Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (21): 3407-3414.doi: 10.12307/2023.133
Previous Articles Next Articles
Antibacterial mechanism and application of nanomaterials in oral infectious diseases
Luo Tingyan1, Gu Yu1, 2, Qin Xiaofei1
- 1Zunyi Medical University Zhuhai Campus, Zhuhai 519041, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guizhou Provincial University Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-05Accepted:2022-05-21Online:2023-07-28Published:2022-11-24 -
Contact:Gu Yu, Master, Associate professor, Zunyi Medical University Zhuhai Campus, Zhuhai 519041, Guangdong Province, China; Guizhou Provincial University Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China Qin Xiaofei, PhD, Associate professor, Zunyi Medical University Zhuhai Campus, Zhuhai 519041, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Luo Tingyan, Zunyi Medical University Zhuhai Campus, Zhuhai 519041, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32060227 (to QXF); Local Universities, National University Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program, No. 20210661041 (to LTY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Tingyan, Gu Yu, Qin Xiaofei. Antibacterial mechanism and application of nanomaterials in oral infectious diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3407-3414.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
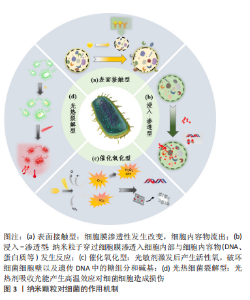
2.1 纳米材料的抗菌机制与特点 利用不同材料(如高分子材料、无机材料硅化物、金属材料、聚合物等)所制备的纳米颗粒,其形态、大小、表面化学性质等均可进行精确地控制,可组成金属纳米颗粒(如金纳米棒、金纳米笼、磁性纳米颗粒)、多聚物纳米颗粒(如壳聚糖纳米颗粒)、硅纳米颗粒(如介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒)[4]、碳量子点、碳纳米管、脂质体和黑磷纳米片等多种功能化的纳米颗粒,使其具备各种独特性能[5]。在纳米材料本身所具有的抗菌性能基础上,赋予了纳米材料运载药物的能力,同时通过表面修饰靶向性配体物质,使其具有靶向抗菌的特性。此外,一些智能纳米材料可根据细菌感染的微环境(如pH值改变、特定毒素和酶的表达、产酸或者温度变化),响应性刺激装载药物的释放,从而达到控制药物和定点原位释放的效果,进而提高药效和满足不同情况下的抗菌需要[6]。根据抗菌纳米颗粒对细菌的作用机制,可将其分为表面接触型、浸入-渗透型、催化氧化型以及光热细菌裂解型,见图3。"
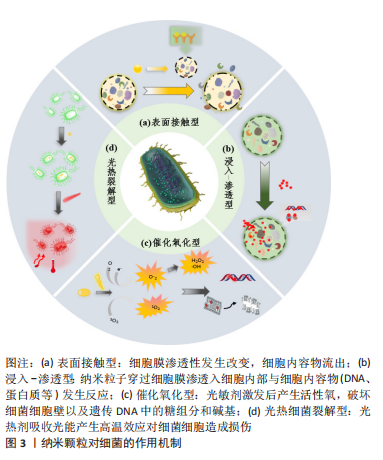
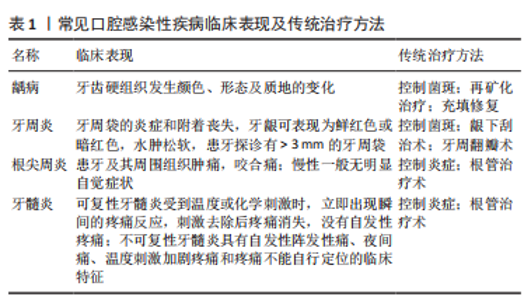
2.1.1 表面接触型 表面接触型的作用对象是细菌的细胞膜。当具有抗菌性能的纳米粒子与细菌接触时,纳米材料自身携带的或产生的正电荷会使其吸附在带有负电荷的细胞膜上 [7]。常见的带有正电荷的纳米颗粒有壳聚糖纳米颗粒、季铵盐类纳米颗粒以及铜等金属纳米颗粒。由于抗菌纳米粒子聚集在细胞表面,细胞膜的完整性会遭到一定的破坏,细胞壁外膜上脂多糖层之间的相互作用被减弱,使大部分的脂多糖和蛋白质从细菌中释放,这些变化增强了细胞渗透性,细胞内外物质的交换受到影响[8]。如果外膜发生破损,细胞内的物质则会流出。 有学者测定了经银纳米颗粒处理的大肠杆菌的蛋白质和还原糖浓度,发现与对照组相比,银纳米颗粒能促进蛋白质的渗透,当处理时间达到4 h时,蛋白质的渗透增加了57%,证实了细胞膜破裂[9]。同时,还原糖的浓度降低,证实了存在泄漏,且随着处理时间的延长,还原糖的泄漏速度会加快。此外,还有研究表明,当纳米材料的表面积越大、电荷密度越高时,与带负电荷的细菌细胞表面的相互作用程度就越大,抗菌活性越高 [10]。 2.1.2 浸入-渗透型 浸入-渗透型针对的目标是蛋白质、酶、遗传物质等细胞内容物,通过与细胞内容物的相互作用使细胞失活。抗菌材料在溶液中释放出细微抗菌粒子或金属离子,如银纳米颗粒、过氧化锌纳米颗粒,由于这些纳米粒径小于 10 nm,Ag+、Zn2+等尺寸非常小的物质会浸入细胞并渗透到细胞内部,与细胞中的物质发生反应[11]。许多研究推测Ag+会与蛋白质巯基发生反应以使蛋白质失活[9,12-14];抑制细菌呼吸链脱氢酶活性;还剥夺了细菌复制DNA的能力,最终导致细胞死亡。在抗菌过程中,抗菌纳米粒子不断地与细胞内的蛋白质等相互作用,从而引起细胞形态、功能以及细胞之间的关系发生改变。KANG等[15]在Ag+处理的大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌每一个样品中都检测到至少5种蛋白质的表达降低。有学者认为,当Ag+进入细胞后会聚集在一起,形成电子致密颗粒,原本应该自由分散的DNA在电子-光区域变成了浓缩形式[16],但DNA只能在松弛的状态下有效复制,当它处于浓缩状态时则会失去复制能力[17],说明DNA会被银纳米颗粒损伤。 2.1.3 催化氧化型 催化氧化型灭菌,又称为活性氧灭菌,是目前研究最广泛,同时也是应用最广泛的纳米材料抗菌机制之一。活性氧是生物有氧能量代谢的副产物,细胞内的活性氧会在有氧条件下,通过氧分子的连续单电子运输产生超氧化物、过氧化氢和毒性剧烈的羟自由基[18]。少量的活性氧可以由细胞中的线粒体和酶产生,而大量的活性氧则是通过细胞外的纳米材料产生。它们可以向分子氧提供电子,并能引发自由基反应,产生活性氧,由此引发自由基的一系列反应,对细胞产生损害。例如,氧化锌纳米颗粒和二氧化钛纳米颗粒产生活性氧的原理是[19-25]:当氧化锌和二氧化钛纳米材料暴露在紫外光下时,由于电子跃迁而产生电子-空穴对,电子-空穴对扩散到材料表面并与H2O分子或其他含有氧的分子进行一系列氧化还原反应。空穴在价带中电离并氧化H2O分子,产生·OH;电子与氧气发生反应,产生一系列的中间体,例如H2O2、HO2·、·O2-等。活性氧进入细胞后,会引起氧化应激反应,而氧化应激反应在细胞内可造成多种损坏,最终导致细胞死亡。目前的研究提出活性氧主要通过2种机制使细菌失活:①将细菌细胞壁破坏从而引起细胞内容物的漏出或损伤正常的膜转运系统功能和损毁相关蛋白酶的正常结构使其失活[26];②DNA损伤:活性氧会破坏遗传DNA中的糖组分和碱基,进而破坏其双螺旋结构,使得细菌的正常增殖和生理代谢功能受到破坏[27]。 2.1.4 光热细菌裂解型 在光热细菌裂解过程中,光热剂首先被引入感染部位,然后选择性地与细菌黏附,通过使用适当波长的光进行照射,光热剂吸收光能,并通过周围环境中的非辐射弛豫迅速将光能转化为热能,产生高温效应,对细菌细胞造成难以修复的损伤,最终导致细菌死亡[28]。在光热抗菌过程中,光热剂起着至关重要的作用,常见的如金纳米颗粒,由于金纳米结构的局域表面等离激元共振(loca-lized surface plasmon resonance,LSPR)效应,这种纳米结构吸收的辐射会被有效地转化为热量,从而导致病原体受到破坏[29-31]。由于皮肤组织对近红外辐射的吸收微弱,近红外辐射能够穿透正常皮肤组织而不会造成太大伤害,因此金纳米颗粒作为光热抗菌的光热剂被广泛用于局域的抗菌治疗,并且其还有着抗氧化性等许多特性。WU等[32]开发了一种硅涂层金-银纳米笼(Au-Ag@ SiO2NCs),结合了金纳米材料的光热效应和银离子的持续释放能力,通过近红外激光的照射用于抗感染治疗。研究发现,当Au-Ag@ SiO2NCs质量浓度为50 mg/mL时,它具有良好的光热性质特性,10 min的近红外光照射下,温度从20.7 ℃上升到了57.4 ℃;体外和体内实验证实:在近红外激光照射下,Au-Ag@ SiO2NCs可以有效抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的生长;在金银纳米笼表面应用SiO2涂层,不仅使药物作用的时间延长,应用12 h仍具有较好的杀菌能力,同时也提高了生物相容性。 2.1.5 联合作用 许多纳米材料并不只是通过单一的一种抗菌机制起效。如常用的纳米银,其比表面积极大,具有明显的宏观隧道效应和表面效应,这种高活性的纳米银微粒可以同时通过催化氧化和浸入-渗透2种不同的作用机制对细菌进行抑制。 使用金属、碳类和聚合物类的复合材料进行光热抗菌比仅使用单一材料的效果更好。除了产生热量外,它们还具有活性氧生成、酶活性(蛋白酶)、离子释放(银离子)促进以及表面电荷和细菌细胞壁(膜)电荷之间静电吸引等特性, 这些特性加上光热抗菌,有助于彻底破坏细菌细胞壁(膜),增强抗菌效果。因此,通过设计和制备多功能复合纳米材料,可以实现多种治疗方法的联合治疗。例如,二硫化钼(MoS2)作为纳米材料具有优异的光热性能和较大的负载药物比表面积,由于其独特的化学和物理特性,可应用于多种生物医学领域,包括生物成像[33]、癌症[34-35]、抑菌治疗等[36-37]。研究人员利用带正电荷的季化壳聚糖对二硫化钼纳米薄片进行改性,制备出一种含有抗生素的光热-载药联合抗菌平台[38]。 有研究提出了一种新的共轭聚合物,经过季铵盐的修饰,共轭聚合物上的季铵基团与细菌膜上所带有的负电荷发生相互作用,提高了局部的抗菌效率,共轭主链在产生活性氧的同时,也会产生热量,从而对细菌造成损害[39]。在近红外激光下同时具有光动力和光热效应,从而实现单光源双光疗。 通过上述的抗菌机制,使得纳米材料的抗菌谱广、抗菌能力强、稳定性好、抗耐药性强,与传统抗菌剂相比,纳米材料具有更长的作用时间、更好的耐热性和生物安全性,是治疗和预防口腔感染的有效方法。目前有大量纳米抗菌剂抑制口腔致病菌生长、预防并控制口腔感染性疾病的发生和发展方面的研究。 2.2 纳米材料在常见口腔感染性疾病中的研究现状 口腔常见的致病菌主要有变异链球菌、牙龈卟啉单胞菌和金黄色葡萄球菌等,这些口腔内的微生物聚集所生成的菌斑会导致龋病、牙周炎、根尖周炎、牙髓炎、义齿性口炎和口腔溃疡等一系列口腔疾病[40], 见表1。针对这些口腔致病菌,研究者制备了多种功能各异的纳米药物,通过上述的一系列抑菌机制,能有效抑制口腔致病菌的生长繁殖,预防和控制口腔感染性疾病的发生和发展。"
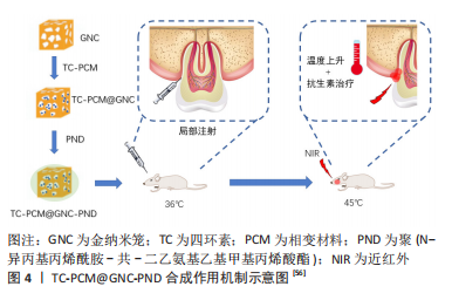
2.2.1 龋病 龋病是最为常见的口腔慢性感染性疾病,其本质是由多种致龋因素造成的牙体硬组织脱矿与再矿化循环的不平 衡[41],其中又以细菌因素最为重要。菌斑生物膜是龋齿形成的起始因素,为细菌的生存和繁殖提供了天然有利的场所和防护屏障[4]。链球菌、乳酸杆菌和放线菌是龋病的病原菌[9]。变异链球菌则是公认的主要致龋菌,它不仅能酵解糖,产生大量酸,破坏牙釉质,还能产生胞外多糖,促进菌斑生物膜的形成和沉积。现代口腔医学的理念是注重早期的预防而不是侵入后的修复,故寻求特效药物作为龋病的预防制剂成为了防龋研究的热点。 目前控制菌斑生物膜是防龋研究的重点。通过抑制细菌的群体感应(quorum sensing,QS)抑制菌斑生物膜的形成是一种有效的预防和治疗龋病的方法。群体感应是一种细胞-细胞间的通讯机制[42],是细菌进行种间或种内交换信息的一种信号转导机制,当群体密度达到一定阈值时,它能够自发产生和释放一些信号分子,通过细胞受体识别信号,调控基因表达,参与许多重要的生物学过程,群体感应现象是生物膜形成过程中十分重要环节之一,因此对群体感应的干扰或抑制可以阻断细菌生物膜的形成,但并不会对细菌的生存产生压力,因此不会过度诱导抗生素耐药性的产生。近期,KANG等[43]设计了可以与Ca2+结合从而锚定在牙齿表面的聚(丙交酯-共-乙交酯)(PLGA/PBMP)微米粒子,由于牙齿表面的主要组成物质是羟基磷灰石,因此,含有磷酸根基团的微米粒子与含有Ca2+的羟基磷灰石结合,通过装载并释放群体感应抑制剂呋喃酮C-30对菌斑生物膜的形成进行抑制。实验证明,该粒子可锚定在牙齿的表面,并有效抑制变异链球菌的生长及其在羟基磷灰石表面形成生物膜的能力,从而阻断龋的形成。 法尼醇(Farnesol)是一种天然的具有防龋作用的物质,在局部使用法尼醇可以有效阻止菌斑生物膜的累积,使菌斑生物膜中多聚糖的含量降低,减弱变异链球菌的产酸能力[44]。然而由于法尼醇几乎不溶于水,它们无法接触到唾液覆盖的牙齿表面,并且更难在牙齿表面长时间停留,限制了其应用,纳米材料的应用使这个问题迎刃而解。赵霞等[45]利用一种含亲水端的嵌段聚合物甲氧基聚乙二醇-聚乳酸(mPEG-PDLLA),制备了可装载法尼醇的纳米胶束,该纳米胶束可作为不同种类药物的载体材料,以提高非水溶性药物的亲水能力,并且当采用200 μmol/L Farnesol/mPEG-PDLLA纳米胶束作用于菌斑时,可观察到菌斑在药物作用下被分散为单个的微小菌落,而采用 400 μmol/L法尼醇纳米胶束时则发现药物明显破坏了部分变异链球菌的表面,同时胞外基质受到破坏,细菌数量明显减少,结果表明Farnesol/mPEG-PDLLA纳米胶束对变异链球菌具有良好的抑制与杀伤作用。 在其他一些研究中同样也将法尼醇用作抗菌药物[46],并利用牙菌斑生物膜中pH值较低的特点开发了新的pH敏感型纳米载药系统。在此纳米体系中,以带正电荷的聚二甲胺甲基丙烯酸乙酯作为外壳与羟基磷灰石有很强的结合力,而pH值敏感的疏水核由二甲胺甲基丙烯酸乙酯、甲基丙烯酸丁酯和2-丙基丙烯酸的聚合物组成。当牙菌斑生物膜中的pH值降低时,载体纳米颗粒中的二甲胺甲基丙烯酸乙酯和2-丙基丙烯酸迅速质子化,从而使纳米颗粒的结构稳定性下降并释放药物法尼醇。实验结果表明,负载法尼醇的纳米颗粒对变形链球菌生物膜的破坏力显著高于游离的法尼醇。 近年来,抗菌光动力疗法(antibacterial photodynamic therapy,aPDT)引起了口腔医学研究者极大的兴趣,其抗菌机制属于催化氧化型。一些纳米粒子自身就可作为光敏剂,或作为载体装载光敏剂通过催化氧化机制对变异链球菌进行有效抑制。使用纳米粒子装载光敏剂不仅解决了一部分光敏剂水溶性较差的问题,并且可以高效地靶向递送光敏剂至细菌作用部位,缓慢释放药物,最大程度地发挥其抗菌药效。例如,甲苯胺蓝作为光敏剂在口腔湿润环境下非常容易聚集,多聚体的形成对光动力作用效果将产生很大的负面影响,这会降低活性氧的产量和寿命,特别是单线态活性氧,使光敏效果下降,对甲苯胺蓝在光动力疗法中的推广应用造成阻碍[47]。石广立[48]制备出碳纳米管,其含有庞大的表面空间,可高效运载高浓度的甲苯胺蓝,抑制了甲苯胺蓝多聚体形成,进而提高了光动力效果,使得该纳米粒子对变异链球菌的抑制效果显著。 复合树脂材料是临床上被广泛应用的龋病治疗充填修复材料[49],但与牙釉质和其他牙齿修复材料相比,复合树脂表面更容易集聚微生物形成生物膜,导致继发龋[50]。为了预防充填树脂与牙齿表面交界处发生脱矿,研究人员制备了能够释放钙离子和磷酸盐的纳米填料,如无水磷酸氢钙纳米颗粒或无定形磷酸钙纳米颗粒,在体外实验中,纳米填料使复合树脂在pH值降低时释放钙离子和磷酸盐,可促进再矿化、提高pH值,达到良好的抗龋效果。此外,材料所释放的氟离子也可减少脱矿,抑制龋齿的发展[49]。 2.2.2 牙周炎 牙周炎的发病率位居第二,仅次于龋病[51],其临床特点为牙槽骨的破坏吸收,严重者可导致牙齿的松动脱落。第四次全国口腔健康流行病学调查显示,大多数中老年人的牙周组织均处于炎症状态[52]。 牙龈卟啉单胞菌(Porphyromonasgingivalis)在牙周炎的发生发展过程中起到重要的作用,是慢性牙周炎的主要致病菌[53]。一些实验人员通过临床研究发现,在使用含纳米银镀层药物4周后,受试者口腔中包括牙龈卟啉单胞菌在内的牙周致病菌数目明显减少,且维持在一个稳定且较低的水平[54]。目前对于牙周炎的治疗临床上多采用洁治术,但机械性的处理方法可能会产生牙齿硬组织损伤、牙龈刺激肿胀等不良反应。而采用纳米光热抗菌疗法则因其尺寸小,能更容易进入根分叉、牙周袋等器械难以触及的部位,在不损伤口腔组织的前提下拥有更好的治疗效果。一些实验人员发现,45 nm 金纳米粒子(gold nanoparticles,AuNPs)可以调节巨噬细胞极化,影响人牙周韧带细胞的分化,使抗炎效果显著,改善牙周的微环境[55]。还有学者设计了pH 响应性季铵壳聚糖脂质体纳米粒子,其能够良好地抑制菌斑生物膜形成和菌群的增殖,并且与人牙周韧带成纤维细胞之间也表现出良好的生物相容性,同时还可抑制牙槽骨的吸收[55]。张灵玲[56]构建了基于金纳米笼(gold nanocage,GNC)的近红外响应性光热/药物协同抗菌体系(TC-PCM@GNC-PND),见图4。"
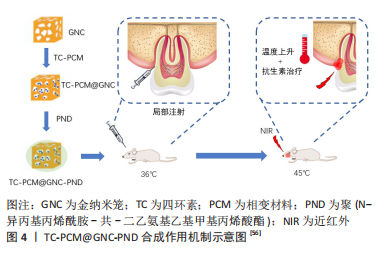
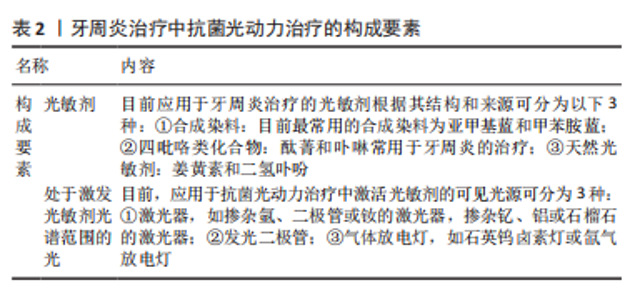
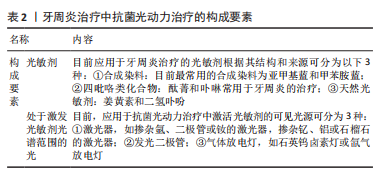
在该研究中金纳米笼内部为空心状态可负载药物,通过将相变材料(phase-change material,PCM)与药物一起“填充”到金纳米笼空腔内,利用相变材料的温度响应性作为“温敏开关”来控制药物的释放。研究者将相变材料和四环素(tetracyclines,TC)熔化并一起填充到金纳米笼内,然后在金纳米笼表面进行修饰以封闭表面孔洞。通过相变材料“液固相转变”和表面的温敏性高分子聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-共-二乙氨基乙基甲基丙烯酸酯)[poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate),PND]的 “线团-球体转变”形成双重温敏性开关,从而完成药物的按需释放,同时实现光热治疗与药物释放的精准协同,达到较为理想的抗菌效果。表面温敏性高分子PND 的修饰,也使得TC-PCM@GNC-PND 具有形成凝胶的能力,能够延长药物在感染部位的存留时间。 牙周炎治疗中抗菌光动力治疗的构成要素,见表2。"

2.2.3 其他 发生牙髓根尖周疾病时,革兰阴性厌氧菌是根管感染的优势菌。彻底清除根管内的细菌及感染物质是成功治疗牙髓根尖周疾病的关键[57]。根管治疗是治疗牙髓、根尖周炎等疾病的主要方法,根管充填则是根管治疗的一个重要环节,使用具有杀菌或抑菌效果的根管充填糊剂可以提高根管治疗的效果[58]。纳米羟基磷灰石根充糊剂就具有较好的抑菌性能。纳米羟基磷灰石的晶体结构与骨的成分相似,它通过氢键与人体细胞膜表面的多糖和蛋白质结合,具有良好的生物相容性、骨引导性和良好的根管封闭能力。游滢滢等[59]通过对纳米羟基磷灰石的体外实验发现其不会引起溶血反应,倒置相差显微镜观察细胞形态,阴性对照组与纳米羟基磷灰石组均表现为无毒性,说明定性评价纳米羟基磷灰石材料的细胞毒性为合格,证明了其良好的生物相容性。此外,纳米羟基磷灰石具有不同于大颗粒羟基磷灰石的独特性质,它具有更大的表面积,对细菌有着较强的吸附能力,并能吸附大量与细菌代谢有关的酶,干扰细菌的代谢。纳米羟基磷灰石根充糊剂中还可以加入Ag+、Cu2+和Zn2+等金属离子或者抗生素等作为抗菌活性因子[60],以羟基磷灰石为载体制成抗菌效果更加显著的根充糊剂,有效提高根管治疗的效果[58]。王建平等[61]建立的粪肠球菌、白色念珠菌感染根管模型,通过使用琼脂扩散法测定纳米羟基磷灰石对2种菌的抑菌效果,结果显示:纳米羟基磷灰石的抑菌效果都较为理想。 随着种植技术的发展,使用种植体对缺失牙进行修复已成为口腔修复的一种重要手段。但口腔中原本就存在着多种细菌,种植体穿过皮肤软组织在骨组织中固位,由于经皮部位直接暴露于外界环境中,在种植体植入和愈合的过程中都极易受到细菌的感染,使得经皮生物学的封闭遭到破坏,导致种植失败[62]。临床上制作种植体的材料多采用医用级钛及其合金,其具有生物相容性好、耐腐蚀性好、低免疫原性等优点,但由于纯钛表面的生物惰性等特点,细菌会与成骨细胞等竞争黏附在钛植入体表面,并最终生成菌斑生物膜。这种潜在致病菌的黏附和扩散与种植体周围的炎症变化有着直接关系,可严重影响骨整合,导致种植义齿失败[63]。PENG等[64]构建了拥有亲水性表面的TiO2纳米管,在制备TiO2纳米管阵列的过程中,一些O原子被F原子取代,F原子在退火温度升高时从TiO2晶格中逃逸出来,导致氧空位,而氧空位更容易被水分子吸引,形成亲水性区域[65-66]。亲水表面促进了成骨细胞黏着斑的形成,加速了成骨细胞的早期黏附,随后增殖、分化,减少了其他细菌黏附定殖。 此外,亲水性TiO2纳米管的表面可促进纤连蛋白黏附,进一步加速了成骨细胞的定殖,并通过与细胞表面受体的相互作用改善早期成骨。种植体经过表面纳米化处理或加入纳米材料,有效地抑制了常见口腔感染细菌的定植与生长,降低了由于种植义齿而发生感染的可能性。 纳米材料在口腔感染性疾病治疗中的应用汇总,见表3[43,45,48,56,60,67-82]。"

| [1] 李洋洋,胡天琦,顾中一.纳米齿科学在抗菌方面的应用进展[J].口腔医学,2017,37(10):950-953. [2] NORRBY SR, NORD CE, FINCH R, et al. Lack of development of new antimicrobial drugs: a potential serious threat to public health. Lancet Infect Dis. 2005;5(2):115-119. [3] JAMES P, WORTHINGTON HV, PARNELL C, et al. Chlorhexidine mouthrinse as an adjunctive treatment for gingival health. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;3(3):CD008676. [4] 强立,冯永海,刘磊.金基纳米结构光热抗菌研究进展[J].科学通报,2022,67(1):64-76. [5] 缪婧,刘畅,王旭,等.纳米材料在口腔医学中的应用研究[J].医学信息,2019,32(12):34-36. [6] 宋智勇,吴阳,韩鹤友.智能化纳米释药系统用于细菌感染治疗的研究进展[J].华中农业大学学报,2020,39(1):1-9. [7] LE OUAY B, STELLACCI F. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: A surface science insight. Nano Today. 2015;10(3):339-354. [8] AMRO NA, KOTRA LP, WADU-MESTHRIGE K, et al. High-Resolution Atomic Force Microscopy Studies of the Escherichiacoli Outer Membrane: Structural Basis for Permeability. Langmuir. 2000;16: 2789-2796. [9] 谌礼佩,熊洁,江青松.纳米抗菌剂在口腔医学中的研究进展[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2019,20(6):351-356. [10] WANG Y, YANG Y, SHI Y, et al. Antibiotic-Free Antibacterial Strategies Enabled by Nanomaterials: Progress and Perspectives. Adv Mater. 2020;32(18):e1904106. [11] KUMAR R, UMAR A, KUMAR G, et al. Antimicrobial properties of ZnO nanomaterials: A review. Ceramics International. 2017;43(5):3940-3961. [12] ECKHARDT S, BRUNETTO PS, GAGNON J, et al. Nanobio silver: its interactions with peptides and bacteria, and its uses in medicine. Chem Rev. 2013;113(7):4708-4754. [13] ZHENG K, SETYAWATI MI, LEONG DT, et al. Antimicrobial silver nanomaterials. Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 2018;357:1-17. [14] HOLT KB, BARD AJ. Interaction of silver(I) ions with the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli: an electrochemical and scanning electrochemical microscopy study of the antimicrobial mechanism of micromolar Ag+. Biochemistry. 2005;44(39):13214 -13223. [15] KANG SJ, CHO YI, KIM KH, et al. Proteomic Analysis to Elucidate the Antibacterial Action of Silver Ions Against Bovine Mastitis Pathogens. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;171(1):101-106. [16] 姚希燕,唐晓宁,王晓楠,等.无机抗菌材料抗菌机理研究进展[J].材料导报,2021,35(1):105-111. [17] RAI M, YADAV A, GADE A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27(1):76-83. [18] 马丽娜,米宏霏,薛云新,等.ROS在细菌耐药及抗生素杀菌中的作用机制[J].遗传,2016,38(10):902-909. [19] 乔越.新型无机纳米生物材料在耐药菌感染慢性难愈合伤口和角膜炎的抗菌促愈功能研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2020. [20] JOE A, PARK SH, KIM DJ, et al. Antimicrobial activity of ZnO nanoplates and its Ag nanocomposites: Insight into an ROS-mediated antibacterial mechanism under UV light. Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 2018;267: 124-133. [21] 赵芙蓉,周晓琴,洪樟连,等.二氧化钛基光催化抗菌材料的研究进展[J].材料导报,2005,19(11):35-38. [22] 雷绍民,郝骞,熊毕华,等.蒙脱石矿物特性及开发利用前景[J].资源环境与工程,2006,20(5):565-569. [23] NITHYA N, BHOOPATHI G, MAGESH G, et al. Neodymium doped TiO2 nanoparticles by sol-gel method for antibacterial and photocatalytic activity. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing. 2018;83:70-82. [24] QI K, CHENG B, YU J, et al. Review on the improvement of the photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO. Journal of Alloys and Compounds. 2017;727:792-820. [25] CAI Y, STRMME M, WELCH K. Disinfection Kinetics and Contribution of Reactive Oxygen Species When Eliminating Bacteria with TiO2 Induced Photocatalysis. Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology. 2014; 5:200-209. [26] KASHEF N, HUANG YY, HAMBLIN MR. Advances in antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation at the nanoscale. Nanophotonics. 2017; 6(5):853-879. [27] HAMBLIN MR, HASAN T. Photodynamic therapy: a new antimicrobial approach to infectious disease? Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2004;3(5): 436-450. [28] LINK S, EL-SAYED MA. Shape and size dependence of radiative,non-radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int Rev Phys Chem. 2000;19:409-453. [29] 张旺全.新型噻吩--哌嗪类荧光分子的设计及其光热/成像性能的研究[D].青岛:青岛大学,2020. [30] O’NEAL DP, HIRSCH LR, HALAS NJ, et al. Photo-thermal tumor ablation in mice using near infrared-absorbing nanoparticles. Cancer Lett. 2004; 209(2):171-176. [31] LOO C, LOWERY A, HALAS N, et al. Immunotargeted nanoshells for integrated cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Lett. 2005;5(4):709-711. [32] WU S, LI A, ZHAO X, et al. Silica-Coated Gold-Silver Nanocages as Photothermal Antibacterial Agents for Combined Anti-Infective Therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(19):17177-17183. [33] LIU T, SHI S, LIANG C, et al. Iron oxide decorated MoS2 nanosheets with double PEGylation for chelator-free radiolabeling and multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy. ACS Nano. 2015;9(1):950-960. [34] ZHU X, JI X, KONG N, et al. Intracellular Mechanistic Understanding of 2D MoS2 Nanosheets for Anti-Exocytosis-Enhanced Synergistic Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano. 2018;12(3):2922-2938. [35] YADAV V, ROY S, SINGH P, et al. 2D MoS2 -Based Nanomaterials for Therapeutic, Bioimaging, and Biosensing Applications. Small. 2019; 15(1):e1803706. [36] YIN W, YU J, LV F, et al. Functionalized Nano-MoS2 with Peroxidase Catalytic and Near-Infrared Photothermal Activities for Safe and Synergetic Wound Antibacterial Applications. ACS Nano. 2016;10(12): 11000-11011. [37] GAO Q, ZHANG X, YIN W, et al. Functionalized MoS2 Nanovehicle with Near-Infrared Laser-Mediated Nitric Oxide Release and Photothermal Activities for Advanced Bacteria-Infected Wound Therapy. Small. 2018; 14(45):e1802290. [38] 杨莹莹,冯闪,马陇豫,等.光热纳米材料在抗菌领域的研究进展[J].河南大学学报(医学版),2021,40(2):147-151. [39] ZHOU S, WANG Z, WANG Y, et al. Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Synergistic Phototherapy for Antimicrobial Therapy. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(3):1730-1737. [40] PANARIELLO BHD, DE ARAÚJO COSTA CAG, PAVARINA AC, et al. Advances and challenges in oral biofilm control.Curr Oral Health Rep. 2017;4(1):29-33. [41] PITTS NB, ZERO DT, MARSH PD, et al. Dental caries. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17030. [42] 莫祯妮,熊盈盈,邱树毅,等.群体感应抑制剂调控食源性微生物生物膜形成的研究进展[J].食品科学,2021,42(17):307-316. [43] KANG M, KIM S, KIM H, et al. Calcium-Binding Polymer-Coated Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Microparticles for Sustained Release of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors to Prevent Biofilm Formation on Hydroxyapatite Surfaces. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(8):7686-7694. [44] KOO H, HAYACIBARA MF, SCHOBEL BD, et al. Inhibition of Streptococcus mutans biofilm accumulation and polysaccharide production by apigenin and tt-farnesol. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;52(5):782-789. [45] 赵霞,徐嘉昊,夏商.Farnesol纳米胶束的构建及对变形链球菌的抑菌作用研究[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(9):875-878. [46] HOREV B, KLEIN MI, HWANG G, et al. pH-activated nanoparticles for controlled topical delivery of farnesol to disrupt oral biofilm virulence. ACS Nano. 2015;9(3):2390-2404. [47] 黄彦楠,程磊.纳米磷酸钙盐改性牙科材料防治牙体牙髓病研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2021,29(9):634-637. [48] 石广立.甲苯胺蓝-碳纳米管复合光敏剂的合成及其表征[D].沈阳:沈阳理工大学,2015. [49] 郗红,周惠,闫秀娟,等.纳米技术在龋病治疗中应用的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2014,41(5):563-566. [50] HAO Y, HUANG X, ZHOU X, et al. Influence of Dental Prosthesis and Restorative Materials Interface on Oral Biofilms. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(10):3157. [51] MANN J, BERNSTEIN Y, FINDLER M. Periodontal disease and its prevention, by traditional and new avenues. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(2): 1504-1506. [52] 王兴.第四次全国口腔健康流行病学调查报告[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2018:25-34. [53] KAVRIKOVA D, BORILOVA LINHARTOVA P, et al. Chemokine Receptor 2 (CXCR2) Gene Variants and Their Association with Periodontal Bacteria in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019: 2061868. [54] DO NASCIMENTO C, PAULO DF, PITA MS, et al. Microbial diversity of the supra- and subgingival biofilm of healthy individuals after brushing with chlorhexidine- or silver-coated toothbrush bristles. Can J Microbiol. 2015;61(2):112-123. [55] 张新坚,张斌.纳米粒子递药系统在牙周炎局部药物治疗中应用的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2022,30(1):73-76. [56] 张灵玲.基于纳米材料的新型光热/药物协同抗菌体系的设计及应用[D].武汉:武汉大学,2019. [57] 马旭东,王健平.纳米复合羟基磷灰石(nHA)根管充填材料的应用基础研究[J].西南军医,2009,11(3):485-487. [58] 李平,肖丽英,李伟,等.新型纳米羟基磷灰石(n-HA)糊剂封闭根尖性能及其对病原菌抗菌活性的体外实验[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2007,17(4):214-218. [59] 游滢滢,冯云枝.纳米含氟羟基磷灰石牙种植体的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(12):1901-1906. [60] WANG L, XIE X, LI C, et al. Novel bioactive root canal sealer to inhibit endodontic multispecies biofilms with remineralizing calcium phosphate ions. J Dent. 2017;60:25-35. [61] 王建平,GEOGI GEORGE.纳米羟基磷灰石复合根充糊剂的抑菌性及微渗漏[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(21):3350-3354. [62] 王昊阳,孟维艳.二氧化钛纳米管抗菌性能在口腔种植领域的研究进展[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2021,19(1):49-53. [63] NILEBÄCK L, WIDHE M, SEIJSING J, et al. Bioactive Silk Coatings Reduce the Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus while Supporting Growth of Osteoblast-like Cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(28):24999-25007. [64] PENG Z, NI J, ZHENG K, et al. Dual effects and mechanism of TiO2 nanotube arrays in reducing bacterial colonization and enhancing C3H10T1/2 cell adhesion. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:3093-3105. [65] 寇钢,白力静,龚振瑶,等.磁控溅射(TiO2 -ZnO) / TiO2梯度复合薄膜的制备及光致亲水性研究[J].人工晶体学报,2012,41(1):94-99. [66] LIU W, SU P, CHEN S, et al. Antibacterial and osteogenic stem cell differentiation properties of photoinduced TiO₂ nanoparticle-decorated TiO₂ nanotubes. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(5):713-723. [67] 马歆茹.多形貌氧化锌对变异链球菌的抑制作用研究[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2021. [68] 肖作慧.仿生肽引导纳米无定形磷酸钙再矿化脱矿牙釉质[D].天津:天津医科大学,2018. [69] 李洁,李福军.复合纳米银托槽粘接剂在大鼠龋病模型上抗菌性的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(5):449-452. [70] NI C, ZHOU J, KONG N, et al. Gold nanoparticles modulate the crosstalk between macrophages and periodontal ligament cells for periodontitis treatment. Biomaterials. 2019;206:115-132. [71] HU F, ZHOU Z, XU Q, et al. A novel pH-responsive quaternary ammonium chitosan-liposome nanoparticles for periodontal treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;129:1113-1119. [72] 邓咏梅,王辉,何松霖,等.盐酸米诺环素纳米脂质体治疗大鼠实验性牙周炎的疗效观察[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2018,34(6):753-757. [73] 齐曼霖.近红外光激发的二氧化钛纳米粒子对牙周炎相关细菌的抗菌性能的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2020. [74] 刘奕,周荣静,吴红崑.4种纳米羟磷灰石复合材料对粪肠球菌抗菌性能的初步研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2015,32(3):301-305. [75] 姚丽萍,张蕾,林玉红,等.纳米银溶液用于慢性根尖周炎根管内封药的实验动物研究[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2020, 14(2):95-100. [76] IBRAHIM MS, ALQARNI FD, AL-DULAIJAN YA, et al. Tuning Nano-Amorphous Calcium Phosphate Content in Novel Rechargeable Antibacterial Dental Sealant. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(9):1544. [77] DARABPOUR E, KASHEF N, MASHAYEKHAN S. Chitosan nanoparticles enhance the efficiency of methylene blue-mediated antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation of bacterial biofilms: An in vitro study. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2016;14:211-217. [78] POURHAJIBAGHER M, ROKN AR, ROSTAMI-RAD M, et al. Monitoring of virulence factors and metabolic activity in Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans cells surviving antimicrobial photodynamic therapy via nano-chitosan encapsulated indocyanine green. Front Phys. 2018;6:124. [79] SASAKI Y, HAYASHI JI, FUJIMURA T, et al. New Irradiation Method with Indocyanine Green-Loaded Nanospheres for Inactivating Periodontal Pathogens. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1):154. [80] GOLMOHAMADPOUR A, BAHRAMIAN B, KHOOBI M, et al. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy assessment of three indocyanine green-loaded metal-organic frameworks against Enterococcus faecalis. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2018;23:331-338. [81] WU Z, XU H, XIE W, et al. Study on a novel antibacterial light-cured resin composite containing nano-MgO. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;188:110774. [82] KO A, YEE M, SKUPIN-MRUGALSKA P, et al. Photodynamic therapy of Porphyromonas gingivalis via liposome-encapsulated sensitizers. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2013;41(11):827-830. [83] 曹飞,惠敏,董西玲,等.载银纳米羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯复合纳米纤维支架的制备及成骨抗菌性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(34):5461-5467. [84] 王静,冀志江,水中和,等.纳米银溶胶与大肠杆菌作用及作用机理研究[J].材料导报,2013,27(24):4-8,21. [85] 姬晓伟,刘娉婷,唐金成,等.二氧化钛纳米管阵列在大肠杆菌不同生长阶段的抗菌机理[J].中国有色金属学报(英文版),2021, 31(12):3821-3830. [86] 程晓昆,张越,吕海军,等.多孔碳纳米材料构建抗肿瘤药物靶向传递系统的研究进展[J].无机材料学报,2021,36(1):9-24. [87] 丁鑫,师红东,刘扬中.以人血清白蛋白为载体的Ru(Ⅲ)和全反式维甲酸共运输纳米药物的构建及抗肿瘤转移作用[J].高等学校化学学报,2021,42(10):3040-3046. [88] 张颖,许霞青,何勐,等.富勒烯-苯丙氨酸多西他赛纳米脂质载体的制备及其体外抗肿瘤活性[J].医药导报,2022,41(4):506-513. [89] 刘红梅,黄开勋,徐辉碧.纳米材料的生物安全性研究进展[J].化工进展,2006,25(9):1040-1044. [90] 徐斐,姜昆,黎燕,等.食物基质和胃肠道对经口暴露纳米颗粒物理化学性质和生物效应的影响[J].食品与生物技术学报,2021,40(8): 17-26. [91] HAN HY, YANG MJ, YOON C, et al. Toxicity of orally administered food-grade titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Appl Toxicol. 2021;41(7):1127-1147. [92] 王嘉,吴国锋,孙冠阳,等.经皮种植体表面纳米二氧化硅抗菌涂层的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(1):5-9. [93] WONG HL, CHATTOPADHYAY N, WU XY, et al. Nanotechnology applications for improved delivery of antiretroviral drugs to the brain. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(4-5):503-517. [94] QIN W, HUANG G, CHEN Z, et al. Nanomaterials in Targeting Cancer Stem Cells for Cancer Therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:1. [95] DEVADASU VR, BHARDWAJ V, KUMAR MN. Can controversial nanotechnology promise drug delivery? Chem Rev. 2013;113(3):1686-1735. [96] KIM CS, DUNCAN B, CRERAN B, et al. Triggered Nanoparticles as Therapeutics. Nano Today. 2013;8(4):439-447. [97] STUART MA, HUCK WT, GENZER J, et al. Emerging applications of stimuli-responsive polymer materials. Nat Mater. 2010;9(2):101-113. |
| [1] | Li Mengfei, Zhang Hong, Zhao Shaojian, Yin Guanghao, Wang Qibao. Expression of forkhead box protein 3 in refractory periapical periodontitis in rats with Enterococcus faecalis infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1187-1192. |
| [2] | Zhao Wei, Feng Wei, Yang Tieyi, Ren Wei, Wang Yuxin, Lyu Huicheng, Chang Zhiqiang, Feng Xiaodong, Wang Ziheng, Guo Shibing. Antibiotic bone cement intramedullary nail prepared using 3D printed mold for the treatment of long bone infection in lower limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1023-1030. |
| [3] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [4] | Xue Ting, Zhang Xinri, Kong Xiaomei. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pneumoconiosis using nanomaterials combined with multi-modal molecular imaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1133-1140. |
| [5] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [6] | Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469. |
| [7] | Han Tao, Hao Jianqiang, Li Wenbo, Shi Jie, Gao Qiuming. Advantages and problems of antibiotic-loaded bone cements for bone and joint infections [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 470-477. |
| [8] | Chen Jinlun, Deng Peng, Ye Pengcheng, Cao Houran, Zeng Huiliang, Feng Wenjun, Zeng Jianchun, Zeng Yirong. Dynamic monitoring of plasma human alpha-defensin 1-3 and peripheral blood inflammatory markers after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4304-4311. |
| [9] | Liu Zhuoran, Li Yumei, Liu Junyan, Yin Tong, Jiang Ming, Li Yourui. Role of chitosan and its derivatives in the field of oral antibacterial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3361-3367. |
| [10] | Duan Jiahao, Tan Xuyi, Lu Min, Kuang Gaoyan, Fang Chuanlong, Xiao Man. Effects of Sanhua Jiegu San on Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3230-3235. |
| [11] | Zhang Yeting, Fu Yan, Li Xue, Wei Cuilan, Li Chuikun, Yuan Qiongjia. Effects of aerobic exercise on learning, memory, and hippocampal neuromorphology in mice with Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3188-3194. |
| [12] | Yuan Shuyue, Liu Chunyan, Liu Bing, Zhao Fei. Macrophage polarization and periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2699-2707. |
| [13] | Zhu Hong, Lin Ziheng, He Rouye, Pan Jinbin, Liu Xiaochuan, He Xiaoling, Zhang Jingying. Antibacterial and hemostatic properties of chitosan collagen sponge [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2525-2533. |
| [14] | Yang Yong, Xu Shunen, Gu Xianyang, Hua Dawei, Teng Jianxiang, Wang Zhen, Ye Chuan. Preparation and property analysis of electrospinning composite sustained-release antibacterial microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2534-2541. |
| [15] | Guo Tingting, Cui Chaoqiang, Liu Baokun, Gu Hao, Zhou Dong. Application of endovascular steerable catheter system in interventional surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2609-2615. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||