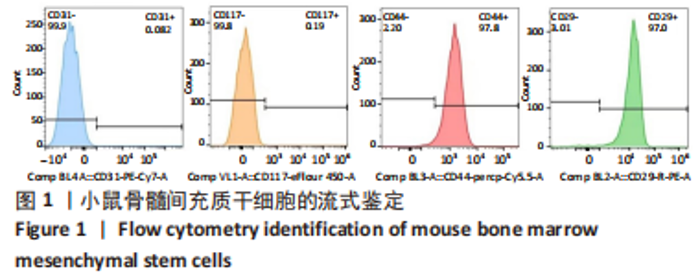
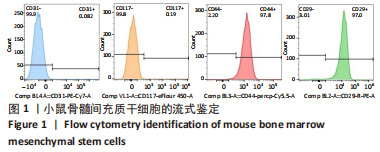
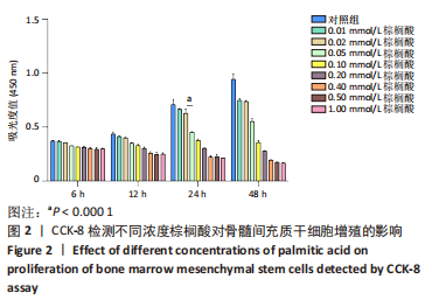
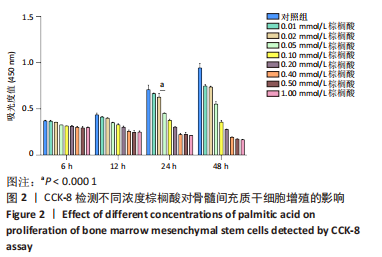
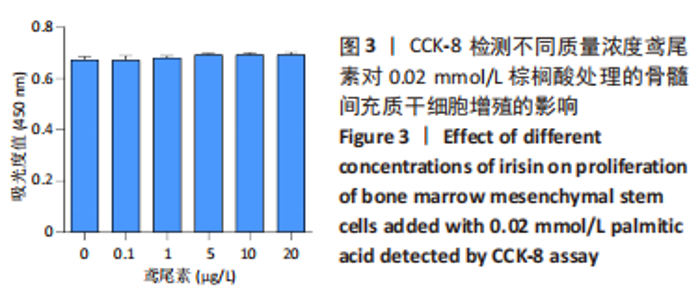
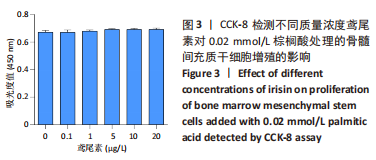
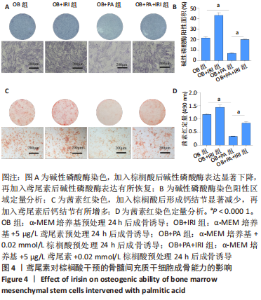
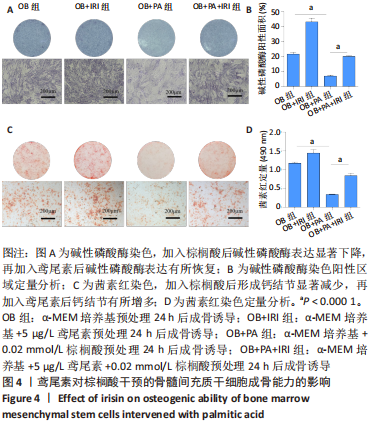
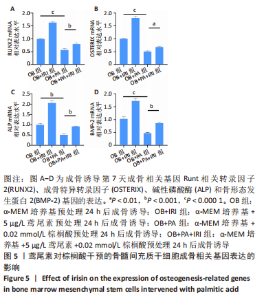
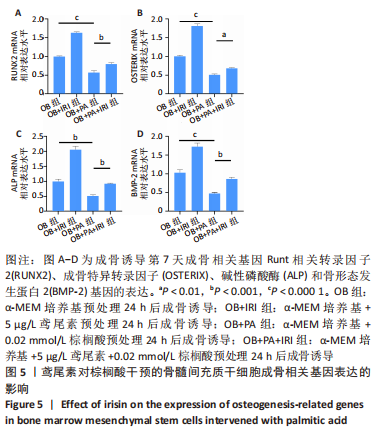
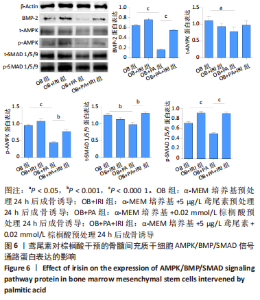
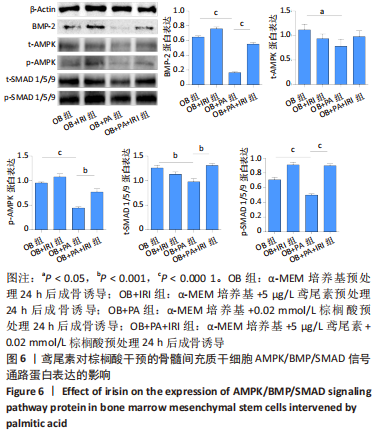
[1] RINONAPOLI G, PACE V, RUGGIERO C, et al. Obesity and Bone: A Complex Relationship. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(24):13662.
[2] HANNAN MT, FELSON DT, ANDERSON JJ. Bone mineral density in elderly men and women: results from the Framingham osteoporosis study. J Bone Miner Res. 1992;7(5):547-553.
[3] EDELSTEIN SL, BARRETT-CONNOR E. Relation between body size and bone mineral density in elderly men and women. Am J Epidemiol. 1993;138(3):160-169.
[4] HU FB. Overweight and obesity in women: health risks and consequences. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2003;12(2):163-172.
[5] Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation.World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2000;894:i-xii, 1-253.
[6] WOSJE KS, KHOURY PR, CLAYTOR RP, et al. Adiposity and TV viewing are related to less bone accrual in young children. J Pediatr. 2009;154(1): 79-85.e2.
[7] DEFRONZO RA. Insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis: the missing links. The Claude Bernard Lecture 2009. Diabetologia. 2010;53(7):1270-1287.
[8] SAMUEL VT, PETERSEN KF, SHULMAN GI. Lipid-induced insulin resistance: unravelling the mechanism. Lancet. 2010;375(9733):2267-2277.
[9] LI L, GU Z, ZHANG J, et al. CTRP9 overexpression attenuates palmitic acid-induced inflammation, apoptosis and impaired migration in HTR8/SVneo cells through AMPK/SREBP1c signaling. Exp Ther Med. 2022;24(1):459.
[10] ÁVALOS Y, HERNÁNDEZ-CÁCERES MP, LAGOS P, et al. Palmitic acid control of ciliogenesis modulates insulin signaling in hypothalamic neurons through an autophagy-dependent mechanism. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):659.
[11] DESIDERIO V, TIRINO V, PAPACCIO G, et al. Bone defects: molecular and cellular therapeutic targets. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;51:75-78.
[12] GRANERO-MOLTO F, WEIS JA, LONGOBARDI L, et al. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine: application to bone and cartilage repair. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008;8(3):255-268.
[13] GIMBLE JM. The function of adipocytes in the bone marrow stroma. New Biol. 1990;2(4):304-312.
[14] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[15] TENCEROVA M, KASSEM M. The Bone Marrow-Derived Stromal Cells: Commitment and Regulation of Adipogenesis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2016;7:127.
[16] ABDALLAH BM, KASSEM M. New factors controlling the balance between osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis. Bone. 2012;50(2):540-545.
[17] JAFARI A, QANIE D, ANDERSEN TL, et al. Legumain Regulates Differentiation Fate of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells and Is Altered in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;8(2): 373-386.
[18] BOSTRÖM P, WU J, JEDRYCHOWSKI MP, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 20121;481(7382):463-468.
[19] XIONG XQ, GENG Z, ZHOU B, et al. FNDC5 attenuates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance via AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization in obesity. Metabolism. 2018;83:31-41.
[20] MURUGANANDAN S, SINAL CJ. The impact of bone marrow adipocytes on osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. IUBMB Life. 2014;66(3): 147-155.
[21] MAAK S, NORHEIM F, DREVON CA, et al. Progress and Challenges in the Biology of FNDC5 and Irisin. Endocr Rev. 2021;42(4):436-456.
[22] KIM H, WRANN CD, JEDRYCHOWSKI M, et al. Irisin Mediates Effects on Bone and Fat via αV Integrin Receptors. Cell. 2018;175(7):1756-1768.e17.
[23] HU S, XUE Y, HE J, et al. Irisin recouples osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis to protect wear-particle-induced osteolysis by suppressing oxidative stress and RANKL production. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(17):5791-5801.
[24] COLAIANNI G, CUSCITO C, MONGELLI T, et al. The myokine irisin increases cortical bone mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(39): 12157-12162.
[25] QIAO X, NIE Y, MA Y, et al. Irisin promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via activating the MAP kinase signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18732.
[26] LUO Y, MA Y, QIAO X, et al. Irisin ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Climacteric. 2020;23(5):496-504.
[27] ZHANG Y, LI R, MENG Y, et al. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes. 2014;63(2):514-525.
[28] MURUGANANDAN S, GOVINDARAJAN R, SINAL CJ. Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Health. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16(4): 434-442.
[29] LI J, CHEN X, LU L, et al. The relationship between bone marrow adipose tissue and bone metabolism in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020;52:88-98.
[30] YE W, WANG J, LIN D, et al. The immunomodulatory role of irisin on osteogenesis via AMPK-mediated macrophage polarization. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;146:25-35.
[31] XUE Y, HU S, CHEN C, et al. Myokine Irisin promotes osteogenesis by activating BMP/SMAD signaling via αV integrin and regulates bone mass in mice. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(2):572-584.
|