Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (14): 2206-2212.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.14.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with lycopene on immune function of D-galactose induced aging mice
Liu Jia1, Wang Yi-zhong1, Cui Xiao-lan2, Shi Han1, Li Qian-qian1, Wang Lin-lin1
- 1Department of Hematology and Endocrinology, Aerospace Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing 100049, China; 2Pharmacology Laboratory, Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2014-02-03Online:2014-04-02Published:2014-04-02 -
Contact:Wang Yi-zhong, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Hematology and Endocrinology, Aerospace Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing 100049, China -
About author:Liu Jia, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Hematology and Endocrinology, Aerospace Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing 100049, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Fund of the Aerospace Clinical Medical College of Peking University, No. 201209
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jia, Wang Yi-zhong, Cui Xiao-lan, Shi Han, Li Qian-qian, Wang Lin-lin. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells combined with lycopene on immune function of D-galactose induced aging mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(14): 2206-2212.
share this article
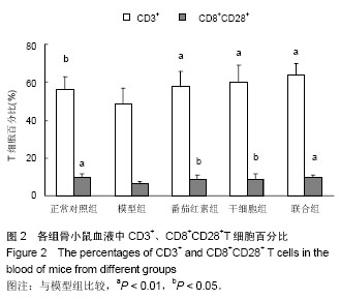
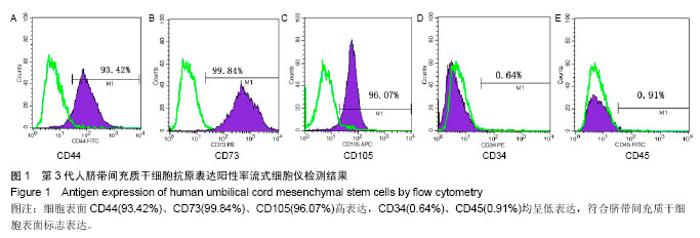
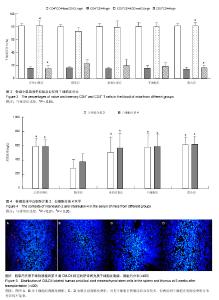
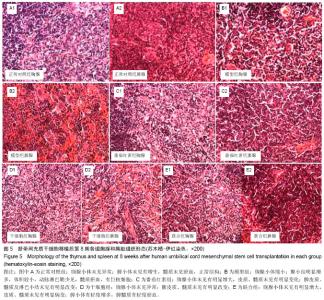
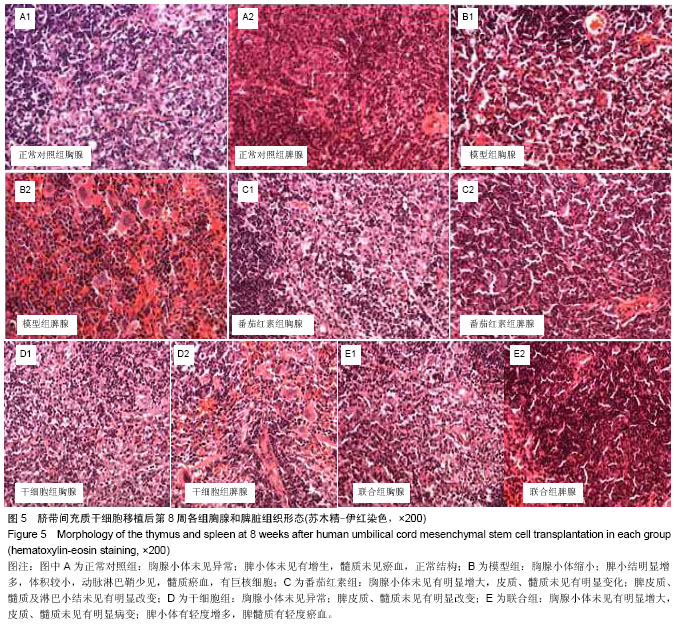
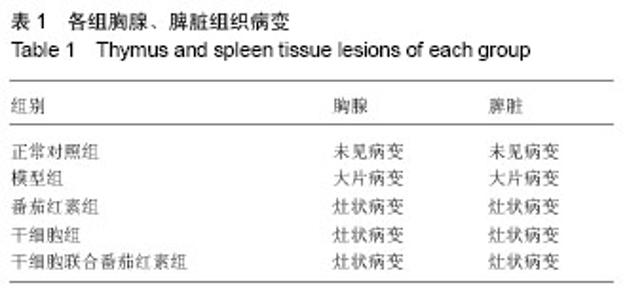
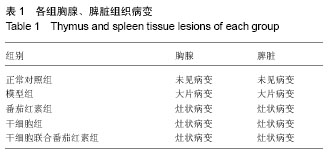
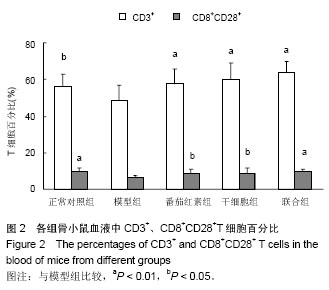
2.1 实验动物数量分析 所有动物均进入结果分析,中途无脱失。 2.2 脐带间充质干细胞的鉴定 流式细胞术检测干细胞表面CD44(93.42%)、CD73(99.84%)、CD105(96.07%)高表达,CD34(0.64%)、CD45(0.91%)均呈低表达,符合脐带间充质干细胞表面标志表达[5-6](图1)。 2.3 血清中衰老免疫相关T淋巴细胞百分比测定 与模型组相比,正常对照组及3个治疗组CD3+、CD8+CD28+T细胞百分比明显升高,且差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),3个治疗组间比较差异不显著(P > 0.05,图2)。 根据CD44和CD62L表达高低可将T细胞分为初始细胞和记忆细胞两个细胞亚群:与模型组相比,正常对照组及3个治疗组初始性CD4(CD4+CD44lowCD62Lhigh)T细胞百分比升高,记忆性CD4+(CD4+CD44high)T细胞百分比降低,但差异不显著(P > 0.05),3个治疗组间相比差异不显著(P > 0.05);与模型组相比,正常对照组及联合组初始性CD8+(CD8+CD44lowCD62Lhigh)T细胞百分比升高,记忆性CD8+(CD8+CD44high)T细胞百分比降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),而干细胞组及番茄红素组初始性CD8+(CD8+CD44lowCD62Lhigh)T细胞百分比升高,记忆性CD8+(CD8+CD44high)T细胞百分比降低,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),各治疗组间比较,差异无显著性意义 (P > 0.05,图3)。 2.4 血清中白细胞介素2、白细胞介素4测定 模型组血清白细胞介素2、白细胞介素4水平与正常对照组及3个治疗组相比明显降低,且有差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),其中联合组血清白细胞介素2、白细胞介素4水平已接近正常对照组,各治疗组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,图4)。"
| [1] Tarazona R, Solana R, Ouyang Q, et al. Basic biology and clinical impact of immunosenescence. Exp Gerontol. 2002; 37(2-3):183-189. [2] De Bruyn C, Najar M, Raicevic G, et al. A rapid, simple, and reproducible method for the isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells from Wharton's jelly without enzymatic treatment. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(3):547-557. [3] Li TX, Yuan J, Chen Y,et al. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord tissue into odontoblast-like cells using the conditioned medium of tooth germ cells in vitro. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:218543. [4] Kim DW, Staples M, Shinozuka K, et al. Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Phenotypic Characterization and Optimizing Their Therapeutic Potential for Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(6): 11692-11712. [5] Li CH, Sun L, Zhang YJ, et al. Expression of Galectins in umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2013;45(3):452-457. [6] McElhaney JE, Effros RB. Immunosenescence: what does it mean to health outcomes in older adults? Curr Opin Immunol. 2009;21(4):418-424. [7] Zanussi S, Serraino D, Dolcetti R, et al. Cancer, aging and immune reconstitution. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013; 13(9):1310-1324. [8] Lee N, Shin MS, Kang I. T-cell biology in aging, with a focus on lung disease. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67(3): 254-263. [9] Dorshkind K, Montecino-Rodriguez E, Signer RA. The ageing immune system: is it ever too old to become young again? Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9(1):57-62. [10] Nikolich-Zugich J. T cell aging: naive but not young. J Exp Med. 2005;201(6):837-840. [11] Dock JN, Effros RB. Role of CD8 T Cell Replicative Senescence in Human Aging and in HIV-mediated Immunosenescence. Aging Dis. 2011;2(5):382-397. [12] Moro-García MA, Alonso-Arias R, López-Larrea C. Molecular mechanisms involved in the aging of the T-cell immune response. Curr Genomics. 2012 ;13(8):589-602. [13] Entrican G, Wattegedera S, Wheelhouse N, et al. Immunological paradigms and the pathogenesis of ovine chlamydial abortion. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010;64(4): 287-294. [14] Bradley MB, Cairo MS. Cord blood immunology and stem cell transplantation. Hum Immunol. 2005;66(5):431-446. [15] 许婷婷,周艳华,李军.人脐带间充质干细胞对小鼠自然衰老过程中骨髓脂肪化的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2010,26(4): 816-818. [16] Maitra B, Szekely E, Gjini K, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells support unrelated donor hematopoietic stem cells and suppress T-cell activation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2004; 33(6):597-604. [17] Bancroft JH. Sex and aging. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(8): 820-822. [18] 马建慧,郑兴征,陈虹,等.番茄红素对D-半乳糖致衰老小鼠的抗氧化作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2010,30(21):3142-3143. [19] 耿珊珊,蔡东联. 番茄红素对免疫功能的调节作用[J].中国临床康复,2005,27(9):148-149. [20] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30. [21] Hirokawa K, Utsuyama M, Hayashi Y, et al. Slower immune system aging in women versus men in the Japanese population. Immun Ageing. 2013;10(1):19. [22] Chao YH, Wu HP, Chan CK, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:759503. [23] Klyushnenkova E, Mosca JD, Zernetkina V, et al. T cell responses to allogeneic human mesenchymal stem cells: immunogenicity, tolerance, and suppression. J Biomed Sci. 2005;12(1):47-57. [24] Jiang WH, Ma AQ, Zhang YM, et al. Migration of intravenously grafted mesenchymal stem cells to injured heart in rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2005;57(5):566-572. [25] Weinberger B, Lazuardi L, Weiskirchner I, et al. Healthy aging and latent infection with CMV lead to distinct changes in CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell subsets in the elderly. Hum Immunol. 2007;68(2):86-90. [26] Ferrando-Martínez S, Ruiz-Mateos E, Hernández A, et al. Age-related deregulation of naive T cell homeostasis in elderly humans. Age (Dordr). 2011;33(2):197-207. [27] Moro-García MA, Alonso-Arias R, López-Larrea C. When Aging Reaches CD4+ T-Cells: Phenotypic and Functional Changes. Front Immunol. 2013;4:107. [28] 李彦红,刘颖,秦川.免疫衰老与T、B细胞改变的相关研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2012,22(6):65-71. [29] Ribot JC, Debarros A, Mancio-Silva L, et al. B7-CD28 costimulatory signals control the survival and proliferation of murine and human γδ T cells via IL-2 production. J Immunol. 2012;189(3):1202-1208. [30] Karanfilov CI, Liu B, Fox CC, et al. Age-related defects in Th1 and Th2 cytokine production by human T cells can be dissociated from altered frequencies of CD45RA+ and CD45RO+ T cell subsets. Mech Ageing Dev. 1999 ;109(2): 97-112. [31] Sakata-Kaneko S, Wakatsuki Y, Matsunaga Y, et al. Altered Th1/Th2 commitment in human CD4+ T cells with ageing. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000;120(2):267-273. [32] 杨德洪,魏勇.细胞因子Th1/Th2偏移与运动及衰老的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(44):8350-8354. [33] Arranz L, Lord JM, De la Fuente M. Preserved ex vivo inflammatory status and cytokine responses in naturally long-lived mice. Age (Dordr). 2010;32(4):451-466. [34] Law S, Chaudhuri S. Mesenchymal stem cell and regenerative medicine: regeneration versus immunomodulatory challenges. Am J Stem Cells. 2013;2(1):22-38. [35] Le Blanc K, Ringdén O. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells and clinical experience. J Intern Med. 2007;262(5): 509-525. [36] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005; 105(4):1815-1822. [37] 卢锋,乔玲,马远方.番茄红素对实验小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2006,22(2): 151-155. [38] 潘喜华,仲伟鉴,肖萍,等. 番茄红素调节免疫作用及机制研究[J]. 上海预防医学杂志,2006,18(6):261-263. [39] Briviba K, Kulling SE, Möseneder J, et al. ects of supplementing a low-carotenoid diet with a tomato extract for 2 weeks on endogenous levels of DNA single strand breaks and immune functions in healthy non-smokers and smokers. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25(12):2373-238. [40] Watzl B, Bub A, Briviba K, et al. Supplementation of a low-carotenoid diet with tomato or carrot juice modulates immune functi-ons in healthy men. Ann Nutr Metab. 2003; 47(6):255-261. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [6] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [7] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||