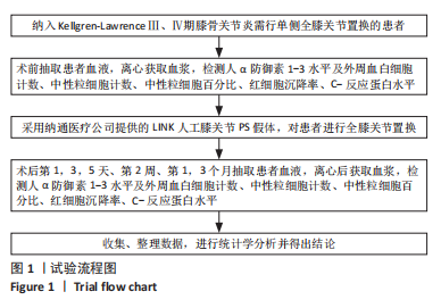
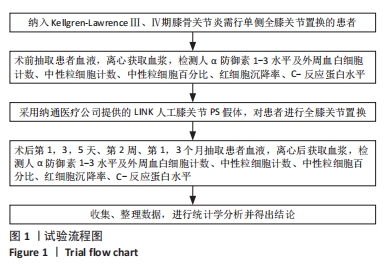
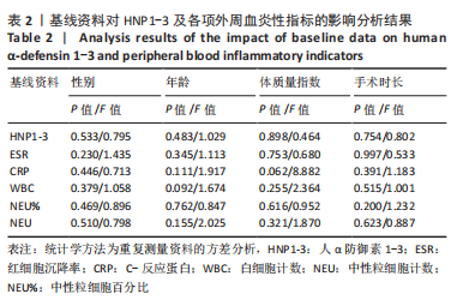
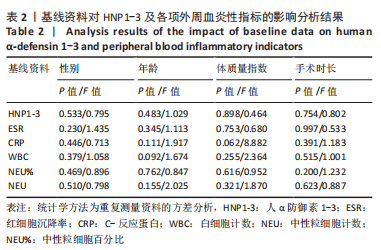
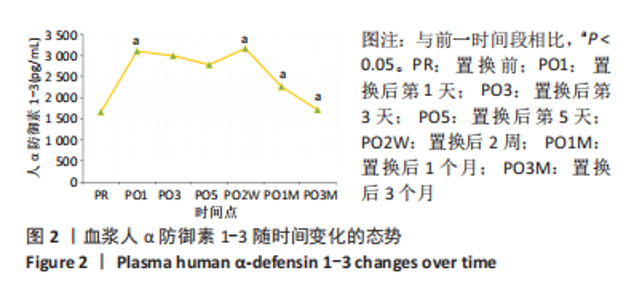
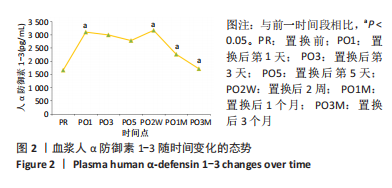
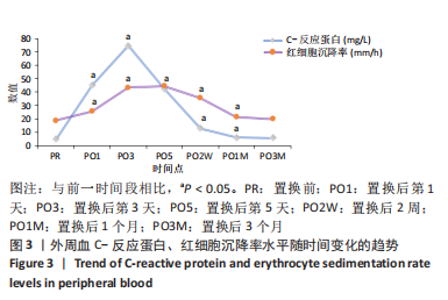
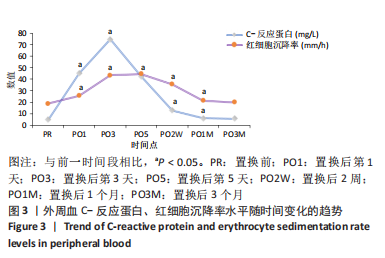
[1] DAMEN J, VAN RIJN RM, EMANS PJ, et al. Prevalence and development of hip and knee osteoarthritis according to American College of Rheumatology criteria in the CHECK cohort. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019; 21(1):4.
[2] JAUREGUI JJ, CHERIAN JJ, PIERCE TP, et al. Long-Term Survivorship and Clinical Outcomes Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(12):2164-2166.
[3] VICTOR J, GHIJSELINGS S, TAJDAR F, et al. Total knee arthroplasty at 15-17 years: does implant design affect outcome? Int Orthop. 2014; 38(2):235-241.
[4] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.
[5] GEORGE J, CHUGHTAI M, KHLOPAS A, et al. Readmission, Reoperation, and Complications: Total Hip vs Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(3):655-660.
[6] LEE DK, KIM HJ, CHO IY, et al. Infection and revision rates following primary total knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis versus osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(12):3800-3807.
[7] POSTLER A, LÜTZNER C, BEYER F, et al. Analysis of Total Knee Arthroplasty revision causes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):55.
[8] WEBER M, RENKAWITZ T, VOELLNER F, et al. Revision Surgery in Total Joint Replacement Is Cost-Intensive. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:8987104.
[9] TARABICHI M, SHOHAT N, GOSWAMI K, et al. Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: The Potential of Next-Generation Sequencing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(2):147-154.
[10] AHMAD SS, HIRSCHMANN MT, BECKER R, et al. A meta-analysis of synovial biomarkers in periprosthetic joint infection: Synovasure™ is less effective than the ELISA-based alpha-defensin test. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(10):3039-3047.
[11] BALATO G, FRANCESCHINI V, ASCIONE T, et al. High performance of α-defensin lateral flow assay (Synovasure) in the diagnosis of chronic knee prosthetic infections. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6):1717-1722.
[12] LEE YS, KOO KH, KIM HJ, et al. Synovial Fluid Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(24):2077-2084.
[13] SALEH A, RAMANATHAN D, SIQUEIRA MBP, et al. The Diagnostic Utility of Synovial Fluid Markers in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(11): 763-772.
[14] GANZ T, SELSTED ME, SZKLAREK D, et al. Defensins. Natural peptide antibiotics of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1985;76(4):1427-1435.
[15] KURTZ SM, LAU E, WATSON H, et al. Economic burden of periprosthetic joint infection in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(8 Suppl): 61-65.e1.
[16] KURTZ SM, HIGGS GB, LAU E, et al. Hospital Costs for Unsuccessful Two-Stage Revisions for Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(2):205-212.
[17] 张海涛,陈锦伦,朱兴阳,等.基于分子对接和网络药理学分析金银花-黄连治疗关节假体周围感染的作用及分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(21):3360-3367.
[18] ZHANG H, SUN X, XIN P, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of D-dimer in periprosthetic joint infection: a diagnostic meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):334.
[19] AICHMAIR A, FRANK BJ, SIMON S, et al. Postoperative IL-6 levels cannot predict early onset periprosthetic hip/knee infections: an analysis of 7,661 patients at a single institution. Eur Cell Mater. 2022;43:293-298.
[20] IORIO R, VIGLIETTA E, MAZZA D, et al. Accuracy and Cost-Effectivenss of a Novel Method for Alpha Defensins Measurement in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(9):3275-3281.
[21] KUO FC, LIN PC, YEN SH, et al. Which Minor Criteria is the Most Accurate Predictor for the Diagnosis of Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infection in the Asian Population? J Arthroplasty. 2022. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2022.05.002.
[22] IVY MI, SHARMA K, GREENWOOD-QUAINTANCE KE, et al. Synovial fluid α defensin has comparable accuracy to synovial fluid white blood cell count and polymorphonuclear percentage for periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(6):1119-1126.
[23] SHOHAT N, YACOVELLI S, CHISARI E, et al. Alpha-defensin does not provide additional benefit over leukocyte esterase in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2021;21(8): 845-849.
[24] GREIDANUS NV, MASRI BA, GARBUZ DS, et al. Use of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level to diagnose infection before revision total knee arthroplasty. A prospective evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(7):1409-1416.
[25] PARVIZI J, GHANEM E, MENASHE S, et al. Periprosthetic infection: what are the diagnostic challenges? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 4: 138-147.
[26] WHITE J, KELLY M, DUNSMUIR R. C-reactive protein level after total hip and total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(5):909-911.
[27] GHANEM E, ANTOCI V JR, PULIDO L, et al. The use of receiver operating characteristics analysis in determining erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein levels in diagnosing periprosthetic infection prior to revision total hip arthroplasty. Int J Infect Dis. 2009;13(6):e444-e449.
[28] ROHE S, BÖHLE S, MATZIOLIS G, et al. C-reactive protein during the first 6 postoperative days after total hip arthroplasty cannot predict early periprosthetic infection. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2022. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04565-4. Online ahead of print.
[29] 林小宁. 髋膝翻修术后炎性相关的血清学变化的动态观察[D].福州:福建医科大学,2018.
[30] LIAO YY, LIN YM. Perioperative testing for joint infection in patients undergoing revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92(5):1314.
[31] JIAO JB, HUANG JC, CHEN X, et al. Albumin to Globulin ratio, Neutrophil to Lymphocyte ratio, and Globulin levels do not outperform ESR or CRP when diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):404.
[32] 倪卫东,罗羲,费军,等.人β防御素-3在人工关节感染患者中的表达及其意义的实验研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2013,15(2):147-151.
|