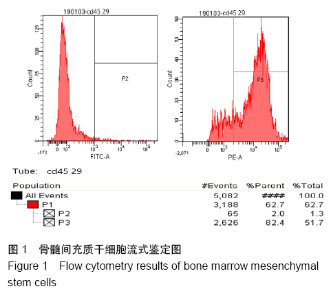
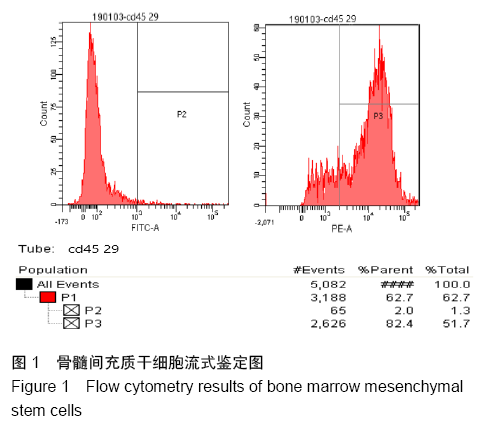
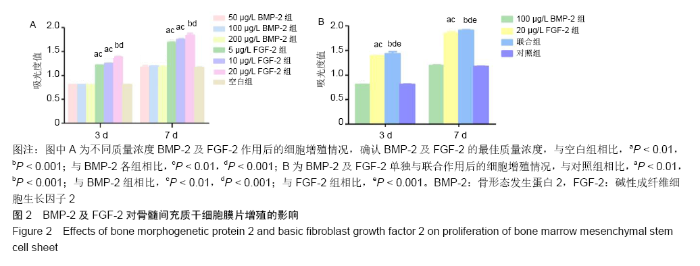
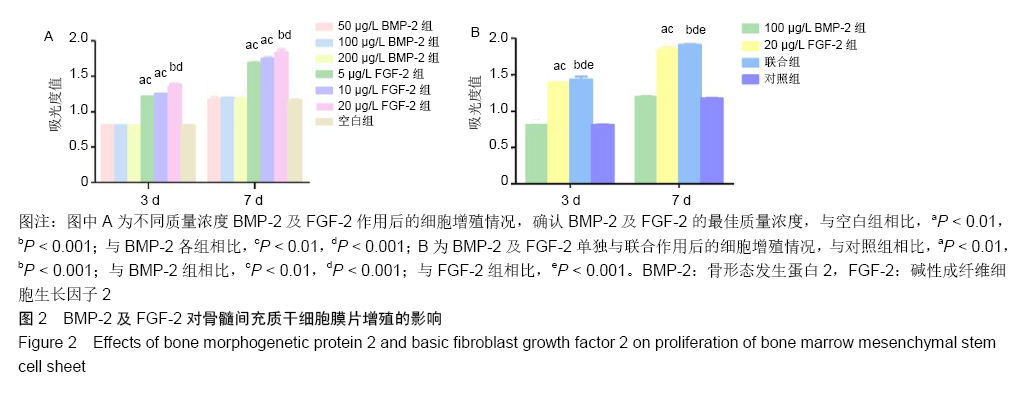
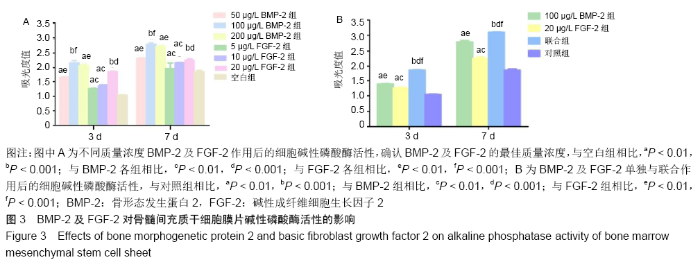
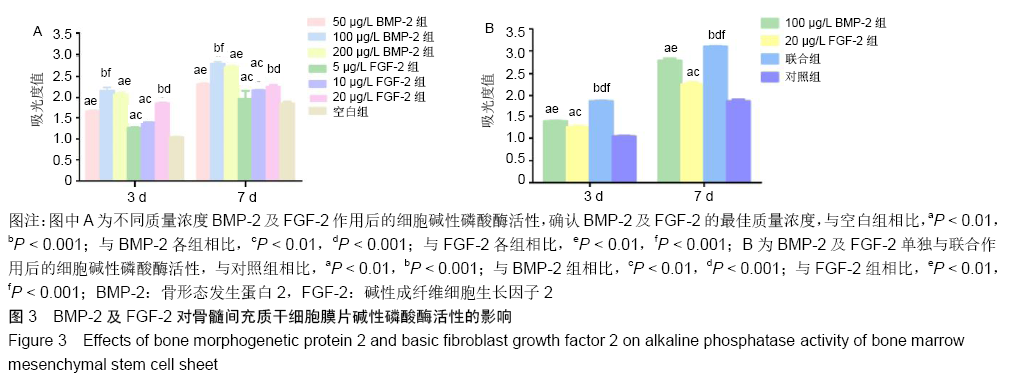
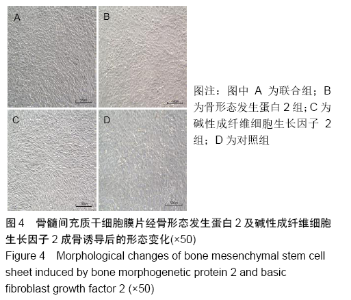
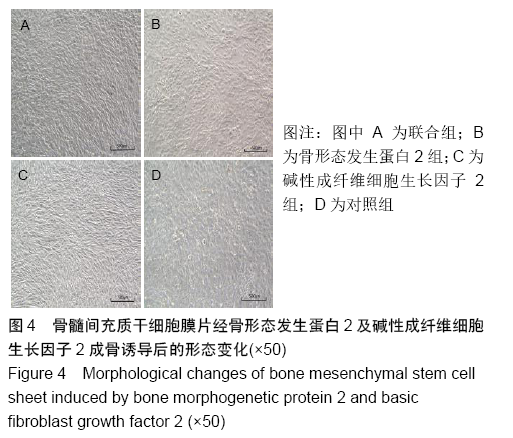
[1] YORUKOGLU AC, KITER AE, AKKAYA S, et al. A Concise Review on the Use of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cell Sheet-Based Tissue Engineering with Special Emphasis on Bone Tissue Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:2374161.
[2] 陈梅红,党旖旎,朱旭东,等.脂肪间充质干细胞膜片移植促进创面愈合的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(5):790-796.
[3] OKA M, MIYABE Y, SUGIURA N, et al. Cell Sheet Engineering and Kidney Diseases. Contrib Nephrol. 2018;195:74-80.
[4] WASHIO K, TSUTSUMI Y, TSUMANUMA Y, et al. In Vivo Periodontium Formation Around Titanium Implants Using Periodontal Ligament Cell Sheet. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24 (15-16):1273-1282.
[5] HARAGUCHI Y, HASEGAWA A, MATSUURA K, et al. Three-Dimensional Human Cardiac Tissue Engineered by Centrifugation of Stacked Cell Sheets and Cross-Sectional Observation of Its Synchronous Beatings by Optical Coherence Tomography. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:5341702.
[6] 李豆豆,周维维,王蕾,等.联合细胞膜片和自组装多肽技术构建一种新型BMSCs膜片-RADA16组织工程复合体的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2019,35(1):5-10.
[7] ZHANG C, MENG C, GUAN D, et al. BMP2 and VEGF165 transfection to bone marrow stromal stem cells regulate osteogenic potential in vitro. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(5): e9787.
[8] LIU H, WEI LK, JIAN XF, et al. Isolation, culture and induced differentiation of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3715-3724.
[9] WANG P, SHU B, XU Y, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor reduces scar by inhibiting the differentiation of epidermal stem cells to myofibroblasts via the Notch1/Jagged1 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):114.
[10] YAN XW, LIU C, TIAN F. Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into Leydig cells. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2015;21(6):494-499.
[11] MIAO Z, LU Z, LUO S, et al. Murine and Chinese cobra venom‑derived nerve growth factor stimulate chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs in vitro: A comparative study. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(3): 3341-3349.
[12] RUAN H, XIAO R, JIANG X, et al. Biofunctionalized self-assembly of peptide amphiphile induces the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019; 450(1-2):199-207.
[13] 张戎. 生长因子FGF-2和VEGF对人牙周膜干细胞增殖、迁移、黏附及成骨分化能力的影响[D].西安:第四军医大学,2013.
[14] CHARLES LF, WOODMAN JL, UENO D, et al. Effects of low dose FGF-2 and BMP-2 on healing of calvarial defects in old mice. Exp Gerontol. 2015;64:62-69.
[15] 姚树生,张柳,郑杰.辛伐他汀对大鼠骨髓基质细胞成骨分化的影响[J]. 医学争鸣, 2006,27(17):1609-1612.
[16] CHARLES LF, WOODMAN JL, UENO D, et al. Effects of low dose FGF-2 and BMP-2 on healing of calvarial defects in old mice. Exp Gerontol. 2015;64:62-69.
[17] PALIOTO DB, COLETTA RD, GRANER E, et al. The influence of enamel matrix derivative associated with insulin-like growth factor-I on periodontal ligament fibroblasts. J Periodontol. 2004; 75(4):498-504.
[18] WANG Z, WU G, WEI M, et al. Improving the osteogenesis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets by microRNA-21-loaded chitosan/hyaluronic acid nanoparticles via reverse transfection. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:2091-2105.
[19] SONG R, WANG D, ZENG R, et al. Synergistic effects of fibroblast growth factor-2 and bone morphogenetic protein-2 on bone induction. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):4483-4492.
[20] KHORSAND B, NICHOLSON N, DO AV, et al. Regeneration of bone using nanoplex delivery of FGF-2 and BMP-2 genes in diaphyseal long bone radial defects in a diabetic rabbit model. J Control Release. 2017;248:53-59.
[21] QI W, YAN J, SUN H, et al. Multifunctional Nanocomposite Films for Synergistic Delivery of bFGF and BMP-2. ACS Omega. 2017; 2(3):899-909.
[22] 白燕,王士斌,陈爱政,等. BMP-2及FGF-2对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2017,42(12):1575-1581.
[23] 高海,陈潇,管东华,等.高糖对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(1):26-30.
[24] QIAN X, ZHANG C, CHEN G, et al. Effects of BMP-2 and FGF2 on the osteogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in hindlimb-unloaded rats. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;70(2): 1127-1136.
[25] WANG CL, XIAO F, WANG CD, et al. Gremlin2 Suppression Increases the BMP-2-Induced Osteogenesis of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Via the BMP-2/Smad/ Runx2 Signaling Pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(2):286-297.
[26] BOSWELL BA, MUSIL LS. Synergistic interaction between the fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathways in lens cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2015;26(13):2561-2572. |