Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 777-782.doi: 10.12307/2024.269
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research status on element selection of medical magnesium alloy
Liu Anhong1, 2, 3, Cai Mengmeng3, Han Xiao3, Wang Zhanhui3
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 3Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Luoyang Central Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-21Accepted:2023-05-08Online:2024-02-18Published:2023-08-17 -
Contact:Wang Zhanhui, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Luoyang Central Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Liu Anhong, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Luoyang Central Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U1404825 (to WZH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Anhong, Cai Mengmeng, Han Xiao, Wang Zhanhui. Research status on element selection of medical magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 777-782.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
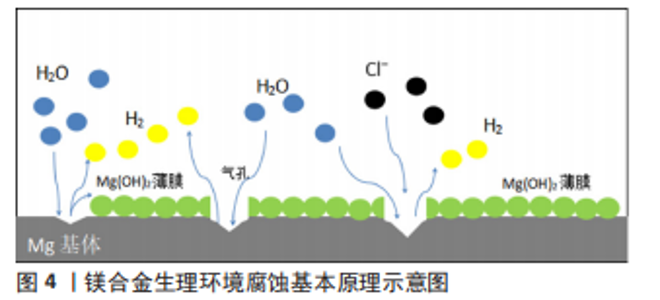
2.1 金属镁及其合金的特性 2.1.1 镁及其合金的一般情况 金属镁是自然界储存量最丰富的元素之一,来源广价格低、性能优越,是生物医学领域很有前途的金属材料。镁是人体保持健康所必需的营养元素之一,参与人体内一系列的新陈代谢过程,是许多组织器官生理功能保持正常所必需的,特别是心脏、大脑、肌肉和骨骼系统[8]。镁合金具有低密度、高比强度、高阻尼性、高可加工性、与骨相似的密度和弹性模量、较小的应力屏蔽效应以及优秀的生物相容性、良好的安全降解性和可吸收性等优点[7,9-11],这些特性使得镁合金十分适合作为可生物降解的暂时性植入器械,例如骨科螺钉和心血管支架。WINDHAGEN等[12]在拇外翻手术中比较了镁合金与钛合金螺钉的疗效,结果表明相较于钛合金组,镁合金组表现出相似的结果,且没有观察到任何异物反应、骨质溶解或全身炎症反应的案例,展现出骨科应用的巨大潜力。ROLA等[13]比较了植入Magmaris镁合金支架与聚合物Absorb支架在非ST段抬高型急性冠脉综合征患者中的1年表现,临床数据表明与Absorb组相比,Magmaris组的急性冠脉综合征临床疗效更佳,同时在Magmaris植入人群中随访12个月后发现没有明确的支架血栓形成。同时,镁合金在MRI中的金属伪影被评估[14],虽然镁合金会导致MRI成像中的图像伪影或失真,但与其他永久性金属植入物相比,镁合金对MRI成像质量的影响较小。当镁合金被植入人体后,在提供足够的生物力学支持后逐渐降解,最终无残留,避免了其他植入式生物材料(如钛合金和不锈钢等)所需要的二次手术和可能造成的二次感染,从而减少了患者出现新并发症的风险;但镁合金也存在降解过程中氢气的析出和局部组织pH值升高等缺点,可能对植入物周围组织造成伤害,特别是耐腐蚀性能差以及其造成的合金完整结构过早丧失,限制了镁合金进一步的发展和应用[7,9-11]。为了增强镁合金的性能、扩大其应用范围,镁及其合金降解过程一直是科研人员的研究热点。 2.1.2 镁及其合金的基本降解过程 镁金属的标准电极电位为-2.37 V,在酸性、中性和弱碱性介质中具有活跃的化学性能,在生理环境中就容易被腐蚀。当镁被置于生理溶液中时其降解开始于阳极反应,在镁基体表面产生了Mg2+和电子(公式1);阴极发生阴极反应,H2O获得这些电子产生H2和OH?(公式2);最终,产物氢氧化镁[Mg(OH)2]薄膜覆盖在镁基体表面(公式3),这限制了离子的进一步迁移,一定程度上降低了合金的腐蚀速率[7,15]。然而,在腐蚀部位产生的H2气体导致了在镁基体表面沉积的Mg(OH)2沉淀物的分裂,因此阻止了在镁基体表面形成均匀的Mg(OH)2薄膜,最终形成的Mg(OH)2薄膜疏松多孔,外部腐蚀介质可以通过这些孔进一步腐蚀暴露的合金基底。因此,镁及其合金的降解不是自抑制的,它会一直持续到底物完全降解为止。值得注意的是,氯离子(Cl?)会导致腐蚀产物Mg(OH)2转化为更可溶的MgCl2[15],Mg(OH)2膜的溶解加速了腐蚀过程(公式4和5)[7,15]。人体内的氯离子浓度约为100 mmol/L,这些氯离子会破坏形成的Mg(OH)2薄膜层,这个过程加速了镁合金在体内的降解,示意图见图4。此外,人体中还存在HCO3-、SO42-和HPO42-等侵袭性离子,它们也会加速合金的腐蚀[16]。"
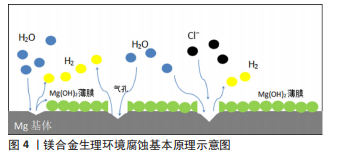
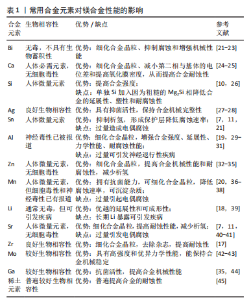
阳极反应:Mg→ Mg2+ + 2e? 公式(1) 阴极反应:2H2O+2e? → 2OH?+H2 公式(2) 总反应式:Mg+2H2O → Mg(OH)2+H2 公式(3) Mg2++2Cl? →MgCl2 公式(4) Mg(OH)2+2Cl? → MgCl2+2OH? 公式(5) 镁及其合金在人体内的腐蚀行为比较复杂,其腐蚀机制取决于多种因素,如腐蚀介质、合金成分、合金微观结构和合金基体表面膜的性能等。人体体液介质存在多种细胞及有机无机物,且介质pH值环境复杂,液体流动速度不尽相同,镁合金在体内的腐蚀类型和速度比模拟环境中的降解更为复杂,降解行为多种多样,不可控因素更多,所以,大多数关于体液对镁腐蚀影响的研究都是通过体外模拟进行的。虽然模拟体液含有不同类型和数量的各种成分、不同的pH值环境等,为腐蚀测试创造了很多可变条件,但从体外和体内实验中获得的结果很多是不一致的,因为体外实验很难模拟真实人体环境的可变性和复杂性。为了解不同类型及不同状态镁合金处于不同部位人体环境中的腐蚀,研究人员做出了相当大的努力,但仍然没有完全理解,镁合金的体内降解仍然需要长远研究。 合金化是已知提升镁合金耐腐蚀性能的方法之一,并可通过添加不同合金成分来改善镁合金各方面性能,是生物医学领域的研究重点。 2.2 镁合金的元素选择 合金化作为材料学上常用的改善金属材料性能的手段之一,是解决镁合金低弹性模量、降解过程中氢气的析出以及耐腐蚀性能差等问题最直接、简单和有效的途径。适当的加入合金成分可以通过细化合金晶粒[17]、改善镁合金的微观结构[18]、优化第二相的类型及分布[19]、改变析出相与基体表面电位差等方式改善镁合金的各种性能[11,20],使其能满足需求。因此,通常向镁及其合金中引入特定的合金元素,通过制备二元、多元合金来调整镁及其合金的性能,扩大其应用范围。镁合金在生物医学领域作为极具潜力的医用植入材料,合金的生物相容性是首先需要考虑的。生物相容性是指医用植入材料能够承受宿主各系统的作用,在机体动态变化过程中保持相对稳定的状态而不被排斥,且不对机体有毒副作用的生物学特性。因此,研究者需要谨慎选择合适的元素和可行的加工方法,优化具有生物力学性能新型镁合金的成分设计,以确保产品能满足需求。目前生物医学领域常研究的合金化元素有铋(Bi)、钙(Ca)、硅(Si)、银(Ag)、锡(Sn)、铝(Al)、锌(Zn)、锰(Mn)、锂(Li)、锶(Sr)、锆(Zr)、钼(Mo)、镓(Ga)和稀土元素等,这些元素对镁合金性能的影响见表1。"
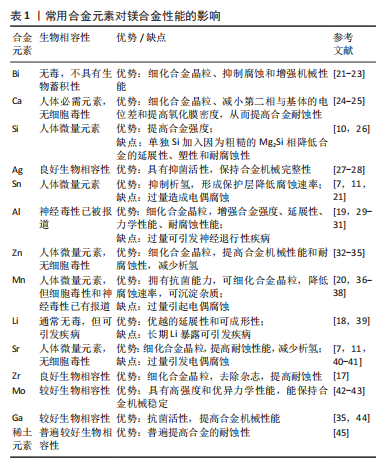

铋(Bi):Mg-Bi合金体系无毒、不具有生物蓄积性、能形成稳定的Mg3Bi2相,同时铋元素在合金基体内部处于溶质状态时可以抑制Mg-Bi基合金的腐蚀速率,具有很大的开发潜力[21]。WANG等[22]进一步的研究表明,添加铋元素可以细化合金的晶粒,且随着铋的加入,合金强度、延展性和热稳定性提高。Somekawa等[23]研究表明,超细晶粒的Mg-Bi合金具有良好的变形能力和优异的抗断裂能力。 钙(Ca):是人体必需的元素之一,无细胞毒性,是人体内含量最多的矿物质。Ca2+是形成骨基质的离子之一,是维持骨微结构的重要元素,且Ca2+通过细胞信号传导影响骨组织再生以及延长骨细胞寿命,同时能促成骨-种植体界面联系形成,这使得Mg-Ca合金作为骨植入材料表现出很大的优势[10]。适量钙加入可以细化合金晶粒、抑制晶界化合物、减小第二相与基体的电位差和提高氧化膜密度,从而阻碍腐蚀,提高镁合金的耐蚀性[24-25]。 硅(Si):是人体必需的微量元素之一,有利于维持骨密度和结缔组织功能;同时它还能促进成骨细胞增殖分化、胶原分泌、骨基质矿化和骨-种植体界面联系的形成,抑制骨吸收,是骨形成过程中不可或缺的元素[10]。硅虽然是镁合金化常用的元素,在镁中加入硅可以提高合金熔体的流动性,同时因为第二相硬化效应而提高了合金强度,但是硅在镁中的溶解度很低(质量分数0.006%),且Mg-Si二元合金中产生的粗糙Mg2Si相降低了合金的延展性、塑性和耐腐蚀性,并且纯镁和Mg-Si合金在屈服强度和极限抗拉强度方面没有显著差异,通常认为单独的硅加入对镁合金性能提升有限,硅需要与其他元素一起添加以改善镁合金的性能[10,26]。 银(Ag):银元素因为其良好的抗菌性能有利于镁合金的生物医学应用。TIE等[27]研究了Mg-Sr-Ag合金作为输尿管支架在猪体内的性能,结果表明银的加入使合金具有明显的抑菌活性,同时不断降解的合金可以抑制生物膜的形成,进而减少与周围感染相关的并发症,且合金降解产物对肝肾功能无明显影响,表现出良好的生物相容性。CHEN等[28]的研究表明,添加银的合金在体外也表现出增强的成骨细胞活性和基因表达活力,以及持久的合金机械完整性。 锡(Sn):是人体内的微量元素之一,能促进组织生长和创伤愈合,有利于生长发育。此前有研究表明,由于锡具有较高的析氢过电位,合金中锡的添加可以抑制其析氢速率[7,11,21]。此外,锡的合金化可以降低Mg-Al基合金的晶粒尺寸,并形成以SnO2为主的腐蚀产物层;SnO2比Mg(OH)2更稳定,SnO2的存在有利于形成致密的由SnO2和Mg(OH)2共同组成的保护层,降低合金基体的溶解速率。然而,锡的电位(?0.14 V)比镁的电位(?2.37 V)更高,过多的锡合金化会导致Mg2Sn相的析出,从而诱发了晶界与镁基体之间的微电偶腐蚀。JIANG等[46]研究了Mg-4Zn-xSn合金(x=0%,1.0%,1.5%和2.0%)的性能,发现锡质量分数超过1.5%时会加速合金的腐蚀。 铝(Al):适量铝元素的添加对镁合金的影响十分有利,可以细化合金晶粒及增强合金的强度、延展性和力学性能,并提高耐腐蚀性能[19,29-30]。添加铝后,在完全重结晶的细晶粒和多级β相(Mg17Al12)沉淀物的协同作用下可有效防止镁合金的进一步腐蚀[19]。虽然铝被认为是无毒的,但此前有研究表明铝会对人类健康产生负面影响。Al3+在神经系统中的沉积会引起炎症,导致脑细胞损伤和病理状况,甚至可能促进大脑衰老,进而引发神经退行性疾病[31],如多发性硬化症、帕金森病和阿尔茨海默病等[47-48]。此外,它还可能破坏组织中的促氧化/抗氧化平衡,导致生理和生化功能障碍[49]。尽管如此,学者们目前对Mg-Al合金的研究热情依旧高涨,例如AZ91等含铝元素的镁合金。RAPIEJKO等[30]用锆(Zr)元素细化AZ91合金的微观结构,结果表明提升了合金的性能。LI等[50]将中药提取物作为一种新型的缓蚀剂,用于AZ91合金的腐蚀研究,结果表明有效缓解了合金的腐蚀。值得注意的是,以AZ31B镁合金为例,按成分标准计算铝含量约为100 μg,铝含量远远低于世界卫生组织(WHO)推荐的每天0.7 mg/kg的安全剂量,因此,估计AZ31B镁合金支架中铝的含量不足以引起神经毒性。ERI?EN等[51]研究了AZ31B合金中铝对神经细胞的负面影响,体外和体内研究证明,在合金降解过程中Al3+浓度不超过21.78 μmol/L,血液和脑脊液中溶解的Al3+不会对神经细胞的活力造成危险。 锌(Zn):是人体保持健康所必需的微量元素之一,无细胞毒性,具有良好的生物相容性。锌在细胞各种功能中起着重要作用,不仅包括促进蛋白质结构调节、细胞转录、细胞信号通路和多种酶的功能保持正常[52-53],还具有良好的成骨作用和抗菌抗炎潜力等[54-55]。锌的加入细化了合金晶粒,提高了合金的表面完整性,使得Mg-Zn合金具有良好的力学性能和较高的耐腐蚀性[32]。同时锌对合金有着时效硬化和固溶强化作用[54],提高了镁合金的机械性能,如硬度、拉伸强度、延展性和可成形性等[33],并显著减少氢气的析出[34-35]。Mg-Zn合金作为新型医用材料的主要研究方向之一,锌的加入对增强镁合金的性能有很大的影响。HU等[32]测试了通过真空热压烧结法制备的含有3种锌含量(质量分数10%,20%,30%)镁合金的性能,发现合金的硬度随着锌含量的增加而增加,以及合金的塑性先上升后下降(20%Zn最佳)。最重要的是随着Mg-Zn合金中锌含量的增加合金的耐腐蚀性能有所提高,其原因是保护膜MgZn覆盖在合金表面,对合金起到保护作用。锌的含量对镁合金的生物医学效果影响很大,也有学者认为在基于机械、腐蚀和生物毒性方面的考虑,建议镁合金中添加少于质量分数6%的锌[33]。 锰(Mn):是维持人体健康和系统功能正常所必需的微量元素之一,维持着体内多种生理功能的正常运转,起着防御氧化应激,促进正常的生长发育、消化和免疫反应等作用[56]。在人体内锰是许多酶的辅助因子,在基因调节及支持骨骼生长发育和保持神经元功能正常等生理过程中起着重要作用,是大脑、神经系统和细胞稳态保持正常功能所必需的[38,56]。锰在医用镁合金中的研究十分广泛。XIE等[20]在ZK30合金[(Mg-3Zn-0.5Zr)-0.2Cu]基础上添加了一定质量分数的xMn(x=0、0.4%,0.8%,1.2%和1.6%),以此研究不同锰含量对合金性能的影响,结果表明锰的加入可以细化晶粒,并在合金表面形成一层有相对保护性的氧化锰膜,降低镁合金腐蚀速率;同时随着锰含量的增加,合金降解速率先下降后升高,在锰含量为0.8%时达到最低;当锰含量小于0.8%时,锰元素可以完全溶解在镁基体中,当锰含量大于0.8%时,则不能完全溶解,形成少量锰相,此时锰与镁分别作为阴极和阳极形成电偶,提高了合金降解速率。此外,锰添加引起的晶粒细化、固溶强化以及第二相强化提高了合金的硬度,同时锰能使得镁合金拥有较强的抗菌能力。有研究表明,合金中加入锰后形成的氧化膜可以防止氯离子的渗入,可进一步提高镁合金的耐腐蚀性能[20,36]。还有学者认为少量的添加锰可以将合金中的杂质元素如铁等转化为无毒的金属间化合物进行沉淀,来提高合金的耐腐蚀性能[36-37]。然而,锰的细胞毒性和神经毒性此前已有学者表明[38],过量的锰暴露可通过引发自由基形成、影响抗氧化酶活性水平等方式进而引起氧化应激和线粒体能量代谢失衡,胆碱能系统等神经递质系统可能受到影响,最终可诱发阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病。值得注意的是,血清中锰的质量浓度为0.4-0.85 μg/L,正常饮食不会引发不良后果,过量锰暴露大多发生于职业活动吸入、工业环境污染和长期全肠外营养治疗等,而对于含锰镁合金植入物,以ZM21合金支架为例[57],其中锰质量分数为0.451 9%,其缓慢释放的Mn2+量远远达不到成年人每天可摄入2-6 mg Mn的安全剂量。 锂(Li):被用作治疗精神疾病的药物已有悠久的历史,低浓度的锂通常被认为是无毒的。锂对多种细菌具有显著的抗菌性,对骨肉瘤细胞有一定抑制作用,并且具有强大的免疫刺激能力,可刺激间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化,促进骨再生愈合,因此锂被认为是一种很有前途的生物活性元素[58-60]。Mg-Li合金的密度为1.3-1.65 g/cm3,其最突出的特性是优越的延展性和可成形性,是非常具有潜力的轻质材料。镁合金中锂的加入会改变Mg-Li合金的微观结构,随着锂含量的增加,Mg-Li合金基体的晶体结构由六方紧密堆积向体心立方转变,进而提高了可成形性[18]。具体来说,当锂含量小于17.5%时,仅存在α相(六方紧密堆积固溶体);而锂质量分数超过28.7%时,仅存在β相(体心立方固溶体);当锂含量介于两者之间时,合金中会出现α相和β相的混合。有学者研究了mg-xLi-Zn合金(x=3%,6%和9%)中锂含量(质量分数)梯度变化对合金性能的影响,以及锂抑制骨肉瘤细胞生长和促进骨生长的情况[60],研究结果发现:铸态Mg-xLi-Zn合金的屈服强度、抗拉强度和伸长率均高于不含锂的铸态Mg-Zn合金;当锂含量为6%时,合金伸长率最高,合金的韧性最好,但随着锂含量的增加,合金强度降低;添加锂对合金的耐腐蚀性有影响,其整体耐蚀性较Mg-Zn合金差;Mg-xLi-Zn合金对骨肉瘤细胞(MG-63)具有浓度依赖性杀伤作用,并促进了骨生长。此前有研究表明,长期暴露在高剂量锂中可引发中毒,导致器官功能的病理改变。PONZER等[39]研究发现,静脉血栓栓塞症、帕金森病和一些肾脏疾病都与长期锂暴露有关。但值得注意的是,该暴露是指伴有某些危险因素的精神疾病患者长期使用含锂药物治疗(3年甚至更久)。而对于含锂的镁合金,以LAZ合金为例,WU等[61]制备了4种不同锂含量(最高质量分数为9%)的LAZ合金并植入小鼠,虽然间接体外细胞毒性实验表明合金具有较低的细胞毒性,但根据组织学分析4种LAZ合金均未显示局部和全身毒性,展现了LAZ合金在血管支架应用中的潜力。 锶(Sr):是人体内的微量元素之一,是人体骨骼的重要成分,无细胞毒性。锶可促进成骨细胞的生长,促进骨骼形成,抑制破骨细胞的激活和分化[7,11],其合金被认为是骨植入十分有潜力的材料。有学者研究了在镁合金中加入锶对合金性能的影响[7,11],结果表明,锶在镁中的溶解度为0.11%,适量锶的加入可通过细化晶粒和第二相强化提高镁合金的耐蚀性能,同时还通过固溶强化效应增强合金的力学行为;而当锶添加量大于0.11%时会导致微电反应,加速腐蚀和氢气的析出。即锶的加入一方面使合金的晶粒细化,有利耐腐蚀;另一方面,锶的加入导致微电偶联,不利于耐腐蚀。当晶界第二相的阻腐蚀作用小于微电反应的加速腐蚀作用时,合金的耐蚀性能会降低。此外还发现,锶过量会形成更多的Mg17Sr2相,其显著降低了合金的塑性;但随着锶含量的增加,机械强度逐渐增加。有学者在镁合金中加入锶(质量分数2%),研究其对镁合金性能的影响[40-41],结果显示锶的加入控制了合金的腐蚀、减少了氢气的产生并提高了机械性能;加入锶的合金显示出明显的抗菌活性,并显著促进了血管生成以及成骨相关基因表达上调。 锆(Zr):具有良好的生物相容性、低细胞毒性和骨相容性。在合金中添加锆不仅可以很有效地细化晶粒尺寸,还可以增强合金的晶界强度[17];同时锆的添加不仅改善了合金的机械性能,还促进了合金基体表面形成稳定的钝化膜,以提高合金的耐腐蚀性能。此外,锆可以减少合金中的铁和镍等杂质,进一步加强合金的耐腐蚀性能。RAPIEJKO等[30]在镁合金AZ91中加入不同质量分数的xZr(x=0.1%-0.6%),并与未改性的AZ91合金比较,加入0.3%含量的锆最有效,高于0.3%含量的锆不会带来额外的好处;此外还表明,锆本来是一种非常有效的纯镁晶粒细化剂,但其在Mg-Al合金中的效果似乎受到了限制。MA等[62]制备了Mg-2%Zn-0.5%Y-1%Nd-0.5%Zr(ZE21C)合金,并通过体外和体内实验研究了ZE21C缝合锚的降解行为,评估了其对韧带-骨连接处的修复作用,同时与Ti6Al4V(TC4)合金进行了比较,结果表明ZE21C组缝合锚具有良好生物安全性,促进了骨愈合和韧带-骨交界处的纤维软骨界面再生,获得了比TC4组更好的效果。 此前有学者表明,钼(Mo)和镓(Ga)也是很有潜力的合金元素[35,42-44]。 钼是一种微量金属,参与人体多种酶促过程,是一种具有高强度和优异力学性能的材料,尽管纯钼植入物在动物实验中显示出低毒性,但大量的钼可通过人体代谢调节进行排泄,且提示钼对人类有毒性的信息有限,其作为合金元素显示出可观潜力,其合金在最近的研究中表现出长时间的机械稳定,是支架材料的理想原料。镓有抗菌活性,能提高骨组织再生能力,还能治疗骨质疏松症等病,作为合金元素可以提高合金的机械性能。 稀土元素指的是镧(La)、铈(Ce)、镨(Pr)、钕(Nd)、钷(Pm)、钐(Sm)、铕(Eu)、钆(Gd)、铽(Tb)、镝(Dy)、钬(Ho)、铒(Er)、铥(Tm)、镱(Yb)、镥(Lu)、钇(Y)和钪(Sc)共17种元素。虽然此前已有稀土元素污染环境对人类健康有不利影响的报道[63],但是在作为合金元素方面,稀土元素以其独特的物理和化学性质(特别是电负性性质)能改变基体合金的合金化顺序[64],依然是合金化的重要研究对象。LIU等[45]在纯镁中分别添加了16种稀土元素,以比较每种稀土元素对镁性能的影响,结果表明,除镥会导致严重的溶血外,其他元素生物相容性较好。在镁中加入钪、钕、钐、铕、钆、铽、铥和镱元素可以提高合金的延展性,加入钇、镧、铈和镨元素可以提高合金的强度,加入钪、钕、钐、铕和镱元素能让合金表现出较好的耐腐蚀性。此外,稀土元素能去除合金中的杂质最终实现合金熔体的净化,Mg-RE二元合金的力学性能得到了显著的调整,Mg-RE样品合金对MC3T3-E1细胞没有细胞毒性影响。总的来说,在镁中加入适当浓度的稀土元素可以增强镁的性能,低含量稀土元素的合金化是发展高性能镁合金的一个方向。LI等[65]的研究进一步表明,镁合金中添加适量稀土元素在细化合金晶粒、改善成形性和增强延展性方面具有潜力。此外也有研究表明,稀土元素具有抗菌活性[66]。目前在医用镁合金研究中较常添加的稀土元素有钆[67]、钕和钇等[68-69],着重介绍了钪和铈[40-41,64,70]。有学者在镁合金中加入钪元素,结果表明,钪的加入细化了合金晶粒、控制了合金的腐蚀、减少了氢气的产生并提高了合金机械性能;加入钪的合金显示出明显的抗菌活性,同时用Mg-Sc-Sr合金培养人骨髓间质细胞表现出高度的生物相容性和体外骨细胞分化显著增加[40-41]。CHEN等[64]研究了铈元素对镁合金性能的影响,结果显示铈在镁中的溶解度为0.52%,铈形成的第二相容易在晶界处析出,有效提高了镁合金的力学性能和抗蠕变性能;铈的适当添加范围为0.2%-0.4%(质量分数),添加适量的铈后镁合金的耐热性和强度均有明显提高。蛋白质在镁合金植入物表面的吸附直接决定了合金的生物相容性,WANG等[70]系统地研究了不同镁合金第二相对蛋白质吸附行为的影响,结果表明,含铈元素的镁合金在长时间浸渍后表面有利于蛋白质吸附。"

| [1] WITTE F. Reprint of: The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2015;23:S28-S40. [2] BIBER R, PAUSER J, BREM M, et al. Bioabsorbable metal screws in traumatology: A promising innovation. Trauma Case Rep. 2017;8:11-15. [3] KÖNNEKER S, SCHÄCHINGER U, VOGT PM. Magnesium-Based Compression Screws in Acute Scaphoid Fractures and Nonunions. World J Surg. 2023;47(5):1129-1135. [4] WENG WJ,ARNE BIESIEKIERSKI A, LI YC, et al. A review of the physiological impact of rare earth elements and their uses in biomedical Mg alloys. Acta Biomater. 2021;130:80-97. [5] ZARTNER PA, SCHRANZ D, MINI N, et al. Acute treatment of critical vascular stenoses with a bioabsorbable magnesium scaffold in infants with CHDs. Cardiol Young. 2020; 30(4):493-499. [6] HAUDE M, TOELG R, LEMOS PA, et al. Sustained Safety and Performance of a Second-Generation Sirolimus-Eluting Absorbable Metal Scaffold: Long-Term Data of the BIOSOLVE-II First-in-Man Trial at 5 Years. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2022;38:106-110. [7] WEN Y, LIU Q, ZHAO W, et al. In Vitro Studies on Mg-Zn-Sn-Based Alloys Developed as a New Kind of Biodegradable Metal. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(7):1606. [8] REDDY ST, SOMAN SS, YEE J. Magnesium Balance and Measurement. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018;25(3):224-229. [9] 王舒,赵贵然,王茹,等.骨内型镁合金牵引器在犬牙槽骨垂直骨增量中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(25):4045-4050. [10] LI W, QIAO W, LIU X, et al. Biomimicking Bone–Implant Interface Facilitates the Bioadaption of a New Degradable Magnesium Alloy to the Bone Tissue Microenvironment. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(23):2102035. [11] WEN Y, LIU Q, WANG J, et al. Improving in vitro and in vivo corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of Mg-1Zn-1Sn alloys by microalloying with Sr. Bioact Mater. 2021; 6(12):4654-4669. [12] WINDHAGEN H, RADTKE K, WEIZBAUER A, et al. Biodegradable magnesium-based screw clinically equivalent to titanium screw in hallux valgus surgery: short term results of the first prospective, randomized, controlled clinical pilot study. Biomed Eng OnLine. 2013;12:62. [13] ROLA P, WŁODARCZAK A, ŁANOCHA M, et al. Outcomes of the two generations of bioresorbable scaffolds (Magmaris vs. Absorb) in acute coronary syndrome in routine clinical practice. Cardiol J. 2022. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2022.0047. [14] ESPIRITU J, BERANGI M, YIANNAKOU C, et al. Evaluating metallic artefact of biodegradable magnesium-based implants in magnetic resonance imaging. Bioact Mater. 2022;15:382-391. [15] MERINO E, DURÁN A, CERÉ S, et al. Hybrid Epoxy-Alkyl Sol-Gel Coatings Reinforced with SiO2 Nanoparticles for Corrosion Protection of Anodized AZ31B Mg Alloy. Gels. 2022;8(4):242. [16] LIANG M J, CUN WU, MA Y, et al. Influences of aggressive ions in human plasma on the corrosion behavior of AZ80 magnesium alloy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;119(53):111521. [17] HZ A, RH A, JY A, et al. Influence of Zirconium (Zr) on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of biodegradable zinc-magnesium alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2020;840:155792. [18] DUAN Y, GAO Q, ZHANG Z, et al. Chemical Ordering induced Strengthening in Lightweight Mg Alloys. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(19):3488. [19] SUN J, XU B, YANG Z, et al. Mediating the strength, ductility and corrosion resistance of high aluminum containing magnesium alloy by engineering hierarchical precipitates. J Alloy Compd. 2021;857:158277. [20] XIE B, ZHAO M, XU R, et al. Biodegradation, Antibacterial Performance, and Cytocompatibility of a Novel ZK30-Cu-Mn Biomedical Alloy Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Int J Bioprint. 2020;7(1):300. [21] LIU Y, CHENG WL, GU XJ, et al. Tailoring the microstructural characteristic and improving the corrosion resistance of extruded dilute Mg-05Bi-0.5Sn alloy by microalloying with Mn. J Magnes Alloy. 2021;9(5):1656-1668. [22] WANG Q, ZHAI H, WANG L, et al. Effect of Bi Addition on the Heat Resistance of As-Extruded AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(3):996. [23] SOMEKAWA H, SINGH A, SAHARA R, et al. Excellent room temperature deformability in high strain rate regimes of magnesium alloy. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):656. [24] MOHAMED A, EL-AZIZ A, BREITINGER HG. Study of the degradation behavior and the biocompatibility of Mg–0.8Ca alloy for orthopedic implant applications. J Magnes Alloy. 2019;7(2):249-257. [25] ZHANG Y, LI JX, LI JY. Effects of calcium addition on phase characteristics and corrosion behaviors of Mg-2Zn-0.2Mn-xCa in simulated body fluid. J Alloy Compd. 2017; 728:37-46. [26] QIN Y, WEN P, GUO H, et al. Additive manufacturing of biodegradable metals: Current research status and future perspectives. Acta Biomater. 2019;98:3-22. [27] TIE D, HORT N, CHEN M, et al. In vivo urinary compatibility of Mg-Sr-Ag alloy in swine model. Bioact Mater. 2021;7:254-262. [28] CHEN K, GE W, ZHAO L, et al. Endowing biodegradable Zinc implants with dual-function of antibacterial ability and osteogenic activity by micro-addition of Mg and Ag (≤0.1wt.%). Acta Biomater. 2023;157:683-700. [29] LI YQ, XU DY, ZHA M, et al. Study on Bulk Texture and Mechanical Properties of As-Extruded Wide Mg-Al-Zn Alloy Sheets with Different Al Addition. Materials (Basel). 2022;L15(12):4147. [30] RAPIEJKO C, MIKUSEK D, JANUSZEWICZ B, et al. Refinement of the Magnesium-Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(24):8982. [31] KHAN MS, TABREZ S, REHMAN TM, et al. Al (III) metal augment thermal aggregation and fibrillation in protein: Role of metal toxicity in neurological diseases. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020;27(9):2221-2226. [32] HU Y, GUO X, QIAO Y, et al. Preparation of medical Mg-Zn alloys and the effect of different zinc contents on the alloy. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(1):9. [33] PRABHU DB, GOPALAKRISHNAN P, RAVI KR. Morphological studies on the development of chemical conversion coating on surface of Mg–4Zn alloy and its corrosion and bio mineralisation behaviour in simulated body fluid. J Alloy Compd. 2020;812:152146. [34] LESZ S, HRAPKOWICZ B, KAROLUS M, et al. Characteristics of the Mg-Zn-Ca-Gd Alloy after Mechanical Alloying. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(1):226. [35] DROBYSHEV A, KOMISSAROV A, REDKO N, et al. Bone Remodeling Interaction with Magnesium Alloy Implants Studied by SEM and EDX. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(21): 7529. [36] CHO DH, LEE BW, PARK JY, et al. Effect of Mn addition on corrosion properties of biodegradable Mg-4Zn-0.5Ca-xMn alloys. J Alloy Compd. 2017;695:1166-1174. [37] BAHMANI A, SRINIVASAN ARTHANARI S, SHIN KS. Corrosion behavior of Mg-Mn-Ca alloy:Influences of Al,Sn and Zn. J Magnes Alloy. 2019;7(1):38-46. [38] MARTINS AC JR, MORCILLO P, IJOMONE OM, et al. New Insights on the Role of Manganese in Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(19):3546. [39] PONZER K, MILLISCHER V, SCHALLING M, et al. Lithium and risk of cardiovascular disease, dementia and venous thromboembolism. Bipolar Disord. 2023.doi: 10.1111/bdi.13300. [40] ABOUTALEBIANARAKI N, ZEBLISKY P, SARKER MD, et al. An osteogenic magnesium alloy with improved corrosion resistance,antibacterial,and mechanical properties for orthopedic applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023;111(4):556-574. [41] ABOUTALEBIANARAKI N, NEAL CJ, SEAL S, et al. Biodegradable Mg-Sc-Sr Alloy Improves Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis to Accelerate Bone Defect Restoration. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):261. [42] TOSCHKA A, PÖHLE G, QUADBECK P, et al. Molybdenum as a Potential Biocompatible and Resorbable Material for Osteosynthesis in Craniomaxillofacial Surgery-An In Vitro Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15710. [43] SIKORA-JASINSKA M, MORATH LM, KWESIGA MP, et al. In-vivo evaluation of molybdenum as bioabsorbable stent candidate. Bioact Mater. 2022;14:262-271. [44] BAZHENOV V, LI A, ILIASOV A, et al. Corrosion Behavior and Biocompatibility of Hot-Extruded Mg-Zn-Ga-(Y) Biodegradable Alloys. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):294. [45] LIU J, BIAN D, ZHENG Y, et al. Comparative in vitro study on binary Mg-RE (Sc, Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb and Lu) alloy systems. Acta Biomater. 2020; 102:508-528. [46] JIANG W, WANG J, ZHAO W, et al. Effect of Sn addition on the mechanical properties and bio-corrosion behavior of cytocompatible Mg-4Zn based alloys. J Magnes Alloy. 2019;7(1):15-26. [47] ABDELGHANY AK, GAMAL A, ABDEL-WAHAB A, et al. Evaluating the neuroprotective effect of Spirulina platensis-loaded niosomes against Alzheimer’ s disease induced in rats. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2023:1-13. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01301-2. [48] FERRERO ME. Neuron Protection by EDTA May Explain the Successful Outcomes of Toxic Metal Chelation Therapy in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2476. [49] BALGOON MJ. Assessment of the Protective Effect of Lepidium sativum against Aluminum-Induced Liver and Kidney Effects in Albino Rat. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4516730. [50] LI H, FAN M, WANG K, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine extracts as novel corrosion inhibitors for AZ91 magnesium alloy in saline environment. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7367. [51] ERIŞEN DE, ZHANG Y, ZHANG B, et al. Biosafety and biodegradation studies of AZ31B magnesium alloy carotid artery stent in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022;110(1):239-248. [52] YANG X, CHEN S, ZHANG S, et al. Intracellular zinc protects Kv7 K+ channels from Ca2+calmodulin-mediated inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2023;299(2):102819. [53] LIU H, GALE J, REYNOLDS I, et al. The Multifaceted Roles of Zinc in Neuronal Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Biomedicines. 2021;9(5):489. [54] ALATEYAH AI, ALAWAD MO, ALJOHANI TA, et al. Influence of Ultrafine-Grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAPed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on the Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(16):5515. [55] ZHANG Y, WU H, YUAN B, et al. Enhanced osteogenic activity and antibacterial performance in vitro of polyetheretherketone by plasma-induced graft polymerization of acrylic acid and incorporation of zinc ions. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(36):7506-7515. [56] MIAH MR, IJOMONE OM, OKOH COA, et al. The effects of manganese overexposure on brain health. Neurochem Int. 2020;135:104688. [57] DOU ZL, CHEN SL, WANG JC, et al. A “built-up” composite film with synergistic functionalities on Mg–2Zn–1Mn bioresorbable stents improves corrosion control effects and biocompatibility. Bioact Mater. 2023;25:223-238. [58] KEIKHOSRAVANI P, MALEKI-GHALEH H, KAHAIE KHOSROWSHAHI A, et al. Bioactivity and Antibacterial Behaviors of Nanostructured Lithium-Doped Hydroxyapatite for Bone Scaffold Application. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9214. [59] TAN Z, ZHOU B, ZHENG J, et al. Lithium and Copper Induce the Osteogenesis-Angiogenesis Coupling of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Crosstalk between Canonical Wnt and HIF-1α Signaling Pathways. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6662164. [60] LI J, ZHOU P, WANG L, et al. Investigation of Mg-xLi-Zn alloys for potential application of biodegradable bone implant materials. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;32(4):43. [61] WU J, ZHAO D, LEE B, et al. Effect of Lithium and Aluminum on the Mechanical Properties, In Vivo and In Vitro Degradation, and Toxicity of Multiphase Ultrahigh Ductility Mg-Li-Al-Zn Quaternary Alloys for Vascular Stent Application. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(4):1950-1964. [62] MA D, WANG J, ZHENG MR, et al. Degradation behavior of ZE21C magnesium alloy suture anchors and their effect on ligament-bone junction repair. Bioact Mater. 2023; 26:128-141. [63] KLINGELHÖFER D, BRAUN M, DRÖGE J, et al. Environmental and health-related research on application and production of rare earth elements under scrutiny. Global Health. 2022;18(1):86. [64] CHEN Y, ZHU Z, ZHOU J, et al. Study on the Strengthening Mechanism of Rare Earth Ce in Magnesium Alloys,Based on First-Principle Calculations and Electronegativity Theory. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(21):6681. [65] LI X, LIU C, WANG J, et al. Tailoring the strength and formability of Mg alloys through rare earth element additions (Gd and Dy) and dynamic recrystallizations. Mater Today Commun. 2021;28:102627. [66] BASSOUS NJ, GARCIA CB, WEBSTER TJ. A Study of the Chemistries,Growth Mechanisms,and Antibacterial Properties of Cerium- and Yttrium-Containing Nanoparticles. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(5):1787-1807. [67] ANISIMOVA N, KISELEVSKIY M, MARTYNENKO N, et al. Anti-tumour activity of Mg-6%Ag and Mg-10%Gd alloys in mice with inoculated melanoma. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;130:112464. [68] NILSSON AHMAN H, D’ ELIA F, MELLIN P, et al. Microstructural Origins of the Corrosion Resistance of a Mg-Y-Nd-Zr Alloy Processed by Powder Bed Fusion-Laser Beam. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:917812. [69] ZEMKOVÁ M, MINÁRIK P, JABLONSKÁ E, et al. Concurrence of High Corrosion Resistance and Strength with Excellent Ductility in Ultrafine-Grained Mg-3Y Alloy. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(21):7571. [70] WANG H, YUAN H, WANG J, et al. Influence of the second phase on protein adsorption on biodegradable Mg alloys’ surfaces: Comparative experimental and molecular dynamics simulation studies. Acta Biomater. 2021;129:323-332. |
| [1] | Zhou Jie, Ye Peng, Zhang Tianxi, Li Xingyu, Li Shasha, Yu Anyong, Deng Jiang. Repair of rabbit cartilage defects with double-layer bionic scaffold loaded with nerve growth factor cartilage and subchondral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(34): 5421-5429. |
| [2] | Yan Nan, Wu Xuanjing, Wang Ziqi, Wu Jing, Zhao Tongtong, Xue Yan, Zhao Weijie, Wang Lijie, Wu Zimei, Zhang Wenqing, Li Jing. Synthesis and drug loading and delivery applications of chiral mesoporous silica nanoparticles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4890-4895. |
| [3] | Fan Haomei, Xiao Dongqin, Shi Feng, Luo Xuwei, Wei Jianlin, Zhuang Huadi, Liu Jinhui, Zhao Juhua. Preparation of calcium silicate microspheres loaded with epigallocatechin gallate and investigation on its antibacterial performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4769-4775. |
| [4] | Zhao Zheng, Ding Wenfei, Shao Shuxin, Wang Jinyan, Jian Xigao. Degradation and drug release behavior of sirolimus-poly(trimethylene carbonate) modified magnesium alloy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(30): 4836-4843. |
| [5] | Lyu Jiayi, Yao Qingqiang, Zhu Yishen. Role and advantages of carbon nanotubes for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 4093-4100. |
| [6] | Shen Yong, Liu Shizhang. Research progress on antibacterial properties of medical copper-containing titanium alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3430-3437. |
| [7] | Niu Lin, Mei Yukun, Zou Rui, Zhang Yuwei, Zhang Yifei, Hao Yaqi, Dong Shaojie. Application of inorganic nonmetal biomaterials in the treatment of osteosarcoma and the regeneration of tumor-related bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3368-3374. |
| [8] | Jiang Chengming, Jiang Sainan, Tang Ye, Jiang Lin. Efficacy of 3D printed microporous titanium fusion device applied to anterior cervical decompression graft fusion and its effects on cervical spine anatomy and stress hormones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2837-2841. |
| [9] | Huang Yanni, Yang Hua, Yang Dongmei, Hu Xulin, Gao Hong, Huang Yina. Rat bone defect repaired with polytrimethylene carbonate/beta-tricalcium phosphate microsphere scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1856-1862. |
| [10] | Wu Boyu, Ye Kai, Chen Jiahan, Wang Jianghua, Wurikaixi·Aiyiti, Jiang Houfeng, Teng Yong. Biocompatibility of 3D printed polyetheretherketone/hydroxyapatite composites [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1932-1937. |
| [11] | Ren Wenyan, Liu Xue, Wang Yiyu. Grophene-family nanomaterials in the treatment of periodontal disease: beneficial for osteogenic differentiation and reconstruction of periodontal support tissues [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1954-1960. |
| [12] | Le Guoping, Zhang Ming, Xi Licheng, Luo Hanwen. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of vancomycin hydrochloride@polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid composite sustained-release microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 528-534. |
| [13] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [14] | Sun Xirao, Bao Jiaxin, Wang Chengyue. Construction of chitosan/mineralized collagen porous scaffold, osteogenic differentiation in vitro and biocompatibility [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5498-5503. |
| [15] | Wu Yuchong, Peng Xu, Yu Xixun. Osteogenesis, angiogenesis and anti-aseptic loosening of europium-doped calcium polyphosphate bone tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4458-4465. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||