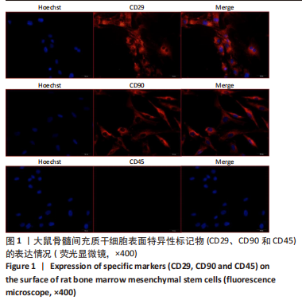
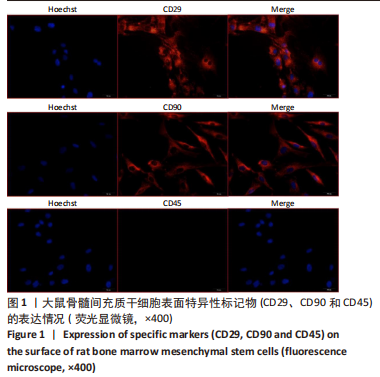
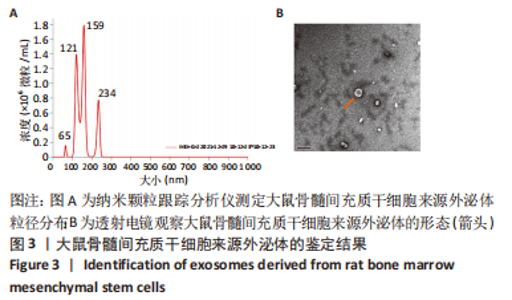
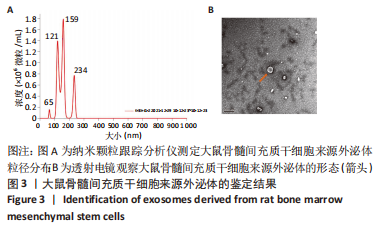
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 44-49.doi: 10.12307/2023.916
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism underlying rat hepatocyte apoptosis regulated by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Zheng Rongjiong, Deng Zerun, Han Dan, Sun Lihua
- Infection and Liver Disease Center of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-10-31Accepted:2023-01-29Online:2024-01-08Published:2023-06-28 -
Contact:Sun Lihua, Chief physician, Infection and Liver Disease Center of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zheng Rongjiong, MD, Associate chief physician, Infection and Liver Disease Center of First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2020D01C243 (to ZRJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Rongjiong, Deng Zerun, Han Dan, Sun Lihua. Mechanism underlying rat hepatocyte apoptosis regulated by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 44-49.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
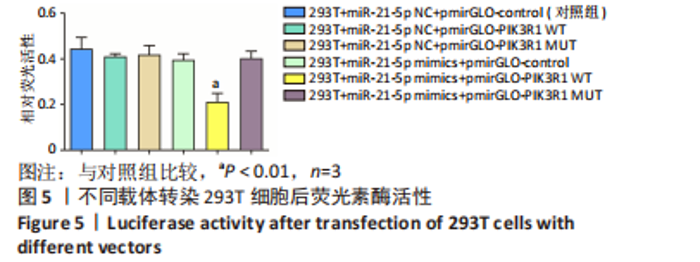
2.5 外泌体中的 miR-21-5p可靶向结合PIK3R1 双荧光素酶报告基因检测结果显示各组荧光素酶活性分别为:对照组为0.45±0.05,PI3KR1野生型载体组为0.41±0.01,PIK3R1突变型载体组为0.42±0.04,miR-21-5p mimics组为0.40±0.03,miR-21-5p mimics联合PI3KR1野生型载体组为0.21±0.04,miR-21-5p mimics联合PI3KR1突变型载体组为0.40±0.03。与对照组相比,PI3KR1野生型载体与miR-21-5p mimics共转染293T细胞时,荧光素酶活性显著下降(P < 0.01),而转染PIK3R1突变型载体后荧光素酶活性无显著变化,表明miR-21-5p靶向结合PIK3R1,见图5。"

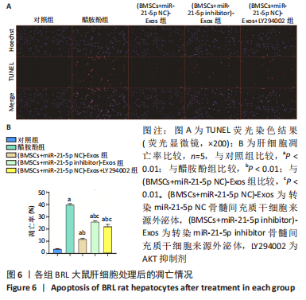
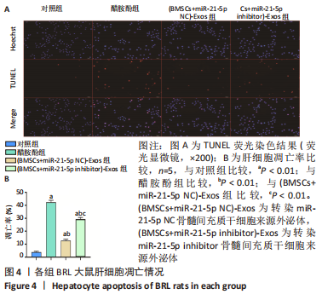
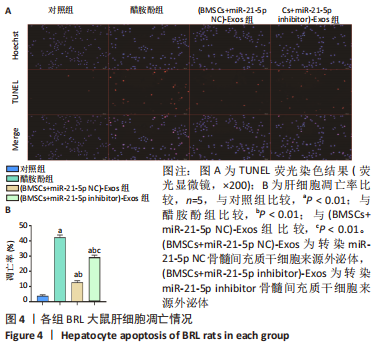
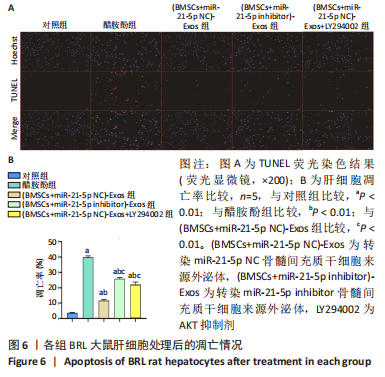
2.6 外泌体中miR-21-5p直接靶向PIK3R1激活PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制BRL大鼠肝细胞凋亡 TUNEL检测结果显示:醋胺酚处理后细胞凋亡率(39.81±0.94)%显著高于对照组(3.67±0.34)%(P < 0.01);与醋胺酚组相比,(BMSCs+miR-21-5p NC)-Exos组细胞凋亡率(11.68±0.81)%显著下降(P < 0.01);与(BMSCs+miR-21-5p NC)-Exos组相比,(BMSCs+miR-21-5p inhibitor)-Exos组细胞凋亡率(25.91±0.84)%显著增加(P < 0.01);与(BMSCs+miR-21-5p NC)-Exos组相比,加入AKT抑制剂LY294002之后,细胞凋亡率(22.14±1.57)%显著增加(P < 0.01),见图6。"
| [1] PEREZ RUIZ DE GARIBAY A, KORTGEN A, LEONHARDT J, et al. Critical care hepatology: definitions, incidence, prognosis and role of liver failure in critically ill patients. Crit Care. 2022;26(1):289. [2] STRAVITZ RT, LEE WM. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2019;394(10201):869-881. [3] TAVABIE OD, BERNAL W. How to manage: acute liver failure. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020;11(1):70-74. [4] LEMMER P, POSPIECH JC, CANBAY A. Liver failure-future challenges and remaining questions. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(8):734. [5] WANG J, LIU Y, DING H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-secreted prostaglandin E2 ameliorates acute liver failure via attenuation of cell death and regulation of macrophage polarization. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):15. [6] DONG V, NANCHAL R, KARVELLAS CJ. Pathophysiology of Acute Liver Failure. Nutr Clin Pract. 2020;35(1):24-29. [7] HARRELL CR, PAVLOVIC D, DJONOV V, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol. 2022; 28(28):3627-3636. [8] HU C, LI L. Improvement of mesenchymal stromal cells and their derivatives for treating acute liver failure. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019;97(8):1065-1084. [9] HU C, WU Z, LI L. Mesenchymal stromal cells promote liver regeneration through regulation of immune cells. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(5):893-903. [10] HARRELL CR, DJONOV V, VOLAREVIC V. The Cross-Talk between Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Immune Cells in Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2472. [11] HUA D, JU Z, GAN X, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate acute liver injury by inhibiting the pro-inflammatory response of liver resident macrophage through autophagy. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(16):392. [12] LIU J, FENG B, XU Y, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of mesenchymal stem cells in chemical-induced liver injury: a high-dimensional analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):262. [13] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [14] MATHIEU M, MARTIN-JAULAR L, LAVIEU G, et al. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):9-17. [15] JEPPESEN DK, FENIX AM, FRANKLIN JL, et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell. 2019;177(2):428-445.e18. [16] DALMIZRAK A, DALMIZRAK O. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as new tools for delivery of miRNAs in the treatment of cancer. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:956563. [17] DING Y, LUO Q, QUE H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10972. [18] TIAN S, ZHOU X, ZHANG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect against liver fibrosis via delivering miR-148a to target KLF6/STAT3 pathway in macrophages. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):330. [19] WU L, TIAN X, ZUO H, et al. miR-124-3p delivered by exosomes from heme oxygenase-1 modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits ferroptosis to attenuate ischemia-reperfusion injury in steatotic grafts. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):196. [20] RAHIMIAN N, NAHAND JS, HAMBLIN MR, et al. Exosomal MicroRNA Profiling. Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2595:13-47. [21] HEO JS. Selenium-Stimulated Exosomes Enhance Wound Healing by Modulating Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11543. [22] PRZYBYL H, GRINDLER J, LAUER D. Unfreezing What’s Hot in Liver Transplantation: A Review of Current Trends. AACN Adv Crit Care. 2022;33(1):56-67. [23] ARROYO V, MOREAU R, JALAN R. Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(22):2137-2145. [24] SHAO M, XU Q, WU Z, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate IL-6-induced acute liver injury through miR-455-3p. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):37. [25] CHIABOTTO G, CECCOTTI E, TAPPARO M, et al. Human Liver Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Target Hepatic Stellate Cells and Attenuate Their Pro-fibrotic Phenotype. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:777462. [26] YAQUB F, LATIEF N, BUTT H, et al. Alpha lipoic acid priming enhances the hepatoprotective effect of adipose derived stem cells in CCl4 induced hepatic injury in-vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;906:174201. [27] JIN Y, WANG J, LI H, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Human Adipose-derived Stem Cells (hASCs) Improve Survival Rate of Rats with Acute Liver Failure by Releasing lncRNA H19. EBioMedicine. 2018;34:231-242. [28] HE Y, GUO X, LAN T, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve the function of liver in rats with acute-on-chronic liver failure via downregulating Notch and Stat1/Stat3 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021; 12(1):396. [29] PENG T, GUO Y, GAN Z, et al. Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) Encourages the Neuroinvasive Potential of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Activating the Warburg Effect and Promoting Tumor Derived Exosomal miRNA-21 Expression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:8445093. [30] MASOUMI-ARDAKANI Y, NAJAFIPOUR H, NASRI HR, et al. Moderate Endurance Training and MitoQ Improve Cardiovascular Function, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in Hypertensive Individuals: The Role of miR-21 and miR-222: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Clinical Trial. Cell J. 2022;24(10):577-585. [31] SAQUEL C, CATALAN RJ, LOPEZ-LEAL R, et al. Neuronal activity-dependent ATP enhances the pro-growth effect of repair Schwann cell extracellular vesicles by increasing their miRNA-21 loading. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:943506. [32] JUNG BK, SONG H, SHIN H, et al. Exosomal miRNA-21 from Toxoplasma gondii-infected microglial cells induces the growth of U87 glioma cells by inhibiting tumor suppressor genes. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):16450. [33] XU L, TIAN L, YAN Z, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-486-5p, miR-451a, miR-21-5p and monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Heart Vessels. 2022. doi: 10.1007/s00380-022-02172-2. [34] LI W, LI Y, JIANG F, et al. Correlation between serum levels of microRNA-21 and inflammatory factors in patients with chronic heart failure. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(38):e30596. [35] LIU L, SUN B, ZHANG F, et al. lncRNA MPFAST Promotes Proliferation and Fatty Acid Synthesis of Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cell by Sponging miR-103 Regulating PI3K-AKT Pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70(38):12004-12013. |
| [1] | Wei Yurou, Tian Jiaqing, He Xianshun, Zhan Zhiwei, Wei Tengfei, Lin Tianye, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Effect of lentiviral silencing of Piezo1 on osteogenic differentiation and TAZ expression in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 12-19. |
| [2] | Wang Xianfeng, Wang Kun, Sun Han, Sun Xiaoliang, Yan Litao. Mechanism underlying exosomal lncRNA H19 derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promotes cartilage injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 20-25. |
| [3] | Zhang Yuanshu, He Xu, Xue Yuan, Jin Yesheng, Wang Kai, Shi Qin, Rui Yongjun. Irisin alleviates palmitic acid-induced osteogenic inhibition in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 26-31. |
| [4] | Zheng Mingkui, Xue Chenhui, Guan Xiaoming, Ma Xun. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce the permeability of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [5] | Ai Fangfang, Xiao Hongyan, Wang Fang, Zhu Yongzhao, Ma Lijun. Reversal effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide in combination with oxaliplatin on drug resistance of colon cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 74-79. |
| [6] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Research hot spots and trends of exosomes in theranostic application for chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 86-92. |
| [7] | Fan Yongjing, Wang Shu, Jin Wulong. Characteristics, advantages and application of osteogenic differentiation of jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [8] | Huang Yongbin, Wang Tao, Lou Yuanyi, Pang Jingqun, Chen Guanghua. Application prospect of mesenchymal stem cells in promoting muscle tissue repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 107-112. |
| [9] | Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Liu Tao, Li Yan, He Yuanxu, He Bo, Wang Weiwei, Wei Xiaotao. Traditional Chinese medicine monomer in the prevention and treatment of flap necrosis by regulating “autophagy” [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| [10] | Shen Feiyan, Yao Jixiang, Su Shanshan, Zhao Zhongmin, Tang Weidong. Knockdown of circRNA WD repeat containing protein 1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chondrocytes in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-6. |
| [11] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [12] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [13] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [14] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [15] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||