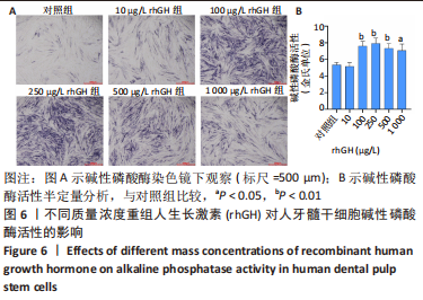
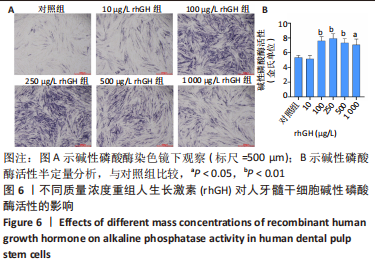
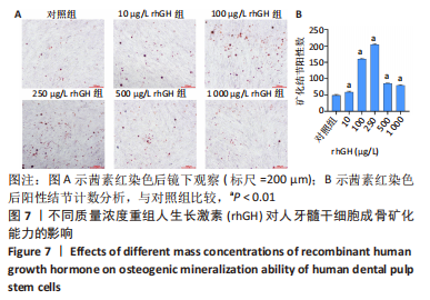
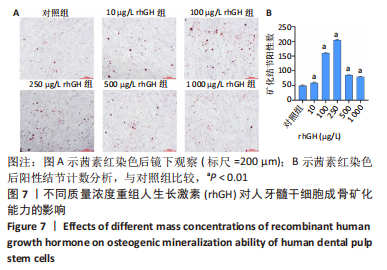
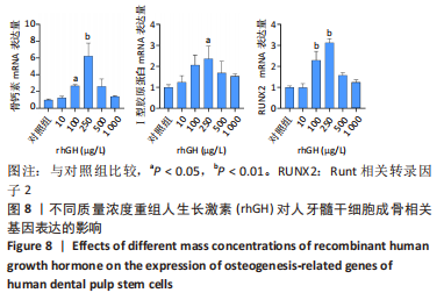
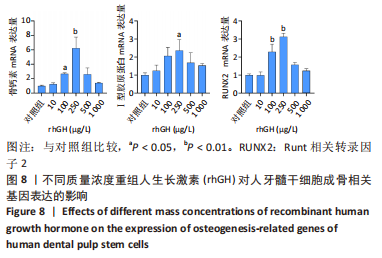
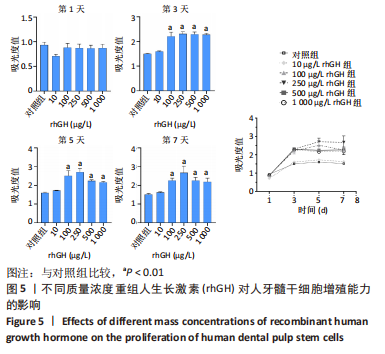
2.2 rhGH对人牙髓干细胞增殖的影响 为了确定人牙髓干细胞的增殖效率,使用CCK-8试剂盒检测rhGH对人牙髓干细胞增殖水平的影响,见图5。第1天,rhGH各组与对照组细胞增殖无明显差异。第3,5,7天,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH组细胞增殖水平明显优于对照组(P < 0.01)。通过细胞增殖曲线可见,在药物干预后的第3天,rhGH各组细胞增殖曲线呈对数型,细胞增殖明显;在药物干预后的第5天, 10,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH组以及对照组的增殖曲线曲度降低,趋于平缓,100,250 μg/L rhGH组细胞增殖曲线曲度稍降低,但仍呈上升趋势;在药物干预后的第7天,各组细胞增殖曲线的曲度均趋于稳定。"
| [1] AL MARUF DSA, GHOSH YA, XIN H, et al. Hydrogel: A Potential Material for Bone Tissue Engineering Repairing the Segmental Mandibular Defect. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(19):4186. [2] DEC P, MODRZEJEWSKI A, PAWLIK A. Existing and Novel Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):529. [3] GRABER E, REITER EO, ROGOL AD. Human Growth and Growth Hormone: From Antiquity to the Recominant Age to the Future. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:709936. [4] BAMBA V, KANAKATTI SHANKAR R. Approach to the Patient: Safety of Growth Hormone Replacement in Children and Adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(3):847-861. [5] 朱怀安,尹苗,陈婉丽,等.基因重组人生长激素对骨髓基质细胞增殖与成骨性分化的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2018,34(3):131-134. [6] WANG JR, AHMED SF, GADEGAARD N, et al. Nanotopology potentiates growth hormone signalling and osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2014;24(6):245-250. [7] TAIHI I, PILON C, COHEN J, et al. Efficient isolation of human gingival stem cells in a new serum-free medium supplemented with platelet lysate and growth hormone for osteogenic differentiation enhancement. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):125. [8] MOHANRAM Y, ZHANG J, TSIRIDIS E, et al. Comparing bone tissue engineering efficacy of HDPSCs, HBMSCs on 3D biomimetic ABM-P-15 scaffolds in vitro and in vivo. Cytotechnology. 2020;72(5):715-730. [9] ZHANG S, ZHANG X, LI Y, et al. Clinical Reference Strategy for the Selection of Treatment Materials for Maxillofacial Bone Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(3): 437-450. [10] JANEBODIN K, HORST OV, IERONIMAKIS N, et al. Isolation and characterization of neural crest-derived stem cells from dental pulp of neonatal mice. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27526. [11] AL-MASWARY AA, O’REILLY M, HOLMES AP, et al. Exploring the neurogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. PLoS One. 2022;17(11): e0277134. [12] HATORI A, FUJII Y, KAWASE-KOGA Y, et al. VCAM-1 and GFPT-2: Predictive markers of osteoblast differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells. Bone. 2023;166:116575. [13] ZHANG Z, OH M, SASAKI JI, et al. Inverse and reciprocal regulation of p53/p21 and Bmi-1 modulates vasculogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(7):644. [14] PERIĆ KAČAREVIĆ Ž, RIDER P, ALKILDANI S, et al. An introduction to bone tissue engineering. Int J Artif Organs. 2020;43(2):69-86. [15] CAO S, HAN J, SHARMA N, et al. In Vitro Mechanical and Biological Properties of 3D Printed Polymer Composite and β-Tricalcium Phosphate Scaffold on Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(14):3057. [16] DI TINCO R, SERGI R, BERTANI G, et al. Effects of a Novel Bioactive Glass Composition on Biological Properties of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(18):4049. [17] GU Y, ZHUANG R, XIE X, et al. Osteogenic stimulation of human dental pulp stem cells with self-setting biphasic calcium phosphate cement. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(4):1669-1678. [18] YAMADA Y, NAKAMURA-YAMADA S, KUSANO K, et al. Clinical Potential and Current Progress of Dental Pulp Stem Cells for Various Systemic Diseases in Regenerative Medicine: A Concise Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1132. [19] FAGEEH HN. Preliminary Evaluation of Proliferation, Wound Healing Properties, Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Potential of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Obtained from Healthy and Periodontitis Affected Teeth. Cells. 2021; 10(8):2118. [20] KARAMZADEH R, ESLAMINEJAD MB, AFLATOONIAN R. Isolation, characterization and comparative differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells derived from permanent teeth by using two different methods. J Vis Exp. 2012;(69):4372. [21] YU Z, GAUTHIER P, TRAN QT, et al. Differential Properties of Human ALP+ Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells vs Their ALP- Counterparts. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;5(7):292. [22] 杨俊辉,罗金莉,袁小平.人生长激素对人牙周膜干细胞增殖及成骨分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25):3956-3961. [23] KOFFI KA, DOUBLIER S, RICORT JM, et al. The Role of GH/IGF Axis in Dento-Alveolar Complex from Development to Aging and Therapeutics: A Narrative Review. Cells. 2021;10(5):1181. [24] LINDSEY RC, MOHAN S. Skeletal effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I therapy. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;432:44-55. [25] CRIPPA GE, BELOTI MM, CARDOSO CR, et al. Effect of growth hormone on in vitro osteogenesis and gene expression of human osteoblastic cells is donor-age-dependent. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104(2):369-376. [26] FENG J, MENG Z. Insulin growth factor-1 promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(2):891. [27] YUAN Y, DUAN R, WU B, et al. Gene expression profiles and bioinformatics analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 promotion of osteogenic differentiation. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019;7(10):e00921. [28] BIAN M, YU Y, LI Y, et al. Upregulating the Expression of LncRNA ANRIL Promotes Osteogenesis via the miR-7-5p/IGF-1R Axis in the Inflamed Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:604400. [29] 周思佳,姜文学,尤佳.骨缺损修复材料:现状与需求和未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(14):2251-2258. [30] TONIETTO L, VASQUEZ AF, DOS SANTOS LA, et al. Histological and structural evaluation of growth hormone and PLGA incorporation in macroporous scaffold of α-tricalcium phosphate cement. J Biomater Appl. 2019;33(6): 866-875. |
| [1] | Wei Yurou, Tian Jiaqing, He Xianshun, Zhan Zhiwei, Wei Tengfei, Lin Tianye, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Effect of lentiviral silencing of Piezo1 on osteogenic differentiation and TAZ expression in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 12-19. |
| [2] | Wang Xianfeng, Wang Kun, Sun Han, Sun Xiaoliang, Yan Litao. Mechanism underlying exosomal lncRNA H19 derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promotes cartilage injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 20-25. |
| [3] | Zhang Yuanshu, He Xu, Xue Yuan, Jin Yesheng, Wang Kai, Shi Qin, Rui Yongjun. Irisin alleviates palmitic acid-induced osteogenic inhibition in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 26-31. |
| [4] | He Lijun, Qi Xiaojuan. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing bone morphogenetic protein 2 promote alveolar bone defect repair in osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 32-37. |
| [5] | Zhou Minghua, Hu Xiaoyu. LncRNA SNHG4 regulates miR-152-3p during osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 38-43. |
| [6] | Zheng Rongjiong, Deng Zerun, Han Dan, Sun Lihua. Mechanism underlying rat hepatocyte apoptosis regulated by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 44-49. |
| [7] | Zheng Mingkui, Xue Chenhui, Guan Xiaoming, Ma Xun. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce the permeability of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [8] | Fan Yongjing, Wang Shu, Jin Wulong. Characteristics, advantages and application of osteogenic differentiation of jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [9] | Huang Yongbin, Wang Tao, Lou Yuanyi, Pang Jingqun, Chen Guanghua. Application prospect of mesenchymal stem cells in promoting muscle tissue repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 107-112. |
| [10] | He Wanyu, Cheng Leping. Strategies and advance on stem cell transplantation for repair of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [11] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [12] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [13] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [14] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [15] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||