Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (17): 2739-2746.doi: 10.12307/2024.449
Previous Articles Next Articles
Functional characteristics and clinical applications of MXene nanoparticles in wound healing
Wang Xindong1, Liang Chengzhi2, Zhang Yongxian3
- 1Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261000, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Trauma, College of Medicine, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China; 3Department of Osteotraumatic Surgery, 960 Hospital of Chinese People’s Liberation Army Joint Logistics Support Force, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-07-07Accepted:2023-08-17Online:2024-06-18Published:2023-12-16 -
Contact:Zhang Yongxian, MD, Chief physician, Department of Osteotraumatic Surgery, 960 Hospital of Chinese People’s Liberation Army Joint Logistics Support Force, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Xindong, Master, Physician, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261000, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xindong, Liang Chengzhi, Zhang Yongxian. Functional characteristics and clinical applications of MXene nanoparticles in wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2739-2746.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
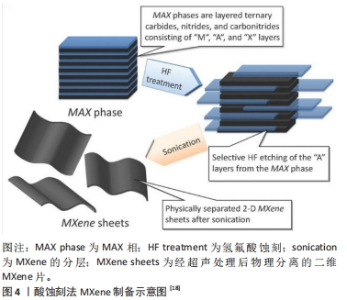
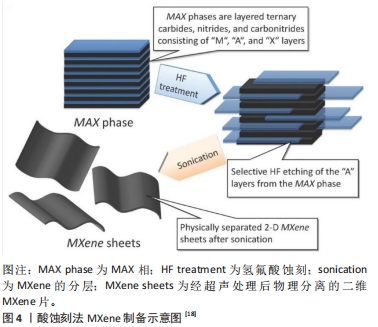
2.1 MXene的合成与改性 2.1.1 MXene的合成 自上而下的合成方法大体分为2个步骤:MAX相的蚀刻和MXene的分层[12]。MAX相的蚀刻是指将MAX相用氢氟酸或含氢氟酸的蚀刻剂或原位形成的氢氟酸通过湿化学蚀刻方法合成MXene的过程,即从MAX相(Mn+1AXn)中除去A元素,例如蚀刻Ti3AlC2中的Al。在MAX相中,A和M元素之间有很强的化学键且难以通过机械手段去除,因此需要通过蚀刻剂选择性蚀刻去除离子键来获得MXene[13]。对于MAX相的合成,以Ti3AlC2 MAX相(Ti3C2Tx的前驱体)为例。Ti3AlC2可通过不同的原料在不同条件下合成。在早期使用Ti2AlC和TiC的混合物来合成Ti3AlC2[14],随着技术的发展,出现了使用较便宜的原材料(TiC,Ti和Al)来合成Ti3AlC2的方法[15]。同时Ti、Al和C,Ti,Al4C3和C,TiO2、 Al和C等混合物也被报道用于合成Ti3AlC2[16-17]。除了上述举例中的铝附着MAX相外,还有其他一些离子连接的MAX相前驱体,如Mn+1SiXn也可用于制备MXene。 第一步骤:首先进行蚀刻,如文献报道所述,浓缩氢氟酸是选择性地从Ti3AlC2中去除Al的首选蚀刻剂。将Max相前体(Ti3AlC2粉末)在室温下浸入体积分数50%氢氟酸中2 h便可选择性蚀刻掉Al。但是高浓度氢氟酸具有显著的毒性,其可诱导细胞死亡、引起全身中毒甚至死亡,因此在制备过程中如何有效避免使用高浓度氢氟酸成为了新的研究课题。有研究比较了30%,10%和5%的3种不同体积分数的氢氟酸,发现仅5%氢氟酸即可去除Al,这说明可以使用稀释蚀刻试剂替代高浓度氢氟酸,以减轻毒性作用。氟化氢盐,如NH4氢氟酸2(30,35)、氟化物基盐(LiF)可以用于原位制备氢氟酸进行蚀刻,虽然原位氢氟酸蚀刻法制备的MXene的性质与氢氟酸合成的方法相似,但其在合成过程中避免了氢氟酸毒性的危害,同时制备出的MXene为单层结构便于进行下一步应用。 除了使用氢氟酸蚀刻或原位形成氢氟酸外,还可以在高温条件下将MAX相中“A”元素替换为其他元素。Al基MAX相和ZnCl2在550 ℃ 的反应下,Al可被Zn取代从而得到基于Zn的MAX相,当使用过量ZnCl2可获得Ti2CCl2和Ti3C2Cl2,因此可以基于氧化还原制备出各种MXene。也有研究报道关于非MAX相前驱体被应用于制备MXene,研究中使用层状三元Zr3Al3C5材料代替MAX相也可在氢氟酸处理下得到MXene。 第二步骤:在通过氢氟酸蚀刻剂选择性地去除Al原子后,进行第二步骤即MXene的分层。在超声处理之前施加插层剂如二甲基亚砜和四烷基氢氧化铵等可以扩大 MXene的层间间距[7],使它们更容易分层形成纯MXene片。因此用插层化合物可以用来扩大MXene薄片的层间间距、削弱2D层之间的相互作用并将MXene脱层成单独的2D片[18],见图4。还有研究通过采用最低强度层分层方法制备MXene[15],该方法不需要超声处理并使用较温和的路线来生产具有更大且缺陷较少的薄片。基于对MXene自上而下合成的目前研究,蚀刻剂选择、蚀刻时间和插层剂类型是确保成功合成生物相容性MXene纳米片的关键参数。"
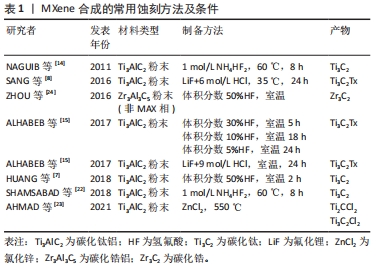
自下而上的合成通常从小的有机/无机分子/原子结构开始,经过晶体生长过程得到2D结构。已有研究使用化学气相沉积技术,在至少1 085 ℃下,用甲烷和铜/钼箔合成碳化钼[19]。通过使用该技术可得到缺陷少、薄而大的高质量纳米片,但通过这种自下而上方法制备的纳米表面缺乏官能团,同时又难以渗透进入细胞,目前来看并不适合大规模应用于生物医学领域。除了化学气相沉积外,有研究报道采用模板法和等离子体增强脉冲激光沉积(plasma enhanced pulsed laser deposition,PELPD)等方法合成MXene[20],如2D氮化物(MoN,V2N和W2N)[21]。自下而上的合成方法可以精确操纵MXene的尺寸分布,形态和表面终止,而这种精确控制其表面端接的合成方式对产物的特性及应用至关重要。因此虽然目前鲜有成功案例,但这种自下而上的合成方式依然值得期待[22-24]。表1归纳了该部分所述的几种用于蚀刻方法及条件。"
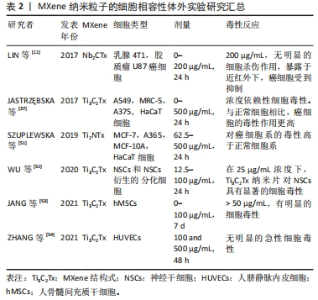
2.1.2 MXene的改性 为了能够更好地应用MXene纳米材料,人们通过各种方法以提高MXenes的生物相容性,有研究通过MXene相表面与胶原蛋白之间的相互作用来控制毒性[25],表面改性提高了 MXenes生物相容性并减少它们的氧化应激,为以后的纳米应用铺平了道路。RASHID等[26]将聚丙二醇和聚乙二醇偶联到Ti3C2Tx纳米片的表面进行修饰并评估了它们对正常(HaCaT和MCF-10 A)和癌性(MCF-7和A375)细胞系的细胞毒性,该研究为伤口敷料的纳米材料应用提供了思路。HUSSEIN等[27]制备了两种基于Ti3C2Tx的纳米复合材料即Au/MXene和Au/Fe3O4/MXene纳米复合材料,在人类乳腺癌细胞系MCF7中,虽然这些纳米复合材料显示出相似的光热治疗效率但杂化纳米复合材料显示出比纯MXene更低的体内毒性,同时使用斑马鱼胚胎进行体内急性毒性测定表明使用Au/MXene和Au/Fe3O4/MXene的胚胎死亡率降低,这项研究证明复合材料能够提高MXene的生物相容性。ROZMYSLOWSKA-WOJCIECHOWSKA等[28]使用阳离子聚合物聚L-赖氨酸(PLL)分子改变Ti3C2 MXene片的表面电荷并在人皮肤恶性黑色素瘤细胞(A375,ATCC)和人类永生角质形成细胞(HaCaT)上测试所得Ti3C2/PLL薄片的细胞毒性,结果显示在高达375 mg/L的浓度范围内,它不显示细胞毒性。同样,WANG等[29]将丝素蛋白包被在MXene薄膜上并使用人皮肤成纤维细胞HSAS1细胞进行体外细胞毒性实验,丝素蛋白包被的MXene在孵育6 d后显示出约99%的细胞活力,荧光图像分析表明即使暴露于丝素蛋白包被的MXene薄膜HSAS1细胞的活力也没有显著变化,这表明丝素蛋白涂层的MXene薄膜具有较好的生物相容性。 如上所述,MXene合成可分为自下而上合成和自上而下合成两种方法。选择适当的合成方法对于合成产物的物理化学性质至关重要,如材料的尺寸、形态和功能等。合成后的MXene可以通过进一步表面修饰来增强生物相容性以便更好地应用于生物医学中。已经有了相当多的关于MXenes表面改性的研究,同时也取得了较为满意的结果,但是仍然缺乏大量体内试验以证明体内短期及长期的安全性。 2.2 MXene 的性质 MXene拥有一系列优异的特性如:亲水性[6,30-31]、抗菌性[32-33]、光热性能[32-34]、导电性[13-15,35-36]、良好的生物相容性[10-11],这些特性都是使其成为出色的皮肤修复材料的基础。 2.2.1 抗菌性能 与氧化石墨烯(GO)相比,Ti3C2Tx对革兰阴性大肠杆菌和革兰阳性枯草芽孢杆菌的抗菌效率更高,且Ti3C2Tx的抗菌活性具有剂量依赖性,还发现在没有Ti3C2Tx的情况下培养的大肠杆菌和枯草芽孢杆菌没有观察到细胞损伤或死亡,而在Ti3C2Tx存在时大部分细菌可观察到不同程度的细胞损伤。同时发现随着 Ti3C2Tx的浓度增加,两种细菌的LDH释放增加,菌落数量也随之减少[32]。SHAMSABADI等[22]研究了4种尺寸的MXene纳米片对大肠杆菌和枯草芽孢杆菌在黑暗中的抗菌性能,黑暗条件以便排除MXene纳米自身光热效应,结果发现MXene纳米片在3 h内便出现细菌DNA泄露及细菌细胞分散。除了对抗菌现象进行观察描述,JASTRZ?BSKA等[37]在结构上进行了研究,系统研究了Ti2C和Ti3C2 MXene原子结构与抗菌性的关系,发现Ti2C和Ti3C2 MXene的表面化学几乎没有差异,但Ti2C MXene不影响细菌的生存而Ti3C2 MXene却表现出抗菌性能,这可能是因为二者在原子尺度上化学成分相同但化学计量不同导致的。除了对常用细菌具有抑制作用,MXene被发现对真菌也具有抑制作用,FENG等[38]研究了Ti3C2Tx MXene的抗真菌特性,使用倒相对比显微镜观察显示在没有MXene的对照组发现有大量的菌丝和孢子,而用脱层Ti3C2Tx(d-Ti3C2Tx)MXene处理的实验组观察到真菌生长抑制现象,同时作者认为d-Ti3C2Tx MXene纳米片通过破坏真菌半球结构达到抑制菌丝生长的效果。在这项工作中开发的d-Ti3C2Tx MXene纳米片可能是一种有前途的抗真菌材料,为促进感染伤口愈合提供了研究基础。以上的各项研究均表明MXene具有良好的抗菌性能,在伤口愈合方面具有巨大达到应用潜力。目前已经有相当多的学者将其与其他材料制备成复合材料用于伤口辅料。 2.2.2 光热性能 有研究结果显示Ti3C2具有100%的光热转换效率,在1个太阳光照射(1 kW/m2)下能达到84%的光-水蒸发效率,这表明MXene是一种有前途的太阳能光热材料。同时该研究证实Ti3C2纳米片在近红外激光照射(808 nm)下表现出较高的近红外吸收和光热转换效率且具有良好的生物相容性[34]。除了Ti3C2外,其他MXene材料也具有相似性能,Nb2C NS表现出极高的光热转换效率(NIR-Ⅰ时为36.4%,NIR-Ⅱ时为45.65%)以及高光热稳定性[11],Ta4C3纳米片被发现具有优异的光热转化性能(效率η为44.7%)[39]。这些研究均表明MXene材料拥有优秀的光热性能,是一种具有应用潜力的新型光热剂。 2.2.3 导电性 MXene的电导率主要取决于其组成成分。如Nb2C,Nb2CF2等成分为金属材料,经过表面改性后可以表现出半导体特性自然也表现出半导体的导电性[40-41]。单个Ti3C2层的结构也类似于半金属且测得其电阻率为≈0.03 μΩm [42] ,这种低电阻率在生物医学应用中具有很大的优势。Ti3C2Tx的电导率可以达到6 500 S/cm [9],同时发现可以通过改变其表面端接来调整带隙从而提高导电性,得到具有高迁移率和适当带隙的2D材料[43]。目前关于MXene的导电性能的报道已有许多[44-45],且已经将其应用到了包括SMC电极、传感器、电子设备、航空航天和生物医学等领域[46]。 2.2.4 亲水性 在MXene表面存在大量亲水性官能团(例如羟基、氧或氟)所以自身表现出了强亲水性[40,45-48],在生物医学应用时与其他疏水性纳米颗粒相比无需进行复杂的表面修饰[49]。优异的亲水性和独特的表面端接提高了MXene的适应能力,经过修饰后的MXene被引入水凝胶等其他复合材料体系时它可以充分地发挥其特性。因为MXene具有优异的亲水性能,目前已被许多学者用作基质材料用于制作新型皮肤伤口敷料。 2.2.5 MXene的生物相容性 MXene因其独特性能理所当然地被广泛用于生物医学研究领域,然而探究其用于医学领域时生物相容性则是绕不开的一个话题。生物相容性是评价一种材料在生物医学领域应用潜力的最关键的参数,没有生物相容性就没有应用的基本条件。MXenes的比表面积和自身电荷使得通过对其表面修饰进行性能控制成为可能[50]。因此,对通过使用聚合物材料、生物大分子或其他各种物质进行表面化学反应来提高生物相容性的方法被诸多学者关注[25]。 一些体外实验发现,MXene对癌细胞系有更强的毒性。有文章探究了MXenes(Ti3C2)对两个正常细胞系(MRC-5和HaCaT)和两个癌性 (A549和A375)细胞系的生物活性影响,结果表明MXenes的悬浮液对HaCaT显示出最佳细胞相容性,此外,与正常细胞相比MXenes对癌细胞的毒性作用更高,同时细胞活力随着Ti3C2浓度的增加而降低。研究同时指出氧化应激现象可能是MXene发挥毒性作用的潜在机制[37]。 SZUPLEWSKA等[51]通过人体皮肤恶性黑色素瘤细胞、人永生化角质形成细胞、人乳腺癌细胞和正常人乳腺上皮细胞4种细胞对Ti2NTx的生物相容性进行体外评价,得出了与JASTRZEBSKA[37]相似的结论,即MXene对癌细胞系的毒性比正常细胞系更高。许多研究发现MXene具有明显的剂量依赖性的毒性,WU等[52]使用神经干细胞衍生细胞和原代神经干细胞研究Ti3C2纳米片的细胞毒性,透射电镜结果表明,在12.5 μg/mL的剂量下,Ti3C2Tx纳米片对神经干细胞或神经干细胞衍生细胞没有观察到不良反应,当质量浓度大于25 μg/mL时,Ti3C2纳米片在神经干细胞中被内化,同时发生显著细胞毒性。JANG等[53]研究发现,高剂量的Ti3C2Tx纳米片(> 50 μg/mL)处理人间充质干细胞时可产生明显的细胞毒性,在50 μg/mL MXenes剂量下,孵育5 d后细胞增殖的开始减少。在100 μg/mL的剂量下,人间充质干细胞细胞增殖显著降低。也有些研究认为MXene对细胞没有毒性作用,ZHANG等[54]用两种不同质量浓度的Ti3C2Tx纳米片(100和500 μg/mL)分别处理人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs)后没有发现明显的急性细胞毒性。用质量浓度为0-200 μg/mL的PVP包被Nb2CTx纳米片处理乳腺4T1癌细胞和胶质瘤U87癌细胞,发现Nb2CTx纳米片没有产生毒性作用[11]。表2将上述讨论的体外生物相容性试验做了汇总。"
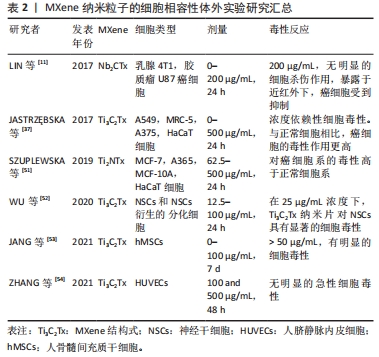
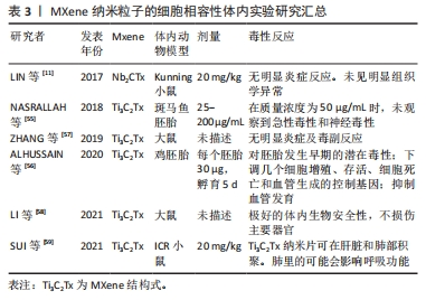
在体内实验中,NASRALLAH等[55]采用斑马鱼胚胎模型来评估Ti3C2Tx纳米片的体内毒性,发现在50 μg/mL的剂量下的Ti3C2Tx纳米片不会影响斑马鱼胚胎的神经元或肌肉活动。而ALHUSSAIN等[56]却得出了相反的结论,其使用鸡胚来探究MXene的发育毒性,以每个胚胎30 μg的剂量进行试验发现Ti3C2Tx纳米片对鸡胚胎产生显著毒性且观察到对脉络膜中血管生成产生抑制作用,分析认为这可能与下调细胞增殖和血管生成相关的基因造成的。ZHANG等[57]将MXene薄膜植入大鼠的皮下和钙质缺损部位,对样本进行micro-CT评估和组织学分析,结果显示MXene薄膜具有良好的骨再生活性和骨诱导性,MXene薄膜既不会诱发毒性副作用也不会引起炎症性副作用。LI等[58]制备出的Bi2S3/Ti3C2Tx-5表现出优异的细胞相容性和生物相容性,可以促进胶原纤维的形成从而加速了伤口愈合。同时其肖特基连接处也显示出优异的体内生物安全性。还有研究通过对注射Nb2CTx后的Kunning小鼠的血液学参数和生化指数进行监测后发现无显著性意义,研究结果表明暴露于Nb2CTx纳米片没有引起明显的炎症[11]。除了以上这些体内实验外还有研究评估了MXene对体内器官的影响,SUI等[59]评估了Ti3C2Tx纳米片对器官功能的影响及其在器官中的分布,对ICR小鼠静脉注射20 mg/kg的Ti3C2Tx纳米片后采集血液、肺、心脏等各大器官标本来测定Ti含量,结果发现Ti3C2Tx纳米片主要分布在肺和肝中,肝脏中积累的纳米片经胆小管逐渐排泄,而肺脏中的纳米片则会干扰呼吸功能,导致呼吸系统疾病。上述关于MXenes的体内实验总结在表3中。"
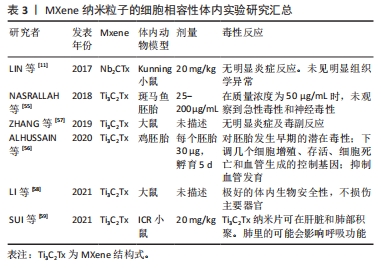
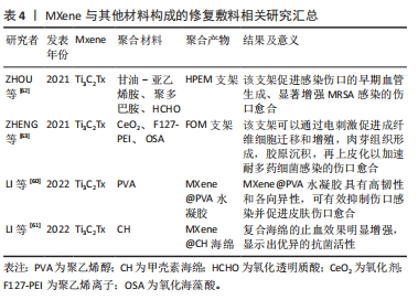
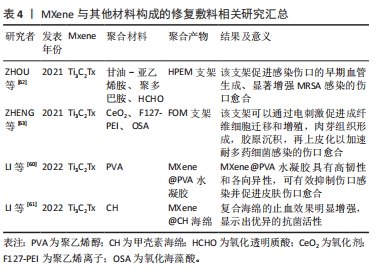
MXene 拥有一系列优异的特性如:亲水性、抗菌性、光热性能、导电性及良好的生物相容性,这些特性都是使其成为出色的皮肤修复材料的基础。在上述体内及体外实验中,MXene展现出良好的生物相容性但目前关于MXene的体内毒性的研究仍然非常有限,MXenes在细胞水平上的细胞毒性和遗传毒性问题和MXene在器官内的生物积累和生物降解性问题均需要进一步研究,这对进一步开发基于MXene纳米的医学应用产品至关重要。 2.3 MXene在伤口愈合中的应用 文章对目前检索到的用于促进皮肤愈合的MXene复合材料进行归纳总结,并按照作用机制分为4部分阐述。 2.3.1 MXene基质材料改善组织修复性能 LI等[60]采用定向冷冻辅助盐析法制备了MXene@PVA水凝胶(anisotropic MXene@PVA hydrogels)。通过对水凝胶进行表征发现该水凝胶具有优异的机械性能(应力高达0.5 MPa,应变高达800%)、出色的光热特性(可以使用NIR激光-808 nm对感染部位进行局部热疗)、广谱抗菌活性(大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制率分别为98.3%和95.5%)及促进NIH-3T3细胞增殖性,在小鼠伤口模型中发现该水凝胶可有效抑制伤口感染并促进皮肤伤口愈合(伤口闭合率为98%)。研究结果表明,MXene@PVA水凝胶具有高韧性和各向异性,是伤口敷料的优秀备选材料。对于新型伤口敷料而言,除了抗菌和促进增殖特性以外,止血性也是一项重要特性,LI等[61]将MXene基纳米材料掺入甲壳素海绵网络中制备出复合海绵以达到止血和促进伤口愈合的目的。在加入MXene基纳米材料后,由于亲血性的改善和血液凝固动力学的加速,复合海绵的止血效果明显增强,此外,复合海绵通过捕获和光热效应之间的协同作用显示出优异的抗菌活性。体内试验证明第9天伤口闭合率可达84%[61]。 除了复合水凝胶、复合海绵等,利用多种材料制备的复合支架系统也被用于皮肤敷料研究中,ZHOU等[62]将聚甘油-亚乙烯胺、Ti3C2Tx MXene@polydopamine (MXene@PDA)纳米片和氧化透明质酸(HCHO)反应制备出HPEM支架。研究证实该支架具有出色的流变性能、自愈性、导电性和组织黏合特性,同时HPEM支架对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和MRSA具有高抗菌活性,还可以刺激细胞增殖、上调α肌动蛋白、胶原蛋白Ⅲ和血管内皮生长因子基因表达。使用全层MRSA感染的伤口模型发现HPEM支架促进感染伤口的早期血管生成、显著增强MRSA感染的伤口愈合[62]。ZHENG等[63]将Ti3C2Tx MXenes与抗氧化剂CeO2相结合制备复合材料,并将其掺入聚乙烯亚胺接枝的聚乙烯离子F127(F127-PEI)和氧化海藻酸钠的动态Schiff基化学交联水凝胶中形成FOM支架。该FOM支架具有多种功能特性,如可注射,抗菌,导电和快速止血等。上述MXene与其他材料构成的修复敷料总结在表4中。体外与体内实验证实该FOM支架可以通过电刺激促进成纤维细胞迁移和增殖,肉芽组织形成,胶原沉积,再上皮化以加速多药耐药菌感染的伤口愈合[64]。"

2.3.2 MXene基质材料辅助光热疗法 基于近红外(NIR)激光的光热疗法把光热剂做为内部能量吸收器,将近红外光能在局部转化为热能产生高热使靶细胞发生坏死或凋亡,近年来随着研究的深入越来越多的学者发现光热疗法除了用于癌症治疗外还可以用于促进皮肤伤口愈合。ZHU等[64]利用光热疗法的思路将具有优异光热特性的 MXene纳米材料和Ag一起构建了Ag/Ti3C2Tx复合材料,在近红外照射下Ag/Ti3C2Tx对革兰阳性金黄色葡萄球菌和革兰阴性大肠杆菌的抗菌作用较单独应用Ag或Ti3C2Tx显著增强,这表明Ag的抗菌特性和Ti3C2Tx光热杀菌产生了协同作用,同时细胞毒性结果表明Ag/Ti3C2Tx具有较好的生物相容性,在此基础上将其包埋于水凝胶用作伤口敷料发现它们在近红外光照射下表现出出色的细菌抑制和促进伤口愈合的性能。ZHANG等[65]通过静电纺丝工艺制备了MXene/沸石咪唑框架8(ZIF-8)/聚乳酸(PLA)复合膜(MZ-8/PLA),该复合膜在808 nm激光照射下表现出有效的光热疗法和光动力疗法(PDT)特性,体外实验表明MZ-8/PLA对大肠杆菌和耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌率分别高达99.9%和99.8%,体内实验证实,MZ-8/PLA可以加速细菌感染的伤口愈合且不产生耐药性。 光敏生物医学材料的抗菌作用除了将NIR转换为局部热能外,还能在光照下产生活性氧[66]。LI等[67]构建了Bi2S3/Ti3C2Tx的界面肖特基结,设想通过加速光诱导电荷转移来增强光催化性能以提高活性氧的产量达到抗菌目的,体外实验中通过铺展板(spread plate),活/死荧光染色(live/dead fluorescence staining)和扫描电镜抗菌图像(SEM antibacterial images)等技术发现Bi2S3/Ti3C2Tx-5对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌有明显抗菌作用,与单独使用活性氧或光热疗法相比活性氧和光热疗法的协同作用拥有更好的抗菌性能,通过构建金黄色葡萄球菌感染的大鼠伤口模型发现,Bi2S3/Ti3C2Tx肖特基结在808 nm近红外照射下显著促进了伤口愈合。同样地,ZHOU等[68]以MXene为基质材料设计并开发了聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物[poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid,PLGA)支架,他们认为PLGA膜可以发挥光热效应在近红外光下产生活性氧并逐渐降解为乳酸盐,同时膜中Lox成分可消耗乳酸盐产生过氧化氢并通过芬顿样反应将产生的过氧化氢催化成羟基自由基实现快速协同灭菌。体内测定表明纳米催化膜通过抗菌、止血、促进伤口局部胶原沉积以及促进血管生成等途径将延迟愈合的慢性伤口重塑再生[68]。通过产生外源性活性氧是一个很好的抗菌新理念,但由于细菌存在内源性抗氧化谷胱甘肽,单纯依靠光疗产生的外源性活性氧可能难以达到理想的抗菌效果,YANG等[69] 通过制备Ti3C2/MoS2生物异质结的抗菌纳米平台提出了解决方案,该平台具有光热、光动力、过氧化物酶样和谷胱甘肽氧化酶样特性,在近红外激光照射下生物异质结既产生局部加热又提高细胞外活性氧水平从而导致细菌失活,同时Mo4+离子可以侵入细菌膜提高细胞内活性氧水平并消耗细胞内谷胱甘肽,内外协同产生抗菌作用。体外实验证实,加载成纤维细胞生长因子21后生物杂交表现出良好的细胞相容性并在体外促进细胞迁移。采用小鼠感染伤口模型进行体内评估证明该抗菌平台具有出色的对抗细菌感染和加速伤口愈合作用。 2.3.3 MXene基质材料辅助电刺激疗法 当上皮受损时自身会产生内源性直流电场(DCEF)和经上皮电位(TEP)差,将电流从受伤区域驱动出来并持续存在于伤口局部直到愈合过程完成。包括人角质形成细胞在内的许多上皮细胞都能够检测到这种电场并做出定向迁移[70]。同时上皮受损产生的生理性直流电场可以主动调节细胞行为,增强血管生成[70],阻断水肿形成,下调炎症因子,促进肉芽组织形成,促进胶原蛋白合成以及诱导皮肤伤口再上皮化[71-78]。当电场被移除时,伤口愈合速度减慢25%[70],这说明电刺激可以有效促进皮肤创口愈合,然而大多数伤口敷料并不具备电活性,因此在愈合过程中无法对伤口部位的生理电信号或外部电刺激做出反应,这成为当前伤口敷料的一大诟病。为了给细胞生长和组织修复提供物理平台同时还允许在伤口部位处实现局部电流递送,MAO等[78]通过化学和物理双交联方法制备出细菌纤维素/MXene (rBC/MXene)水凝胶系统,能够根据内源性电场作用响应外源性电刺激模拟伤口愈合机制从而加速皮肤愈合。试验证明在外部电刺激的存在下,水凝胶和电刺激可以产生协同作用显著提高体外NIH3T3细胞的增殖活性并积极加速体内伤口愈合过程(如伤口面积的减少,胶原蛋白合成和血管形成的增强),同时与非电刺激对照相比可以促进肉芽组织形成,再上皮以及生长因子释放[78]。 2.3.4 MXene材料作为促进皮肤损伤修复的药物载体 使用化学或生物制剂如药物干预是促进伤口愈合的最受欢迎的方法之一,已有学者提出了基于不同形态设计的药物递送系统,以延长药物的释放时间并降低药物的潜在毒性[79-80]。目前刺激响应水凝胶系统已成为伤口管理中有非常前途的药物递送载体。YANG等[81]开发了由MXene包裹的磁性胶体和聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)-海藻酸盐双网水凝胶组成的水凝胶系统向慢性伤口深部递送光敏和磁性响应药物,结果表明该研究构建的水凝胶体系具有可控的药物递送能力,可减少药物的毒副反应并促进伤口愈合,通过大鼠的全层皮肤伤口和皮下感染伤口模型证明了其具有促进皮肤修复的作用。HAO等[82]开发了一种基于导电MXene纳米片和温度敏感PNIPAm聚合物的K-M/PNIPAm水凝胶敷料,该新型水凝胶敷料被发现具有菌株敏感性以及对NIR相变和体积变化的响应性,当用作应变柔性传感器时水凝胶表现出高灵敏度(表规因子-GF为4.491),宽应变范围(约为250%),快响应速度(接近160 ms),良好循环稳定性(在20%应变下为3 000 s)。因此,这种K-M/PNIPAm水凝胶可用作有效的NIR光控药物释放载体以实现药物在伤口深部的按需释放[82]。 除了水凝胶系统外,微针系统因可以无创无痛地穿透皮肤,在构建药物输送系统方面也受到极大的研究兴趣[83-84],SUN等[85]基于以上问题以3-(丙烯酰胺基)苯硼酸-(PBA-)集成聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯(PEGDA)水凝胶作为主体材料制备微针贴片,作者认为衍生的PBA贴片不仅可以提供外源性腺苷还具有螯合内源性腺苷以进行损伤修复的能力,同时在近红外(NIR)照射下MXene可以迅速将光转化为热能从而加速负载的腺苷的释放,体外实验表明,MXene整合的PBA水凝胶对细胞生长没有负面影响,同时腺苷包封的MXene集成微针贴片具有增强血管生成的作用,动物模型结果证明功能性微针贴片能有效地促进血管生成、加速伤口愈合过程。该微针贴片系统可以主动递送且使用天然分子,极大地丰富了该类研究的种类。GUO等[86]受到鲨鱼牙齿扁平和倾斜结构的启发,通过复制激光雕刻制造的负片模具并使用折纸来制备仿生微针贴片,该仿生结构使微针贴片在组织中具有稳定的黏附力,利用多孔有序结构和温度响应性水凝胶在微针贴片上构建可控的药物释放系统。 静电纺丝工艺已被广泛用于生物医学领域,静电纺丝纳米纤维膜具有三维网络结构,因其可以维持伤口部位的吸湿平衡,促进伤口愈合,因此被广泛研究为一种有前途的伤口愈合敷料[87]。XU等[88]将阿莫西林(AMX),MXene和聚乙烯醇(PVA)混合并电纺成抗菌纳米纤维膜(MXene-AMX-PVA纳米纤维膜)用于制作伤口敷料。在复合纳米纤维膜中,PVA基质可以控制AMX的释放以对抗细菌感染,而MXene可以将近红外激光转化为热量,从而导致局部热疗促进AMX释放;同时,局部高热还可以协同导致细菌失活;在金黄色葡萄球菌感染小鼠皮肤缺陷模型上系统验证了复合纳米纤维膜的抑菌活性和伤口愈合能力,该膜不仅起到了AMX和MXene共载物理屏障的作用,而且表现出高抗菌和加速伤口愈合能力。 目前已有许多学者开发出了用于制作伤口敷料的新型复合材料,这些复合材料基于MXene纳米材料并充分利用了其如前所述的优异特性,在皮肤创口局部起到了杀菌、载药缓释、主动调节细胞因子等作用,极大地丰富了治疗慢性伤口的思路与手段。通过MXene纳米材料复合各种传统材料制备出水凝胶、复合海绵及复合支架等新型复合材料用于制备伤口敷料,这些敷料不仅表现出MXene的固有性能还可以发挥出其他传统辅料的功能特性,协同互补提高敷料的组织修复能力达到促进伤口愈合的目的,为伤口治疗提供了新的手段也为伤口新型敷料研发提供了新的思路。MXene纳米材料的光热特性能将其用作复合材料的光热剂产生抗菌特性并与其自身或其他材料的抗菌性产生协同作用,使MXene成为替代抗生素解决药物耐药性及感染伤口的最佳选项之一。可生物降解的电活性rBC/MXene水凝胶是作为皮肤伤口愈合的伤口敷料的一个有希望的候选者,同时该项研究为促进伤口修复提供了有效的协同治疗策略,这对于MXene辅助电刺激疗法促进伤口治疗的发展具有重要意义。基于MXene纳米材料的载药系统能够解决难以在组织深部局部用药的难题,为组织修复提出了新的解决方案。以MXene的各种性能为基础研发出的各种复合材料在创口抗菌及修复中得到满意的结果,显示出其在促进皮肤修复领域正处于发展的初始阶段且具有巨大的发展前景。"

| [1] ZHAO X, WU H, GUO B, et al. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials. 2017;122:34-47. [2] WALKER BW, LARA RP, MOGADAM E, et al. Rational design of microfabricated electroconductive hydrogels for biomedical applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2019;92: 135-157. [3] GUILLAMAT-PRATS R. The Role of MSC in wound healing, scarring and regeneration. Cells. 2021;10(7):1729. [4] ALVEN S, ADERIBIGBE BA. Hyaluronic acid-based scaffolds as potential bioactive wound dressings. Polymers. 2021;13(13):2102. [5] EL-AASSAR MR, IBRAHIM OM, FOUDA MMG, et al. Wound healing of nanofiber comprising polygalacturonic/hyaluronic acid embedded silver nanoparticles: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;238:116-175. [6] NAGUIB M, GOGOTSI Y. Synthesis of two-dimensional materials by selective extraction. Accounts Chem Res. 2015;48(1):128-135. [7] HUANG K, LI Z, LIN J, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2018;47(14):5109-5124. [8] SANG X, XIE Y, LIN MW, et al. Atomic defects in monolayer titanium Carbide(Ti(3)C(2)T(x))MXenes. ACS.nano. 2016;10(10):9193-9200. [9] AKUZUM B, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Rheological characteristics of 2D titanium carbide (MXene) dispersions: a guide for processing MXenes. ACS Nano. 2018;12(3):2685-2694. [10] CHEN K, QIU N, DENG Q, et al. Cytocompatibility of Ti(3)AlC(2), Ti(3)SiC(2), and Ti(2)AlN: in vitro tests and first-principles calculations. ACS Biomate Sci Eng. 2017;3(10):2293-2301. [11] LIN H, GAO S, DAI C, et al. A two-dimensional biodegradable niobium carbide (MXene) for photothermal tumor eradication in NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139(45):16235-16247. [12] HUANG K, LI ZJ, LIN J, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2018;47(14): 5109-5124. [13] ZAMHURI A, LIM GP, MA NL, et al. MXene in the lens of biomedical engineering: synthesis, applications and future outlook. Biomed Eng Online. 2021;20(1):33. [14] NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv Mater. 2011;23(37):4248-4253. [15] ALHABEB M, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene). Chem Mat. 2017;29(18):7633-7644. [16] SCHEIBE B, KUPKA V, PEPLIŃSKA B, et al. The influence of oxygen concentration during MAX Phases (Ti₃AlC₂) preparation on the α-Al₂O₃ microparticles content and specific surface area of multilayered MXenes (Ti₃C₂Tx). Materials (Basel). 2019;12(3):353. [17] BÄRMANN P, HANEKE L, WROGEMANN JM, et al. Scalable synthesis of max phase precursors toward titanium-based mxenes for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(22):26074-26083. [18] WU J, YU Y, SU G. Safety Assessment of 2D MXenes: in vitro and in vivo. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(5):828. [19] KIM Y, WOO WJ, KIM D, et al. Atomic-layer-deposition-based 2D transition metal chalcogenides: synthesis, modulation, and applications. Adv Mater. 2021; 33(47):e2005907. [20] LIU H, CAI Y, GUO Z, et al. Two-dimensional V2N MXene monolayer as a high-capacity anode material for lithium-ion batteries and beyond: first-principles calculations. ACS Omega. 2022;7(21):17756-17764. [21] ZHANG Y, SHEN Q, LI Q, et al. Ultrathin two-dimensional plasmonic ptag nanosheets for broadband phototheranostics in both NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(17):e2100386. [22] SHAMSABADI AA, GH MS, ANASORI B, et al. Antimicrobial mode-of-action of colloidal Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2018;6(12):16586-16596. [23] AHMAD S, ASHRAF I, MANSOOR MA, et al. An overview of recent advances in the synthesis and applications of the transition metal carbide nanomaterials. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland). 2021;11(3):776. [24] ZHOU J, ZHA X, CHEN FY, et al. A Two-dimensional zirconium carbide by selective etching of Al3C3 from nanolaminated Zr3Al3C5. Angewandte Chemie (International ed in English). 2016;55(16):5008-5013. [25] ROZMYSLOWSKA-WOJCIECHOWSKA A, SZUPLEWSKA A, WOJCIECHOWSKI T, et al. A simple, low-cost and green method for controlling the cytotoxicity of MXenes, Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl. 2020;111:8. [26] RASHID B, ANWAR A, SHAHABUDDIN S, et al. A comparative study of cytotoxicity of PPG and PEG surface-modified 2-D Ti3C2 MXene flakes on human cancer cells and their photothermal response. Materials. 2021;14(16):14. [27] HUSSEIN EA, ZAGHO MM, RIZEQ BR, et al. Plasmonic MXene-based nanocomposites exhibiting photothermal therapeutic effects with lower acute toxicity than pure MXene. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:4529-4539. [28] ROZMYSLOWSKA-WOJCIECHOWSKA A, MITRZAK J, SZUPLEWSKA A, et al. Engineering of 2D Ti3C2 MXene surface charge and its influence on biological properties. Materials. 2020;13(10):18. [29] WANG DY, WANG LL, LOU Z, et al. Biomimetic, biocompatible and robust silk Fibroin-MXene film with stable 3D cross-link structure for flexible pressure sensors. Nano Energy. 2020;78:8. [30] ALWARAPPAN S, NESAKUMAR N, SUN D, et al. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for sensors and biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022;205:113943. [31] ZHANG YJ, WANG L, ZHANG NN, et al. Adsorptive environmental applications of MXene nanomaterials: a review. RSC Adv. 2018;8(36):19895-19905. [32] RASOOL K, HELAL M, ALI A, et al. Antibacterial activity of Ti₃C₂Tx MXene. ACS nano. 2016;10(3):3674-3684. [33] LI RY, ZHANG LB, SHI L, et al. MXene Ti3C2: an effective 2D light-to-heat conversion material. ACS nano. 2017;11(4):3752-3759. [34] LIN H, WANG XG, YU LD, et al. Two-dimensional ultrathin mxene ceramic nanosheets for photothermal conversion. Nano Lett. 2017;17(1):384-391. [35] ZHAO MQ, XIE XQ, REN CE, et al. Hollow MXene Spheres and 3D Macroporous MXene frameworks for Na-ion storage. Adv Mater. 2017. doi: 10.1002/adma. 201702410. [36] KIM SJ, KOH HJ, REN CE, et al. Metallic Ti3C2TX MXene gas sensors with ultrahigh signal-to-noise ratio. ACS nano. 2018;12(2):986-993. [37] JASTRZĘBSKA AM, SZUPLEWSKA A, WOJCIECHOWSKI T, et al. In vitro studies on cytotoxicity of delaminated Ti3C2 MXene. J Hazard Mater. 2017;339:1-8. [38] FENG A, HOU T, JIA Z, Et al. Preparation and characterization of epoxy resin filled with Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets with excellent electric conductivity. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020;10(1):162. [39] LIN H, WANG Y, GAO S, et al. Theranostic 2D tantalum carbide (MXene). Adv Mater. 2020;32(42):e2003085. [40] YU H, LIN W, ZHANG Y, et al. Exploring the potentials of Ti3N2 and Ti3N2X2 (X=O, F, OH) monolayers as anodes for Li or non-Li ion batteries from first-principles calculations. RSC Adv. 2019;9(69):40340-40347. [41] YANG X, GAO N, ZHOU S, et al. MXene nanoribbons as electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction with fast kinetics. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2018; 20(29):19390-19397. [42] YAO Z, SUN H, SUI H, et al. 2D/2D heterojunction of R-scheme Ti3C2 MXene/MoS2 nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic performance. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2020;15(1):78. [43] LAI S, JEON J, JANG SK, et al. Surface group modification and carrier transport properties of layered transition metal carbides (Ti2CTx, T: -OH, -F and -O). Nanoscale. 2015;7(46):19390-19396. [44] ZAZOUM B, BACHRI A, NAYFEH J. Functional 2D MXene inks for wearable electronics. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2021;14(21):6603. [45] AHMAD S, ASHRAF I, MANSOOR MA, et al. An overview of recent advances in the synthesis and applications of the transition metal carbide nanomaterials. Nanomaterials. 2021;11(3):34. [46] ZHANG YZ, LEE KH, ANJUM DH, et al. MXenes stretch hydrogel sensor performance to new limits. Sci Adv. 2018;4(6):7. [47] HE SS, SUN X, ZHANG H, et al. Preparation strategies and applications of MXene-polymer composites: a review. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2021;42(19):23. [48] DAMIRI F, RAHMAN MH, ZEHRAVI M, et al. MXene (Ti3C2Tx)-embedded nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications: a review. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2022;15(5):1666. [49] LI L, JIANG G, AN C, et al. Hierarchical Ti3C2@TiO2 MXene hybrids with tunable interlayer distance for highly durable lithium-ion batteries. Nanoscale. 2020; 12(18):10369-10379. [50] CHIMENE D, ALGE DL, GAHARWAR AK. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for biomedical applications: emerging trends and future prospects. Adv Mater. 2015;27(45):7261-7284. [51] SZUPLEWSKA A, ROZMYSŁOWSKA-WOJCIECHOWSKA A, POŹNIAK S, et al. Multilayered stable 2D nano-sheets of Ti(2)NT(x) MXene: synthesis, characterization, and anticancer activity. J Nanobiotechnol. 2019;17(1):114. [52] WU W, GE H, ZHANG L, et al. Evaluating the cytotoxicity of Ti3C2 MXene to neural stem cells. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020;33(12):2953-2962. [53] JANG JH, LEE EJ. Influence of MXene particles with a stacked-lamellar structure on osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2021;14(16):192-194. [54] ZHANG DK, ZHENG W, LI X, et al. Investigating the effect of Ti3C2 (MXene) nanosheet on human umbilical vein endothelial cells via a combined untargeted and targeted metabolomics approach. Carbon. 2021;178:810-821. [55] NASRALLAH GK, AL-ASMAKH M, RASOOL K, et al. Ecotoxicological assessment of Ti3C2Tx (MXene) using a zebrafish embryo model. Environ Sci-Nano. 2018;5(4): 1002-1011. [56] ALHUSSAIN H, AUGUSTINE R, HUSSEIN EA, et al. MXene nanosheets may induce toxic effect on the early stage of embryogenesis. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2020;16(3):364-372. [57] ZHANG JB, FU Y, MO AC. Multilayered titanium carbide MXene film for guided bone regeneration. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:10091-10102. [58] LI J, LI Z, LIU X, et al. Interfacial engineering of Bi2S3/Ti3C2T(x) MXene based on work function for rapid photo-excited bacteria-killing. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1): 1224. [59] SUI B, LIU X, SUN J. Biodistribution, inter-/intra-cellular localization and respiratory dysfunction induced by Ti3C2 nanosheets: Involvement of surfactant protein down-regulation in alveolar epithelial cells. J Hazard Mater. 2021;402:123562. [60] LI Y, HAN MM, CAI Y, et al. Muscle-inspired MXene/PVA hydrogel with high toughness and photothermal therapy for promoting bacteria-infected wound healing. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(4):1068-1082. [61] LI S, GU B, LI X, et al. MXene-enhanced chitin composite sponges with antibacterial and hemostatic activity for wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(12):e2102367. [62] ZHOU L, ZHENG H, LIU ZX, et al. Conductive antibacterial hemostatic multifunctional scaffolds based on Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets for promoting multidrug-resistant bacteria-infected wound healing. ACS nano. 2021;15(2): 2468-2480. [63] ZHENG H, WANG SQ, CHENG F, et al. Bioactive anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, conductive multifunctional scaffold based on MXene@CeO2 nanocomposites for infection-impaired skin multimodal therapy. Chem Eng J. 2021;424:12. [64] ZHU XQ, ZHU YN, JIA K, et al. A near-infrared light-mediated antimicrobial based on Ag/Ti3C2T(x)for effective synergetic antibacterial applications. Nanoscale. 2020;12(37):19129-19141. [65] ZHANG SQ, YE JW, LIU X, et al. Titanium carbide/zeolite imidazole framework-8/polylactic acid electrospun membrane for near-infrared regulated photothermal/ photodynamic therapy of drug-resistant bacterial infections. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021;599:390-403. [66] LI M, LI L, SU K, et al. Highly effective and noninvasive near-infrared eradication of a staphylococcus aureus biofilm on implants by a photoresponsive coating within 20 min. Adv Sci. 2019;6(17):1900599. [67] LI JF, LI ZY, LIU XM, et al. Interfacial engineering of Bi2S3/Ti3C2Tx MXene based on work function for rapid photo-excited bacteria-killing. Nature Commun. 2021;12(1):10. [68] ZHOU X, WANG ZY, CHAN YK, et al. Infection micromilieu-activated nanocatalytic membrane for orchestrating rapid sterilization and stalled chronic wound regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(7):23. [69] YANG ZP, FU XL, MA DC, et al. Growth factor-decorated Ti3C2 MXene/MoS2 2D bio-heterojunctions with quad-channel photonic disinfection for effective regeneration of bacteria-invaded cutaneous tissue. Small. 2021;17(50):18. [70] PAI VP, COOPER BG, LEVIN M. Screening biophysical sensors and neurite outgrowth actuators in human induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived neurons. Cells. 2022;11(16):2470. [71] BENITO-MARTÍNEZ E, SENOVILLA-HERGUEDAS D, DE LA TORRE-MONTERO JC, et al. Local and contralateral effects after the application of neuromuscular electrostimulation in lower limbs. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(23): 9028. [72] UD-DIN S, SEBASTIAN A, GIDDINGS P, et al. Angiogenesis is induced and wound size is reduced by electrical stimulation in an acute wound healing model in human skin. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):22. [73] RAMPAZO ÉP, LIEBANO RE, PINFILDI CE, et al. High voltage pulsed current in collagen realignment, synthesis, and angiogenesis after Achilles tendon partial rupture. Braz J Phys Ther. 2016;20(4):312-319. [74] KIM KL, PARK GY, MOON YS, et al. The effects of treatment using polydeoxyribonucleotide through extracorporeal shock wave therapy: synergic regeneration effects on atrophied calf muscles in immobilized rabbits. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(16):853. [75] JANG D, SHIM J, SHIN DM, et al. Magnesium microneedle patches for under-eye wrinkles. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35(9):e15732. [76] REID B, ZHAO M. The Electrical response to injury: molecular mechanisms and wound healing. Adv Wound Care. 2014;3(2):184-201. [77] THRIVIKRAMAN G, BODA SK, BASU B. Unraveling the mechanistic effects of electric field stimulation towards directing stem cell fate and function: a tissue engineering perspective. Biomaterials. 2018;150(1):60-86. [78] MAO L, HU SM, GAO YH, et al. Biodegradable and electroactive regenerated bacterial Cellulose/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) composite hydrogel as wound dressing for accelerating skin wound healing under electrical stimulation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(19):13. [79] KIM HS, SUN X, LEE JH, et al. Advanced drug delivery systems and artificial skin grafts for skin wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146(1):209-239. [80] LIANG Y, ZHAO X, HU T, et al. Adhesive hemostatic conducting injectable composite hydrogels with sustained drug release and photothermal antibacterial activity to promote full-thickness skin regeneration during wound healing. Small. 2019;15(12):e1900046. [81] YANG X, ZHANG CQ, DENG DW, et al. Multiple stimuli-responsive MXene-based hydrogel as intelligent drug delivery carriers for deep chronic wound healing. Small. 2022;18(5):10. [82] HAO F, WANG LY, CHEN BL, et al. Bifunctional smart hydrogel dressing with strain sensitivity and NIR-responsive performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(39):46938-46950. [83] ZHANG X, CHEN G, BIAN F, et al. Encoded microneedle arrays for detection of skin interstitial fluid biomarkers. Adv Mater. 2019;31(37):e1902825. [84] YANG SY, O’CEARBHAILL ED, SISK GC, et al. A bio-inspired swellable microneedle adhesive for mechanical interlocking with tissue. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1702. [85] SUN L, FAN L, BIAN F, et al. MXene-integrated microneedle patches with innate molecule encapsulation for wound healing. Research (Wash D C). 2021; 2021(6):126-129. [86] GUO MZ, WANG YQ, GAO BB, et al. Shark tooth-inspired microneedle dressing for intelligent wound management. ACS Nano. 2021;15(9):15316-15327. [87] DING YP, LI W, ZHANG F, et al. Electrospun fibrous architectures for drug delivery, tissue engineering and cancer therapy. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(2):35. [88] XU X, WANG SG, WU H, et al. A multimodal antimicrobial platform based on MXene for treatment of wound infection. Colloid Surf B-Biointerfaces. 2021; 207(1):10. |
| [1] | Liu Anhong, Cai Mengmeng, Han Xiao, Wang Zhanhui. Research status on element selection of medical magnesium alloy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 777-782. |
| [2] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [3] | Zhu Liwei, Wang Jiangyue, Bai Ding. Application value of nanocomposite gelatin methacryloyl hydrogels in different bone defect environments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 753-758. |
| [4] | Chen Pinrui, Pei Xibo, Xue Yiyuan. Function and advantages of magnetically responsive hydrogel in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 452-457. |
| [5] | Xu Jing, Lyu Huixin, Bao Xin, Zhang Yi, Wang Yihan, Zhou Yanmin. Application of near infrared responsive hydrogels in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 486-492. |
| [6] | Zhu Yongzhao, Fang Chao, Zhao Fang, Zhang Qing, Zhao Dan. Mechanism by which lycium barbarum polysaccharides inhibit keratinocyte apoptosis in burn wounds via autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3686-3691. |
| [7] | Xiao Ziteng, Wang Tingyu, Zhang Wenwen, Tan Fengyi, Su Haiwei, Li Siting, Wu Yahui, Zhou Yanfang, Peng Xinsheng. Exosomes and skin wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(19): 3104-3110. |
| [8] | Gang Fangli, Shi Rui, Ma Chunyang, Xiao Yi. Low-temperature condensation deposition method for 3D printing of bone tissue engineering poly-L-lactic acid/pearl powder composite scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2702-2707. |
| [9] | Wang Jinlei, Li Ke, Zhao Liang. Platelet-camouflaged silver nanoparticle hydrogel accelerates wound healing in type 1 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2659-2666. |
| [10] | He Wei, Zhou Zheng, Wu Lingling, Wang Kai, Mu Caiyun. Moxibustion and reduced graphene oxide/cerium dioxide nanocomposites for repairing infectious wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2307-2314. |
| [11] | Guo Yuxin, Wang Hao, Li Mingqi, Chen Yueying, Pan Juhong, Huang Xin, Wang Zhiwen, Zhou Qing. Ultrasound-optimized hydrogel scaffold used to promote transdermal delivery of gold nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(15): 2330-2337. |
| [12] | Dong Hongfei, Huang Xi, Li Xianhui, Zhang Yanbiao, Wang Xuyang, Wang Bing, Sun Hongyu. Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in promoting acute skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2047-2053. |
| [13] | Zhao Lixin, Tang Qingxi, Zhang Kezhong. Influence of adipose tissue and its derivative on wound repair and vascularization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2120-2125. |
| [14] | Lyu Shangyi, He Huiyu, Wufanbieke · Baheti, Yang Quan, Ma Lisha, Han Xiangzhen. Physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of graphene oxide-hydroxyapatite composite coating materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1477-1483. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Zhang Wen, Zhu Can, Sun Jie, Ding Yicheng, Shi Qin. Inhibitory effect of bovine serum albumin-chitosan nanoparticles loaded with EPZ6438 on osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1512-1518. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||