Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 165-171.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2969
Role and mechanism of focal adhesion kinase in inducing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts cells
Li Zhen, Huang Yonghui, Sun Jifu, Sun Haitao
- Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-24Revised:2019-12-27Accepted:2020-02-22Online:2021-01-18Published:2020-11-21 -
Contact:Huang Yonghui, Master, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Li Zhen, Master, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Project of Zhenjiang City, No. SH2017007
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhen, Huang Yonghui, Sun Jifu, Sun Haitao. Role and mechanism of focal adhesion kinase in inducing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 165-171.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
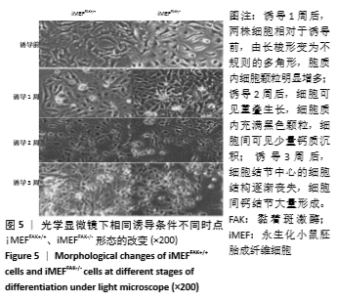
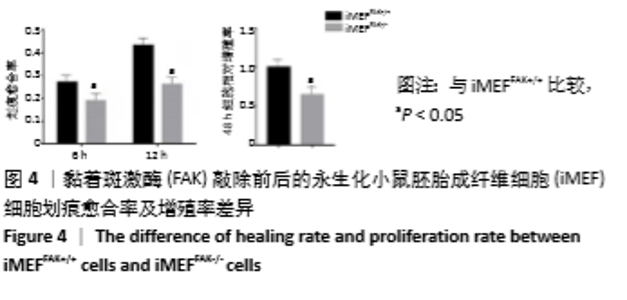
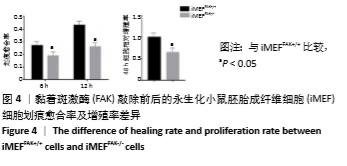
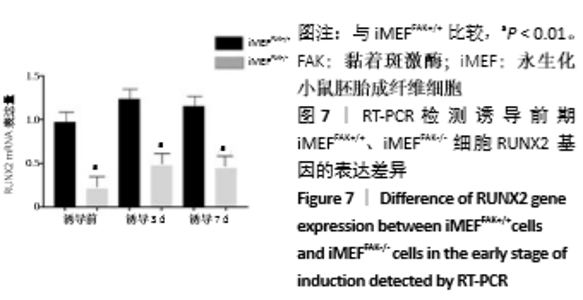
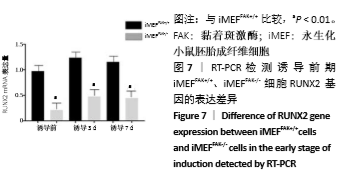
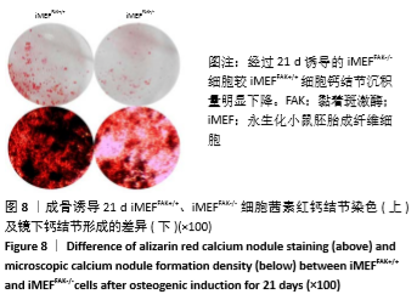
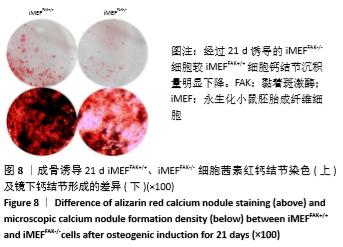
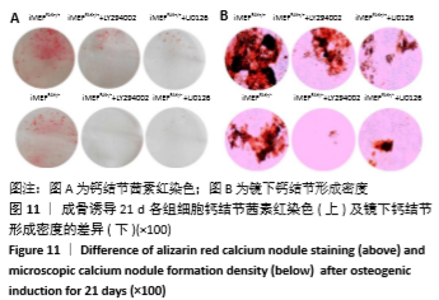
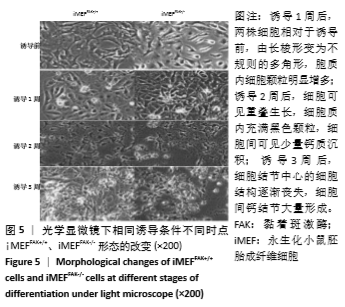
2.2 FAK参与增强iMEF细胞的成骨分化 待贴壁生长的iMEFFAK+/+、iMEFFAK-/-细胞同时融合达80%后,分别加入相同的成骨诱导培养基,在相同的诱导条件下对两株细胞定向诱导,并对细胞形态进行观察。如图5所示,诱导1周后,两株细胞相对于诱导前,由长梭形变为不规则的多角形,胞质内细胞颗粒明显增多;诱导2周后,细胞可见重叠生长,细胞质内充满黑色颗粒,细胞间可见少量钙质沉积;诱导3周后,细胞结节中心的细胞结构逐渐丧失,细胞间钙结节大量形成。分别采用Western blot、RT-PCR 检测诱导前期(诱导前、诱导3 d、诱导1周)iMEFFAK+/+、iMEFFAK-/- 细胞RUNX2蛋白及基因的表达情况(图6,7),其结果显示:诱导前期iMEFFAK-/- 较iMEFFAK+/+ RUNX2蛋白及基因表达量明显下降(P < 0.01)。最后采用茜素红钙结节染色方法分别对诱导21 d后的iMEFFAK+/+、iMEFFAK-/-钙结节染色并在光学显微镜下观察钙结节的密度差异(图8)。结果显示:经过21 d诱导的iMEFFAK-/- 细胞较iMEFFAK+/+ 细胞钙结节沉积量明显下降。结合上述实验,可以得出结论:静默FAK表达可降低Runx2表达,继而降低小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞的成骨效应。即FAK可正向调控Runx2表达继而增强小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞成骨分化,静默FAK表达可明显降低小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞成骨分化效应。 "

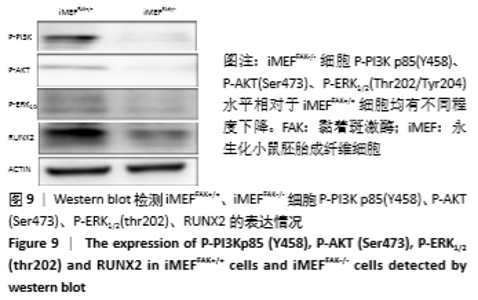
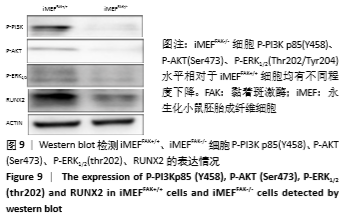
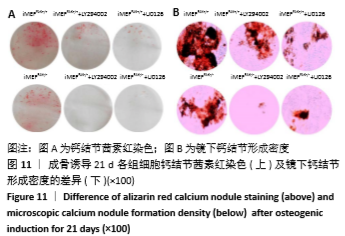
为进一步验证假设:静默FAK表达是否可通过降低PI3K/AKT、ERK1/2磷酸化水平,进而降低RUNX2基因表达水平,最终抑制降低iMEF细胞的成骨分化。接下来,将iMEFFAK+/+、iMEFFAK-/-细胞均匀等量接种于六孔板中,待细胞生长至80%左右加入成骨诱导培养基,处理组分别加入PI3K/AKT抑制剂LY294002和ERK1/2抑制剂U0126同诱导培养基共同诱导(换液后需重新添加,持续抑制)。分别在诱导早期和诱导21 d对成骨效应进行检测,结果示:①加入LY294002处理的iMEFFAK+/+、iMEFFAK-/-细胞与对照组相比早期RUNX2表达量及晚期成骨效应明显下降;②加入U0126处理的iMEFFAK+/+、iMEFFAK-/-细胞与对照组相比早期RUNX2表达量及晚期成骨效应明显下降(图10,11)。因此得出在小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞成骨分化过程中,PI3K/AKT、ERK1/2的磷酸化水平与Runx2及其成骨分化效应成正相关。根据iMEFFAK-/-细胞P-PI3K p85(Y458)、P-AKT(Ser473)、P-ERK1/2(Thr202/Tyr204)水平相对于iMEFFAK+/+细胞均下降,最终得出结论,静默FAK表达可通过降低PI3K/AKT、ERK1/2磷酸化水平,降低Runx2表达水平,进而抑制小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞成骨分化。 "

| [1] 马远征,王以朋,刘强,等.中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2018)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2019,39(1):38-61. [2] 鲁先闯, 张志峰,黄健. 骨髓间充质干细胞修复软骨缺损的应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(19):3093-3088. [3] CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Time to Change the Name! Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(6):1445-1451. [4] ZAJDEL A, KALUCKA M, KOKOSZKA-MIKOLAJ E, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue and Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord. Acta Biochim Pol. 2017; 64(2):365-369. [5] ARTHUR A, ZANNETTINO A, GRONTHOS S. The therapeutic applications of multipotential mesenchymal/stromal stem cells in skeletal tissue repair. J Cell Physiol. 2009;218(2):237-245. [6] HUANG E, BI Y, JIANG W, et al. Conditionally immortalized mouse embryonic fibroblasts retain proliferative activity without compromising multipotent differentiation potential. PLoS One. 2012; 7(2):e32428. [7] Nelson FR, Brighton CT, Ryaby J, et al. Use of physical forces in bone healing. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003; 11(5):344-354. [8] 廉静. Notch信号通路在BMP2诱导iMEF细胞成骨分化中的作用及机制研究[D]. 重庆:重庆医科大学,2016. [9] KOMORI T. Regulation of proliferation, differentiation and functions of osteoblasts by Runx2. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(7):1694. [10] KOMORI T. Molecular mechanism of runx2-dependent bone development. Mol Cells. 2020;43(2):168-175. [11] 陈力莹,范锟铻,王金水,等. Wnt-1基因对人表皮干细胞的分化与增殖的影响研究[J]. 中华损伤与修复杂志,2012,7(1):29-33. [12] 施彦,舒斌,杨荣华,等. Wnt和Notch信号通路在大鼠创面愈合模型中的表达作用[J].中华损伤与修复杂志,2014,9(2):31-34. [13] GU H, HUANG Z, YIN X, et al. Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2015; 339(1):112-121. [14] KAMAMOTO M, MACHIDA J, MIYACHI H, et al. A novel mutation in the C-terminal region of RUNX2/CBFA1 distal to the DNA-binding runt domain in a Japanese patient with cleidocranial dysplasia. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 40(4):434-437. [15] FRANCESCHI RT, XIAO G. Regulation of the osteoblast-specific transcription factor, Runx2: responsiveness to multiple signal transduction pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2003; 88(3):446-454. [16] SCHLAEPFER DD, HAUCK CR, SIEG DJ. Signaling through focal adhesion kinase. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1999;71(3-4):435-478. [17] ZHAO X, GUAN JL. Focal adhesion kinase and its signaling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63(8): 610-615. [18] MITRA SK, SCHLAEPFER DD. Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006; 18(5):516-523. [19] ZACHARY I, ROZENGURT E. Focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK): a point of convergence in the action of neuropeptides, integrins, and oncogenes. Cell. 1992;71(6):891-894. [20] HAKUNO D, TAKAHASHI T, LAMMERDING J, et al. Focal adhesion kinase signaling regulates cardiogenesis of embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(47):39534-39544. [21] SHEN TL, PARK AY, ALCARAZ A, et al. Conditional knockout of focal adhesion kinase in endothelial cells reveals its role in angiogenesis and vascular development in late embryogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2005; 169(6):941-952. [22] SUN X, ZHENG W, QIAN C, et al. Focal adhesion kinase promotes BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation of human urinary stem cells via AMPK and Wnt signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(5): 4954-4964. [23] FURUTA Y, ILIC D, KANAZAWA S, et al. Mesodermal defect in late phase of gastrulation by a targeted mutation of focal adhesion kinase, FAK. Oncogene. 1995;11(10):1989-1995. [24] ILIC D, FURUTA Y, KANAZAWA S, et al. Reduced cell motility and enhanced focal adhesion contact formation in cells from FAK-deficient mice. Nature.1995; 377(6549):539-544. [25] WANG J, XIANG B, DENG J, et al. Inhibition of viability, proliferation, cytokines secretion, surface antigen expression, and adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells by seven-day exposure to 0.5 t static magnetic fields. Stem Cells Int. 2016; 2016:7168175. [26] 胡新永,吕原,杨华清,等.糖皮质激素对膝关节周围成骨细胞一氧化氮合酶和骨重建的影响[J].中华损伤与修复杂志,2008, 3(4):439-444. [27] HSU LW, GOTO S, NAKANO T, et al. The effect of exogenous histone H1 on rat adipose-derived stem cell proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(10): 3417-3425. [28] HU P, ZHU X, ZHAO C, et al. Fak silencing impairs osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells induced by uniaxial mechanical stretch. J Dent Sci.2019;14(3):225-233. [29] HU J, LIAO H, MA Z, et al. Focal adhesion kinase signaling mediated the enhancement of osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells induced by extracorporeal shockwave. Sci Rep.2016; 6:20875. [30] 扎拉嘎胡,徐忠伟,兰晓霞,等. 层粘连蛋白促脐带间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化与黏着斑激酶表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2011, 15(6):29-33. [31] XIE H, CAO T, FRANCO-OBREGON A, et al. Graphene-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation Is Mediated by the Integrin/FAK Axis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(3):574. [32] YUAN C, GOU X, DENG J, et al. FAK and BMP-9 synergistically trigger osteogenic differentiation and bone formation of adipose derived stem cells through enhancing Wnt-beta-catenin signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 105:753-757. [33] WU J, ZHAO J, SUN L, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 mediates mechanical tension-induced osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via FAK by sponging miR-138. Bone. 2018;108: 62-70. [34] LIU Y, MA Y, ZHANG J, et al. MBG-Modified beta-TCP Scaffold Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cells Adhesion and Osteogenic Differentiation via a FAK/MAPK Signaling Pathway. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017; 9(36):30283-30296. [35] THORPE LM, YUZUGULLU H, ZHAO JJ. PI3K in cancer: divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015; 15(1):7-24. [36] YU JS, CUI W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development. 2016;143(17):3050-3060. [37] GU YX, DU J, SI MS, et al. The roles of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in regulating MC3T3-E1 preosteoblast proliferation and differentiation on SLA and SLActive titanium surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013; 101(3):748-754. [38] CHEN LL, HUANG M, TAN JY, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway involvement in the osteogenic effects of osteoclast culture supernatants on preosteoblast cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(19-20):2226-2232. [39] ZHANG Y, YANG JH. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by oxidative stress mediates high glucose-induced increase of adipogenic differentiation in primary rat osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(11): 2595-2602. [40] GARTY J, KAUPPI M, KAUPPI A. Differential responses of certain lichen species to sulfur-containing solutions under acidic conditions as expressed by the production of stress-ethylene. Environ Res. 1995; 69(2):132-143. [41] TWIGG SR, VORGIA E, MCGOWAN SJ, et al. Reduced dosage of ERF causes complex craniosynostosis in humans and mice and links ERK1/2 signaling to regulation of osteogenesis. Nat Genet. 2013; 45(3): 308-313. [42] BAI B, HE J, LI YS, et al. Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway during the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on substrates modified with various chemical groups. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:361906. [43] XU L, MENG F, NI M, et al. N-cadherin regulates osteogenesis and migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;40(3):2533-2539. [44] MIRAOUI H, OUDINA K, PETITE H, et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 promotes osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal cells via ERK1/2 and protein kinase C signaling. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284(8):4897-4904. |
| [1] | Yu Xingge, Lin Kaili. Application of nanocomposite hydrogels in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5441-5446. |
| [2] | Liu Hao, Liu Jun, Rui Yongjun, Tang Fenglin, Lu Miao, Ding Tao. Co-transfection by Nell-1 and Noggin-shRNA promotes osteoblast differentiation of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4966-4970. |
| [3] |
Zou Gang, You Qi, Shen Mengjie, Zhang Jun, Tang Jingfeng, Jin Ying, Liu Yi.
In vitro construction of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cell sheet and its osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4023-4027. |
| [4] |
Li Junqing, Wu Jiayuan.
Effect of mechanical stimulation on dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4054-4059. |
| [5] | Zhao Yilang, Liu Tao, Yang Huilin, He Fan. Extracellular matrix improves antioxidant capacity of human umbilical cord stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3953-3958. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||