Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (在线): 1-10.doi: 10.12307/2023.608
Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis
Nong Fuxiang1 , Jiang Zhixiong3 , Li Yinghao1 , Xu Wencong1 , Shi Zhilan1 , Luo Hui1 , Zhang Qinglang1 , Zhong Shuang1 , Tang Meiwen2
- 1Department of Spleen and Stomach, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-05-18Online:2023-01-08Published:2022-08-18 -
Contact:Tang Meiwen, Professor, MD, Master’s supervisor, Doctoral supervisor, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Nong Fuxiang, Master candidate, Department of Spleen and Stomach, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 8176150376 (to TMW); University Level Key Postgraduate Research and Innovation Project, No. YCSZ2022014 (to LYH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10.
share this article
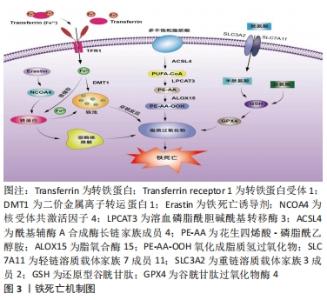
2.1 外泌体的生物特性 外泌体是一种由多种细胞分泌的直径约40-160 nm的细胞外囊泡,通过胞内的多泡体与细胞膜融合释放到细胞外而产生[7]。外泌体可以被巨噬细胞、肿瘤细胞、间充质干细胞、上皮细胞、肥大细胞、内皮祖细胞和成纤维细胞等不同类型的细胞释放出来[8],并普遍分布在人体尿液、唾液、血液、脑脊液及胆汁等各种体液中[9]。外泌体主要由脂质、蛋白质以及RNA等生物分子组成。外泌体的脂双层富含胆固醇、鞘磷脂和神经酰胺,具有保护生物活性成分免受细胞溶质酶降解的能力[10]。蛋白质组成有参与膜转运或融合的蛋白质(Rab-GTPa ses, annexins)和胞外体生物发生相关的蛋白质(ESCRT复合物,Alix,TSG101),热休克蛋白(HSP70,HSP90),肌球蛋白重链(Myosin heavy chain,MHC)Ⅱ类蛋白,整合素,跨膜蛋白(CD63,CD81,CD82)等[11];参与膜转运和融合蛋白在外泌体生物发生、分泌和下游细胞融合中发挥作用。外泌体RNA主要包括miRNA和 rRNA,lncRNA,tRNA,mRNA以及小的非编码 RNA,在和靶细胞的沟通中发挥重要的信息输送作用[12]。 外泌体蛋白质、RNA和代谢物分子在细胞间的信息沟通方式主要是通过吞噬作用、微胞饮作用、由网格蛋白介导和小窝蛋白依赖性内吞作用或直接与质膜融合被受体细胞吸收,参与细胞内信号传导,将细胞质生物活性成分递送到靶细胞中[13-14]。同时,外泌体是一种重要的疾病诊断的生物标志物,在癌症早期诊断中发挥着重要的作用,如乳腺癌和卵巢癌等[15]。目前研究认为,外泌体是调节人体生理功能的重要效应分子和细胞间物质交换、信息传导的载体,具有调节细胞微环境,参与靶细胞多种生物学的过程的功能,如促进血管生成、抗免疫原性、抑制细胞凋亡、影响肿瘤细胞增殖、抗纤维化以及各种抗炎过程[16-18]。 2.2 铁死亡机制 铁死亡是一种铁依赖性和脂质大量累积导致的细胞死亡方式,当细胞内铁稳态失衡、脂质过氧化物大量累积、氨基酸抗氧化失衡时,细胞发生铁死亡。文章阐述了铁死亡发生的主要代谢途径,以更清晰地了解铁死亡的作用机制,见图3。 "
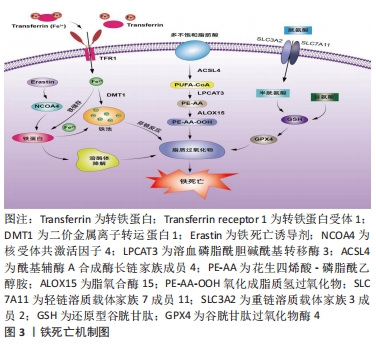
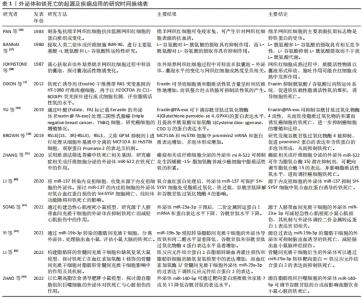
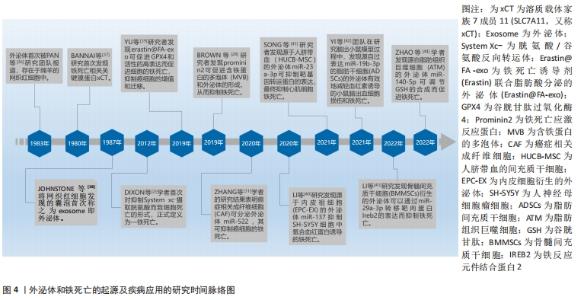
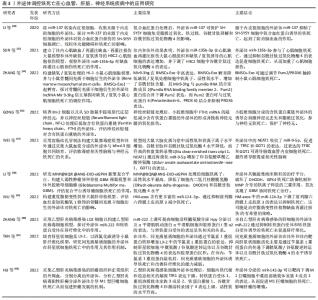
2.2.1 铁代谢紊乱 细胞铁死亡的敏感性由铁离子水平决定,不稳定的铁产生自由基通过芬顿反应(Fenton)介导脂质过氧化导致铁死亡。在正常情况下,血液循环中的三价铁离子与细胞膜上转铁蛋白(Transferrin,TF)结合后,被转铁蛋白和转铁蛋白受体1(Transferrin receptor 1,TFR1)运输到细胞内。细胞内的二价铁离子则由三价铁离子氧化还原而来,最终Fe2+被二价金属离子转运蛋白1(Divalentmetal-iontransporter-1,DMT1))释放到细胞质铁池中,多余的铁离子则被运输到铁蛋白中[4]。铁蛋白包括铁蛋白轻链 (Ferritin light chain,FTL) 和铁蛋白重链1(Ferritin heavy chain 1,FTH1),用来存储多余的铁离子。当不稳定的铁池中存在过量的Fe2+时,通过铁离子催化的芬顿反应,脂质过氧化会诱导氧化应激,引发铁死亡[19]。研究表明,Erastin作为一种铁死亡诱导剂,通过促进核受体共激活因子4(Nuclear receptor coactivator 4,NCOA4)介导的细胞中的铁蛋白吞噬的表达,导致了铁蛋白的溶酶体降解和铁释放到不稳定铁池中,使得游离铁对铁死亡的敏感性增加[20]。综上所述,铁代谢过程中铁离子以及铁蛋白的失调可以影响细胞发生铁死亡。 2.2.2 脂质过氧化物累积 脂质代谢与细胞铁死亡的敏感性密切相关。游离的多不饱和脂肪酸(Polyunsaturated fatty acids,PUFA),如花生四烯酸(Arachidonic acid,AA)和肾上腺素(Adrenaline,AdA)磷脂可被细胞内活性氧氧化,并产生导致铁死亡的脂质过氧化物(Lipid peroxide,LPO)[21]。研究者们发现,溶血磷脂酰胆碱酰基转移酶3(Recombinant lysophosphatidylcholine cyltransfe rase 3,LPCAT3)和酰基辅酶A合成酶长链家族成员4(Acyl-Co A synthetase long- chain family member 4,ACSL4)是参与磷脂酰乙醇胺(Phosphatidyl ethanolamine,PE)生物合成和重构、激活多不饱和脂肪酸跨膜特性的两种酶,同时也是铁死亡的重要驱动因素[22]。脂质过氧化物积累过程主要是花生四烯酸和肾上腺素磷脂由酰基辅酶A合成酶长链家族成员4酯化为脂酰辅酶A衍生物,随后被溶血磷脂酰胆碱酰基转移酶3酯化形成花生四烯酸-磷脂酰乙醇胺(Arachidonic acid-phosphatidylethanolamine,PE-AA),最后被介导铁死亡过氧化的脂氧合酶 15(Lipoxygenases15,ALOX15)氧化成脂质氢过氧化物,最终导致铁死亡[23]。相反,溶血磷脂酰胆碱酰基转移酶3和酰基辅酶A合成酶长链家族成员4的缺失会激活多不饱和脂肪酸或将活化的多不饱和脂肪酸整合到磷脂(Phospholipids,PL)中,从而抑制铁死亡[24]。上述一系列参与调节多不饱和脂肪酸合成和分解的酶,如溶血磷脂酰胆碱酰基转移酶3、酰基辅酶A合成酶长链家族成员4及脂氧合酶15,对调节细胞对铁死亡的敏感性十分重要。因此,脂质代谢决定了细胞铁死亡的敏感性,是铁死亡发生的核心机制之一。 2.2.3 氨基酸抗氧化系统失衡 胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆转运体(System xc–)是一种位于细胞膜上的由轻链溶质载体家族7成员11(Light chain solute carrier family 7 member 11,SLC7A11)和重链溶质载体家族3成员2 (Heavy chain solute carrier family 3 member 2,SLC3A2)组成的异二聚体跨膜复合物,具有介导谷氨酸(Glutamate)的三磷酸腺苷(Adenosine triphosphate,ATP)和胱氨酸(Cystine)依赖性交换的功能[25]。谷胱甘肽以还原型谷胱甘肽(Glutathione,GSH)形式和氧化型谷胱甘肽(Glut- athione disulfide,GSSG) 形式存在,还原型谷胱甘肽是谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4(Glutathione pe- roxidase,GPX4)的主要辅助因子,谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4是铁死亡的关键因子,二者对细胞铁死亡起着至关重要的作用[26]。抗氧化系统失衡的核心机制是由胱氨酸经过轻链溶质载体家族7成员11、重链溶质载体家族3成员2进入细胞后迅速被还原成半胱氨酸和谷氨酸共同合成谷胱甘肽,被谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4利用后可以阻断轻链溶质载体家族7成员11转运蛋白的活性,催化脂质过氧化物的还原反应使得谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶失活,导致活性氧的积累,最终诱导铁死亡[27]。由此可见,胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆转运体主要通过维持细胞内外胱氨酸与谷氨酸的平衡,调节还原型谷胱甘肽的水平来诱导铁死亡。 2.3 外泌体调控铁死亡的主要途径 近年来的研究提示,外泌体不仅在靶细胞沟通方面显示出巨大的潜力,还参与了细胞铁死亡的过程,有可能成为疾病治疗的新的方向[6]。文章总结了外泌体调节铁死亡的主要途径,在作用机制上揭示了二者的联系。 2.3.1 铁蛋白代谢 铁蛋白的水平影响了铁死亡的敏感性,外泌体参与了铁蛋白代谢的过程,调节细胞铁死亡。一项研究发现,Prominin2是一种铁死亡应激反应蛋白,可促进含铁蛋白的多泡体和将铁转运出细胞的外泌体的形成,而Prominin2介导的铁蛋白输出抑制了铁死亡,阻断多泡体/外泌体介导的铁蛋白输出抑制了谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4,使得细胞内铁积累[28]。该研究首次提出外泌体清除细胞内铁离子是驱动铁死亡抵抗的重要机制,对于进一步揭示外泌体和铁死亡的关系具有深远意义。随后一项研究显示,内皮细胞分泌的外泌体通过抑制铁蛋白吞噬依赖性铁死亡,对逆转糖皮质激素诱导的成骨细胞成骨抑制起到重要的调节作用[29]。此外还发现,间皮细胞质中富含大量铁蛋白,铁蛋白是铁死亡依赖性细胞外泌体转运的主要蛋白,外泌体通过受体细胞的内吞作用将铁从巨噬细胞转运到间皮细胞的细胞质中,抑制了细胞铁死亡[30]。因此,载有铁蛋白的外泌体对调控机体的铁代谢、影响铁死亡的敏感性起到了重要的作用。 2.3.2 脂质代谢 脂质过氧化物累积是驱动铁死亡的关键因素,外泌体中的脂质、核酸参与了脂质过氧化的调控,对细胞发生铁死亡至关重要。关于外泌体参与铁死亡脂质代谢的探索始于ZHANG等[31]团队研究发现,癌症相关成纤维细胞分泌的外泌体miR-522可抑制花生四烯酸脂氧合酶15表达水平,并减少脂质活性氧积累;而阻断成纤维细胞分泌的外泌体介导的脂质活性氧抑制可导致癌细胞中铁死亡水平升高。该研究首次证明了外泌体与铁死亡脂质过氧化反应有关。另有一项研究证明,肿瘤细胞释放的外泌体通过增加细胞cir93的表达,上调了脂肪酸结合蛋白3的水平,当脂肪酸结合蛋白3转运花生四烯酸、与牛磺酸发生反应后,产生了N-花生四烯酰牛磺酸;当N-花生四烯酰牛磺酸阻止花生四烯酸掺入质膜时,外泌体就会特异性地降低多不饱和脂肪酸脂质过氧化的水平,减少活性氧的形成,抑制铁死亡,阻断外泌体生物合成有助于提高癌细胞对铁死亡的敏感性[32]。由此可知,外泌体通过影响脂质过氧化水平调控细胞铁死亡的发生。 2.3.3 氨基酸代谢 外泌体还通过改变氨基酸代谢的标志物水平,调控了铁死亡的发生,从而在疾病中发挥了作用。体内和体外实验表明,铁死亡是四氯化碳诱导的小鼠肝损伤的关键驱动因素,来自间充质干细胞外泌体显着减弱了四氯化碳泛素化引发的脂质过氧化,还可以通过维持轻链溶质载体家族7成员11水平来抑制细胞的铁死亡,介导了急性肝损伤小鼠的肝脏修复[33]。这为外泌体参与铁死亡的抗氧化系统平衡途径起到治疗疾病的作用提供了新的研究证据。在另外一项关于地塞米松和内皮祖细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡治疗小鼠类固醇诱导的骨质疏松症的生物信息学研究中,通过对京都基因和基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Gnomes,KEGG)通路富集分析,一方面发现地塞米松的治疗诱导激活了铁死亡途径;另一方面,经地塞米松诱导后的内皮祖细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡的治疗逆转了地塞米松诱导的小鼠成骨细胞的铁死亡。此外,内皮祖细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡改变了重链溶质载体家族3成员2、轻链溶质载体家族7成员11和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4等铁死亡标记物的表达[34]。后有一项基于探讨M2巨噬细胞(M2 macrophages)来源的外泌体对喉癌铁死亡调控作用的研究表明,M2巨噬细胞源性外泌体能够诱导Erastin处理的TU212细胞中的谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和还原型谷胱甘肽的高表达,下调活性氧和丙二醛的表达,从而抑制癌细胞铁死亡的发生[35]。总之,这些研究证明了外泌体可以通过调节氨基酸代谢途径中的关键介质和代谢物来调控铁死亡过程。 上述结果进一步表明,外泌体除了参与细胞铁死亡中的铁蛋白代谢、脂质代谢途径,也参与了氨基酸代谢途径,起到了调节铁死亡的作用,但是外泌体RNA、蛋白质、脂质的共同作用对铁死亡的调控机制还需要未来的研究进一步探明。 2.4 外泌体调控铁死亡在疾病中的应用 外泌体作为细胞间通讯的重要介质,参与了铁死亡的过程,已有研究探索外泌体调控铁死亡在疾病中的应用,文章主要纵向阐述了外泌体调控铁死亡在肿瘤、心血管、神经系统、肝脏疾病等领域的研究进展,横向比较了外泌体调节铁死亡在疾病中的作用,以期为外泌体调控铁死亡成为一种新的干预因素提供思路借鉴[36-44],见表1,图4,表2和表3。"


2.4.1 外泌体调控铁死亡在肿瘤中的应用 癌症是死亡率最高的疾病之一[45]。目前手术、化疗、靶向药物、免疫治疗在癌症中的有效性是有限的。因此,探索其他诱导癌症特异性细胞死亡的策略尤为紧迫。越来越多的研究证明,外泌体通过诱导癌细胞铁死亡,抑制了肿瘤的增殖、转移,并且对寻求诱导铁死亡作为一种抗癌治疗途径具有广泛的意义[31,35]。文章将对外泌体调控细胞铁死亡在肿瘤中应用的最新研究进展进行总结,进一步了解肿瘤发生的病理机制,为恶性肿瘤的靶向治疗寻找新的方法和途径。 外泌体RNA参与了肿瘤细胞铁死亡的过程,抑制了肿瘤的发生,影响肿瘤细胞的增殖、转移,降低了肿瘤化疗的耐药性。已有研究证明,来自胃癌细胞的外泌体lnc-ENDOG-1:1(lncFERO)直接与硬脂酰辅酶A去饱和酶-1(Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1,SCD1)mRNA相互作用,通过聚集异质核核糖核蛋白 A1 (Heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein A1,hnRNPA1)来促进硬脂酰辅酶A去饱和酶-1的表达,导致多不饱和脂肪酸水平下调,抑制了胃癌干细胞铁死亡[46]。因此,靶向外泌体介导的胃癌干细胞铁死亡可能是预防化疗耐药和胃肿瘤复发的有效方法。 在一项研究对顺铂治疗反应性的非小细胞肺癌患者的组织样本中,结果表明与顺铂敏感的组织衍生外泌体相比,顺铂耐药的肿瘤组织衍生外泌体中miR-4443水平上调,并且过表达的外泌体miR-4443可负调控癌细胞A549-S中甲基转移酶样蛋白3诱导的人成纤维细胞特异蛋白1 m6A修饰,介导铁死亡,促进非小细胞肺癌的耐药性[47]。这表明以外泌体miR-4443作为重要的靶点调控基因,沉默该外泌体的表达而促进癌细胞铁死亡,可以更好的抑制癌细胞增殖、转移,降低化疗的耐药性。随后在一项肺腺癌小鼠模型和来自肺腺癌患者的血浆/组织标本实验中,研究者们证明了外泌体RNA-蛋白质相互作用可以调节癌细胞铁死亡,其机制可能是外泌体circRNA_101093(cir93)与脂肪酸结合蛋白3相互作用,后者转运花生四烯酸并促进其与牛磺酸的反应,导致整体花生四烯酸减少,降低了脂质过氧化,使肺腺癌细胞对铁死亡脱敏。因此,外泌体cir93对肺癌细胞铁死亡的脱敏至关重要,减少外泌体对细胞铁死亡的脱敏可能有助于未来的肺腺癌治疗[32]。该研究为外泌体的生物分子多途径调控癌细胞铁死亡提供了参考。此外,有研究表明,铁死亡诱导剂(Erastin)联合脂肪酸分泌的外泌体(Erastin@FA-exo)治疗抑制了细胞内谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶的表达,从而上调了半胱氨酸双加氧酶(Cysteine dioxyge nase,CDO1)的表达。此外,Erastin@FA-exo显著增加MDA-MB-231细胞的谷胱甘肽的消耗和的活性氧的过度生成,有效地诱导了三阴乳腺癌细胞的铁死亡[39]。因此,基于Erastin的外泌体靶向递药系统可能为靶向三阴乳腺癌细胞的化疗提供了一个具有创新性且强大的递送平台。以上这些研究结果都有助于证明外泌体RNA诱导肿瘤细胞铁死亡在阻止细胞增殖、转移以及逆转恶性肿瘤化疗的耐药性的靶向作用。 外泌体也通过诱导癌细胞铁死亡,介导细胞免疫反应、调节肿瘤微环境,发挥抗肿瘤的效果。研究证明,鼠类肉瘤病毒癌基因(Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene,KRAS)作为癌细胞-巨噬细胞通讯的关键介质,KRASG12D蛋白可通过氧化应激反应从死于自噬依赖性铁死亡的癌细胞中释放,而包装成外泌体的细胞外KRASG12D被巨噬细胞摄取后,导致巨噬细胞通过转录激活因子3(Signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT3)依赖脂肪酸氧化,转变为 M2 样促肿瘤表型,促进M2巨噬细胞极化,在体内刺激了巨噬细胞诱导的胰腺肿瘤生长[48]。这表明阻止致癌巨噬细胞摄取外泌体KRASG12D型蛋白质,对于诱导铁自噬的癌细胞,调节肿瘤微环境的免疫代谢起到重要作用。随后HU等[49]团队研发了成纤维细胞活化蛋白-α(Fibroblast activation protein-alpha,FAP)基因工程肿瘤细胞衍生的外泌体样囊泡疫苗(eNVs-FAP)。结果表明,成纤维细胞活化蛋白α基因工程肿瘤细胞衍生的外泌体样囊泡疫苗激活的细胞免疫反应可通过从细胞毒性T淋巴细胞释放干扰素-γ并消耗FAP+来促进肿瘤铁死亡,起到抗肿瘤免疫的作用。这首次证明通过研发有效的外泌体相关疫苗诱导细胞铁死亡在癌症治疗中具有抗肿瘤免疫的效果。另有研究发现,外泌体抑制剂(GW4869)和铁死亡诱导剂(Erastin)通过两亲性透明质酸构建的纳米单元中的两种活性成分之间的合作,与抗外泌体程序性细胞死亡蛋白1(Programmed death-1,PD-1)的新型协同作用诱导了铁死亡,增强了对黑色素瘤细胞的抗肿瘤免疫反应,并刺激了细胞毒性T淋巴细胞和免疫记忆,阻止了肿瘤细胞在全身的转移[50]。这些研究发现,加强外泌体对铁死亡的诱导作用可能更好发挥的抗肿瘤免疫作用,为肿瘤的免疫治疗提供了一种新的靶向抗癌策略。 多项研究证明,外泌体通过促进癌细胞铁死亡,起到了抑制细胞增殖、增强机体免疫反应、调节肿瘤微环境的作用,为肿瘤化疗的耐药性提供了更深入的见解和实验依据。但是目前外泌体携带的蛋白质、脂质的共同作用诱导肿瘤细胞铁死亡在抗血管生成,见表2。炎症反应等病理过程的研究尚未得到明确描述,因此外泌体调控铁死亡在肿瘤领域的应用仍不全面。 2.4.2 外泌体调控铁死亡在心血管疾病中的应用 外泌体调控铁死亡参与了心血管系统疾病的生理病理过程,起到了减轻心肌损伤的作用。研究表明,缺血再灌注损伤是组织、器官缺血后再灌注,组织、器官的功能和结构损伤会更加严重[51]。基于这一结果,SUN等[52]通过构建体内心肌缺血再灌注损伤大鼠模型和体外缺氧/复氧(H/R)诱导的H9C2心肌细胞损伤模型,发现外泌体miR-135b-3p在心肌缺血组织的表达增加,通过抑制谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4的表达,降低了脂质过氧化水平,促进细胞铁死亡,从而加重了心肌细胞损伤。这证明了靶向 miR-135b-3p调控铁死亡可能是治疗心肌缺血-再灌注损伤的潜在方法。在另一项急性心肌梗死的实验性研究中,研究发现,来源于人脐带血的间充质基质细胞外泌体倾向于通过miR-23a-3p显着抑制靶基因转运蛋白的表达,最终抑制心肌细胞铁死亡,改善了心功能和组织学损伤[41]。随后ZHANG等[53]在构建缺氧/复氧处理的HL-1小鼠心肌细胞模型中,发现骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体孵育显着促进了细胞增殖,增加了谷胱甘肽含量,并降低了缺氧/复氧处理细胞中的铁离子浓度、活性氧和铁死亡标记蛋白水平;骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体治疗还通过调节Pum2/PRDX6轴抑制心肌细胞铁死亡,从而减轻了心肌缺血再灌注损伤,改善了心肌组织的缺血缺氧状态。基于以上结果,心肌组织缺血再灌注损伤的改善作用可依赖于外泌体对铁死亡的抑制作用,可能成为修复心肌组织缺血再灌注损伤后的研究新方向。 一项关于长期高脂饮食诱导的肥胖导致的心肌细胞损伤的小鼠实验研究结果显示,肥胖的脂肪组织巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体治疗引起更高水平的列腺素内过氧化物合成酶2(Prostag landine-ndoperoxide synthase 2,PTGS2)、丙二醛、4羟基壬烯酸抗体、脂质活性氧和线粒体损伤。肥胖的脂肪组织巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体中的miR-140-5p可促进心肌细胞的铁死亡,进一步引发了心脏损伤;相反,当外泌体-miR-140-5p表达下调时,溶质载体家族7成员11的表达上调促进了谷胱甘肽水平的升高,抑制了铁死亡的发生,减轻了心脏损伤[44]。该研究为肥胖引起的心脏损伤中靶向肥胖脂肪组织巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体调节铁死亡改善心肌损伤提供了新的证据。此外,在关于药物化疗引起的心脏毒性的临床研究中,TIAN等[54]认为,长时间使用抗生素多柔比星化疗会导致心脏毒性,活性氧或氧化应激在心脏毒性中起着关键作用。作为多柔比星诱导的心脏毒性的生物标志物,外泌体可以通过某些蛋白质、遗传物质(miRNA和lncRNA)有效的发挥其药物输送载体作用,降低活性氧水平,抑制细胞铁死亡,减轻心脏毒性。这首次证明了基于外泌体的载体作用,抑制细胞铁死亡可以降低化疗引起的心脏毒性。 因此,外泌体通过抑制细胞铁死亡改善了不同原因引起的心肌细胞、组织损伤,降低心脏毒性,尤其是参与了心肌组织缺血再灌注损伤的病理恢复过程,有望成为一个新的干预因素,为心血管领域疾病的临床治疗提供潜在的新靶点。 2.4.3 外泌体调控铁死亡在神经系统疾病中的应用 外泌体通过调控铁死亡,参与了神经系统疾病的病理过程。一项研究表明,作为轴突细胞骨架蛋白复合物的一部分,神经丝轻链已被认为是各种神经系统疾病的病理标志,如脑出血、血管性脑痴呆、神经系统小血管疾病等。铁蛋白重链不仅反映了小胶质细胞的年龄相关状态,还可能分泌到细胞外空间。神经丝轻链作为轴突损伤本身的生物标志物,包含铁蛋白重链的外泌体把神经丝轻链从小胶质细胞分泌到细胞外基质中,参与神经元铁死亡,改善了神经元损伤[55]。这表明外泌体可通过将神经丝轻链分泌到细胞外而参与神经元铁死亡,起到保护神经元的作用。 脑出血被定义为自发性血液外渗到脑实质中的毁灭性中风[56],具有高致残率和死亡率,如何减少脑出血的发生是亟待解决的问题。YI等[42]通过构建胶原酶诱导的小鼠脑出血模型,用血红素诱导培养神经元铁死亡,证明源自过表达miR-19 b-3p的脂肪干细胞的外泌体有效地减轻了血红素诱导的小鼠脑出血细胞损伤和铁死亡;关于其潜在作用机制,可能与其靶向铁调节蛋白2(Iron regu- latory protein,IRP2)有关,在脑出血小鼠中观察到miR-19b-3p表达降低和铁调节蛋白表达增加。该研究首次表明来自miR-19b-3p修饰的脂肪干细胞的外泌体可减轻脑出血铁死亡和神经损伤。另有相似的研究发现,内皮祖细胞的外泌体miR-137过表达增强了对氧合血红蛋白(OxyHb)造成的线粒体功能障碍的神经保护作用,内皮祖细胞的外泌体miR-137还上调了氧合血红蛋白诱导的miR-137水平,抑制SH-SY5Y细胞中氧合血红蛋白诱导的铁死亡,从而减少脑出血的发生[40]。上述研究表明,外泌体可通过抑制铁死亡发挥防治脑出血的作用,有助于寻找出血性脑卒中的潜在新治疗靶点,这也启示了外泌体调控铁死亡是否可以作为指导缺血性脑卒中的有效治疗手段,需要更多的研究来证实。 外泌体通过调控铁死亡对减轻脓毒症引起的脓毒症相关性脑病同样至关重要。WEI等[57]在建立大鼠脓毒症模型时,发现脓毒症诱导了浆液性外泌体衍生的核富集转录物1的高表达,并且可能通过调节miR-9-5p和谷氨酸草酰乙酸转氨酶1轴和升高丙二醛的表达,使得谷胱甘肽和谷胱甘肽过氧化酶4水平降低,诱导细胞铁死亡,促进脓毒症的发生。而体内实验证明,被外泌体衍生的核富集转录物1吸收的 miR-9-5p通过抑制转铁蛋白受体和谷氨酸草酰乙酸转氨酶1的表达来减轻脓毒症诱导的铁死亡。该研究证明了外泌体调控铁死亡,可能成为防治脓毒性脑病新的干预方式。 胶质母细胞瘤目前在临床治疗上仍然缺乏治疗效果显著的手段,如何有效地穿透血脑屏障,为治疗胶质母细胞瘤提供药物或基因是困扰研究者的难题。LI等[58]首次提出了一种可以把将磁性纳米粒子的磁性靶向特征、药物递送特性与具有血脑屏障穿透能力的外泌体、siRNA封装特性相结合的新型复合治疗平台。动物实验结果显示,外泌体-共轭磁性纳米粒子可以被小鼠头颅核磁共振成像检测到,由颅内胶质母细胞瘤的活体核磁共振成像能确定肿瘤的位置。因此,基于工程化外泌体共轭磁性纳米颗粒的治疗平台,可以促进胶质母细胞瘤细胞的铁死亡,具有穿透血脑屏障、抑制胶质瘤生长的作用和促进磁共振成像的可能。 综上可知,外泌体通过调控细胞铁死亡起到了保护神经元、改善出血性脑卒中、减轻脓毒症、抗肿瘤的效果,体现了在神经系统疾病领域的应用价值;由于当前的研究有限,外泌体调控铁死亡在神经系统疾病中的的应用研究仍然需要深入探索,以发现更多的药物靶点,拓宽神经系统疾病的精确诊断和精准治疗前景。 2.4.4 外泌体调控铁死亡在肝脏疾病中的应用 根据现有基础与临床研究,外泌体通过调节细胞内脂质过氧化水平,抑制或诱导了细胞铁死亡。文章总结了外泌体参与铁死亡途径在肝脏缺血再灌注损伤、肝纤维化、肝细胞癌等疾病的应用,证明外泌体通过调控铁死亡在改善肝组织缺血再灌注、抗肝纤维化,防治肝细胞癌等方面发挥了重要作用。 供肝短缺是目前制约临床肝移植的主要因素,研究者们致力于寻找治疗更有效的治疗途径。WU等[59]首次通过构建重度脂肪变性供肝大鼠肝移植模型和脂肪变性肝细胞缺氧复氧(H/R)模型发现,一方面,血红素加氧酶氧1修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体处理增加了移植物中miR-124-3p的含量,显著降低了铁稳态因子前列腺六跨膜上皮抗原3的水平,抑制肝细胞铁死亡,降低具有严重脂肪变性供肝的肝移植中的缺血再灌注损伤。另一方面,miRNA并不是外泌体中唯一参与这一过程的物质,其他机制可能参与外泌体对细胞铁性死亡的调控。这证明外泌体具有抑制肝细胞铁死亡的作用,并改善了脂肪肝缺血再灌注损伤,体现了在肝损伤治疗方面,尤其是肝脏组织再生修复的潜力,为未来解决供肝短缺的问题提供了理论参考。 肝纤维化是肝硬化再到肝癌的关键一步,已有大量研究表明,外泌体、铁死亡都可改善肝纤维化,但外泌体如何调控铁死亡抗肝纤维化的机制仍然不明确。基于此,ZHANG等[60]团队通过细胞实验证明,来自HBV感染的LO2细胞的外泌体羟脯氨酸分泌和α平滑肌肌动蛋白和胶原蛋白Ⅰ型α2)表达升高显着增强了肝星状细胞系LX-2细胞的活化,过表达的miR-222上调细胞活力、羟脯氨酸分泌以及α平滑肌肌动蛋白和胶原蛋白Ⅰ型α2的水平都被转铁蛋白受体的过表达所阻断。进一步的研究表明,外泌体miR-222通过抑制转体蛋白受体和转铁蛋白受体诱导的铁死亡来促进肝纤维化,因此,沉默外泌体miR-222的表达对诱导肝细胞铁死亡,抗肝纤维化具有重要意义。另一项关于来自间充质基质细胞的外泌体在肝星状细胞系LX-2和四氯化碳诱导的小鼠肝纤维化模型中,研究者们发现通过促进人肝星状细胞系LX-2中活性氧形成、线粒体功能障碍、二价铁离子释放和脂质过氧化来触发肝星状细胞铁死亡;其机制可能是由于外泌体介导的苄氯素1重组蛋白抑制胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆转运体以及谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4的表达来促进肝星状细胞铁死亡,改善肝纤维化[61]。以上研究表明,外泌体可诱导肝星状细胞铁死亡并改善肝纤维化,因此具有治疗肝硬化的临床应用潜力。 外泌体参与了肝癌细胞铁死亡的过程,起到抗肿瘤的作用。HU等[62]研究团队在一项乙型肝炎病毒感染的肝细胞癌患者的病理组织标本研究中,发现与乙型肝炎病毒+miR-142-3p抑制剂组相比,当与miR-142-3p抑制剂和si-SLC3A2同时培养时,细胞内丙二醛、二价铁离子,还原型谷胱甘肽水平显着降低,活性氧的水平升高。这说明外泌体MiR-142-3p通过抑制重链溶质载体家族3成员2促进M1巨噬细胞的铁死亡,加速肝癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭,敲低miR-142-3p的表达则削弱肝癌细胞的侵袭能力。表明外泌体对重链溶质载体家族3成员2的调控有助于阐明乙型肝炎病毒感染诱发肝癌的发病机制。随后该团队在临床乙型肝炎病毒感染阳性和阴性的肝癌患者组织和外周血实验中,证实了乙型肝炎病毒阳性肝癌细胞外泌体miR-142-3p可通过诱导M1型巨噬细胞铁死亡来促进肝癌的进展[63]。因此,这进一步揭示了外泌体miR-142-3p可以调节癌细胞铁死亡,为原发性肝癌的临床治疗提供了新的理论基础和治疗靶点。此外,DU等[64]团队设计了一个基于外泌体的平台,以高特异性将铁死亡诱导剂(Erastin)和光敏剂(Rose Bengal,RB)递送到肿瘤组织中;结果表明载药外泌体(Er/RB@ Exo sCD47)在532 nm激光照射后Hepa1-6细胞中的活性氧水平升高,有效诱导了肿瘤细胞的铁死亡,发挥了抗肿瘤的作用。并且Er/RB@ExosCD47对肝和肾的造成毒性是最小的。上述结果说明利用外泌体的载药特性调控铁死亡不仅具有抗肿瘤效果,还明显降低了对肝脏的毒性,进一步验证了二者的共同作用在肝癌治疗的有效性,或许是评估肝癌预后新的干预方式。 因此,基于上述关于外泌体调控铁死亡在癌症、心血管、神经系统、肝脏疾病的应用研究总结发现,一方面,外泌体可诱导癌细胞铁死亡,抑制了肿瘤的生长、转移,逆转了肿瘤化疗的耐药性;另一方面,外泌体通过抑制铁死亡在心血管、神经系统、肝脏疾病方面体现了显著的治疗效果,见表3。这些领域的研究进展都证明了外泌体通过诱导或抑制铁死亡对疾病的治疗具有重要作用,可能成为新的靶点。期待未来有更多研究为外泌体调控铁死亡成为一种更有效的临床治疗新模式提供途径和思路。 "

| [1] GURUNATHAN S, KANG MH, KIM JH. A comprehensive review on factors influences biogenesis, functions, therapeutic and clinical implications of exosomes. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:1281-1312. [2] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012,149(5):1060-1072. [3] DEHART DN, FANG D, HESLOP K, et al. Opening of voltage dependent anion channels promotes reactive oxygen species generation, mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018,148:155-162. [4] STOCKWELL BR, JIANG X, GU W. Emerging mechanisms and disease relevance of ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2020,30(6):478-490. [5] WU S, LI T, LIU W, et al. Ferroptosis and cancer: complex relationship and potential app- lication of exosomes. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:733751. [6] WANG W, ZHU L, LI H, et al. Alveolar macrophage-derived exosomal tRF-22-8BWS7K092 activates Hippo signaling pathway to induce ferroptosis in acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;107:108690. [7] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020. doi: 10.1126/science.aau6977. [8] SONG H, LIU B, DONG B, et al. Exosome-based delivery of natural products in cancer therapy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:650426. [9] JIANG L, GU Y, Du Y, et al. Exosomes: diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic delivery vehicles for cancer. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(8):3333-3349. [10] SKOTLAND T, SAGINI K, SANDVIG K, et al. An emerging focus on lipids in extracellular vesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;159:308-321. [11] DOYLE L M, WANG MZ. Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells. 2019;8(7):727. [12] TURCHINOVICH A, DRAPKINA O, TONEVITSKY A. Transcriptome of extracellular vesicles: state-of-the-art. Front Immunol. 2019;10: 202. [13] MATHIEU M, MARTIN-JAULAR L, LAVIEU G, et al. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):9-17. [14] JADLI AS, BALLASY N, EDALAT P, et al. Inside(sight) of tiny communicator: exosome biogenesis, secretion, and uptake. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;467(1-2):77-94. [15] NOROUZI-BAROUGH L, ASGARI K SA, MOHEBZADEH F, et al. Early diagnosis of breast and ovarian cancers by body fluids circulating tumor-derived exosomes. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:187. [16] PALAZZOLO S, MEMEO L, HADLA M, et al. Cancer extracellular vesicles: next-generation diagnostic and drug delivery nanotools. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(11):3165. [17] YE M, NI Q, QI H, et al. Exosomes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells-endothelia cells promotes postnatal angiogenesis in mice bearing ischemic limbs. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(1):158-168. [18] TAVASOLIAN F, HOSSEINI AZ, RASHIDI M, et al. The impact of immune cell-derived exosomes on immune response initiation and immune system function. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(2):197-205. [19] ZHU J, XIONG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. The molecular mechanisms of regulating oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis and therapeutic strategy in tumors. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020: 8810785. [20] GRYZIK M, ASPERTI M, DENARDO A, et al. NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy promotes ferroptosis induced by erastin, but not by RSL3 in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021;1868(2):118913. [21] SU L J, ZHANG J H, GOMEZ H, et al. Reactive oxygen species-induced lipid peroxidation in apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:5080843. [22] KAGAN V E, MAO G, QU F, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13(1):81-90. [23] ZOU Y, PALTE MJ, DEIK AA, et al. A GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1617. [24] CHENG J, FAN Y Q, LIU B H, et al. ACSL4 suppresses glioma cells proliferation via activating ferroptosis. Oncol Rep. 2020;43(1):147-158. [25] CHEN X, LI J, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 2021;17(9):2054-2081. [26] URSINI F, MAIORINO M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:175-185. [27] KIM KM, CHO SS, KI SH. Emerging roles of ferroptosis in liver pathophysiology. Arch Pharm Res. 2020;43(10):985-996. [28] BROWN CW, AMANTE JJ, CHHOY P, et al. Prominin2 drives ferroptosis resistance by stimulating iron export. Dev Cell. 2019;51(5):575-586. [29] YANG RZ, XU WN, ZHENG HL, et al. Exosomes derived from vascular endothelial cells antagonize glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis by inhibiting ferritinophagy with resultant limited ferroptosis of osteoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(9):6691-6705. [30] ITO F, KATO K, YANATORI I, et al. Ferroptosis-dependent extracellular vesicles from macrophage contribute to asbestos-induced mesothelial carcinogenesis through loading ferritin. Redox Biol. 2021;47:102174. [31] ZHANG H, DENG T, LIU R, et al. CAF secreted miR-522 suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):43. [32] ZHANG X, XU Y, MA L, et al. Essential roles of exosome and circRNA_101093 on ferroptosis desensitization in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2022;42(4):287-313. [33] LIN F, CHEN W, ZHOU J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells protect against ferroptosis via exosome-mediated stabilization of SLC7A11 in acute liver injury. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13 (3):1-11. [34] LU J, YANG J, ZHENG Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles from endothelial progenitor cells prevent steroid-induced osteoporosis by suppressing the ferroptotic pathway in mouse osteoblasts based on bioinformatics evidence. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):16130. [35] XU LC, CAO J, LI WJ, et al. Ferroptosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and its regulation by M2 macrophage-derived exosomes. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2022;57(3):324-332. [36] PAN BT, BLOSTEIN R, JOHNSTONE RM. Loss of the transferrin receptor during the maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro. An immunological approach. Biochem J. 1983;210(1):37-47. [37] BANNAI S, KITAMURA E. Transport interaction of L-cystine and L-glutamate in human diploid fibroblasts in culture. J Biol Chem, 1980,255(6):2372-2376. [38] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420. [39] YU M, GAI C, LI Z, et al. Targeted exosome-encapsulated erastin induced ferroptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(10):3173-3182. [40] LI Y, WANG J, CHEN S, et al. miR-137 boosts the neuroprotective effect of endothelial progenitor cell-derived exosomes in oxyhemoglobin-treated SH-SY5Y cells partially via COX2/PGE2 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):330. [41] SONG Y, WANG B, ZHU X, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs exosome attenuate myocardial injury by inhibiting ferroptosis in acute myocardial infarction mice. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37(1):51-64. [42] YI X, TANG X. Exosomes from mir-19b-3p-modified adscs inhibit ferroptosis in intrac- erebral hemorrhage mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:661317. [43] LI X, WU L, TIAN X, et al. miR-29a-3p in exosomes from heme oxygenase-1 modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates steatotic liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing ferroptosis via iron responsive element binding protein 2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:6520789. [44] ZHAO X, SI L, BIAN J, et al. Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomes induce ferroptosis via glutathione synthesis inhibition by targeting SLC7A11 in obesity-induced cardiac injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;182: 232-245. [45] SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, FUCHS HE, et al. Cancer Statistics. 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7-33. [46] ZHANG H, WANG M, HE Y, et al. Chemotoxicity-induced exosomal lncFERO regulates ferroptosis and stemness in gastric cancer stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(12):1116. [47] SONG Z, JIA G, MA P, et al. Exosomal miR-4443 promotes cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma by regulating FSP1 m6A modification-mediated ferroptosis. Life Sci. 2021;276:119399. [48] DAI E, HAN L, LIU J, et al. Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis drives tumor-associated macrophage polarization via release and uptake of oncogenic KRAS protein. Autophagy. 2020;16(11):2069-2083. [49] HU S, MA J, SU C, et al. Engineered exosome-like nanovesicles suppress tumor growth by reprogramming tumor microenvironment and promoting tumor ferroptosis. Acta Biomater. 2021;135:567-581. [50] WANG G, XIE L, LI B, et al. A nanounit strategy reverses immune suppression of exosomal PD-L1 and is associated with enhanced ferroptosis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):5733. [51] KUMAR K, SINGH N, JAGGI AS, et al. Clinical applicability of conditioning techniques in ischemia-reperfusion injury: a review of the literature. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2021;17(3):306-318. [52] SUN W, SHI R, GUO J, et al. miR-135b-3p promotes cardiomyocyte ferroptosis by targeting GPX4 and aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:663832. [53] ZHANG JK, ZHANG Z, GUO ZA, et al. The BMSC-derived exosomal lncRNA Mir9-3hg suppresses cardiomyocyte ferroptosis in ischemia-reperfusion mice via the Pum2/PRDX6 axis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2022;32(2):515-527. [54] TIAN C, YANG Y, BAI B, et al. Potential of exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic carriers for doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(5):1328-1338. [55] GONG L, YU Q, WANG H, et al. Neurofilament light chain (NF-L) stimulates lipid peroxidation to neuronal membrane through microglia-derived ferritin heavy chain (FTH) secretion. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:3938940. [56] LIN PB, WANG PK, PANG CY, et al. Moderate ethanol pre-treatment mitigates ich-induced injury via ER stress modulation in rats. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:682775. [57] WEI X B, JIANG W Q, ZENG JH, et al. Exosome-derived lncRNA NEAT1 exacerbates sepsis-associated encephalopathy by promoting ferroptosis through regulating miR-9-5p/TFRC and GOT1 axis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(3):1954-1969. [58] LI B, CHEN X, QIU W, et al. Synchronous disintegration of ferroptosis defense axis via engineered exosome-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for glioblastoma therapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. doi: 10.1002/advs.202105451. [59] WU L, TIAN X, ZUO H, et al. miR-124-3p delivered by exosomes from heme oxygenase-1 modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits ferroptosis to attenuate ischemia- reperfusion injury in steatotic grafts. J Nanobiotechnol. 2022;20(1):196. [60] ZHANG Q, QU Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Exosomes derived from hepatitis B virus-infected hepatocytes promote liver fibrosis via miR-222/TFRC axis. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022. doi: 10.1007/s10565-021-09684-z. [61] TAN Y, HUANG Y, MEI R, et al. HucMSC-derived exosomes delivered BECN1 induces ferroptosis of hepatic stellate cells via regulating the xCT/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(4):319. [62] HU Z, YIN Y, JIANG J, et al. Exosomal miR-142-3p secreted by hepatitis B virus (HBV)-hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells promotes ferroptosis of M1-type macrophages through SLC3A2 and the mechanism of HCC progression. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;13(2):754-767. [63] HU Z, ZHANG H, LIU W, et al. Mechanism of HBV-positive liver cancer cell exosomal miR-142-3p by inducing ferroptosis of M1 macrophages to promote liver cancer progression. Transl Cancer Res. 2022;11(5):1173-1187. [64] Du J, WAN Z, WANG C, et al. Designer exosomes for targeted and efficient ferroptosis induction in cancer via chemo-photodynamic therapy. Theranostics. 2021;11(17):8185-8196. [65] BAXTER AA. Stoking the fire: how dying cells propagate inflammatory signalling through extracellular vesicle trafficking. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7256. [66] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261. |
| [1] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Ruan Ling, Wang Guanghua, Wu Rongping, Jin Zhan, Lyu Zhenqing, Zhang Nan, Li Shoubang. Correlation between exercise intensity and lipid metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in a high-diet rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [6] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [8] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [9] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [10] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [11] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [12] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [13] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [14] | Bai Siqi, Xiao Zhen, Liu Jing. Application potential of adipose-derived stem cells in female pelvic floor dysfunction diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 921-927. |
| [15] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 291
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 565
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||