Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 1133-1140.doi: 10.12307/2023.083
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pneumoconiosis using nanomaterials combined with multi-modal molecular imaging
Xue Ting, Zhang Xinri, Kong Xiaomei
- National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Pneumoconiosis, Key Laboratory of Prophylaxis and Treatment and Basic Research for Respiratory Diseases of Shanxi Province, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-03Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-03-08Published:2022-07-20 -
Contact:Kong Xiaomei, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Pneumoconiosis, Key Laboratory of Prophylaxis and Treatment and Basic Research for Respiratory Diseases of Shanxi Province, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Xue Ting, Lecturer, National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Pneumoconiosis, Key Laboratory of Prophylaxis and Treatment and Basic Research for Respiratory Diseases of Shanxi Province, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, The First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Basic Research Project of Natural Science in Shanxi Province, No. 20210302124039 (to XT); the Scientific and Technological Innovation Program of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi Province, No. 2020L0201 (to XT); the Start-up Foundation for Doctoral Scientific Research of Shanxi Province, No. SD1905 (to XT); the Start-up Foundation for Doctoral Scientific Research of Shanxi Medical University, No. XD1905 (to XT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xue Ting, Zhang Xinri, Kong Xiaomei. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for pneumoconiosis using nanomaterials combined with multi-modal molecular imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1133-1140.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
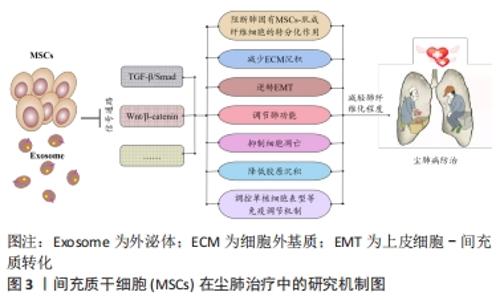
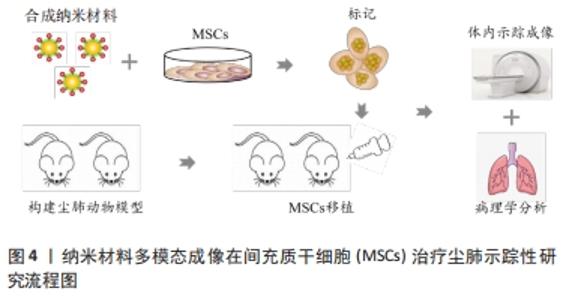
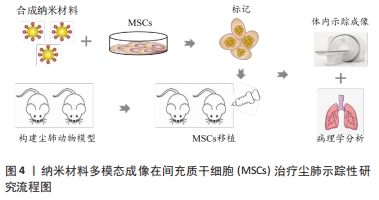
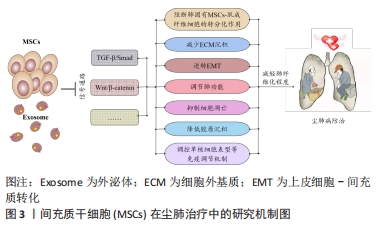
2.1 尘肺治疗研究现状 尘肺病肺纤维化不可逆转,由于尘肺病发病人群及致病因素的特殊性,缺乏对劳动者工作场所粉尘的有效防御措施,尚无早期、可靠、特异的诊断方法及理想特效的治疗药物;治疗原则主要包括加强全面健康管理,开展病因和对症治疗、积极防治并发症以及康复治疗的临床综合治疗,以延缓病情进展,提高患者生活质量;治疗方案有药物治疗、大容量全肺灌洗术、肺康复治疗和肺移植,不同方案各有其优点和局限性,根据患者病情严重程度及相关适应证和禁忌证而推广实施[3-7]。 目前,临床常用尘肺病的治疗药物如哌喹类、铝制剂和皮质固醇类等,可减少矽结节形成、减轻肺部炎症、改善临床症状并延缓病情进展,但具体疗效不确切且药物毒副反应较大[8];生物碱类、黄酮类等中医药可益气扶正,毒副反应较小,在临床尘肺治疗中取得一定疗效,但具体机制需进一步探索[9-12];吡非尼酮和尼达尼布是2014年经美国FDA批准用于治疗特发性纤维化模型的药物[13],其主要作用是改善肺功能,进而缓解特发性纤维化患者病情进展,已被证实是一种安全有效的广谱抗多器官纤维化药物,可作为潜在有效防治尘肺病的临床用药[14-16]。尘肺动物研究表明尼可地尔、薯蓣皂苷及丹参酮等均可有效缓解肺纤维化形成,发挥保护性作用[17-20];此外,靶向阻断MARCO、调控CD44-RhoA-YAP、RhoA/Rho激酶、TNF-α-TNFR、TAK1-MAPK-Snail/NF-κB及FAS-caspase-8信号通路和自噬等多种机制均参与改善肺组织损伤和肺纤维化程度的过程[21-26];非编码RNA如miR-29c、LncRNAs HOTAIR和HOTAIR/miR-326被证实可作为尘肺病治疗的候选靶点[27-31]。 尽管相关研究仍处临床前阶段,肺纤维化进程中多个炎症和与纤维化相关的靶点及信号通路可作为治疗尘肺的新靶标已被揭示,有望为制定尘肺病治疗策略以及研发新药及药物治疗靶点提供新思路。由此可见,尘肺病临床治疗方案仍非常有限,应着眼将预防、诊断和治疗作为将来的研究重点。近年来,细胞疗法已成为最重要的新兴医学疗法之一,随着干细胞研究的深入推进,探索间充质干细胞治疗尘肺病逐渐成为职业病防治领域的研究热点。 2.2 间充质干细胞在尘肺治疗中的研究 间充质干细胞来源丰富,具有多分化潜能、免疫调控及自我更新等特点,SiO2诱导肺纤维化的临床前实验研究表明,间充质干细胞可通过旁分泌机制归巢至肺损伤部位,迁移并分化为肺泡上皮细胞促进肺实质再上皮化,抑制促炎因子表达和促纤维化因子释放,分泌多种生物活性分子调节免疫反应,减少肺部炎症反应和肺结节形成,修复受损肺组织,降低肺组织重塑,改善肺部胶原沉积和肺纤维化程度,延缓尘肺进展[32-35]。 有研究表明,间充质干细胞外泌体(MSCs-Exo)可通过负向调控TGF-β/Smad、Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,阻断肺固有间充质干细胞-肌成纤维细胞的转分化作用,进而减少细胞外基质沉积,逆转上皮细胞-间充质转化,调节肺功能并降低胶原沉积,抑制细胞凋亡,调控单核细胞表型等免疫调节机制,减轻肺纤维化程度,为尘肺临床治疗提供依据[34,36-41],此外,基于肺组织干细胞分泌组(LSC-Sec)及其所包含microRNA家族中microRNA-30a,-99,let-7,-186和肺组织干细胞外泌体(LSC-Exo)研制的制剂促进肺组织损伤修复再生的抗肺纤维化疗效优于间充质干细胞外泌体,极有可能消除间充质干细胞治疗的安全性担忧,成为替代间充质干细胞有效防治肺纤维化的非常有前景的新候选治疗策略[42-43]。 间充质干细胞及外泌体在肺纤维化治疗中的研究为尘肺临床治疗提供了新的视角和策略,然而尚存在诸多局限性,如间充质干细胞或外泌体应用剂量、给药方式等的确定,尤其是间充质干细胞的细胞活性及其在体内的归巢、迁移与分化和治疗安全性有效性的评估,是目前间充质干细胞应用于尘肺治疗中急需解决的问题,新型功能性纳米材料的体内示踪及其安全性有效性的探究为此带来希望,见图3。 "
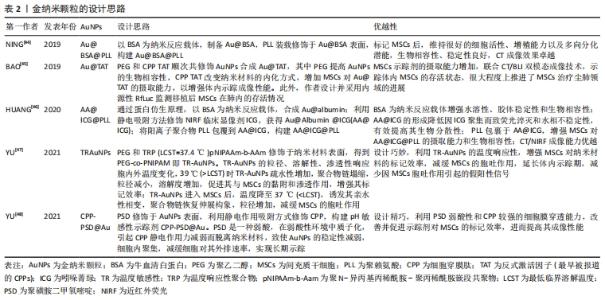
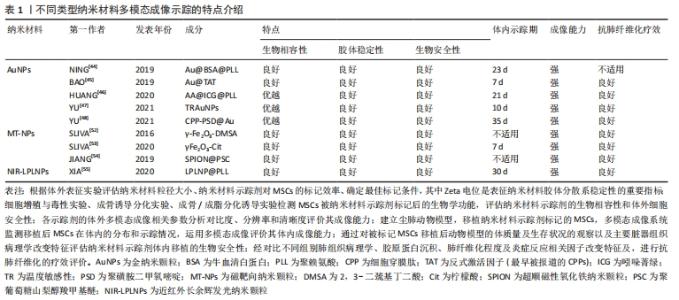
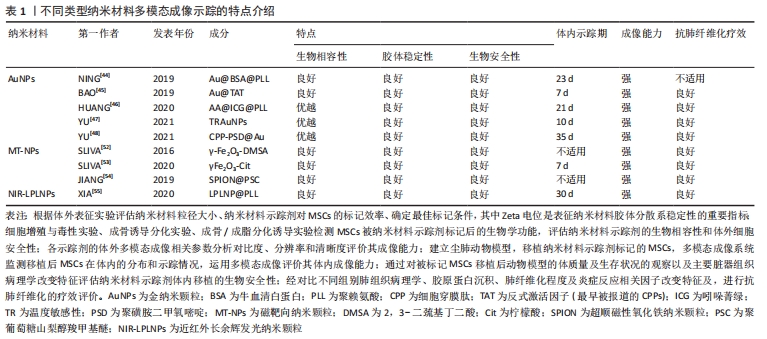
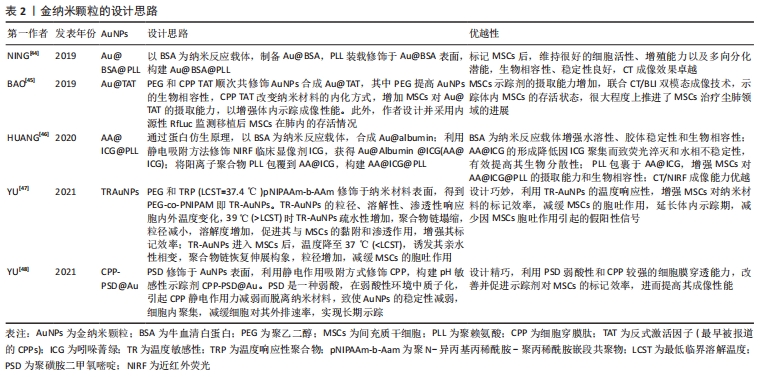
2.3.1 金纳米颗粒多模态成像在间充质干细胞治疗尘肺中的示踪性研究 金纳米颗粒(Gold nanoparticles,AuNPs)具有良好的稳定性和生物相容性、灵敏的光学特性、易于表面修饰、传感性能好等优点,经过一定功能化修饰后,可作为稳定剂或药物运载工具,靶向病变部位,提高药物疗效,增强病变部位对放射成像的敏感性,为肿瘤等疾病治疗提供了新技术,开启在生物医学领域应用的新时代。 NING等[44]基于AuNP制备了聚赖氨酸(poly-L-lysine,PLL)和牛血清白蛋白(bovine serum albumin,BSA)包覆的金纳米颗粒Au@BSA@PLL,运用NP标记间充质干细胞后评估对间充质干细胞的毒性作用,结果显示Au@BSA@PLL标记间充质干细胞后对间充质干细胞增殖和分化无影响,具有良好的生物相容性、胶体稳定性和生物安全性及较强的体内外Micro-CT成像对比能力,且对博来霉素(Bleomycin,BLM)诱导特发性纤维化动物模型的体内示踪实验显示Au@BSA@PLL标记的间充质干细胞体内示踪时程可达23 d,证实Au@BSA@PLL可作为一种长期的体内纳米示踪剂,但尚缺少疗效验证。BAO等[45]用聚乙二醇(PEG)和高效细胞穿膜肽(CPP)反式激活因子(TAT,最早被报道的CPPs)顺次共修饰AuNPs合成Au@TAT,利用高穿透、高分辨、高灵敏度的CT联合生物发光成像(bioluminescence imaging,BLI),即CT/BLI双模态成像技术,分析其表征,采用Au@TAT与萤火虫荧光素酶(red-emitting firefly luciferase,Rf-Luc)双标记间充质干细胞,联合CT/BLI双模态成像技术,实现间充质干细胞移植治疗特发性纤维化动物模型的体内监测,存活间充质干细胞的示踪期为7 d,并初步证实其抗肺纤维化作用,与其他研究不同的是Au@TAT-CT/BLI双模态成像技术可示踪体内间充质干细胞的存活状态,很大程度上推进了间充质干细胞治疗尘肺领域的进展。 在上述研究的基础上,AuNPs多模态成像在间充质干细胞治疗尘肺的示踪及疗效评价中的科研设计、技术水平和示踪系统长效性上均有了新的突破。HUANG等[46]通过蛋白仿生原理采用具有临床应用前景的白蛋白(Albumin)作为纳米反应载体合成Au@albumin (AA),增强AuNPs的水溶性、胶体稳定性和生物相容性,利用静电吸附方法修饰由FDA批准的近红外荧光(near infrared fluorescence,NIRF)临床显像剂吲哚菁绿(indocyanine green,ICG)至AA表面,AA@ICG的形成降低因ICG聚集而致荧光淬灭和水相不稳定性,有效提高其生物分散性,随后将阳离子树枝状聚合物聚赖氨酸(PLL)包裹于AA@ICG,增强间充质干细胞对AA@ICG@PLL的摄取能力和生物相容性,经表征和双模态成像研究发现AA@ICG@PLL具备优越的CT/NIRF成像能力,且标记间充质干细胞后不影响其细胞功能,并证实体内示踪期达21 d,肺纤维化模型胶原蛋白沉积、纤维化程度及巨噬细胞参与的炎症反应显著减少,提示AA@ICG@PLL可作为安全有效双模态成像体内长期示踪剂,为间充质干细胞治疗尘肺领域的研究奠定实验基础。上述研究证实AuNPs在间充质干细胞治疗尘肺的组织修复与再生具有CT成像示踪较强的X射线衰减系数以及优良的生物相容性,提示AuNPs是多模态成像的最佳示踪剂。 间充质干细胞治疗尘肺呈周期性,示踪剂浓度随间充质干细胞自身增殖与胞吐作用而逐渐降低,导致成像信号减弱甚至消失,难以实现间充质干细胞体内长期示踪。对此,YU等[47]设计并制备了用聚乙二醇-聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺(PEG-co-PNIPAM)修饰AuNPs的温度敏感性(temperature-responsive,TR)示踪剂(TR-AuNPs),其粒径、溶解性、渗透性响应胞内外温度变化,39 ℃时TR-AuNPs疏水性增加,聚合物链塌缩,粒径减小,溶解度增加,促进其与间充质干细胞的黏附和渗透作用,增强其标记效率,TR-AuNPs进入间充质干细胞后,温度降至37 ℃,诱发其亲水性相变,聚合物链恢复伸展构象,粒径增加,减缓间充质干细胞的胞吐作用,延长体内示踪期(10 d),减少因间充质干细胞胞吐作用引起的假阳性信号,然而此标记策略在应用CT/BLI双模态示踪中存在局限性,该研究者进一步合成稳定性、生物相容性更优、CT成像对比性能显著增强的pH敏感性示踪剂CPP-PSD@Au,在转运过程中在历经胞内核内体/溶酶体弱酸性环境而质子化形成聚集体,增强其疏水性,减缓胞吐速度,延长标记时间,体内实验表明pH敏感的新型AuNPs抗肺纤维化疗效显著且示踪期长达35 d[48]。YU等[48-49]的研究克服了间充质干细胞对摄入AuNPs的胞吐作用,实现了体内长期示踪,为实现间充质干细胞治疗尘肺的长期示踪提供的新思路。 由此可见,AuNPs作为最具前景的纳米材料之一,其多模态成像在间充质干细胞治疗尘肺的示踪及疗效评价中的科研设计、技术水平和示踪长效性等方面均取得新突破,为实现临床间充质干细胞治疗尘肺提供了可靠新技术。此外,由于其独特的理化特性可单独应用于癌症光热治疗,促进肿瘤细胞消融,还可作为抗癌药物载体发挥双重靶向抗肿瘤作用[49-51],据此推测AuNPs通过与聚乙二醇偶联或在其表面包覆介孔SiO2(m-SiO2)等表面修饰的方法与吡非尼酮等抗纤维化药物优化合成药物载体,既而标记间充质干细胞发挥治疗尘肺的双重生物学效应将成为可能,探索此过程前尚需解决增强靶向积累、提高细胞摄取和控制细胞缓释效力、延长药物半衰期以及维持稳定血药浓度等关键问题。 文章总结并归纳了不同AuNPs多模态成像在间充质干细胞治疗尘肺中示踪性研究的特点及设计思路,见表2。 "
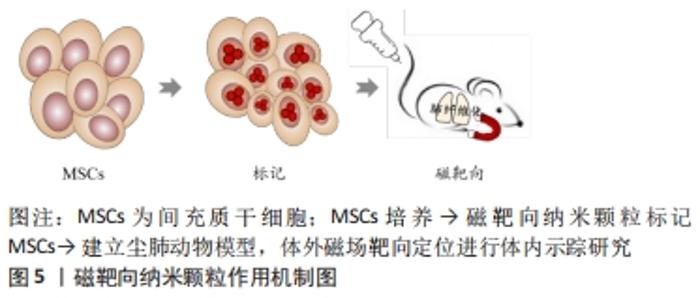
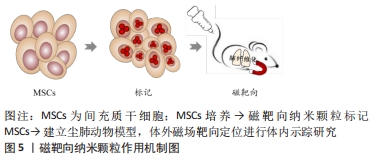
2.3.2 磁靶向纳米颗粒多模态成像 磁性纳米颗粒(magnetic nanoparticles,M-NPs)具备量子效应、尺寸效应、表面效应和独特的磁性效应等性能,具有良好的磁导向性、生物相容性和生物降解性等特点,可结合多种生物功能分子,在磁靶向(magnetic targeting,MT)、磁控对比剂、药物、基因治疗、医学诊断、热疗、MRI成像等生物医学方面应用颇广。SLIVA等[52]用2,3-二巯基丁二酸(2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid,DMSA)分别修饰AuNPs和超顺磁性γ-Fe2O3纳米材料并标记间充质干细胞,表征和体外细胞实验显示二者生物相容性和安全性良好,未引起间充质干细胞分化、增殖等生物学功能的改变,均表现出较强的Micro-CT成像分辨能力,随后建立矽肺模型,于小鼠胸部固定钕磁铁,通过体外磁场进行靶向定位运用Micro-CT验证上述2种纳米材料的体内示踪性,研究结果显示:体外有磁场组间充质干细胞数量较无磁场组明显增高,但未检测到Au-DMSA标记的间充质干细胞,证实体外磁场可促进间充质干细胞靶向迁移,γ-Fe2O3-DMSA是一种潜在体内磁靶向示踪剂,提示磁靶向技术为间充质干细胞治疗矽肺的疗效加强提供了可能性;该团队在此基础上对磁靶向技术进行了改进,采用柠檬酸对磁性材料γFe2O3进行表面修饰,合成具有优良生物相容性和高稳定性的M-NPs γFe2O3-Cit,其标记的间充质干细胞保持原有细胞活性的同时具有磁敏感型,体内示踪及矽肺疗效实验显示胸部固定磁体通过体外磁场进行靶向定位小鼠肺内磁化间充质干细胞数量以及单核细胞趋化因子1和基质细胞衍生因子1的表达显著增加,在肺内滞留时间延长至7 d,且炎症因子转化生长因子β、白细胞介素1β表达下降,肺组织静态顺应性及肉芽肿形成明显降低,疗效显著,表明被γFe2O3-Cit标记间充质干细胞具有磁敏感性,表明该技术有助于间充质干细胞的磁靶向归巢,延长了间充质干细胞在肺内的滞留,进而发挥修复肺损伤效应且疗效显著[53]。 γFe2O3-Cit不会随间充质干细胞的分化而自体复制,其浓度随间充质干细胞的分化逐渐降低,间充质干细胞旁分泌和间充质干细胞衍生的细胞外囊泡(MSC-EVs)的治疗作用因时间推移趋于终止,间充质干细胞凋亡引发M-NPs分散,虽然在此研究中,通过表征和细胞功能学及体内动物实验表明磁靶向剂量安全,不足以引起细胞和动物体内毒性,但纳米材料中γ-Fe2O3释放到肺微环境中而沉积易致肺组织损伤和肺纤维化的潜在不利影响,尚需进一步探讨。内皮-间充质转化(endothelial-mesenchymal transition,EndoMT)与肺纤维化进展密切相关,内质网应激与自噬信号通路参与EndoMT过程,而间充质干细胞对SiO2诱导肺纤维化过程中EndoMT的作用及其具体机制尚未阐明。 JIANG等[54]用聚葡萄糖山梨醇羧甲基醚(polyglucose sorbitol carbo xymethyether,PSC)表面修饰超顺磁性氧化铁纳米颗粒(Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles,SPION)合成SPION@PSC,建立Tie2-GFP小鼠肺纤维化模型,经体外细胞及体内实验研究发现SPION@PSC标记间充质干细胞可改善SiO2诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞表面特异性标记蛋白VE-Cad、CD31的缺失表达和间充质特异性表面标志Col 1A1及α-SMA的上调表达及其细胞形态内皮样鹅卵石形态转变为梭形或纺锤形间充质样细胞形态等影响,证实SPION@PSC标记间充质干细胞通过调控内质网应激与自噬信号通路逆转SiO2诱导肺纤维化进程中内皮-间充质转化EndoMT,缓解SiO2对内皮细胞增殖和迁移的促进性诱导作用,减轻血管重塑,发挥抗肺纤维化作用,提示SPION@PSC是间充质干细胞治疗尘肺安全、有效的体内示踪剂,并阐明间充质干细胞旁分泌作用在其治疗尘肺中的相关机制,但间充质干细胞旁分泌因子的参与及机制研究有待完善,见图5。 "

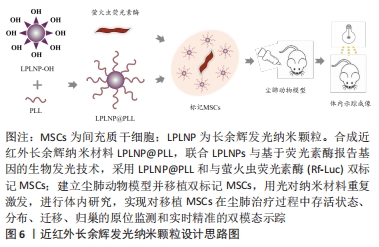
2.3.3 近红外长余辉发光纳米颗粒多模态成像 近红外长余辉发光纳米颗粒(near-infrared-long persistent luminescence nanoparticles,NIR-LPLNPs)具有稳定、持久且优良的高强度余辉(persistent luminescence,PL)发射性能,经外光源预激发而储存能量,激发停止后以持久余辉的形式缓慢释放光能,可经多种光源重复激发而恢复光学特性,无需连续外光源激发,可维持数天至数周,克服了传统荧光成像需外部激发光源实时激发生物体内荧光探针而产生的生物组织背景荧光进而影响成像分辨率和信噪比的局限性,避免了因外部激发光源照射产生潜在过热现象而易损伤生物组织的缺陷,显著提高了活体光学成像的穿透深度、空间分辨率、灵敏度和信噪比,扩展了近红外长余辉发光纳米颗粒成像技术在生物医学中的应用。 基于Cr3+掺杂PLNPs经NIR激发,组织穿透性和余辉性能超强,余辉在可穿透组织的红光照射之下可恢复,减弱余辉衰减寿命对成像影响的研究,XIA等[55]设计合成PLL修饰的LPLNPs(Zn1.1Ga1.8Ge0.1O4:Cr3+,Eu3+)即LPLNP@PLL,经NIR激发具有持久的NIR-LP成像性能,表征研究结果显示其稳定性、生物相容性和安全性优良,运用LPLNP@PLL联合Rf-Luc双标记间充质干细胞,设计思路图见图6。 "

体内实验表明LPLNP@PLL的余辉成像能力强,余辉联合BLI双模态成像空间成像分辨率高,检测灵敏度更强,在间充质干细胞治疗肺纤维化过程中实现对间充质干细胞原位监测及体内归巢、迁移、分布及存活状态等长达30 d实时精准的动态NIR-LPL/BLI双模态示踪,该纳米材料独特的光学特性提升了对肺纤维化治疗过程中间充质干细胞自发行为和迁移的深入理解,更重要的是该技术独特的余辉光学性能对生物体组织损伤程度小,开启了LPLNPs示踪剂在体内安全使用的保障及临床间充质干细胞治疗尘肺进一步推进的新篇章。 2.4 纳米载体药物递送体系联合间充质干细胞双靶向治疗尘肺前景 基于纳米材料的药物装载与控制释放的研究,多功能纳米材料药物递送体系可增强药物靶向性、降低药物毒性。TASSALI等[56]应用超短回声时间MRI序列法联合气管内给药新型钆基纳米颗粒,增强并动态监测BLM诱导肺纤维化动物模型肺组织的MRI成像,量化MRI对比剂的摄取与排空,为进一步了解肺纤维化的炎症与病理进程表征以及实时监控抗肺纤维化药物疗效与治疗靶向性提供可靠技术手段。固体淫羊藿苷脂质体纳米颗粒可提高淫羊藿苷的生物利用度,显著抑制肺纤维化大鼠血管生成,且该抑制作用与药物剂量与时间密切相关,是一种较好的口服缓释纳米载体材料,为淫羊藿苷作为未来靶向治疗尘肺药物提供了理论依据[57]。百里醌(TQ)-PLGA-PVA纳米颗粒通过调节炎症因子(白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β1)和iNOS信号通路在博来霉素诱导肺纤维化中发挥抗炎及抗氧化应激的作用,进而有效缓解肺纤维化肺纤维化进程[58]。透明质酸修饰脂质体基于透明质酸特异性受体CD44在肺纤维化进展中的作用,可成为靶向治疗肺纤维化的药物递送体系[59]。壳聚糖-海藻酸盐纳米载体可作为吡非尼酮的药物递送体系,增强经皮给药方式治疗特发性纤维化的药物穿透性[60]。上述纳米材料装载适当抗肺纤维化药物的相关研究,克服了常规口服药物吸收较慢等局限性,直接靶向递送至肺损伤部位,有望实现间充质干细胞联合尘肺治疗药物双靶向治疗的美好愿景,对于临床转化应用具有非常重要的价值。 "

| [1] QI XM, LUO Y, SONG MY, et al. Pneumoconiosis: current status and future prospects. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(8):898-907. [2] The Lancet. Improving occupational health in China. Lancet. 2019; 394(10197):443. [3] MROZ MM, FERGUSON JH, FAINO AV, et al. Effect of inhaled corticosteroids on lung function in chronic beryllium disease. Respir Med. 2018;138S:S14-S19. [4] ZHANG Y, LU P, QIN H, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with pulmonary drug delivery system and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: rationale and therapeutic potential. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:111072. [5] WU X, HUANG J, WANG J, et al. Multi-pharmaceutical activities of chinese herbal polysaccharides in the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis: concept and future prospects. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:707491. [6] XIAO S, YU Y, XIONG Y, et al. Chinese herbal medicines for the treatment of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(44):e22991. [7] GUO J, LI B, WU W, et al. Chinese herbal medicines compared with n-acetylcysteine for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:5170638. [8] ROGLIANI P, CALZETTA L, CAVALLI F, et al. Pirfenidone, nintedanib and N-acetylcysteine for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2016;40:95-103. [9] GUO J, YANG Z, JIA Q, et al. Pirfenidone inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis in the rat silicosis model. Toxicol Lett. 2019;300:59-66. [10] WOLLIN L, DISTLER JHW, REDENTE EF, et al. Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 2019;54(3):1900161. [11] VALENZUELA C, TORRISI SE, KAHN N, et al. Ongoing challenges in pulmonary fibrosis and insights from the nintedanib clinical programme. Respir Res. 2020;21(1):7. [12] EL-KASHEF DH. Nicorandil ameliorates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of silicosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;64:289-297. [13] HUANG H, CHEN M, LIU F, et al. N-acetylcysteine tiherapeutically protects against pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model of silicosis. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(7):BSR20190681. [14] DU S, LI C, LU Y, et al. Dioscin alleviates crystalline silica-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through promoting alveolar macrophage autophagy. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):1878-1892. [15] FENG F, CHENG P, ZHANG H, et al. The protective role of tanshinone iia in silicosis rat model via TGF-beta1/Smad signaling suppression, NOX4 inhibition and Nrf2/ARE signaling activation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019; 13:4275-4290. [16] LI S, LI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Targeting mechanics-induced fibroblast activation through CD44-RhoA-YAP pathway ameliorates crystalline silica-induced silicosis. Theranostics. 2019;9(17):4993-5008. [17] WEI Z, XU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor alpha silencing attenuates silicosis by inhibiting RhoA/Rho kinase signalling. Exp Cell Res. 2019;380(2):131-140. [18] QIAN Q, CAO X, WANG B, et al. TNF-alpha-TNFR signal pathway inhibits autophagy and promotes apoptosis of alveolar macrophages in coal worker’s pneumoconiosis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5953-5963. [19] ZHAO H, WANG Y, QIU T, et al. Autophagy, an important therapeutic target for pulmonary fibrosis diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;502:139-147. [20] YANG M, QIAN X, WANG N, et al. Inhibition of MARCO ameliorates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol Lett. 2019;301:64-72. [21] LI X, YAN X, WANG Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition attenuates silica-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2018;362(2):489-497. [22] WANG X, XU K, YANG XY, et al. Upregulated miR-29c suppresses silica-induced lung fibrosis through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in mice. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2018;37(9):944-952. [23] PAN SC, CUI HH, QIU CG. HOTAIR promotes myocardial fibrosis through regulating URI1 expression via Wnt pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(20):6983-6990. [24] ZHOU H, GAO L, YU ZH, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes renal interstitial fibrosis by regulating Notch1 pathway via the modulation of miR-124. Nephrology (Carlton). 2019;24(4):472-480. [25] YU F, CHEN B, DONG P, et al. HOTAIR epigenetically modulates PTEN expression via MicroRNA-29b: a novel mechanism in regulation of liver fibrosis. Mol Ther. 2020;28(12):2703. [26] XY T, YAN W, WU Q, et al. MiR-326 Inhibits inflammation and promotes autophagy in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis through targeting TNFSF14 and PTBP1. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(11):2192-2203. [27] ODINTSEVA OV, SEMENIKHIN VA, LEE GA. Total broncho-alveolar lavage in respiratory diseases among coal mining workers. Med Tr Prom Ekol. 2015;(5):25-29. [28] ZHAO H, XIE Y, WANG J, et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation can improve the functional capacity and quality of life for pneumoconiosis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6174936. [29] ZHAO H, XIE Y, WANG J, et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation for pneumoconiosis: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e025891. [30] ROSENGARTEN D, FOX BD, FIREMAN E, et al. Survival following lung transplantation for artificial stone silicosis relative to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Ind Med. 2017;60(3):248-254. [31] HOY RF, CHAMBERS DC. Silica-related diseases in the modern world. Allergy. 2020;75(11):2805-2817. [32] ZHANG E, YANG Y, CHEN S, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis potentially by attenuating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):311. [33] LI X, WANG Y, AN G, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis via paracrine mechanisms. Toxicol Lett. 2017;270:96-107. [34] MANSOURI N, WILLIS GR, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes prevent and revert experimental pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of monocyte phenotypes. JCI Insight. 2019;4(21):e128060. [35] CHEN S, CUI G, PENG C, et al. Transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates pulmonary fibrosis of silicosis via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis effects in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):110. [36] Wei J, Zhao Q, Yang G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibition of inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(13):6417-6428. [37] XIE L, ZENG Y. Therapeutic potential of exosomes in pulmonary fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:590972. [38] ZHUANG WZ, LIN YH, SU LJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapy: mechanism, systemic safety and biodistribution for precision clinical applications. J Biomed Sci. 2021;28(1):28. [39] XU C, ZHAO J, LI Q, et al. Exosomes derived from three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse silicosis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):503. [40] Cao H, Wang C, Chen X, et al. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling suppresses myofibroblast differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells and pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13644. [41] Li X, An G, Wang Y, et al. Targeted migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):335. [42] DINH PC, PAUDEL D, BROCHU H, et al. Inhalation of lung spheroid cell secretome and exosomes promotes lung repair in pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1064. [43] ZHOU J, LIN Y, KANG X, et al. microRNA-186 in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via interaction with SOX4 and DKK1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):96. [44] NING X, BAO H, LIU X, et al. Long-term in vivo CT tracking of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with Au@BSA@PLL nanotracers. Nanoscale. 2019;11(43):20932-20941. [45] BAO H, XIA Y, YU C, et al. CT/Bioluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Tracking of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Small. 2019;15(46):e1904314. [46] HUANG J, HUANG J, NING X, et al. CT/NIRF dual-modal imaging tracking and therapeutic efficacy of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells labeled with Au nanoparticles in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(8):1713-1727. [47] YU C, BAO H, CHEN Z, et al. Enhanced and long-term CT imaging tracking of transplanted stem cells labeled with temperature-responsive gold nanoparticles. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(12):2854-2865. [48] YU C, CHEN Z, LI X, et al. pH-triggered aggregation of gold nanoparticles for enhanced labeling and long-term CT imaging tracking of stem cells in pulmonary fibrosis treatment. Small. 2021;17(33):e2101861. [49] LI W, CAO Z, LIU R, et al. AuNPs as an important inorganic nanoparticle applied in drug carrier systems. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019; 47(1):4222-4233. [50] DAS P, FATEHBASHARZAD P, COLOMBO M, et al. Multifunctional Magnetic Gold Nanomaterials for Cancer. Trends Biotechnol. 2019; 37(9):995-1010. [51] MA Y, HUANG J, SONG S, et al. Cancer-targeted nanotheranostics: recent advances and perspectives. Small. 2016;12(36):4936-4954. [52] SILVA LH, DA SILVA JR, FERREIRA GA, et al. Labeling mesenchymal cells with DMSA-coated gold and iron oxide nanoparticles: assessment of biocompatibility and potential applications. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016;14(1):59. [53] SILVA LHA, SILVA MC, VIEIRA JB, et al. Magnetic targeting increases mesenchymal stromal cell retention in lungs and enhances beneficial effects on pulmonary damage in experimental silicosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(10):1244-1256. [54] JIANG R, LIAO Y, YANG F, et al. SPIO nanoparticle-labeled bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit pulmonary EndoMT induced by SiO2. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(1):111492. [55] XIA Y, BAO H, HUANG J, et al. Near-infrared-persistent luminescence/bioluminescence imaging tracking of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in pulmonary fibrosis. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(11):3095-3105. [56] TASSALI N, BIANCHI A, LUX F, et al. MR imaging, targeting and characterization of pulmonary fibrosis using intra-tracheal administration of gadolinium-based nanoparticles. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2016;11(5):396-404. [57] WANG J, SUN Y, TIAN X. The inhibitory effect of icariin nanoparticles on angiogenesis in pulmonary fibrosis. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021; 21(11):5429-5435. [58] SAGHIR SAM, AL-GABRI NA, KHAFAGA AF, et al. Thymoquinone-PLGA-PVA nanoparticles ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats via regulation of inflammatory cytokines and iNOS signaling. Animals (Basel). 2019;9(11):951. [59] PANDOLFI L, Frangipane V, BOCCA C, et al. Hyaluronic acid-decorated liposomes as innovative targeted delivery system for lung fibrotic cells. Molecules. 2019;24(18):3291. [60] ABNOOS M, MOHSENI M, MOUSAVI SAJ, et al. Chitosan-alginate nano-carrier for transdermal delivery of pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):1319-1325. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [3] | Xu Cong, Zhao He, Sun Yan. Regeneration of facial nerve injury repaired by biomaterial nerve conduits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1089-1095. |
| [4] | Li Rui, Liu Zhen, Guo Zige, Lu Ruijie, Wang Chen. Aspirin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and polydopamine modified titanium sheets improve osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 374-379. |
| [5] | Jiang Haifang, Liu Rong, Hu Peng, Chen Wei, Wei Zairong, Yang Chenglan, Nie Kaiyu. Application of 3D printing technology in the precise and personalized treatment of cleft lip and palate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 413-419. |
| [6] | Ning Ziwen, Wang Xu, Shi Zhengliang, Qin Yihua, Wang Guoliang, Jia Di, Wang Yang, Li Yanlin. Meniscal injury repair methods for non-blood supply area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 420-426. |
| [7] | Wang Ziyang, Zuo Enjun. Application of biological materials in vital pulp therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 427-433. |
| [8] | Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469. |
| [9] | Ma Munan, Xie Jun, Sang Yuchao, Huang Lei, Zhang Guodong, Yang Xiaoli, Fu Songtao. Electroacupuncture combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 1-7. |
| [10] | Zhang Yujuan, Yuan Yitong, Du Ruochen, Tian Feng, Fu Yuan, Wang Chunfang. miR-31 promotes the proliferation and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 66-71. |
| [11] | Gao Yixuan, Wang Lingfeng, Ba Te, Li Fang, Cao Shengjun, Li Junliang, Zhou Biao, Chen Qiang. Adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing growth hormone promote proliferation and migration of fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 8-14. |
| [12] | Liu Siqi, Wu Mingrui, Qiao Lingran, Xie Liying, Chen Siyu, Han Zhibo, Zuo Lin. Effects of hydrogel loaded with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on diabetic wound repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 21-27. |
| [13] | Fu Chunmei, Zhang Pu, Wang Yang, Li Xiaolin, Xue Yan, Fu Jie, Zhang Cixian, Yang Yujuan, Duan Yaya, Feng Kai. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the treatment of 24 patients with severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 15-20. |
| [14] | Wei Yanzhao, Zheng Xiaohan, Gao Shijun, Huang Ting, Wei Xufang, Chen Xinxu, Zhao Zhenqiang. Expression of autocrine macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its receptors of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 34-41. |
| [15] | Yang Yan, Wang Jingxian, Zhang Ronghong, Li Chen, Fan Anran, Cui Dongbing, Wu Shumei. Effects of conditioned media of different sources on the proliferation of human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 49-53. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||