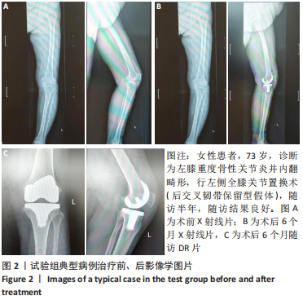
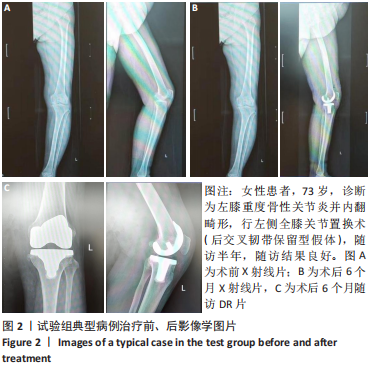
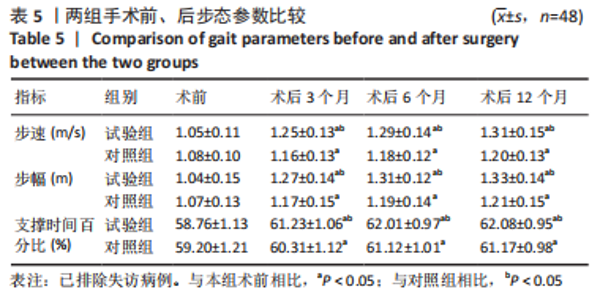
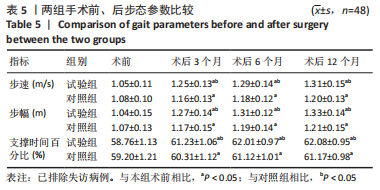
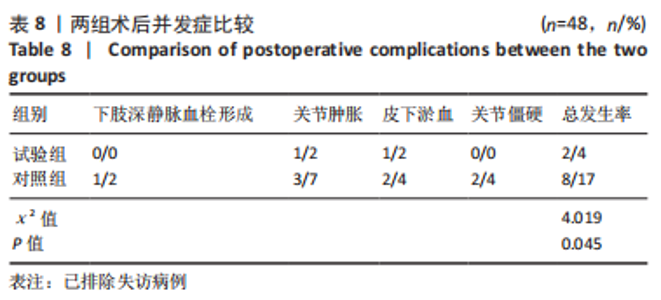
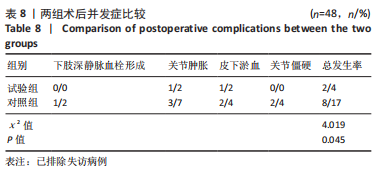
[1] 帖小佳,郑如庚,赵梦,等.中国中老年人膝关节骨关节炎患病率的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(4):650-656.
[2] 陈汉东,田向东,谭冶彤,等.胫骨高位截骨联合外侧支持带松解治疗内翻型膝骨性关节炎合并髌骨外侧高压综合征[J].中国骨伤, 2021,34(1):57-62.
[3] DE LIMA F, MELO G, FERNANDES DA, et al. Effects of total knee arthroplasty for primary knee osteoarthritis on postural balance: A systematic review. Gait Posture. 2021;89(1):139-160.
[4] YACOVELLI S, GRAU LC, HOZACK WJ, et al. Functional Outcomes are Comparable Between Posterior Stabilized and Cruciate-Substituting Total Knee Arthroplasty Designs at Short-Term Follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(3):986-990.
[5] 侯广原,张继学,张志军,等.矢状位假体位置与CR型全膝关节置换对关节活动度的影响[J].安徽医学,2020,41(1):63-65.
[6] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[7] SMALL LT, LAMPKIN M, VURAL E, et al. American Society of Anesthesiologists Class as Predictor for Perioperative Morbidity in Head and Neck Free Flaps. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;161(1):91-97.
[8] 中华人民共和国卫生部.人工膝关节置换技术管理规范(2012年版)[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2013(3):67-69.
[9] NARIN S, UNVER B, BAKıRHAN S, et al. Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the Hospital for Special Sur gery (HSS) Knee Score.Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(3): 241-248.
[10] BEHREND H, GIESINGER K, GIESINGER JM, et al. The “forgotten joint” as the ultimate goal in joint arthroplasty: validation of a new patient-reported outcome measure.J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(3):430-436.e1.
[11] PRIMORAC D, MOLNAR V, ROD E, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of Pathogenesis and State-Of-The-Art Non-Operative Therapeutic Considerations.Genes (Basel). 2020;11(8):854.
[12] 徐一宏,年申生,韩学全,等.全膝关节置换的后稳定型假体和保留后交叉韧带疗效比较[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020, 14(6):685-690.
[13] 曲铁兵,马德思.后交叉韧带保留型人工全膝关节置换浅谈[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(27):2148-2151.
[14] MAYNE A, HARSHAVARDHAN HP, JOHNSTON LR, et al. Cruciate Retaining compared with Posterior Stabilised Nexgen total knee arthroplasty: results at 10 years in a matched cohort.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2017; 99(8):602-606.
[15] 王慧慧,茹嘉,段广斌,等.后交叉韧带保留型假体与后交叉替代型假体在全膝关节置换术治疗中的早期效果研究[J].中国临床实用医学,2021,12(5):51-55.
[16] WANG Z, DENG W, SHAO H, et al. Forgotten Joint Score Thresholds for Forgotten Joint Status and Patient Satisfaction after Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty in Chinese Patients. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(10): 2825-2829.
[17] LEE JY, LOW YM, JIANG L, et al. The Forgotten Joint Score-12 in Anterior Cruciate Ligament injuries. J Orthop. 2020;21(1):117-121.
[18] 杨鑫煜,王伟韬,赵波,等.初次膝关节置换术后一年步态分析参数与患者满意度的研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021,10(7):497-501.
[19] ONISHI S, ISEKI T, KANTO R, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for deep vein thrombosis in patients undergoing osteotomies around the knee: comparative analysis of different osteotomy types. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(10):3488-3494.
[20] DAI X, DING W, LI H, et al. Associations of Serum Lipids and Deep Venous Thrombosis Risk After Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Primary Knee Osteoarthritis. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2020;19(1):51-56.
|