Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (17): 2747-2752.doi: 10.12307/2024.446
Previous Articles Next Articles
Potential of shikonin and its derivatives in oral soft and hard tissue regeneration
Bian Zhihong1, Zhang Yuntao2, Li Zeming1, Hou Yudong3
- 1Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 3School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264010, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-06-27Accepted:2023-08-09Online:2024-06-18Published:2023-12-16 -
Contact:Hou Yudong, Master, Professor, School of Stomatology, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai 264010, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Bian Zhihong, Master candidate, Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bian Zhihong, Zhang Yuntao, Li Zeming, Hou Yudong. Potential of shikonin and its derivatives in oral soft and hard tissue regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(17): 2747-2752.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
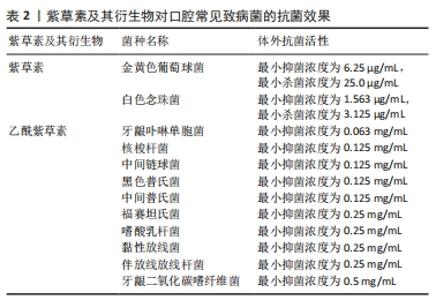
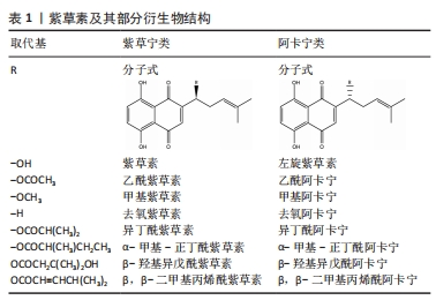
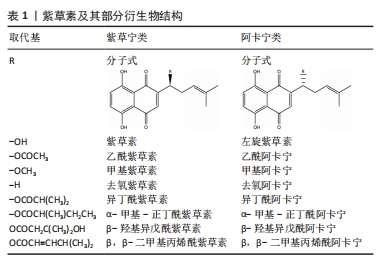
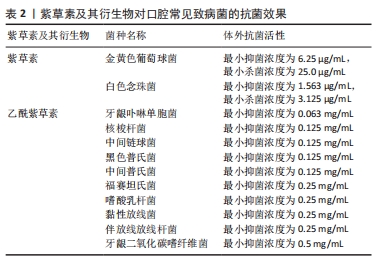
2.1.2 安全性与毒性 紫草红有着优越的着色能力,被批准作为食用色素用于人类食品中[8],在化妆品和纺织品领域也有着广泛的应用。《名医别录》认为紫草“无毒,主治腹肿胀满痛,以合膏,治小儿疮及面皻”。紫草含有吡格里西啶生物碱,研究表明吡格里西啶生物碱本身没有毒性或毒性较低,需经肝微粒体细胞色素酶代谢激活才能产生毒性[9],因此紫草作为外用药物时相对口服具备更多的安全性。 紫草素具有一定的细胞毒性。1×10-5 mol/L 的紫草素处理心肌细胞48,72 h后,对大鼠心肌细胞有明显毒性[10]。紫草素对人牙周膜干细胞的半数致死量(LD50)为1.7 μg/mL(第1天)和1.1 μg/mL(第3,7天)[11]。 有学者比较了紫草素和乙酰紫草素对仓鼠肺细胞(V79)的细胞毒性,发现紫草素的半数有效浓度(EC50)低于乙酰紫草素,表明紫草素对正常细胞株的细胞毒性高于乙酰紫草素[12]。而在体内研究中观察到的紫草素毒性比体外的小。与紫草素给药方式有关的急性毒性数据表明,小鼠经口给药的半数致死量> 1 g/kg[13],小鼠腹腔给药的半数致死量为20 mg/kg,家兔静脉给药的半数致死量为16 mg/kg,这些数据说明与其他给药方式相比,口服途径的紫草素毒性较小。 2.2 促进口腔黏膜病损愈合 2.2.1 治疗口腔阿弗他溃疡、扁平苔藓、白斑 张珊等[14]评价了一种以紫草和香油为原料制备的紫草油治疗口腔阿弗他溃疡的临床疗效,将120例阿弗他溃疡患者随机分为紫草油治疗组(60例)和碘甘油治疗组(60例),每日4次涂擦溃疡面,治疗7 d后发现紫草油组患者的治疗有效率、改善的溃疡面积均明显高于碘甘油组,溃疡期明显短于后者,并且未观察到不良反应,患者易于接受。 有学者制备了一种含有紫草素及其衍生物的纤维素薄膜[15],将其应用于30例(34-72岁)口腔黏膜糜烂性溃烂扁平苔藓和白斑患者的治疗中,结果显示这种薄膜可以更快地缓解疼痛,使颊黏膜炎性破坏灶上皮化,减轻颊黏膜病变的形态征象,且所有患者对该药物的耐受性良好,未发现任何不良反应。这种机制可能与紫草素具有广泛的抗菌、抗炎、抗肿瘤活性有关。 2.2.2 治疗口腔念珠菌病 有临床报道称,含有紫草素及其衍生物的软膏可治疗严重口腔念珠菌病,但对此机制并不清楚[16]。PANG等[17]的研究表明,紫草素对白色念珠菌的氧化损伤作用使其具有很强的抗菌活性,特别是对一些氟康唑耐药菌株。除此之外,紫草素对其他念珠菌、曲霉菌、隐球菌和皮肤癣菌也有较强的体外抗真菌活性,且对哺乳动物的细胞毒性低,提示紫草素是一种潜在的抗真菌药物。进一步分析紫草素抗白色念珠菌的确切机制,发现紫草素可以诱导一系列的细胞凋亡特征,包括磷脂酰丝氨酸外化、染色质凝集与碎裂、细胞色素c氧化酶活性降低以及切冬酶激活,此外,麦角甾醇含量也明显降低。KAUR等[18]也对此机制进行了研究,发现除了诱导细胞凋亡外,紫草素还可以通过破坏生物膜和细胞壁来延缓白色念珠菌生长,为治疗口腔念珠菌感染提供了一种潜在的治疗策略。 总之,紫草素及其衍生物可以通过抗真菌感染来治疗口腔念珠菌病,其机制可能与诱导细胞凋亡、破坏生物膜和细胞壁有关。关于紫草制剂治疗其他口腔黏膜病的机制研究十分罕见。口腔阿弗他溃疡、扁平苔癣等疾病的病因十分复杂,免疫因素是其重要之一。有文献表明,紫草素可以作为一种免疫调节剂作用于炎性肠病、类风湿关节炎、超敏反应等免疫相关性疾病中,重建免疫平衡、缓解临床症状[19]。但目前尚未有研究阐述紫草素治疗口腔黏膜病与免疫调节的关系,还需大量研究。 2.3 促进牙周软硬组织再生 2.3.1 抗牙周致病菌 有文献报道,紫草素对许多常见菌株都表现出良好的抗菌能力,甚至与市场上常用抗菌药物左氧氟沙星相当[20]。LI等[21]使用44种不同中药提取物对4种不同的口腔细菌(核梭杆菌、牙龈卟啉单胞菌、变形链球菌和嗜酸乳杆菌)进行体外抑菌实验,发现这些中药中,紫草提取物中的乙酰紫草素对这些细菌的抑菌效果最好,进一步的研究发现,革兰阴性菌对乙酰紫草素的敏感性高于革兰阳性菌[22]。乙酰紫草素对革兰阴性菌显示出比对革兰阳性菌更广泛的抗菌活性,其中,牙龈卟啉单胞菌尤其受到乙酰紫草素的抑制,且这种抑制作用可能是通过抑制胰蛋白酶样蛋白酶和糖苷酶的活性实现的。紫草素及其衍生物对口腔常见致病菌的抗菌效果,见表2。"
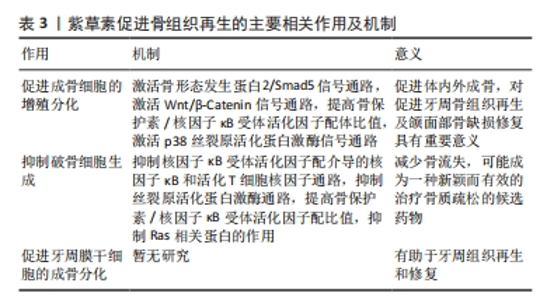
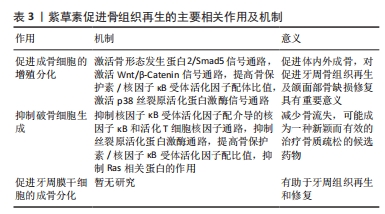
2.3.2 抗炎 牙周病变中发生的免疫反应在牙周病的发生和发展中不容忽视,特别是细胞因子在牙周病的发病机制中起着重要作用[23]。白细胞介素1、白细胞介素4、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质金属蛋白酶等炎性递质参与牙周病的发生与发展[24],并可能影响白细胞、成骨细胞和破骨细胞的活性,抑制牙周组织修复。脂多糖是革兰阴性细菌细胞壁中的一种成分,可诱导各种炎症细胞因子的分泌,如白细胞介素1和白细胞介素6。牙周膜干细胞在是牙周组织中的天然间充质干细胞,具有形成牙槽骨、牙周韧带和牙骨质等多种功能。此外,牙周膜干细胞在维持正常牙周组织的动态平衡和修复受损牙周组织方面也发挥着重要作用。面对内毒素,牙周膜干细胞会产生一系列的炎症细胞因子,如白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶2和基质金属蛋白酶9,它们可以激活循环免疫细胞、破坏胶原纤维和吸收牙槽骨[25]。经过国内外数十年的研究,紫草素已被证明对多发性硬化症、哮喘、系统性红斑狼疮、炎症性肠病、牛皮癣和类风湿性关节炎等疾病具有抗炎作用[26]。 SHINDO等[27]探讨了紫草素能否影响人牙周膜干细胞产生白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和趋化因子(C-C 基元)配体20(CCL20),他们用不同浓度紫草素(0-2 μmol/L)干预白细胞介素1β或肿瘤坏死因子α刺激下的人牙周膜干细胞,通过酶联免疫吸附测定法测定细胞产生的白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和CCL20的水平,并且利用蛋白质印迹法检测到了核因子κB通路在人牙周膜干细胞中的激活。此次实验首次证明了一定浓度范围的紫草素(0-2 μmol/L)可呈剂量依赖性抑制白细胞介素1β或肿瘤坏死因子α介导的人牙周膜干细胞中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和CCL20的产生以及核因子κB抑制蛋白α的磷酸化和降解。这些结果表明,紫草素可能通过减少牙周病变中白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8和CCL20的产生而减轻牙周炎症。 FAN等[11]研究了紫草素对脂多糖刺激的人牙周膜干细胞炎症相关细胞因子表达的影响,采用定量反转录聚合酶链式反应(qRT-PCR)检测紫草素(0.25,0.5 μg/mL)作用下人牙周膜干细胞中各炎症因子的表达,蛋白质印迹法分析紫草素在人牙周膜干细胞中触发的信号转导通路。结果显示,紫草素可抑制脂多糖诱导的人牙周膜干细胞产生白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶9和环氧合酶2的水平,下调细胞外调节蛋白激酶和核因子κB的表达,上调核因子κB抑制因子的表达。这些结果表明,紫草素可能通过磷酸化细胞外调节蛋白激酶在核因子κB/I-κB信号通路对脂多糖刺激的人牙周膜干细胞中表现抗炎作用,可能是一种潜在的牙周炎抗炎药物。 感染牙龈卟啉单胞菌的口腔癌细胞可分泌细胞因子和趋化因子,尤其是白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8,白细胞介素8是口腔癌细胞侵袭能力增强的重要因素之一[28]。乙酰紫草素已被证明具有抗炎和抗菌特性[29]。CHO等[30]研究探讨了乙酰紫草素对牙龈假单胞菌感染的YD10B口腔癌细胞的抗侵袭作用及其机制,结果表明慢性牙周炎与口腔癌细胞侵袭性之间存在联系,YD10B口腔癌细胞在主要致病菌牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染的慢性牙周炎中变得更有攻击性,而乙酰紫草素可以通过抑制白细胞介素8和基质金属蛋白酶来显著抑制牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染的YD10B口腔癌细胞的侵袭。这些证据表明,乙酰紫草素可能是一个预防和治疗慢性牙周炎病原体感染口腔癌的候选药物。 2.3.3 促进牙龈创面愈合 牙周手术是牙周病的一种常见治疗方法,而软组织愈合是治疗成功的关键。然而,伤口部位的感染和过度炎症会推迟伤口愈合。伤口愈合是一个复杂的过程,涉及多种细胞类型的迁移、增殖和分化、损伤组织的移除以及细胞外基质的形成。在伤口愈合过程中,免疫细胞(中性粒细胞、单核细胞、淋巴细胞和树突状细胞)、内皮细胞、角质形成细胞和成纤维细胞被招募到伤口部位[31]。人牙龈成纤维细胞在牙龈创伤愈合的细胞生长和重塑阶段发挥着重要作用。细胞外信号调节激酶1/2(ERK1/2)参与了伤口愈合过程,细胞外信号调节激酶1/2的磷酸化在不同类型细胞中均为细胞增殖、迁移和细胞外基质形成产生重要贡献。 IMAI等[32]研究了紫草素对牙周组织创伤愈合过程中人牙龈成纤维细胞的影响,1 μmol/L紫草素处理后,人牙龈成纤维细胞上清液中的Ⅰ型胶原增加,荧光免疫染色强度、DAB染色强度增强,在伤口愈合中起主要作用的血管内皮生长因子和细胞黏附因子FN的基因表达在1 μmol/L紫草素处理24 h后显著增加。为了探讨紫草素诱导人牙龈成纤维细胞增殖和迁移的机制,他们进一步检测了细胞外信号调节激酶1/2的激活,发现紫草素刺激的人牙龈成纤维细胞在30 min内细胞外信号调节激酶1/2的磷酸化水平显著增加,激活了ERK1/2信号通路。这一发现表明紫草素可能通过ERK1/2信号通路来加强牙龈结缔组织的粘连,促进创面愈合。 2.3.4 促进骨缺损修复 (1)促进成骨细胞增殖分化:骨形态发生蛋白2是影响成骨细胞增殖、分化和功能的关键成分。Smad5是骨形态发生蛋白2的细胞内介质,可被骨形态发生蛋白2的受体磷酸化[33],磷酸化的Smad5与Smad4形成复合体并进入细胞核,激活Runx2[34]。FANG等[35]评估了不同质量浓度紫草素(10,50和100 ng/mL)对小鼠前成骨细胞(MC3T3-E1 cells)的影响,发现紫草素(尤其是50 ng/mL)可以增强细胞活力,使更多的细胞处于S期,还可以上调骨形态发生蛋白2、Smad5、Runx2、骨钙素和碱性磷酸酶等成骨相关基因的表达。此研究首次证明了紫草素可以刺激成骨细胞增殖和分化,且通过骨形态发生蛋白2/Smad5信号通路实现。CHEN等[36]用0.2,0.4 μmol/L的紫草素作用于小鼠前成骨细胞,验证了前人的结论。基于体外实验的结果建立了去卵巢小鼠模型,治疗组于卵巢切除1周后一周2次静脉注射紫草素3 mg/kg,连续治疗2个月后发现紫草素可增加小鼠骨体积/组织体积比值、骨小梁厚度与数量、小鼠股骨骨小梁附近o型成骨细胞数量,具有促进体内骨形成的作用。 Wnt/β-Catenin通路可以通过调节破骨细胞的分化,诱导成骨细胞表达骨保护素,进而对骨吸收过程产生影响[37]。调节Wnt/β-Catenin信号可以促进脂肪干细胞分化为成骨细胞[38],β-连环蛋白可以降低破骨细胞在骨表面的黏附和聚集水平[39]。ZHOU等[40]检测了紫草素(50,150,250 nmol/L)影响下骨髓间充质干细胞中Wnt1信号通路蛋白、β-连环蛋白、糖原合成酶激酶3β、磷酸化糖原合成酶激酶3β、碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和骨钙素的表达,发现其通过调节Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路提高骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞的水平,且与剂量和时间呈依赖关系。此外,一定浓度的紫草素对骨髓间充质干细胞中糖原合成酶激酶3β的蛋白表达水平无明显影响,但可增强磷酸化糖原合成酶激酶3β的表达。 作为主要的丝裂原活化蛋白激酶亚家族之一,p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶可以通过三级级联反应被磷酸化激活,参与细胞生长、发育和分化等基本生物学过程[41]。LIN等[42]的研究发现,安全浓度下的紫草素(0.05,0.1,0.5 μg/mL)能明显增强体外培养骨髓间充质干细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性、钙蓄积、骨钙素和Runx2的表达,增加p38的磷酸化。p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路的特异性抑制剂SB203580可以抑制紫草素诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞成骨标志物的表达,表明了p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路对紫草素诱导的成骨过程具有正向调节作用。基于此研究结果,进一步建立了大鼠牙周骨缺损模型,应用显微CT和免疫荧光技术评价其对体内骨形成的影响,结果表明紫草素治疗后骨体积/组织体积和骨桥蛋白表达增加,证明紫草素具有促进体内成骨的能力,可能成为治疗牙周骨缺损的一种有前途的药物。 骨保护素/核因子κB受体活化因子配体比值增高可抑制破骨细胞的激活,提高成骨细胞的活性,促进成骨分化[43-44]。王莉平等[45]发现紫草素(0.062 5-0.5 μmol/L)呈浓度依赖性促进小鼠前成骨细胞的增殖、分化和矿化,促进了骨保护素、Runx2、Ⅰ 型胶原的表达并削弱核因子κB受体活化因子配体的水平,得出紫草素可能是通过调高骨保护素/核因子κB受体活化因子配体的比值和成骨相关基因表达水平来发挥促成骨作用的结论。 (2)促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化:有研究报道,将人牙周膜干细胞移植到免疫低下的啮齿动物体内时,会逐渐形成牙本质的骨样和牙周结构[46],其成骨分化可能有助于牙周组织再生和修复。侯夏沛等[47]的研究发现,适当浓度的紫草素(1,10 μmol/L)升高了人牙周膜干细胞中碱性磷酸酶活性、促进了钙化结节形成,并上调了Runx2、骨钙素和Smad4的转录和表达,而当浓度过低(0.1 μmol/L)或过高(100 μmol/L)时,则不能促进甚至抑制其成骨分化。结果提示,同时具有抗炎与成骨作用的紫草素可能成为牙周组织再生修复中有潜力的候选新药,但其机制尚未明确,仍需进一步探索。 (3)抑制破骨细胞生成:除了提高成骨细胞增殖矿化水平,紫草素还可能通过抑制破骨细胞生成促进骨缺损的修复。破骨细胞分化和激活主要由核因子κB受体活化因子配体通过核因子κB、AKT、MAPK、JNK等多种信号通路促进[48-49]。活化T细胞核因子1已被证明是核因子κB受体活化因子配体介导的破骨细胞分化的关键转录因子,可诱导破骨细胞分化相关的各种基因的转录,如抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、组织蛋白酶K、和降钙素受体[50]。 CHEN等[51]以骨髓间充质干细胞和小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞(RAW264.7)为研究对象,用巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导贴壁,发现紫草素(0.2,0.6,1.8 μmol/L)在体外可抑制破骨细胞的生成,显著缩小骨吸收范围,且主要作用于单核细胞分化为破骨细胞的阶段。鬼笔环肽染色发现,紫草素显著减少了破骨细胞肌动蛋白环的大小和数目,影响了破骨细胞骨架的形成。对经典的破骨细胞信号通路行免疫印迹检测,发现紫草素可以通过阻止破骨细胞c-jun氨基末端激酶、细胞外调节蛋白激酶和P38蛋白的磷酸化来抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路。紫草素处理后,活化T细胞核因子1及破骨细胞分化相关基因(如基质金属蛋白酶9、组织蛋白酶K、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和降钙素受体)的表达显著下调,并且抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导后肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6的表达。这些结果表明,紫草素通过抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的核因子κB和活化T细胞核因子信号通路而显示出抗破骨细胞的作用。基于以上研究结果建立了去卵巢小鼠模型,发现紫草素可以抑制去卵巢小鼠促炎症细胞因子的分泌、降低破骨细胞的活性、明显抑制骨体积的降低。此研究首次证明了紫草素在体外可抑制破骨细胞生成、在体内可抑制卵巢切除所致骨丢失的生物学作用。 CHEN等[36]使用不同浓度(0.1-0.8 μmol/L)的紫草素作用于核因子κB受体活化因子配体介导的骨髓源巨噬细胞,也证明了紫草素通过核因子κB受体活化因子配体介导的核因子κB和活化T细胞核因子1通路抑制破骨细胞的形成,减少去卵巢小鼠的骨损失。 王少峰等[52]用125,250 nmol/L的紫草素干预核因子κB受体活化因子配体和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子诱导的骨髓源巨噬细胞,发现紫草素通过抑制活化T细胞核因子1、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和原癌基因Fos的表达,抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体诱导的破骨细胞分化,并有效改善去卵巢小鼠骨质疏松。ZHOU等[40]的研究发现,紫草素(50,150,250 nmol/L)降低了抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、组织蛋白酶K、活化T细胞核因子和原癌基因Fos的表达,并通过增加骨保护素/核因子κB受体活化因子配体的比值抑制骨髓源巨噬细胞向破骨细胞的分化。 Ras相关蛋白在小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞或小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞的破骨分化后期表达强烈上调,可以削弱集落刺激因子1受体和核因子κB受体活化因子受体的表面丰度,上调活化T细胞核因子1的信号,从而诱导破骨细胞分化。栾静[53]构建了硬脂酰辅酶A脱饱和酶1(SCD1)敲除小鼠模型,发现紫草素纠正了SCD1-/-小鼠一定程度骨质疏松的骨骼表型。将Ras相关蛋白激活剂加入小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞破骨诱导体系中,发现活化T细胞核因子1、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、组织蛋白酶K的表达均有提高,生成了更多的破骨细胞多核细胞;而加入紫草素后多核细胞的数量显著下降,这表明紫草素可通过抑制Ras相关蛋白的作用进而抑制破骨细胞生成。 综上所述,紫草素通过调控多条信号通路发挥促进成骨细胞生成、促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化、抑制破骨细胞生成、抗骨质疏松症等作用,对促进牙周骨组织再生及颌面部骨缺损修复具有重要的意义,见表3。"

紫草素及其衍生物的广泛生物活性可以从多方面抑制牙周炎,促进牙周组织再生:①抑制牙周致病菌,特别是牙龈卟啉单胞菌;②减少炎症环境下人牙周膜干细胞产生的细胞因子和趋化因子;③诱导人牙龈成纤维细胞增殖和迁移,促进牙周创面愈合;④通过调控多条信号通路来促进成骨细胞和人牙周膜干细胞的增殖分化、抑制破骨细胞生成,从而促进牙周骨组织再生。这些证据指向紫草素及其衍生物可能是一种有潜力的治疗牙周炎的药物,但相关研究内容仍较少,且大部分为细胞实验,还需要继续深入研究证实后再考虑应用于临床。 2.4 促进牙本质再生,保护牙髓 牙本质涎磷蛋白是参与牙齿发育和矿化的关键非胶原蛋白之一,是牙本质矿化的诱导物,被认为是成牙本质细胞分化的标志物[54]。据报道,人骨髓间充质干细胞、人牙囊细胞和大鼠骨髓基质细胞的成骨分化均涉及AKT信号通路[55-57]。然而,也有研究报道,AKT抑制来自根尖乳头的干细胞的成牙分化[58-59]。因此,关于AKT-mTOR信号的功能存在争议。KAJIURA等[60]发现紫草素能够以对映体选择性的方式诱导牙髓干细胞中牙本质涎磷蛋白的表达,在CD44蛋白存在的情况下通过AKT-mTOR信号诱导牙髓干细胞向成牙本质细胞分化,对牙髓有一定的保护作用。"

| [1] DUQUE AD, MALHEIROS Z, STEWART B, et al. Strategies for the prevention of periodontal disease and its impact on general health in Latin America. Section III: Prevention. Braz Oral Res. 2020;34(supp1 1):e25. [2] SEZEN D, HATIPOGLU M, USTUN K. Evaluation of the clinical and biochemical efficacy of erbium, chromium:ytrium-scandium-gallium-garnet (ER,CR:YSGG) laser treatment in periodontitis. Lasers Med Sci. 2020;35(7): 1567-1575. [3] BROWN JP. Long-Term Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021;36(3):544-552. [4] NOORI A, ASHRAFI SJ, VAEZ-GHAEMI R, et al. A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12: 4937-4961. [5] ZHOU H, WANG S, XUE Y, et al. Regulation of the levels of Smad1 and Smad5 in MC3T3-E1 cells by Icariine in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(2):590-594. [6] 廖梅,张声源.新疆紫草的化学成分研究[J].中药材,2020,43(11):2701-2706. [7] GUO C, HE J, SONG X, et al. Pharmacological properties and derivatives of shikonin-A review in recent years. Pharmacol Res. 2019;149:104463. [8] GB 28315-2012 食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂 紫草红[S].中华人民共和国卫生部,2012. [9] 涂美娟.OCT1及CYP3A4介导的吡咯里西啶生物碱肝脏转运及毒性研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2014. [10] 陈菊英,黄文东,高琦,等.不同浓度紫草素对培养大鼠心肌细胞的毒性作用分析[J].哈尔滨医药,2022,42(4):3-5. [11] FAN C, ZHANG X, UPTON Z. Anti-inflammatory effects of shikonin in human periodontal ligament cells. Pharm Biol. 2018;56(1):415-421. [12] FIGAT R, ZGADZAJ A, GESCHKE S, et al. Cytotoxicity and antigenotoxicity evaluation of acetylshikonin and shikonin. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2021;44(2): 140-147. [13] YADAV S, SHARMA A, NAYIK GA, et al. Review of Shikonin and Derivatives: Isolation, Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Pharmacology and Toxicology. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:905755. [14] 张珊,万兵,谢艳霞,等.自制紫草油治疗复发性口腔溃疡的疗效评价[J].中国医药指南,2015,13(6):208. [15] ZAGORODNYAYA EB, OSKOL’SKII GI, BASHAROV AY, et al. Biopolymeric film containing bioactive naphthoquinone (shikonin) in combined therapy of inflammatory destructive lesions in the buccal mucosa. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2013;156(2):232-235. [16] KENROH S, HIDETOMO A, TOMOKO H, et al. Recovery of Oral Candidosis by Oral Ointment Containing Antifungal Naphthoquinone Derivatives Isolated from Shikon. Kampo Medicine. 2004;55(2):261-264. [17] PANG C, CHEN J, LIU S, et al. In vitro antifungal activity of Shikonin against Candida albicans by inducing cellular apoptosis and necrosis. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(2):1079-1087. [18] KAUR K, SINGH A, KAUR R, et al. In silico molecular modelling studies and antibiofilm efficacy of shikonin against Candida albicans: mechanistic insight. Arch Microbiol. 2023;205(3):93. [19] 宋腾,周亚琪,周广玺,等.紫草素在免疫相关性疾病中作用的研究进展[J].中国医药,2023,18(4):629-632. [20] 黄贵莲,周月广,金鑫,等.紫草素体外抗菌活性的实验研究[J].三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2017,39(S1):8-10. [21] LI MY, XU ZT, ZHU CL, et al. Effect of Different Derivatives of Shikonin from Lithospermum erythrorhizon Against the Pathogenic Dental Bacteria. Curr Pharmaceut Anal. 2012;8(3):255-260. [22] LI MY, ZHU LK, LAI GY, et al. The Inhibition of Acetylshikonin on Bacteria and its Trypsin-like Protease and Glycosidic Enzyme may be Essential to Conquer Periodontal Ecological Niche. Lett Drug Des Discov. 2014;11(10):1162-1166. [23] ZHAO XT, LIN HB, DING T, et al. Overview of the main biological mechanisms linked to changes in periodontal ligament stem cells and the inflammatory microenvironment. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2023;24(5): 373-386. [24] 周佳佳,赵蕾,徐欣.牙周炎相关基因多态性的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2022,49(4):432-440. [25] SHU L, GUAN SM, FU SM, et al. Estrogen modulates cytokine expression in human periodontal ligament cells. J Dent Res. 2008;87(2):142-147. [26] GUO Y, ZHOU M, MU Z, et al. Recent advances in shikonin for the treatment of immune-related diseases: Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory mechanisms. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115138. [27] SHINDO S, HOSOKAWA Y, HOSOKAWA I, et al. Shikonin Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. Inflammation. 2016;39(3):1124-1129. [28] HA NH, PARK DG, WOO BH, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis increases the invasiveness of oral cancer cells by upregulating IL-8 and MMPs. Cytokine. 2016;86:64-72. [29] ZHANG Z, BAI J, ZENG Y, et al. Pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics of acetylshikonin: a review. Pharm Biol. 2020;58(1):950-958. [30] CHO BH, JUNG YH, KIM DJ, et al. Acetylshikonin suppresses invasion of Porphyromonas gingivalis-infected YD10B oral cancer cells by modulating the interleukin-8/matrix metalloproteinase axis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(2): 2327-2334. [31] GURTNER GC, WERNER S, BARRANDON Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321. [32] IMAI K, KATO H, TAGUCHI Y, et al. Biological Effects of Shikonin in Human Gingival Fibroblasts via ERK 1/2 Signaling Pathway. Molecules. 2019;24(19): 3542. [33] WANG L, ZHANG X, GUO Y, et al. Involvement of BMPs/Smad signaling pathway in mechanical response in osteoblasts. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2010;26(6):1093-1102. [34] GHOSH-CHOUDHURY N, SINGHA PK, WOODRUFF K, et al. Concerted action of Smad and CREB-binding protein regulates bone morphogenetic protein-2-stimulated osteoblastic colony-stimulating factor-1 expression. J Biol Chem, 2006;281(29):20160-20170. [35] FANG T, WU Q, MU S, et al. Shikonin stimulates MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation and differentiation via the BMP-2/Smad5 signal transduction pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1269-1274. [36] CHEN Y, XIE Z, ZHANG Y, et al. Shikonin relieves osteoporosis of ovariectomized mice by inhibiting RANKL-induced NF-kappaB and NFAT pathways[. Exp Cell Res. 2020;394(1):112115. [37] 陈靖,贺无恙,陈庆伟.Wnt信号通路与骨质疏松的关系研究进展[J].现代医药卫生,2017,33(8):1172-1174. [38] BANDARA N, GURUSINGHE S, LIM SY, et al. Molecular control of nitric oxide synthesis through eNOS and caveolin-1 interaction regulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells by modulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):182. [39] WEI W, ZEVE D, SUH JM, et al. Biphasic and dosage-dependent regulation of osteoclastogenesis by beta-catenin. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(23):4706-4719. [40] ZHOU L, WANG J, ZHAO J, et al. Shikonin promotes osteogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(12): 8099-8110. [41] CUADRADO A, NEBREDA AR. Mechanisms and functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 2010;429(3):403-417. [42] LIN X, WANG Y, GUO X, et al. Shikonin promotes rat periodontal bone defect repair and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by p38 MAPK pathway. Odontology. 2023;111(3):649-657. [43] YANG B, LI S, CHEN Z, et al. Amyloid beta peptide promotes bone formation by regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and the OPG/RANKL/RANK system. FASEB J. 2020;34(3):3583-3593. [44] LI L, ZHOU J, XU Y, et al. C-C chemokine receptor type 6 modulates the biological function of osteoblastogenesis by altering the expression levels of Osterix and OPG/RANKL. Biosci Trends. 2021;15(4):240-248. [45] 王莉平,林静,薄雨佳,等.紫草素对MC3T3-E1细胞增殖、分化、矿化及成骨相关基因表达的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2022,38(5):583-588. [46] SEO BM, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155. [47] 侯夏沛,刘芬.紫草素对人牙周膜干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].山西医科大学学报,2022,53(12):1576-1582. [48] BOYLE WJ, SIMONET WS, LACEY DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337-342. [49] BAUD’HUIN M, DUPLOMB L, RUIZ V C, et al. Key roles of the OPG-RANK-RANKL system in bone oncology. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2007;7(2): 221-232. [50] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901. [51] CHEN K, YAN Z, WANG Y, et al. Shikonin mitigates ovariectomy-induced bone loss and RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via TRAF6-mediated signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126:110067. [52] 王少峰,孔祥东,沙勇,等.紫草素抑制破骨细胞分化及改善去卵巢诱导的小鼠骨质疏松[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(24):4645-4649. [53] 栾静.紫草素对外泌体棕榈油酸介导的破骨分化的影响及其机制研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学中西医结合基础,2022. [54] LI S, LIN C, ZHANG J, et al. Quaking promotes the odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9): 7292-7304. [55] VIALE-BOURONCLE S, KLINGELHOFFER C, ETTL T, et al. The AKT signaling pathway sustains the osteogenic differentiation in human dental follicle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;406(1-2):199-204. [56] MENG YB, LI X, LI ZY, et al. microRNA-21 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the PI3K/beta-catenin pathway. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(7):957-964. [57] ZHAI YK, GUO XY, GE BF, et al. Icariin stimulates the osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells via activating the PI3K-AKT-eNOS-NO-cGMP-PKG. Bone. 2014;66:189-198. [58] TANAKA Y, SONODA S, YAMAZA H, et al. Suppression of AKT-mTOR signal pathway enhances osteogenic/dentinogenic capacity of stem cells from apical papilla. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):334. [59] TANAKA Y, SONODA S, YAMAZA H, et al. Acetylsalicylic Acid Treatment and Suppressive Regulation of AKT Accelerate Odontogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla. J Endod. 2019;45(5):591-598. [60] KAJIURA K, UMEMURA N, OHKOSHI E, et al. Shikonin induces odontoblastic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via AKT-mTOR signaling in the presence of CD44. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(6):689-697. [61] 袁曦玉,从兆霞,吴泽钰,等.新疆软紫草粗提物对口腔主要致龋菌体外作用的研究[J].时珍国医国药,2020,31(3):552-555. [62] 郑德志,刘瑞杰,王婷婷,等.左旋紫草素自组装纳米粒对破骨细胞分化的抑制作用研究[J].西南国防医药,2021,31(1):11-14. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Huang Haoran, Fan Yinuo, Wei-Yang Wenxiang, Jiang Mengyu, Fang Hanjun, Wang Haibin, Chen Zhenqiu, Liu Yuhao, Zhou Chi. Urolithin A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1149-1154. |
| [3] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [4] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [5] | Xue Chunyang, Wang Xiuhui. Icariin regulates acidic microenvironment to alleviate pain caused by postmenopausal osteoporosis in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4461-4468. |
| [6] | Chen Xiangshan, Liu Hua, Sun Weikang, Li Huanan. Mechanism of m6A methylation regulating bone metabolism for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4572-4577. |
| [7] | Yang Qipei, Chen Feng, Cui Wei, Zhang Chi, Wu Ruiqi, Song Zhenheng, Meng Xin. Signaling pathways related to kaempferol active monomers in the treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4242-4249. |
| [8] | Luo Peng, Wang Yi, Wang Ansu, Dang Yi, Ma Yaping, Zhang Yi, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-8 in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(24): 3910-3914. |
| [9] | Ye Zhikui, Zhang Zhimin, Cui Linna, Jiang Xiaowen. Mechanism by which alendronate promotes rapid mandibular distraction osteogenesis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3642-3648. |
| [10] | Ma Wanli, Yang Hongsheng, Qu Bo, Zhang Zhengdong, Gong Kai, Lin Yanshui. Mechanisms by which baicalein protects against steriod-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3661-3668. |
| [11] | Han Yue, Wang Yufei, Liu Wanqing, Dong Ming, Niu Weidong. Effects of icariin on proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells in an inflammatory environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3709-3714. |
| [12] | Han Jie, Peng Qinglin, Xu Zhiwei, Wu Yukun, Ren Guowu, Xie Xiaozhong, Jin Wanqing, Yang Ling. Active ingredients of Panax notoginseng regulate signaling pathways related to steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3751-3758. |
| [13] | Wang Xin, Wubulikasimu·Mijiti, Huang Jinyong, Xie Zengru. Regulation of bone tissue cells by tumor necrosis factor-alpha [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(21): 3400-3406. |
| [14] | Tian Ai, Li Li, Xiao Tianjiao, Kang Jiabing, Zhan Jifan, Wei Yan, Chen Helin. Deferoxamine mesylate improves the repair of jaw bone defects in an ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3143-3149. |
| [15] | Wang Zengshun, Suonan Angxiu, Liu Limin, Zhou Jingyuan. Role and mechanism of miR-155/leptin receptor/adenosine phosphate-dependent protein kinase axis in tuberculin-induced osteoclast formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3190-3195. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||