Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (26): 4242-4249.doi: 10.12307/2024.338
Previous Articles Next Articles
Signaling pathways related to kaempferol active monomers in the treatment of osteoporosis
Yang Qipei1, Chen Feng2, Cui Wei2, Zhang Chi2, Wu Ruiqi1, Song Zhenheng1, Meng Xin1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-04-26Accepted:2023-06-03Online:2024-09-18Published:2023-10-07 -
Contact:Cui Wei, Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yang Qipei, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Chinese Medicine Interdisciplinary Innovation Team Project, No. GZKJ2310 (to CF); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 2021GXNSFAA220089 (to CF); Guangxi Postgraduate Education Innovation Program, No. YCBZ2021075 (to ZC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Qipei, Chen Feng, Cui Wei, Zhang Chi, Wu Ruiqi, Song Zhenheng, Meng Xin. Signaling pathways related to kaempferol active monomers in the treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4242-4249.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
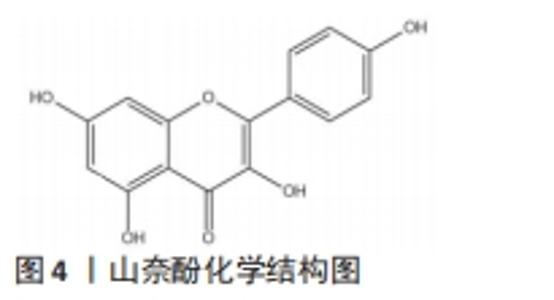
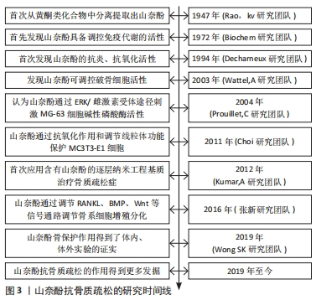
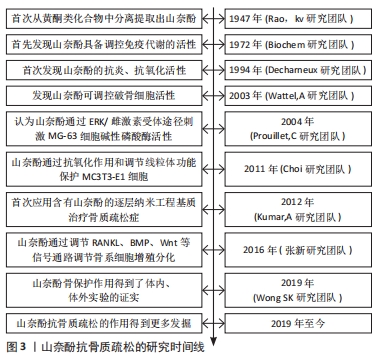
2.2 山奈酚活性单体对于骨细胞系及发挥抗骨质疏松的作用 在正常生理条件下,骨组织中复杂的通信网络由3 种关键的细胞类型组成,分别是成骨细胞、破骨细胞和BMSCs。然而,过于活跃的成骨细胞介导的成骨活动或破骨细胞依赖性骨吸收导致骨质量或数量的病理学改变,从而出现骨质的硬化或骨质疏松症。山奈酚作为黄酮类化合物,其在黄酮类中的含量仅次于槲皮素和杨梅素[5]。山奈酚又称山奈素、山奈黄酮醇等,分子结构式为C15H10O6,相对分子质量为286.236,见图4。目前大部分实验结果表明山奈酚有抗氧化、抗炎和抗肿瘤等作用,而随着科学研究的深入发现山奈酚在促进骨形成、抑制骨丢失等方面同样具有较大应用价值[12]。"
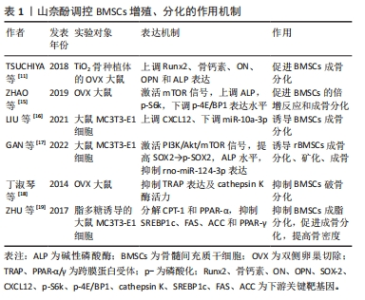
2.3 山奈酚对BMSCs的作用 间充质干细胞是人体内的多能干细胞,广泛存在于成人骨髓中,BMSCs被认为是具有分化为成骨细胞、成软骨细胞和成脂细胞潜力的成体干细胞[13]。然而,有相当多的证据支持BMSCs分化偏向脂肪细胞谱系而非成骨细胞谱系,可以直接导致骨形成/吸收的失衡,并最终导致骨丢失。转录因子Runx2和Osterix的表达是BMSCs促进成骨形成的主要决定因素之一,相比之下,转录因子过氧化物酶体增殖激活受体(peroxisome proliferators-activated receptorsγ,PPAR)γ则是驱动BMSCs成脂分化的关键因素[14]。 TSUCHIYA等[11]用含50 μmol/L山奈酚/100%乙醇的基质溶液固定化处理的TiO2牙种植体行对比实验,并用双侧卵巢切除术大鼠rBMSCs分别进行体外培养和体内实验,7 d后rBMSCs中Runx2、骨钙素、Osteonectin(ON)、骨桥蛋白和碱性磷酸酶等与骨形成能力密切相关蛋白及其mRNA的表达量显著提高;而在体内实验中,TiO2种植体附近没有新生破骨细胞生成,这表明了该浓度的山奈酚可刺激成骨并抑制破骨。ZHAO等[15]研究发现,山奈酚能提高Runx2、Osx水平,提高碱性磷酸酶活性,增加核糖体蛋白S6激酶(phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 kinase,p-S6K)的表达,降低磷酸化真核生物始动因子4E结合蛋白1(phosphorylated 4E binding protein 1,p-4E/BP1)的水平来达到促进BMSCs的倍增反应和成骨分化的作用,从而改善双侧卵巢切除诱导的大鼠骨质疏松。LIU等[16]研究发现,山奈酚通过下调miR-10a-3p、上调CXCL12并由此启动多个下游信号来促进BMSCs成骨分化,但过高浓度的山奈酚则会逆转该过程,如其浓度在75 μmol/L 和100 μmol/L 时。GAN等[17]用10 μmol/L的山奈酚对大鼠BMSCs进行抗骨质疏松实验,发现山奈酚可能通过PI3K/Akt/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路,提高SOX2表达并促进SOX2磷酸化,从而抑制miR-124-3p表达,最终提高rBMSCs的成骨钙化、碱性磷酸酶活性。同时,应用山奈酚可显著抑制双侧卵巢切除大鼠细胞中TRAP和cathepsin K酶活力增高现象,有利于抑制rBMSCs向破骨细胞前体转化,可应用于抗绝经后骨质疏松[18]。ZHU等[19]发现山奈酚可刺激经脂多糖诱导的BMSCs脂质分解代谢相关基因(CPT-1和PPAR-α)的表达,同时抑制脂质合成代谢相关基因的表达(SREBP1c、FAS、ACC和PPAR-γ),提高BMSCs的成骨分化。 以上研究表明,山奈酚的促成骨能力主要是通过调控BMSCs的分化而体现,对BMSCs中主要成骨相关因子Runx2、Osx、碱性磷酸酶的表达具有刺激作用;考虑到BMSCs分化的多样性,山奈酚能抑制成脂基因PPAR-γ的表达并上调脂质代谢因子CPT-1和PPAR-α水平从而抑制BMSCs成脂分化。山奈酚对BMSCs分化方向的调控是通过多种信号通路发挥作用,但不同浓度的山奈酚对BMSCs成骨分化的作用效果并不一致。较高浓度的山奈酚反而会抑制BMSCs成骨分化,合适的浓度区间是发挥山奈酚促成骨的重要影响因素,但最终目的 是促进BMSCs成骨分化、提高骨密度,这将为后续科学实验作出指引。山奈酚调控BMSCs增殖、分化的作用机制如表1。"

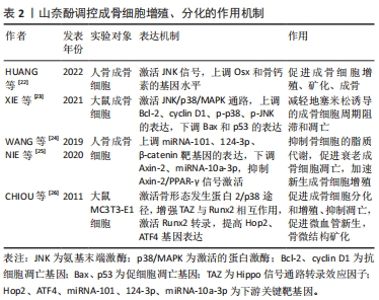
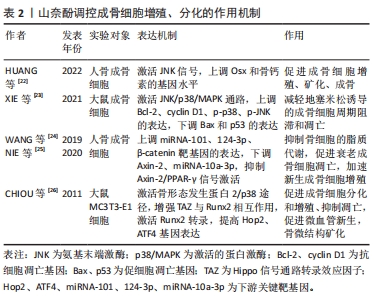
2.4 山奈酚对成骨细胞的作用 成骨细胞主要是源自多能间充质干细胞的骨形成细胞,Runx2和Osx被认为是成骨细胞谱系的主调节因子[20]。在成骨细胞增殖、分化与凋亡的生命周期中,成骨细胞在不同分化阶段可产生不同活性物质,包括生长因子、凋亡因子、趋化因子和mRNA等来调节其成骨代谢[21]。 山奈酚可通过调节多种骨代谢途径和骨调节因子的表达而影响成骨细胞的增殖与分化。山奈酚可通过JNK激酶途径诱导成骨细胞特异性转录因子Osx的表达,作用于下游成骨基因骨钙素OCN的表达,这说明山奈酚促进Osx的表达,促进成骨细胞增殖、矿化、成骨[22]。XIE等[23]发现山奈酚可通过激活JNK/p38/MAPK信号通路,上调Bcl-2和cyclin D1的表达,下调Bax和p53的表达,减轻地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞周期阻滞和凋亡,并显著上调了p-p38和p-JNK,改善了临床应用糖皮质激素导致的骨质疏松。鉴于mRNA在骨代谢中的作用,山奈酚通过上调成骨细胞中miRNA-101、124-3p等基因的表达,然后激活Wnt/β-catenin、P13k/Akt/mTOR通路,下调Axin-2的表达,抑制Axin-2/PPAR-γ信号通路参与成骨细胞脂质代谢,上调β-catenin表达,从而促进成骨细胞增殖和分化;同时也可以下调miRNA-10a-3p等相关基因的表达促进衰老的成骨细胞凋亡,加速成骨前体细胞增殖分化为年轻的成骨细胞,提高骨密度[24-25]。CHIOU等[26]研究发现山柰酚衍生物-8可通过BMP-2/p38途径增加TAZ(具有PDZ结合基序的转录辅激活因子)和Runx2的相互作用以增强Runx2的转录活性从而提高成骨细胞中Hop2、ATF4基因的表达,并能促进微血管新生提高骨密度和细胞活性。 综上所述,山奈酚对成骨细胞的作用是促进其增殖、分化并抑制其凋亡而发挥抗骨质疏松的目的,能够提高主要成骨因子Runx2、Osx水平,抑制细胞凋亡因子Bcl-2、cyclin D1和促凋亡因子Bax、p53表达,通过对微小骨结构的修复,促进血管新生并调节脂质代谢发挥积极的抗骨质疏松作用。尽管目前已有细胞及动物实验来表明山奈酚与“血管生成-成骨”偶联具有相关性,但仍需进一步深入探讨其在成骨细胞系信号通路中不同蛋白因子的相互作用机制,才有望更加明确其在相关通路中的作用机制,为临床应用打下坚实的基础。山奈酚调控成骨细胞增殖、分化的作用机制如表2。"
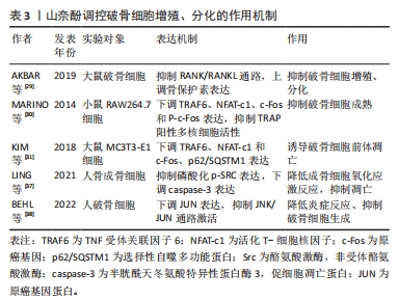
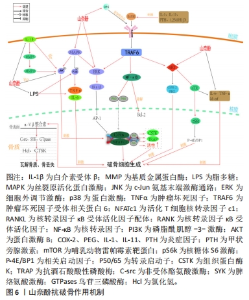
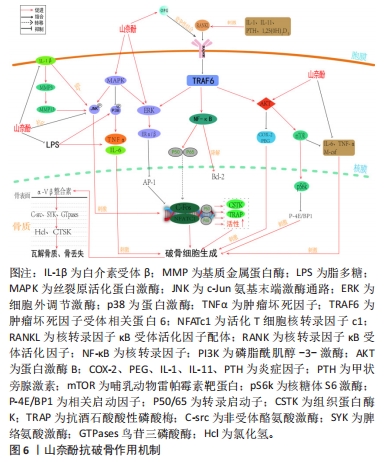
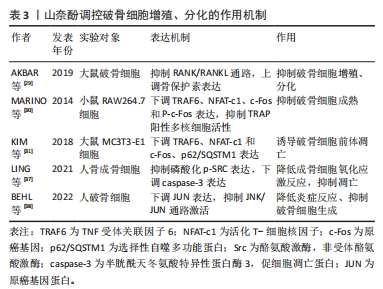
2.5 山奈酚对破骨细胞的作用 破骨细胞的形成、活化和存活主要受巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、RANK、RANKL和骨保护素的调控。破骨细胞通过分泌多种与骨代谢相关活性物质如转化生长因子β、SLC、c-Fos、活化T细胞核因子(nuclearfactorcells,NFAT)c1等参与调解破骨细胞或前体细胞的形成和分化。 山奈酚对破骨细胞的作用主要在于抑制破骨前体细胞分化,或直接参与调节破骨细胞分泌相关骨代谢因子和基因表达,促进其自噬凋亡或抑制增殖分化。RANK是一种Ⅰ型同源三聚体跨膜蛋白,是目前已知的RANKL唯一受体激活剂[27],主要功能是在破骨细胞及其原始细胞表面与RANKL结合,促使破骨前体细胞具备分化为成熟破骨细胞的潜力[28]。 一定浓度的山奈酚可刺激骨保护素的表达并与RANKL竞争性的结合RANK,使未结合的RANKL活性丧失,RANKL/RANK通路启动失败,从而抑制成熟破骨细胞的形成、存活和激活[29]。山奈酚通过RANKL/RANK通路作用于破骨前体细胞抑制其与破骨细胞分化密切相关的活性物质如肿瘤坏死因子受体相关蛋白6(tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6,TRAF6)、NFAT-c1、c-Fos和P-c-Fos的表达,抑制RANKL诱导的RAW264.7细胞中TRAP阳性多核细胞和吸收坑的形成,这是破骨细胞分化的指标[30]。山奈酚通过下调TRAF6、NFAT-c1和c-Fos、p62/SQSTM1的表达,诱导破骨前体细胞的凋亡[31]。肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)是响应氧化应激产生的最早的炎症递质,能促进炎症递质的产生,并诱导巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的表达[32]。肿瘤坏死因子α通过激活NF-κB、促进RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化和增加骨吸收来影响骨质疏松症愈合[33]。现有研究表明,山奈酚可以显著降低肿瘤坏死因子α的表达和分泌来减少炎症反应中的氧化应激,从而抗骨质疏松[34]。原癌基因酪氨酸蛋白激酶SRC(Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase,Src)是参与骨代谢的重要基因,其在驱动成骨细胞增殖和细胞外基质重塑中起着关键作用,Caspases蛋白家族是促细胞凋亡重要调节蛋白[35],而caspase-3的上调可以激活p53信号通路,破坏成骨细胞成熟,抑制软骨细胞分化,从而抑制骨质疏松愈合[36]。LING等[37]在对细胞凋亡的实验中发现山奈酚可通过直接抑制磷酸化p-SRC的过表达来调节血清炎症因子的产生,并能显著减少caspase-3的表达,降低成骨细胞氧化应激反应,抑制其凋亡。JUN是JNK信轴中的调节因子,在炎症反应和破骨细胞生成中起关键作用,可激活炎症反应和破骨细胞形成,BEHL等[38]发现山奈酚可以通过抑制JUN来调节抗炎反应、抑制破骨细胞生成。 上述研究表明,破骨细胞是骨代谢失衡的重要影响因素,RANKL/RANK信号通路是调节破骨细胞活性的最主要通路,因此通过该通路调节破骨细胞的活性显得尤为重要。山奈酚能够抑制RANKL通路激活并下调NFAT-c1、c-Fos、TRAF6、转化生长因子β等主要促破骨细胞形成因子水平抑制破骨细胞的增殖、分化。炎症因子在提高破骨细胞活性中具有重要作用,山奈酚降低炎症递质的产生,揭示了抗炎与抗骨质疏松的关系。同时,山奈酚也能够影响促细胞凋亡因子caspase-3表达来促进破骨细胞凋亡,起到相对性的减少破骨细胞数量防治骨质疏松的目的。山奈酚调控破骨细胞增殖、分化、凋亡的作用机制如表3。"
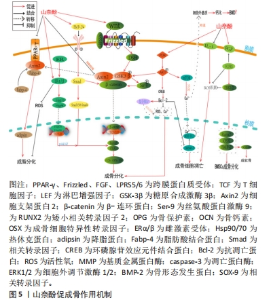
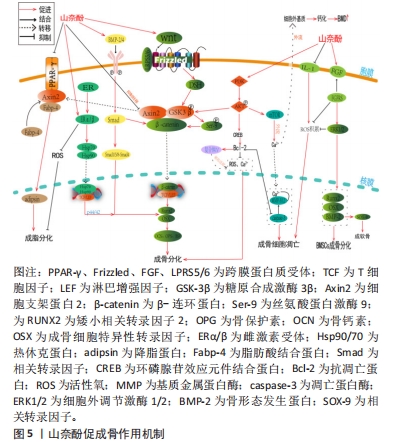
综上所述,山奈酚对BMSCs、成骨细胞的增殖分化及破骨细胞的活性与凋亡均具有调节作用,控制各细胞的分化方向及数量是维持骨形成/骨吸收平衡的重要方式。山奈酚从多种途径起到诱导成骨分化、抑制破骨吸收、抑制/促进对应细胞凋亡而达到防治骨质疏松的目的。 2.6 山奈酚调控相关信号通路防治骨质疏松症 2.6.1 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 Wnt/β-catenin通路是已知成骨细胞功能和骨形成的重要调节剂,是高度保守的分泌型糖蛋白家族成员,富含半胱氨酸残基。该途径是受卷曲蛋白和低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白的结合触发,继而Wnt/β-catenin激活DSH蛋白家族,这些蛋白促进糖原合成酶激酶3β(Glycogen synthase kinase-3β,GSK-3β)的磷酸化和失活,并阻止β-catenin的降解以及促进其转移到细胞核中,在细胞核中β-catenin与T细胞因子(TCF)/淋巴增强因子(LEF)结成复合物,诱导成骨细胞基因的转录[39]。 HUANG等[40]发现山奈酚能促进GSK-3β的磷酸化,GSK-3β作为一种骨代谢的负性调节因子,它主要通过磷酸化的方式来调控骨代谢疾病,提高BMSCs细胞核中β-catenin的水平。Wnt信号通路的激活促进了GSK-3β的磷酸化,使β-catenin的合成增多,抑制Axin2的活性并下调了成脂基因PPAR-γ、脂肪酸结合蛋白4和adipsin的表达水平,从而证实了山奈酚通过Wnt通路对BMSCs分化的干预作用。SHARMA等 [41]用山奈酚处理SaOS-2细胞7 d时,细胞内碱性磷酸酶的活性得到最大诱导,关键成骨转录因子Runx2和Osx较空白组提升2-2.5 倍,早期成骨细胞分化标志物OPN和晚期成骨分化标志物BSP的mRNA水平分别提高1.5/2.5 倍,而在细胞核内,检测到β-catenin与DNA结合蛋白TCF/LEF组成的成骨靶基因的高表达,证实了山奈酚诱导的SaOS-2细胞中Wnt信号通路的激活,从而增加了成骨。在另一项确定Wnt和雌激素信号通路在碱性磷酸酶活性诱导成骨分化相关性的研究中,SaOS-2细胞同时表达雌激素受体ER-α和ER-β,山奈酚和17β-雌二醇(一种已知的激动剂)分别处理48 h后均诱导了成骨细胞ERE-luc活性的激活,而使用ICI182780(两种ER的有效抑制剂)的预处理后完全消除了山奈酚诱导的ERE-luc活性并降低了胞内碱性磷酸酶活性,这证实了山奈酚可以作用于雌激素信号通路的下游,进而进行负反馈调节激活Wnt通路促进成骨细胞分化[42]。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路是调控骨形成/骨吸收重要的通路,β-catenin的表达是该通路中最为关键步骤,山奈酚能够激活Wnt通路并提高β-catenin表达来达到诱导成骨分化。同时Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活还能影响雌激素缺失导致的骨质疏松,这可能是山奈酚治疗绝经后骨质疏松的重要途径之一。总之,山奈酚对该通路的作用主要是调控β-catenin、GSK-3β、碱性磷酸酶水平发挥抗骨质疏松的作用。 2.6.2 RANKL/RANK信号通路 RANKL/RANK系统以其在破骨细胞分化、骨骼生长和骨重塑中的作用而闻名。RANK是RANKL最主要的受体,常见于破骨细胞的胞膜上,两者的结合可刺激胞内TRAF6与RANK形成复合体,继而激活下游主要信号如NF-κB、ERK或p38/MAPK,诱导c-Fos转移至细胞核与NFAT-c1结成复合物,最终诱导破骨细胞基因的转录[43]。而骨保护素是RANKL的诱饵受体,在该通路中扮演典型的抗RANKL/RANK系统激活调节剂[44]。 XU等[45]对BMSCs成骨分化的研究中,发现山奈酚可以使RANKL诱导的下游调节因子c-Fos、c-src和NFAT-c1的表达降低,进而降低了破骨细胞靶向生成蛋白(如组织蛋白酶K和TRAP)的水平。在另一项研究中发现山奈酚可抑制脂多糖诱导的RANKL表达,升高脂多糖抑制的骨保护素的表达,使RANKL/RANK通路失活;此外,山奈酚可抑制白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、COX-2及前列腺素E2等促破骨炎性递质的产生,降低炎性反应,从而抑制了破骨细胞分化和骨吸收[46]。RAMESH等[47]体外研究发现若干促破骨因子如白细胞介素11、白细胞介素1、甲状旁腺激素和1,25-(OH)2D3通过刺激RANKL与RANK结合间接促进破骨细胞的形成,这导致了下游信号通路的激活,如Akt、MAPK通路,这些通路的激活使与RANKL通路相关的促破骨因子,如NF-κB、c-fos、c-src、TRAF-6和NFAT-C1及转录启动子p50,p65的表达增高,而山奈酚则可阻断这一过程。LEE等[48]的研究中指出,山奈酚可抑制白细胞介素1β刺激的、RANKL介导的破骨细胞分化,还抑制白细胞介素1α刺激的、RANKL介导的ERK1/2、p38和JNK-MAPK激酶的磷酸化,进而抑制c-Fos和NFA-Tc1的表达和NF-κB降解,这表明了山奈酚的抗炎和抗破骨细胞生成的协同作用。FENG等[49-50]的研究证实了RANKL通路的激活使破骨前体细胞分化后通过α-Vβ整合素与骨表面形成关联,传递调节细胞骨架组织的信号,这些信号进而激活c-Src、SYK、GTPases表达,并通过分泌盐酸和组织蛋白酶K,在骨小梁表面形成微观沟槽,进入细胞外溶酶体空间,以降解骨基质和矿物部分,在山奈酚的作用下抑制了以上基因的表达,起到了抑制骨吸收、平衡关节软骨和软骨下骨的代谢作用。HOOSHIAR等[51]发现山奈酚可增加骨保护素水平,降低RANKL表达,抑制RANKL/RANK信号通路的激活。 综上所述,RANKL/RANK信号通路是促骨丢失通路,如何抑制该通路的激活是决定山奈酚发挥抗破骨作用的关键。山奈酚通过竞争性结合RANK从而抑制该通路的激活,进一步阻止下游促破骨分化因子c-fos、NFATC-1转录及表达。同时鉴于炎症因子与RANKL/RANK通路和破骨细胞的密切关系,通过该通路调节炎症因子亦是山奈酚的发挥作用的方式之一,但这需要进一步科学研究来证明其在抗骨质疏松中的作用关系。 2.6.3 PI3K/Akt信号通路 PI3K/Akt信号通路在细胞信号转导和代谢中发挥着重要作用,广泛参与调节细胞的代谢活动,随着近年来研究的深入,发现该通路可双向调节成骨细胞与破骨细胞的增殖、分化与凋亡[52]。PI3K是一种胞质激酶,Akt是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,它能保护细胞免受凋亡,受到信号刺激后其胞膜上的PIP2会转化成PIP3,并作用于靶基因Akt参与细胞的增殖分化。此外,PI3K/Akt信号通路可以通过拮抗氧化应激和降低炎性因子的产生来减少成骨细胞凋亡并预防骨质疏松[53]。 赵明智等[54]对人炎性乳腺癌SUM190细胞株实验发现,山奈酚可通过上调PI3K、Akt磷酸化水平,进而上调下游GSK-3β磷酸化,GSK-3β氨基端的丝氨酸9(ser-9)磷酸化后会抑制酶活性,提高细胞中β-catenin水平,进而促进骨形成。mTOR是一种保守的丝/苏氨酸蛋白质激酶,是PI3K/Akt信号传导过程中的关键介质,已被证实在成骨形成中有用[15]。 崔琳娜等[55]对使用10 μmol/L山奈酚处理施加10%单轴牵张力下小鼠BMSCs成骨分化影响时发现,山奈酚通过激活PI3K/Akt从而促进了mTOR磷酸化,增加Runx2和Osx以及mTOR通路下游调节因子p-S6K的表达水平,降低p-4E/BP1水平,并加速了细胞内Ca2+的外流释放从而促进细胞外基质钙化,提高了牵张力下小鼠BMSCs成骨活性和骨密度。在一项对抗炎及抗软骨细胞凋亡的研究中,杜仲活性提取物山奈酚活性单体通过PI3K/Akt信号轴抑制肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的产生以及COX-2和前列腺素E的分泌来减轻炎症反应,抑制破骨细胞增殖分化,此外,基质金属蛋白酶3的分泌也被抑制,基质金属蛋白酶被认为是可能细胞外基质的主要蛋白水解酶,表明了山奈酚对骨组织的保护作用[56]。CHOI等[57]在研究山奈酚对抗霉素A诱导的成骨细胞样MC3T3-E1细胞毒性的保护作用时发现,山奈酚可诱导碱性磷酸酶抑制的PI3K/Akt和环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白(CREB)的激活,抑制环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白磷酸化从而抑制线粒体膜电位的耗散、复合体IV失活、钙离子升高和活性氧的产生,保护了MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化。 以上研究表明,PI3K/Akt信号通路是促成骨方面的重要通路之一,在山奈酚的介导下不仅具备独立调控下游促成骨分化因子和抗成骨凋亡因子的能力,而且其对磷酸化GSK-3β、Runx2、Osx水平的调控与Wnt通路结成交互关系。同时该通路具有促进部分Ca2+外流钙化和与活性氧结合增强成骨基因转录以及抑制Ca2+与mTOR下游促凋亡因子结合的独特作用。这提示PI3K/Akt通路与RANKL、mTOR通路间的互动关系,因此山奈酚作用于PI3K/Akt通路可能是发生多级联合反应来达到防治骨质疏松症,但这仍需要进一步的实验发掘。 2.6.4 ER/ERK信号通路 雌激素缺乏是绝经后妇女骨质疏松症的主要原因。雌激素受体有两种类型,即ER-α和ER-β。ER-α和ER-β在成骨细胞、骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨髓基质细胞上的表达表明,骨细胞是雌激素的直接靶点。雌激素通过基因组和非基因组途径对骨骼的保护作用在历史上已经确立[58]。在传统的基因组途径中,雌激素与其受体的结合导致雌激素受体的构象变化,热休克蛋白90和热休克蛋白70形成雌激素受体二聚体,随后,二聚体易位到细胞核中,并直接与特定的雌激素反应元件(estrogen response element,ERE)序列结合,以增强其转录反应[59]。除此之外,雌激素-雌激素受体复合物的非基因组作用可能通过激活下游信号分子介导,包括PI3K/Akt,MAPK和PKC[60]。 ONDRICEK等[61]在利用植物雌激素减轻氧化应激诱导细胞凋亡中作用的比较研究发现,山奈酚和染料木素从碘乙酸诱导的细胞死亡中拯救了RGC-5细胞,减少了半胱天冬酶活化和活性氧生成。早期的一项体外研究表明,山奈酚通过PKC途径增加了MG-63成骨细胞中碱性磷酸酶的活性,但在用细胞外调节激酶抑制剂和雌激素受体拮抗剂治疗后,这种活性降低,这表明,山奈酚增加碱性磷酸酶活性是由于PKC/ERK信号轴的激活[62]。山奈酚可诱导成骨细胞中表达ERE、ERα磷酸化,上调碱性磷酸酶、骨分化标志物(Runx2、Osx、COL1、骨钙素和骨连蛋白)和成骨细胞矿化的萤光素酶活性[63]。YANG等[64]的另一项研究证实,山奈酚提高了成骨细胞样UMR-106中的碱性磷酸酶活性,激活了ERβ介导的ERE报告基因转录,并通过激活ERα/β介导的AP-1报告基因表达显示出有效的ER拮抗剂活性。女性绝经后雌激素水平的下降是影响绝经后女性骨质疏松较为突出的因素之一,然而对于山奈酚与雌激素信号通路的作用关系尚不够清晰,相关研究较为缺乏,但上述研究已提供了思路,包括雌激素受体与PI3K/Akt、MAPK通路的关系以及对活性氧水平的调控,说明山奈酚具备通过雌激素受体激动机制来维持绝经后女性体内骨代谢平衡的能力。 2.6.5 BMP/Smad信号通路 BMP信号通路是体外调控成骨分化和体内骨形成的重要途径之一,其亚型BMP-2/4在促进骨形成和成骨分化中较活跃,是转化生长因子β超家族的成员。它通过与四聚体受体复合物结合,在骨骼发育、骨骼形成和骨骼稳态过程中调节BMSCs的分化。BMP-2与其受体的结合通过Smad和p38/MAPK信号传导的抑制因子传递信号。Smad信号的传导涉及其下游信号因子Smad1/5/8-Smad4复合物的形成,该复合物可诱导成骨相关因子的表达[65]。 HE等[66]使用骨碎补提取物山奈酚对大鼠BMSCs分化的研究中发现山奈酚增加了大鼠BMP的mRNA水平,上调了Runx2和Osx表达,并抑制ERK的磷酸化,表明山奈酚过激活成骨细胞中的BMP/ERK信号通路来增强骨形成。JIAN等[67]用骨髓基质ST2细胞进行成骨分化培养,并用山奈酚磺基衍生物(kaempferol-3)处理后发现,ST2细胞中碱性磷酸酶活性、骨钙素 mRNA表达和成骨细胞矿化过程加强,并增强了BMP-2、p-Smad1/5/8、β-catenin和Runx2的表达,表明kaempferol-3通过调节BMP/Smad/Wnt信号通路促进ST2细胞的成骨分化。ADHIKARY等[68]研究发现,山奈酚可能通过BMP-2/Runx2通路刺激MC3T3-E1细胞的分化和矿化,增强碱性磷酸酶、Runx2、Osx和骨钙素的表达,促进BMSCs向成骨细胞分化,并且Runx2表达的提高可降低成骨细胞的氧化损伤,同时还通过下调PPAR-γ抑制BMSCs向脂肪细胞的分化。 目前,对山奈酚在BMP/Smad信号通路在发挥抗骨质疏松的作用机制认识尚浅,其可能是通过介导BMP/Samd信号通路上调下游成骨基因Runx2、Osx、骨钙素、BMP表达,以提高成骨细胞转录活性并加速骨细胞钙化、矿化,最终提高骨密度,未来仍需要投入更多相关实验研究来完善其通过该通路发挥的抗骨质疏松作用机制。 2.6.6 MAPK信号通路 MAPK是一个二级信使家族,负责将信号从细胞表面传递到细胞核,在细胞对生长因子、成骨因子或环境应激的反应中发挥重要作用[69]。其中3 个主要的MAPK家族负责对MAPK信号的传导:ERK参与细胞的增殖、转化和存活,c-Jun氨基末端参与应激反应、p38/MAPK参与多种细胞过程[70]。 已经发现,菟丝子的水提取物山奈酚的药理学实验可通过MARK/ERK信号传导,增强新生小鼠颅骨成骨细胞的增殖,并抑制凋亡[71]。XIONG等[72]发现山奈酚通过p38/MARK途径抑制脂多糖诱导的破骨细胞性骨吸收和白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,并通过上调骨保护素基因的表达,最终促进MG-63细胞的增殖和分化。HE等[73]通过Western blotting检测分析表明,山奈酚可抑制脂多糖诱导的破骨细胞生成和破骨细胞性骨吸收,抑制脂多糖介导的破骨细胞p38/JNK的活化,提示山奈酚可通过p38/JNK途径抑制破骨细胞的分化。另一项研究指出,山奈酚可激活ERK信号通路,诱导BMSCs向成骨细胞增殖和分化,增加BMP-2、Runx2和Osx的mRNA水平[74]。WANG等[75]在白细胞介素1β诱导的IDD体外模型中,山奈酚处理显著减弱了白细胞介素1β诱导的活性氧积累和凋亡,以及基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13、SOX9的增加,并显著缓解了白细胞介素1β刺激对p38、JNK和ERK1/2磷酸化的促进作用。成纤维细胞生长因子受体(fibroblast growth factor receptors,FGFRs)是与FGF结合的跨膜受体家族,参与调节细胞的生长和增殖,血管生成和许多发育过程,对骨系细胞具有促进生成大量的成骨细胞、抑制破骨细胞的作用。山奈酚通过FGF/FGFRs信号轴激活MAPKs通路,上调Runx2的表达,并抑制过量活性氧带来的氧化损伤,促进成骨细胞的分化和增殖[76]。总之,山奈酚介导的MAPK信号通路与BMSCs和成骨细胞的增殖分化密切相关,主要是抑制炎症因子产生和活性氧积累,刺激BMP-2、Runx2和Osx表达。由于MAPK是一个二级信使家族,其与RANKL通路的交互关系可开展更为深入的科学研究,以便发挥山奈酚抗破骨作用的最大价值。 综上所述,山奈酚具备通过干预Wnt/β-catenin、RANKL/RANK、PI3K/Akt、ER/ERK、MAPK、BMP/samd通路防治骨质疏松的能力。在上述通路中,山奈酚又可以使各通路间的信号传导交互发生,这表明山奈酚发挥其能力是一个复杂机制过程。山奈酚对一些通路如PI3K/Akt、MAKP、ER/ERK具有双重作用,能刺激成骨也能刺激破骨,这取决于山奈酚的浓度以及其对应靶信号的开启,因此,以现有资料分别将山奈酚促成骨相关及抑制破骨相关通路关系作图5,6,以为后续明确山奈酚的骨保护浓度及多区域信号的作用机制提供重要的思路参考和指导意义。"
| [1] 彭斯伟,宋敏,范凯,等.单味中药治疗肾虚型骨质疏松症机制研究状况[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(1):76-80. [2] 陈镜,冯正平.骨质疏松症治疗药物研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021,27(5):776-780. [3] 武瑞骐,崔伟,杨启培,等.激素性股骨头坏死的中医药治疗机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(17):2763-2771. [4] 侯伟,杜斌.中医药治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2021,16(10):1956-1960. [5] 丘志河,谢卫勇,黄刚,等.山奈酚通过调控miR-21/SOX9对骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J].中国药师,2022,25(12):2073-2078. [6] RAKHA A, UMAR N, RABAIL R, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic potential of dietary flavonoids:A review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156: 113945. [7] NEJABATI HR, ROSHANGAR L. Kaempferol: A potential agent in the prevention of colorectal cancer. Physiol Rep. 2022;10(20):e15488. [8] IMRAN M, RAUF A, SHAH ZA, et al. Chemo-preventive and therapeutic effect of the dietary flavonoid kaempferol: A comprehensive review. Phytother Res. 2019;33(2):263-275. [9] IMRAN M, RAUF A, SHAH ZA, et al. Chemo-preventive and ther-apeutic effect of the dietary flavonoid kaempferol:A comprehen-sive review. Phytother Res. 2019;33:263-275. [10] 袁真,闵珺,王恺,等.杜仲黄酮类3种药物成分治疗大鼠骨质疏松的比较研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(2):244-248. [11] TSUCHIYA S, SUGIMOTO K, KAMIO H, et al. Kaempferol-immobilized titanium dioxide promotes formation of new bone: effects of loading methods on bone marrow stromal cell differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:1665-1676. [12] DA LUZ BB, MARIA-FERREIRA D, DALLAZEN JL, et al. Effectiveness of the polyphenols-rich Sedum dendroideum infusion on gastric ulcer healing in rats:Roles of protective endogenous factors and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;278:114260. [13] LU X, LI J, ZHOU B, et al. Taohong Siwu Decoction enhances human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells proliferation, migration and osteogenic differentiation via VEGF-FAK signaling in vitro [published online ahead of print, 2023 Jan 20]. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;307:116203. [14] FAGHFOURI AH, KHAJEBISHAK Y, PAYAHOO L, et al. Alivand M. PPAR-gamma agonists: Potential modulators of autophagy in obesity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;912:174562. [15] ZHAO J, WU J, XU B, et al. Kaempferol promotes bone formation in part via the mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(6):5197-5207. [16] LIU H, YI X, TU S, et al. Kaempferol promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and improves osteoporosis by downregulating miR-10a-3p and upregulating CXCL12. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;520:111074. [17] GAN L, LENG Y, MIN J, et al. Kaempferol promotes the osteogenesis in rBMSCs via mediation of SOX2/miR-124-3p/PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;927:174954 [18] 丁淑琴,杨风琴,张玮,等.山奈酚治疗去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松的实验研究[J].中国新药杂志,2014,23(24):2925-2929+2932. [19] ZHU J, TANG H, ZHANG Z, et al. Kaempferol slows intervertebral disc degeneration by modifying LPS-induced osteogenesis/adipogenesis imbalance and inflammation response in BMSCs. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;43:236-242. [20] WONG SK, CHIN KY, IMA-NIRWANA S. The Osteoprotective Effects Of Kaempferol: The Evidence From In Vivo And In Vitro Studies. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13: 3497-3514. [21] 任明诗,丁羽,李子涵,等.成骨细胞与破骨细胞相互调节作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):822-827. [22] HUANG AY, XIONG Z, LIU K, et al. Identification of kaempferol as an OSX upregulator by network pharmacology-based analysis of qianggu Capsule for osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1011561. [23] XIE B, ZENG Z, LIAO S, et al. Kaempferol ameliorates the inhibitory activity of dexamethasone in the osteogenesis of MC3T3-E1 cells by JNK and p38-MAPK pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:739326. [24] WANG Y, CHEN H, ZHANG H. Kaempferol promotes proliferation,migration and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells via up-regulation of microRNA-101. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1050-1056. [25] NIE F, ZHANG W, CUI Q, et al. Kaempferol promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020;258:118143. [26] CHIOU WF, LEE CH, LIAO JF, et al. 8-Prenylkaempferol accelerates osteoblast maturation through bone morphogenetic protein-2/p38 pathway to activate Runx2 transcription. Life Sci. 2011;88:335-342. [27] TOBEIHA M, MOGHADASIAN MH, AMIN N, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: A Mechanism Involved in Exercise-Induced Bone Remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6910312. [28] ASAI K, FUNABA M, MURAKAMI M. Enhancement of RANKL-induced MITF-E expression and osteoclastogenesis by TGF-β. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014;32:401-409. [29] AKBAR IZ, DEWI FRP, SETIAWAN B. In Silico Interaction of the Active Compounds of Scurrula Atropurpurea with the RANK/RANKL/OPG System in Diabetoporosis. Acta Inform Med. 2019;27(1):8-11. [30] MARINO S, LOGAN JG, MELLIS D, et al. Generation and culture of osteoclasts. Bonekey Rep. 2014;3:570. [31] KIM CJ, SHIN SH, KIM BJ, et al. The Effects of Kaempferol-Inhibited Autophagy on Osteoclast Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):125. [32] KITAURA H, ZHOU P, KIM HJ, et al. M-CSF mediates TNF-induced inflammatory osteolysis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(12):3418-3427. [33] YAO Z, GETTING SJ, LOCKE IC. Regulation of TNF-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Cells. 2021;11(1):132. [34] SANG C, ZHANG Y, CHEN F, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses osteogenic differentiation of MSCs by inhibiting semaphorin 3B via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in estrogen-deficiency induced osteoporosis. Bone. 2016;84:78-87. [35] LIU WJ, JIANG ZM, CHEN Y, et al. Network pharmacology approach to elucidate possible action mechanisms of Sinomenii Caulis for treating osteoporosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;257:112871. [36] WU J, YANG Y, HE Y, et al. EFTUD2 gene deficiency disrupts osteoblast maturation and inhibits chondrocyte differentiation via activation of the p53 signaling pathway. Hum Genomics. 2019;13(1):63. [37] LING Y, XU H, REN N, et al. Prediction and Verification of the Major Ingredients and Molecular Targets of Tripterygii Radix Against Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:639382. [38] BEHL T, MEHTA K, SEHGAL A, et al. Exploring the role of polyphenols in rheumatoid arthritis. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(19):5372-5393. [39] 郭一览,孙朋.Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在运动调控骨形成中的机制[J].生命科学,2022,34(12):1519-1529. [40] HUANG JM, BAO Y, XIANG W, et al. Icariin Regulates the Bidirectional Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:8085325. [41] SHARMA AR, NAM JS. Kaempferol stimulates WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway to induce differentiation of osteoblasts. J Nutr Biochem. 2019; 74:108228. [42] NIE F, ZHANG W, CUI Q, et al. Kaempferol promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020;258:118143. [43] YASUDA H. Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):2-11. [44] TOBEIHA M, MOGHADASIAN MH, AMIN N, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: A Mechanism Involved in Exercise-Induced Bone Remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6910312. [45] XU Q, CHEN G, LIU X, et al. Icariin inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via modulation of the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;508(3):902-906. [46] XIAO Y, LIU L, ZHENG Y, et al. Kaempferol attenuates the effects of XIST/miR-130a/STAT3 on inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Future Med Chem. 2021;13(17):1451-1464. [47] RAMESH P, JAGADEESAN R, SEKARAN S, et al. Flavonoids: Classification, Function, and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Bone Remodelling. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:779638. [48] LEE WS, LEE EG, SUNG MS, et al. Kaempferol inhibits IL-1β-stimulated, RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis via downregulation of MAPKs, c-Fos, and NFATc1. Inflammation. 2014;37(4):1221-1230. [49] FENG WQ, LIU KY, ZHANG JN, et al. Study on mechanism of Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata for treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022; 47(19):5336-5343. [50] BOYCE BF, YAO Z, XING L. Osteoclasts have multiple roles in bone in addition to bone resorption. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009;19(3):171-180. [51] HOOSHIAR SH, TOBEIHA M, JAFARNEJAD S. Soy Isoflavones and Bone Health: Focus on the RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2022; 2022:8862278. [52] 陈巧玲,白亦光,别俊,等.靶向抑制Akt对成骨细胞分化PI3K/Akt信号通路调控的研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2020,37(12):2123-2128. [53] 王秉义,潘剑.丹参素拮抗氧化应激所致骨质疏松并通过PI3k/Akt通路减少成骨细胞的凋亡[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(1):1-5+11. [54] 赵明智,张磊,周丹,等.山奈酚调控PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β信号通路促进人炎性乳腺癌SUM190细胞株凋亡的研究[J].广西医科大学学报,2019, 36(6):872-877. [55] 崔琳娜,蒋校文,黄华庆,等.山奈酚通过mTORC1信号促进牵张力下小鼠骨髓间充质细胞成骨分化机制研究[J].口腔疾病防治,2021,29(4): 234-240. [56] HUANG L, LYU Q, ZHENG W, et al. Traditional application and modern pharmacological research of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Chin Med. 2021; 16(1):73. [57] CHOI EM. Kaempferol protects MC3T3-E1 cells through antioxidant effect and regulation of mitochondrial function. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011;49(8): 1800-1805. [58] CHENG CH, CHEN LR, CHEN KH. Osteoporosis Due to Hormone Imbalance: An Overview of the Effects of Estrogen Deficiency and Glucocorticoid Overuse on Bone Turnover. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1376. [59] CHEN P, LI B, OU-YANG L. Role of estrogen receptors in health and disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:839005. [60] PRAKASH R, MISHRA T, DEV K, et al. Phenanthrenoid Coelogin Isolated from Coelogyne cristata Exerts Osteoprotective Effect Through MAPK-Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021; 109(1):32-43. [61] ONDRICEK AJ, KASHYAP AK, THAMAKE SI, et al. A comparative study of phytoestrogen action in mitigating apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. In Vivo. 2012;26(5):765-775. [62] PROUILLET C, MAZIÈRE JC, MAZIÈRE C, et al. Stimulatory effect of naturally occurring flavonols quercetin and kaempferol on alkaline phosphatase activity in MG-63 human osteoblasts through ERK and estrogen receptor pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004;67(7):1307-1313. [63] GUO AJ, CHOI RC, ZHENG KY, et al. Kaempferol as a flavonoid induces osteoblastic differentiation via estrogen receptor signaling. Chin Med. 2012;7:10. [64] YANG L, CHEN Q, WANG F, et al. Antiosteoporotic compounds from seeds of Cuscuta chinensis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;135(2):553-560. [65] WU M, CHEN G, LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016;4:16009. [66] HE G, GUO W, LOU Z, et al. Achyranthes bidentata saponins promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through the ERK MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;70(1):467-473. [67] JIAN J, SUN L, CHENG X, et al. Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside stimulates osteoblast differentiation through regulating the BMP/WNT signaling pathways. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 2015;5(5):454-460. [68] ADHIKARY S, CHOUDHARY D, AHMAD N, et al. Dietary flavonoid kaempferol inhibits glucocorticoid-induced bone loss by promoting osteoblast survival. Nutrition. 2018;53:64-76. [69] CHAKRABORTY C, SHARMA AR, PATRA BC, et al. MicroRNAs mediated regulation of MAPK signaling pathways in chronic myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget. 2016;7(27):42683-42697. [70] WANG Z, GOU X. Receptor-Like Protein Kinases Function Upstream of MAPKs in Regulating Plant Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7638. [71] ZHANG ND, HAN T, HUANG BK, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine formulas for the treatment of osteoporosis: Implication for antiosteoporotic drug discovery. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;189:61-80. [72] XIONG Z, ZHENG C, CHANG Y, et al. Exploring the Pharmacological Mechanism of Duhuo Jisheng Decoction in Treating Osteoporosis Based on Network Pharmacology. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021; 2021:5510290. [73] HE G, GUO W, LOU Z, et al. Achyranthes bidentata saponins promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through the ERK MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;70(1):467-473. [74] ZHOU L, WU T. A Network Pharmacology-Based Study on Vital Pharmacological Pathways and Targets of Eucommiae Cortex Acting on Osteoporosis. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8510842. [75] WANG X, TAN Y, LIU F, et al. Pharmacological network analysis of the functions and mechanism of kaempferol from Du Zhong in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). J Orthop Translat. 2023;39:135-146. [76] HASSANZADEH A, NAIMI A, HAGH MF, et al. Kaempferol Improves TRAIL-Mediated Apoptosis in Leukemia MOLT-4 Cells by the Inhibition of Anti-apoptotic Proteins and Promotion of Death Receptors Expression. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2019;19(15):1835-1845. |
| [1] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [2] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [3] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [4] | Wei Juan, Li Ting, Huan Mengting, Xie Ying, Xie Zhouyu, Wei Qingbo, Wu Yunchuan. Mechanism by which static exercise improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [5] | Huang Haoran, Fan Yinuo, Wei-Yang Wenxiang, Jiang Mengyu, Fang Hanjun, Wang Haibin, Chen Zhenqiu, Liu Yuhao, Zhou Chi. Urolithin A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1149-1154. |
| [6] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [7] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [8] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [9] | Liu Xin, Hu Man, Zhao Wenjie, Zhang Yu, Meng Bo, Yang Sheng, Peng Qing, Zhang Liang, Wang Jingcheng. Cadmium promotes senescence of annulus fibrosus cells via activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1217-1222. |
| [10] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [11] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [12] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [13] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [14] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| [15] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||