Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 86-92.doi: 10.12307/2023.765
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research hot spots and trends of exosomes in theranostic application for chronic kidney disease
Chen Guanting1, Zhang Linqi2, Li Qingru1
- 1First Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-01Accepted:2022-12-24Online:2024-01-08Published:2023-06-28 -
Contact:Zhang Linqi, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Guanting, Doctoral candidate, First Clinical Medical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Special Project for Scientific Research of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Henan Province, No. 2019ZYZD05 (to ZLQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Research hot spots and trends of exosomes in theranostic application for chronic kidney disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 86-92.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
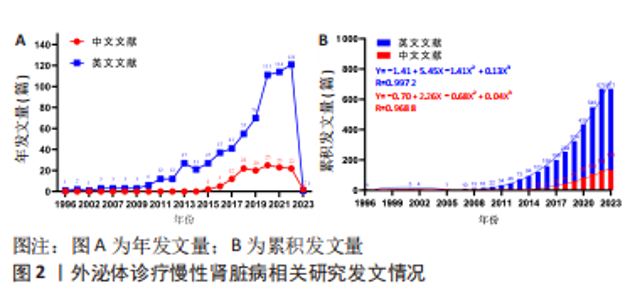
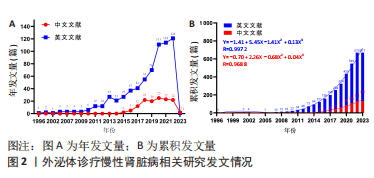
2.1 文献检索结果 此次研究中文数据库共纳入文献406篇,其中CNKI数据库226篇、万方数据库132篇、维普网26篇、CBM数据库22篇;英文数据库共纳入文献1 030篇,其中Cochrane Library数据库12篇、Embase数据库414篇、PubMed数据库198篇、Web of Science数据库406篇,通过Citespace软件检索去重中文文献69篇、英文文献471篇,并按照纳入与排除标准,最终纳入中文文献133篇,英文文献671篇,共计804篇。 2.2 发文量分析 外泌体诊疗慢性肾脏病相关研究文献英文数据库首发于1996年,中文数据库首发于2015年,对该领域发文量进行汇总,其年发文量通常可以在一定程度上反映学者的关注程度,而累积发文量则可判断目前所处研究阶段。如图2A所示,通过对年发文量进行统计,中英文文献数量总体呈现上升趋势,中国相关研究起步较晚,发文量较少。自2013年美国及德国科学家因发现并阐释细胞囊泡运输系统及其调控机制并获得诺贝尔生理学或医学奖后,外泌体相关研究迎来快速发展阶段,至2022年年均发文量英文文献约26篇,中文文献约19篇,2022-2023年因纳入文献不全且存在网络见刊及期刊见刊时间差异,故不做分析。累积发文量通常按照增长模型趋势分为4个阶段,即初始期、快速增长期、增长减缓期及饱和期 [11]。如图2B所示,英文文献自2013年,中文文献自2016年后便处于快速增长期,该阶段外泌体诊疗慢性肾脏病相关研究成果丰硕,尤其在基础研究方面受到科研人员的广泛关注。利用SPSS 23.0进行回归拟合,中英文文献均符合三次项函数增长,二者R2分别为0.997 2,0.968 8,均接近于1,意味着拟合程度较好,即外泌体诊疗慢性肾脏病相关研究仍会作为未来的研究热点,其文献量仍会保持较前快速增长的发展趋势。"

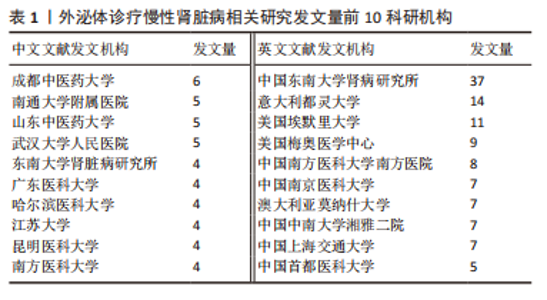
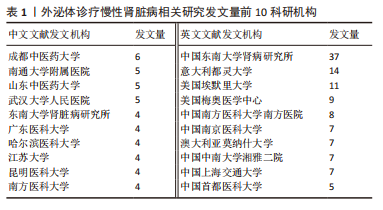
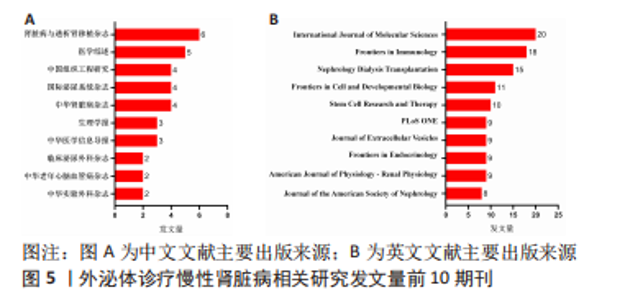
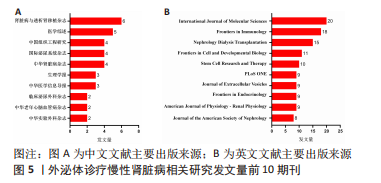
2.3 发文机构与杂志社分析 通过Citespace对外泌体诊疗慢性肾脏病相关研究发文机构及杂志社进行统计,结果显示2007-2023年该领域相关研究机构共计498家,其中中文文献发文机构77家,英文文献发文机构327家,见图3,该领域文献共计被400个期刊收录,其中中文期刊50辑,英文期刊350辑。由图4可知,机构多为高校及附属科研中心与医院,中文发文机构合作网络连线稀疏,机构间多为独立研究或地域性局部合作,英文发文机构相较于中文发文机构合作更多,形成了稳定的跨区域协同合作框架。但值得注意的是,国内该领域研究机构数量共计124家,占全球机构数24.9%,其中有70家机构仅发表英文文献,且发文量前10核心机构中60%为国内院校,见表1,以东南大学中心性最强,跨区域合作范围最大,文章发表量最多,因此在分析时会出现中文发文机构数量稀少,发文量空寥且缺乏合作的假象。文献方面,国内期刊以《肾脏病与透析肾移植》《医学综述》及《中国组织工程研究》收录最多,前10期刊中中国中文核心期刊5辑、中国科技核心期刊7辑,英文方面以《International Journal of Molecular Sciences》期刊发文量最多,前10期刊中按照中科院JCR分区为一区期刊8辑,二区期刊2辑,见图5。"

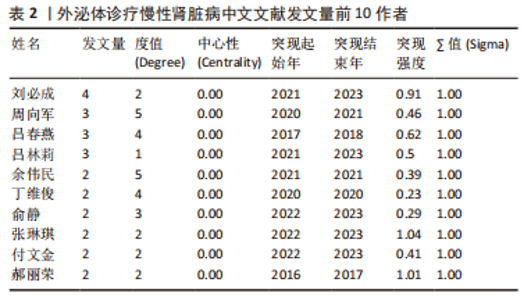
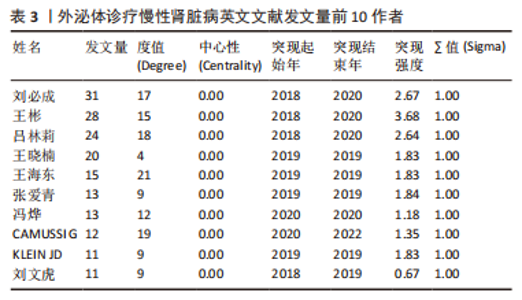
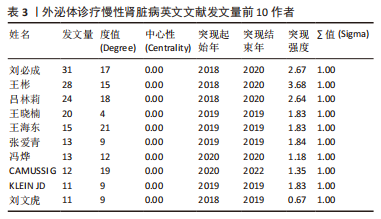
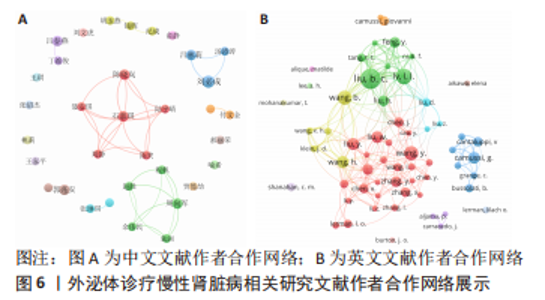
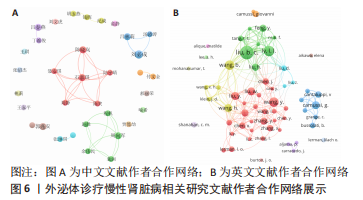
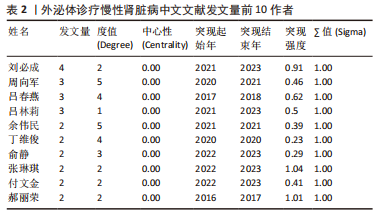
2.4 作者合作网络分析 此次研究共纳入作者3 649位,其中中文文献作者326位,英文文献作者3 323位,发文量前10作者见表2,3,中英文均以刘必成发文量最多。根据普赖斯定律,中英文核心作者最小发文量P分别为1.30,4.17,即中文核心作者最小发文量为2篇,英文核心作者最小发文量为5篇,筛选后得到核心作者合作网络,如图6所示,其中中文核心作者形成了以刘必成、周向军、吕春燕等人为主的多个稳定的研究团队,英文核心作者方面则形成了以刘必成、王彬、Camussi G等人为代表的研究团队,且核心作者团队所在单位与上述前10发文机构基本一致,相较于中文核心作者网络,英文核心作者网络较为集中,团队间合作更为密切。"

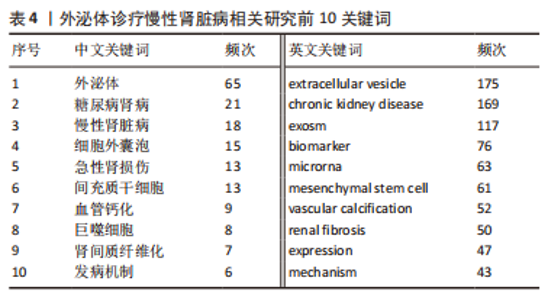
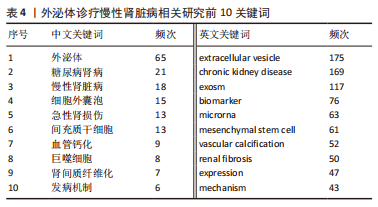
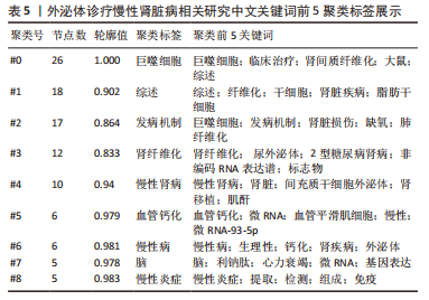
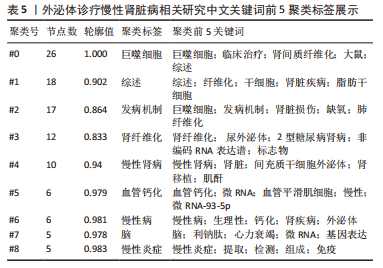
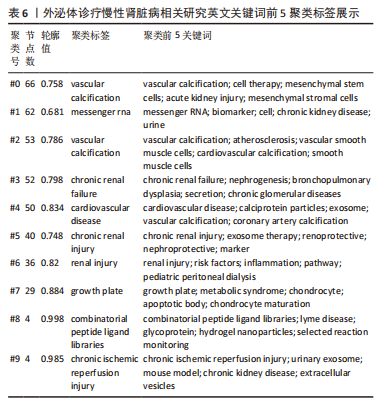
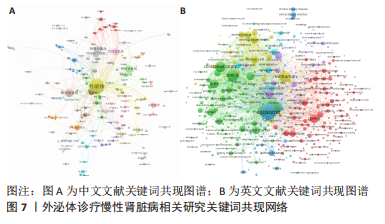
2.5 关键词共现及聚类分析 此次纳入文献共涉及4 493个关键词,其中中文关键词321个,英文关键词4 172个。通过VOSviewer软件绘制关键词共现网络并对高频关键词进行汇总,如图7,表4所示,中文图谱以高频关键词“外泌体、糖尿病肾病、慢性肾脏病”等为中心,英文图谱以高频关键词“extracellular vesicle,chronic kidney disease,exosomes”等为中心,文献多侧重于对该领域病理机制方向的基础研究。利用Citepsace软件对数似然率算法(Log-likelihood rate,LLR)对关键词进行聚类分析,如图8,表5,6所示,共获得9个中文关键词模块,10个英文关键词模块,通常聚类模块值(Modularity Q) > 0.3即意味聚类机构显著,聚类加权平均轮廓值(Weighted Mean Silhouette S) > 0.7代表聚类结果确切[12],此次研究中英文关键词聚类图谱中聚类模块值(Modularity Q)分别为0.640 8,0.529 6,聚类加权平均轮廓值(Weighted Mean Silhouette S)分别为0.932 3,0.794 8,说明聚类内部子集相关性高,此次结果令人信服。各模块多富集于慢性肾脏病肾间质纤维化的病理机制、外泌体来源细胞及所含内容物等方面,且模块间相互关联,内部子集联系紧密,表明该领域整体发展方向多样,包含了临床与基础在内的多类组学研究,各学科间相互验证,共同发展。"

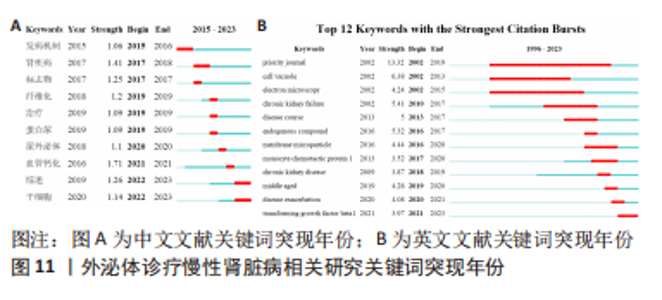
2.6 研究前沿与热点分析 通过Citespace软件绘制该领域相关文献关键词时区图谱,可以直观反映该领域不同研究主题在时间上的演化和发展,而突现性分析对高频关键词的出现情况进行汇总,提示其相关热点研究的持续时间,二者能够大致明确应用外泌体诊疗慢性肾脏病相关研究热点发展与趋势划分[13],结果如图9-11所示。其中中文文献自2015年出现关于外泌体诊疗慢性肾脏病方面相关研究,关键词多集中于外泌体通过干预炎症反应、氧化应激等生理病理机制调控肾间质纤维化及血管钙化的发展进程,并作为反映肾脏损伤的早期诊断标志物进行相关研究。英文文献方面大致分为3个阶段:①1996-2012年,该阶段主要探讨细胞外囊泡在慢性肾脏病及心血管并发症中的潜在作用机制,并对其作为早期生物标志进行评估。②2013-2020年,该阶段关键词丰富,频次较高,说明处于快速发展阶段,研究通过蛋白质组学、转录组学、代谢组学等多组学数据整合,构建基因表达网络,寻找外泌体的调控作用及因果关系,对疾病的早期诊断及对肾间质纤维化及血管钙化病理进展的作用机制做更深层次研究。③2021-2022年,该阶段研究出现了细胞疗法、肾内给药、外泌体治疗等新方法,热点附着于外泌体的靶向运输机制及间充质干细胞衍生外泌体的组织工程研究上。该领域关键词热度无论中文亦或者英文文献,近些年来不断迭代,体现了相关科研工作的飞速进展及对不同时期所关注热点的改变。"

| [1] 《慢性肾脏病3~5期非透析中西医结合诊疗专家共识》编写组. 慢性肾脏病3~5期非透析中西医结合诊疗专家共识[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2022, 42(7):791-801. [2] 王九生,王新,王蓓.独立透析中心探路基层之可行性与展望[J].中国医院院长,2022,18(9):22-27. [3] 谢院生,李清刚.肾脏病学临床研究新进展[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2020,21(6):471-473. [4] WANG M, HU HH, CHEN YY, et al. Novel poricoic acids attenuate renal fibrosis through regulating redox signalling and aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Phytomedicine. 2020;79:153323. [5] WASUNG ME, CHAWLA LS, MADERO M. Biomarkers of renal function, which and when? Clin Chim Acta. 2015;438:350-357. [6] HARRILL AH, SANDERS AP. Urinary MicroRNAs in Environmental Health: Biomarkers of Emergent Kidney Injury and Disease. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2020;7(2):101-108. [7] 盘俊春.撰写和管理论文的实用辅助工具:NoteExpress[J].中国信息技术教育,2019(20):68-70. [8] VAN ECK NJ, WALTMAN L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538. [9] 侯剑华,胡志刚.CiteSpace软件应用研究的回顾与展望[J].现代情报,2013, 33(4):99-103. [10] 丁学东.文献计量学基础[M].北京:北京大学出版社,1993:373. [11] 毕晨,赵琦睿,朱琳.基于文献计量的国际移民管理研究概况与发展趋势可视化分析[J].科学观察,2021(6):53-66. [12] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015,33(2):242-253. [13] 梁依敏,梁文心,杨鑫龙,等.基于CiteSpace和VOSviewer的国内近30年来中医药治疗胃癌前病变研究的文献计量学分析[J].时珍国医国药,2022, 32(3):752-755. [14] TANG TT, LYU LL, LIU BC. Research progress of extracellular vesicles in the treatment of renal disease. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022;74(1):67-72. [15] TANG TT, WANG B, LV LL, et al. Extracellular vesicles for renal therapeutics: State of the art and future perspective. J Control Release. 2022;349:32-50. [16] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. [17] PARK SJ, KIM JM, KIM J, et al. Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis of apoptotic exosome-like vesicles and their roles as damage-associated molecular patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(50): E11721-E11730. [18] ZHANG A, WANG H, WANG B, et al. Exogenous miR-26a suppresses muscle wasting and renal fibrosis in obstructive kidney disease. FASEB J. 2019;33(12): 13590-13601. [19] WANG B, ZHANG A, WANG H, et al. miR-26a Limits Muscle Wasting and Cardiac Fibrosis through Exosome-Mediated microRNA Transfer in Chronic Kidney Disease. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):1864-1877. [20] THONGBOONKERD V. Roles for Exosome in Various Kidney Diseases and Disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2020;10:1655. [21] WANG H, WANG B, ZHANG A, et al. Exosome-Mediated miR-29 Transfer Reduces Muscle Atrophy and Kidney Fibrosis in Mice. Mol Ther. 2019;27(3):571-583. [22] NOGUEIRA A, PIRES MJ, OLIVEIRA PA. Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Renal Fibrosis: A Review of Animal Models and Therapeutic Strategies. In Vivo. 2017;31(1):1-22. [23] FARRIS AB, COLVIN RB. Renal interstitial fibrosis: mechanisms and evaluation. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012;21(3):289-300. [24] LV W, FAN F, WANG Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of microRNAs for the treatment of renal fibrosis and CKD. Physiol Genomics. 2018;50(1):20-34. [25] ICHII O, HORINO T. MicroRNAs associated with the development of kidney diseases in humans and animals. J Toxicol Pathol. 2018;31(1):23-34. [26] KADDOURAH A, BASU RK, BAGSHAW SM, et al. Epidemiology of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children and Young Adults. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):11-20. [27] RAMACHANDRAN K, SAIKUMAR J, BIJOL V, et al. Human miRNome profiling identifies microRNAs differentially present in the urine after kidney injury. Clin Chem. 2013;59(12):1742-1752. [28] 季康寿,杨茗茜,陈文娜,等.外泌体miRNA与中医理论关联及在冠心病中的机制研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2021,39(5):48-52. [29] 鲍博艺,李卫萍.外泌体miRNA在急性心肌梗死中的研究进展[J].首都医科大学学报,2022,43(2):199-204. [30] BELTRAMI C, CLAYTON A, NEWBURY LJ, et al. Stabilization of Urinary MicroRNAs by Association with Exosomes and Argonaute 2 Protein. Noncoding RNA. 2015; 1(2):151-166. [31] NIK MOHAMED KAMAL NNSB, SHAHIDAN WNS. Non-Exosomal and Exosomal Circulatory MicroRNAs: Which Are More Valid as Biomarkers? Front Pharmacol. 2020;10:1500. [32] YU Y, BAI F, QIN N, et al. Non-Proximal Renal Tubule-Derived Urinary Exosomal miR-200b as a Biomarker of Renal Fibrosis. Nephron. 2018;139(3):269-282. [33] LV CY, DING WJ, WANG YL, et al. A PEG-based method for the isolation of urinary exosomes and its application in renal fibrosis diagnostics using cargo miR-29c and miR-21 analysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50(5):973-982. [34] KUMARI M, MOHAN A, ECELBARGER CM, et al. Corrigendum: miR-451 Loaded Exosomes Are Released by the Renal Cells in Response to Injury and Associated With Reduced Kidney Function in Human. Front Physiol. 2020;11:844. [35] ZANG J, MAXWELL AP, SIMPSON DA, et al. Differential Expression of Urinary Exosomal MicroRNAs miR-21-5p and miR-30b-5p in Individuals with Diabetic Kidney Disease. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10900. [36] 陈笑,石嘉琪,聂安琪,等.外泌体miR-93-5p在慢性肾脏病患者中的表达及临床意义[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2021,37(10):835-838. [37] ZHOU S, FANG J, HU M, et al. Determining the influence of high glucose on exosomal lncRNAs, mRNAs, circRNAs and miRNAs derived from human renal tubular epithelial cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(6):8467-8480. [38] ZHAO S, LI W, YU W, et al. Exosomal miR-21 from tubular cells contributes to renal fibrosis by activating fibroblasts via targeting PTEN in obstructed kidneys. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8660-8673. [39] ZHOU X, ZHAO S, LI W, et al. Tubular cell-derived exosomal miR-150-5p contributes to renal fibrosis following unilateral ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating fibroblast in vitro and in vivo. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(14):4021-4033. [40] GUAN H, PENG R, MAO L, et al. Injured tubular epithelial cells activate fibroblasts to promote kidney fibrosis through miR-150-containing exosomes. Exp Cell Res. 2020;392(2):112007. [41] LIU X, MIAO J, WANG C, et al. Tubule-derived exosomes play a central role in fibroblast activation and kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2020;97(6):1181-1195. [42] JING H, TANG S, LIN S, et al. The role of extracellular vesicles in renal fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(5):367. [43] DESDÍN-MICÓ G, MITTELBRUNN M. Role of exosomes in the protection of cellular homeostasis. Cell Adh Migr. 2017;11(2):127-134. [44] 刘苏,徐巍龙,查敏,等.miR-296-5p在糖尿病肾病db/db小鼠血浆外泌体中的表达及功能[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2022, 42(1):14-22. [45] 王东,徐兴欣,范哲,等.高糖环境下肾小管上皮细胞来源外泌体诱导巨噬细胞激活的作用与机制[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2018,34(9):681-688. [46] FENG Y, ZHONG X, TANG TT, et al. Rab27a dependent exosome releasing participated in albumin handling as a coordinated approach to lysosome in kidney disease. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(7):513. [47] 饶超峰,薛笑楠,朱明英,等.巨噬细胞外泌体通过抑制自噬诱导高血糖对肾小球足细胞的损伤作用[J].天津医药,2021,49(2):119-125. [48] 黄小抗,朱启金,吴永贵.高糖刺激的巨噬细胞源外泌体对小鼠肾组织中TGF-β1/Smad3通路的影响作用[J].安徽医科大学学报,2020,55(1):1-6. [49] WU X, GAO Y, XU L, et al. Exosomes from high glucose-treated glomerular endothelial cells trigger the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and dysfunction of podocytes. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9371. [50] ANIL KUMAR P, WELSH GI, SALEEM MA, et al. Molecular and cellular events mediating glomerular podocyte dysfunction and depletion in diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014;5:151. [51] 郑可,李雪梅.慢性肾脏病贫血与心血管疾病[J].中国实用内科杂志,2020, 40(11):903-907. [52] LIU Y, GUO W, GUO Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve renal fibrosis via regulating Smurf 2/Smad 7. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022;27(1):17. [53] LU Y, YANG L, CHEN X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improve renal fibrosis by reducing the polarisation of M1 and M2 macrophages through the activation of EP2 receptors. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2022;16(1):14-24. [54] LIU L, WU Y, WANG P, et al. PSC-MSC-Derived Exosomes Protect against Kidney Fibrosis In Vivo and In Vitro through the SIRT6/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Int J Stem Cells. 2021;14(3):310-319. [55] WANG Y, CAO X, YAN L, et al. WITHDRAWN: Exosome-derived long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 controls cardiac fibrosis in chronic kidney disease. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13. [56] CHEN L, WANG Y, LI S, et al. Exosomes derived from GDNF-modified human adipose mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate peritubular capillary loss in tubulointerstitial fibrosis by activating the SIRT1/eNOS signaling pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(20):9425-9442. [57] WANG B, WANG ZM, JI JL, et al. Macrophage-Derived Exosomal Mir-155 Regulating Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis and Hypertrophy in Uremic Cardiomyopathy. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020;5(2):148-166. [58] GWON MG, AN HJ, KIM JY, et al. Anti-fibrotic effects of synthetic TGF-β1 and Smad oligodeoxynucleotide on kidney fibrosis in vivo and in vitro through inhibition of both epithelial dedifferentiation and endothelial-mesenchymal transitions. FASEB J. 2020;34(1):333-349. [59] CHINNADURAI R, RAJAN D, QAYED M, et al. Potency Analysis of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Using a Combinatorial Assay Matrix Approach. Cell Rep. 2018;22(9): 2504-2517. [60] ZHU F, CHONG LEE SHIN OLS, PEI G, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells employed exosomes to attenuate AKI-CKD transition through tubular epithelial cell dependent Sox9 activation. Oncotarget. 2017;8(41):70707-70726. [61] TKACH M, THÉRY C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226-1232. [62] 孙雄林,林婷婷,陈少豪,等.骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体微小RNA-200a通过Wnt/β-连环蛋白通路抑制肾小管上皮细胞上皮-间充质转化[J].中华实验外科杂志,2020,37(12):2207-2210. [63] VOELKL J, TUFFAHA R, LUONG TTD, et al. Zinc Inhibits Phosphate-Induced Vascular Calcification through TNFAIP3-Mediated Suppression of NF-κB. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(6):1636-1648. [64] LIU Y, GUO Y, BAO S, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-381-3p alleviates vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease by targeting NFAT5. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(3):278. [65] GUO Y, BAO S, GUO W, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes alleviate high phosphorus-induced vascular smooth muscle cells calcification by modifying microRNA profiles. Funct Integr Genomics. 2019; 19(4):633-643. [66] HUANG H, LIU H, TANG J, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-25-3p improves high glucose-induced podocytes injury through activation autophagy via inhibiting DUSP1 expression. IUBMB Life. 2020;72(12):2651-2662. [67] ZHANG A, LI M, WANG B, et al. miRNA-23a/27a attenuates muscle atrophy and renal fibrosis through muscle-kidney crosstalk. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018;9(4):755-770. [68] 欧阳过,蔡虎志,王雅乐,等.外泌体miR-155调控p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路影响心肾综合征大鼠的心肾细胞凋亡[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2019,28(6):532-537. |
| [1] | Huang Yongbin, Wang Tao, Lou Yuanyi, Pang Jingqun, Chen Guanghua. Application prospect of mesenchymal stem cells in promoting muscle tissue repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 107-112. |
| [2] | Wang Xianfeng, Wang Kun, Sun Han, Sun Xiaoliang, Yan Litao. Mechanism underlying exosomal lncRNA H19 derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promotes cartilage injury repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 20-25. |
| [3] | Zheng Rongjiong, Deng Zerun, Han Dan, Sun Lihua. Mechanism underlying rat hepatocyte apoptosis regulated by exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 44-49. |
| [4] | Zheng Mingkui, Xue Chenhui, Guan Xiaoming, Ma Xun. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes reduce the permeability of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [5] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [6] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [7] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [8] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [9] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [10] | Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 903-908. |
| [11] | Gao Ting, Ma Xiaohong, Li Xiaorong. Extraction and identification of exosomes from three different sources of ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| [12] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| [13] | Yin Shuoxin, Zhang Tao, Wang Shuping, Lu Xin, Huang Xuping, Yin Mengying, Yang Yuwei, Yuan Bingmao, Mao Zhihua, Chen Yuanneng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of researches on gastric cancer stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 941-947. |
| [14] | Xu Qijing, Yang Yichun, Lei Wei, Yang Ying, Yu Jiang, Xia Tingting, Zhang Meng, Zhang Tao, Zhang Qian. Advances and problems in cell-free treatment of diabetic skin chronic wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 962-969. |
| [15] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||