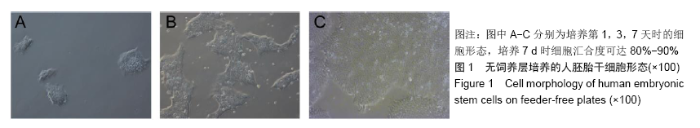
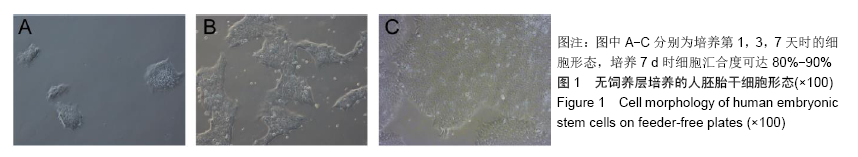
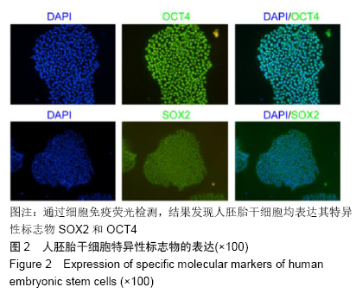
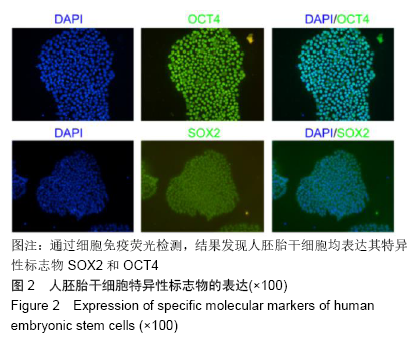
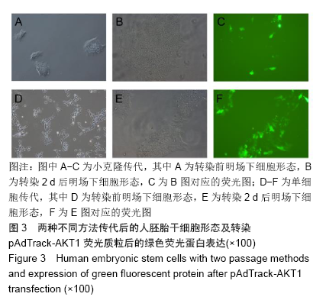
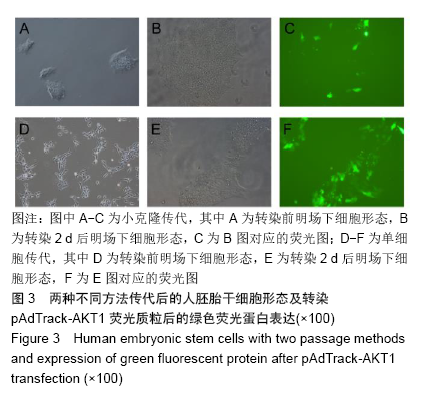
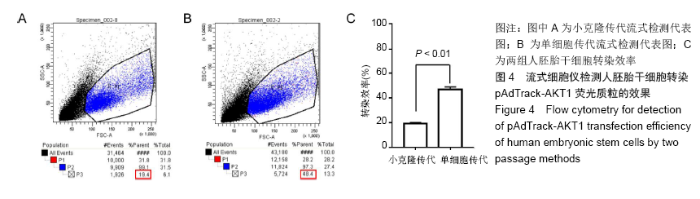
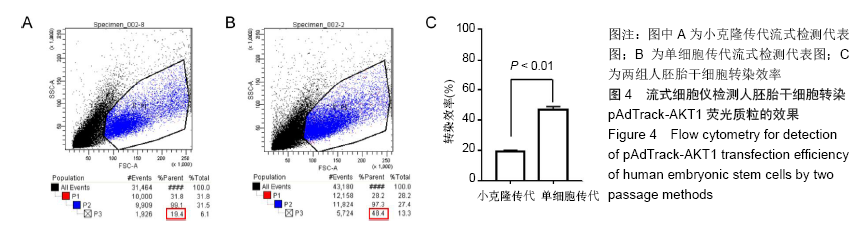
[1] THOMSON JA, ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SHAPIRO SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282(5391):1145-1147.
[2] MORA C, SERZANTI M, CONSIGLIO A, et al. Clinical potentials of human pluripotent stem cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2017;33(4):351-360.
[3] SUGAYA K, VAIDYA M. Stem cell therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018; 1056:61-84.
[4] CUASCUT FX, HUTTON GJ. Stem cell-based therapies for multiple sclerosis: current perspectives. Biomedicines. 2019; 7(2):E26.
[5] PRINGPROA K, SATHANAWONGS A, KHAMPHILAI C, et al. Intravenous transplantation of mouse embryonic stem cells attenuates demyelination in an ICR outbred mouse model of demyelinating diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(10): 1603-1609.
[6] KIM YS, HWANG KA, GO RE, et al. Gene therapy strategies using engineered stem cells for treating gynecologic and breast cancer patients (Review). Oncol Rep. 2015;33(5): 2107-2112.
[7] LUO C, LÜ D, PAN J, et al. Improving the gene transfection in human embryonic stem cells: balancing with cytotoxicity and pluripotent maintenance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016; 8(13):8367-8375.
[8] LAKSHMIPATHY U, PELACHO B, SUDO K, et al. Efficient transfection of embryonic and adult stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):531-543.
[9] TARAHOVSKY YS. Cell transfection by DNA-lipid complexes - lipoplexes. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2009;74(12):1293-1304.
[10] CAO F, XIE X, GOLLAN T, et al. Comparison of gene-transfer efficiency in human embryonic stem cells. Mol Imaging Biol. 2010;12(1):15-24.
[11] FONG H, ELLIOTT KA, LOCK LF, et al. Nucleofection of human embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;767: 333-341.
[12] DAVÉ UP, JENKINS NA, COPELAND NG. Gene therapy insertional mutagenesis insights. Science. 2004;303(5656): 333.
[13] MA Y, RAMEZANI A, LEWIS R, et al. High-level sustained transgene expression in human embryonic stem cells using lentiviral vectors. Stem Cells. 2003;21(1):111-117.
[14] ZWAKA TP, THOMSON JA. Homologous recombination in human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(3): 319-321.
[15] CORREA S, BOEHNKE N, DEISS-YEHIELY E, et al. Solution conditions tune and optimize loading of therapeutic polyelectrolytes into layer-by-layer functionalized Liposomes. ACS Nano. 2019;13(5):5623-5634.
[16] XING Y, WEN CY, LI ST, et al.Non-viral liposome-mediated transfer of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood-brain barrier.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(4):617-622.
[17] RAHIMI P, MOBARAKEH VI, KAMALZARE S, et al. Comparison of transfection efficiency of polymer-based and lipid-based transfection reagents. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2018; 119(11):701-705.
[18] BUNTING KD. ABC transporters as phenotypic markers and functional regulators of stem cells. Stem Cells. 2002;20(1): 11-20.
[19] WATANABE K, UENO M, KAMIYA D, et al. A ROCK inhibitor permits survival of dissociated human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(6):681-686.
[20] HASEGAWA K, FUJIOKA T, NAKAMURA Y, et al. A method for the selection of human embryonic stem cell sublines with high replating efficiency after single-cell dissociation. Stem Cells. 2006;24(12):2649-2660.
[21] GAO X, SPRANDO RL, YOURICK JJ. A rapid and highly efficient method for the isolation, purification, and passaging of human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Reprogram. 2018;20(5):282-288.
[22] SINGH AM. An efficient protocol for single-cell cloning human pluripotent stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:11.
[23] TSUKAMOTO M, NISHIMURA T, YODOE K, et al. Generation of footprint-free canine induced pluripotent stem cells using auto-erasable sendai virus vector. Stem Cells Dev. 2018; 27(22):1577-1586.
[24] BAI Q, RAMIREZ JM, BECKER F, et al. Temporal analysis of genome alterations induced by single-cell passaging in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(5): 653-662. |