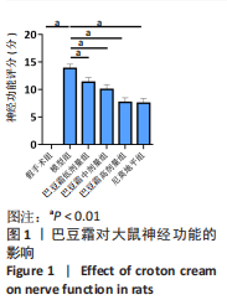
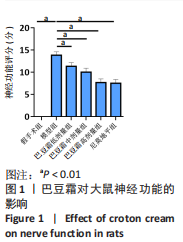
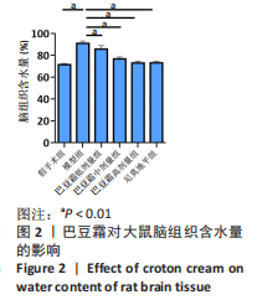
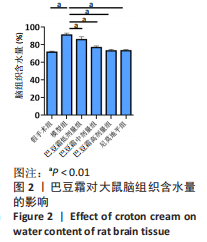
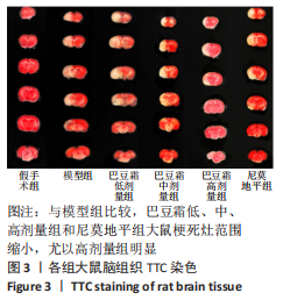
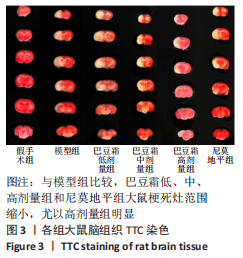
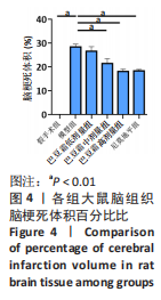
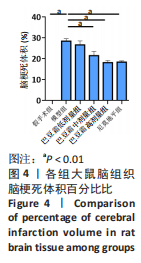
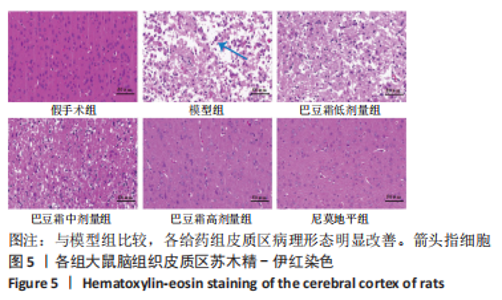
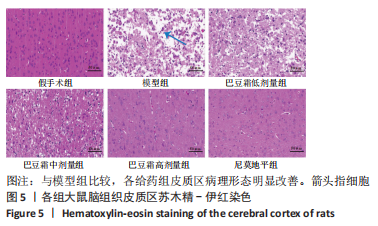
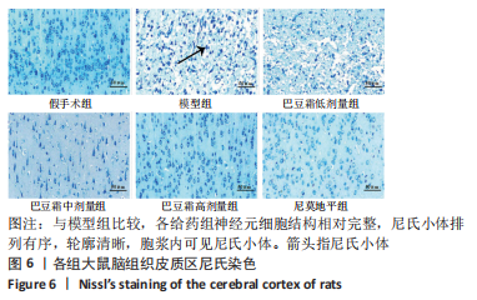
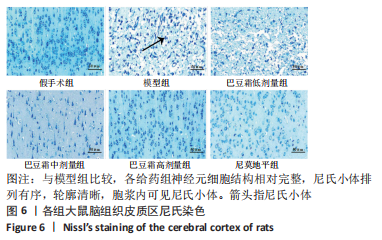
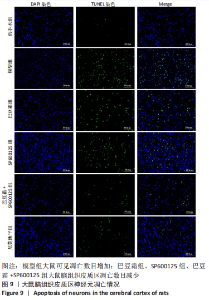
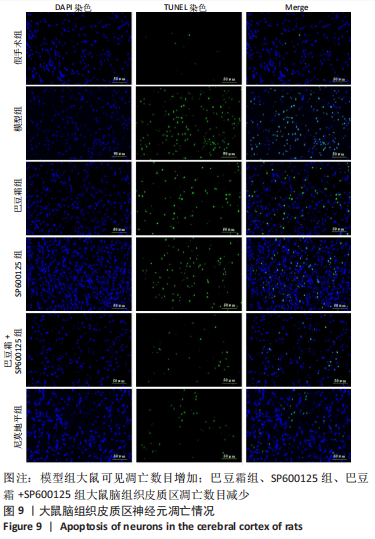
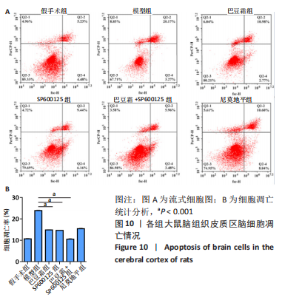
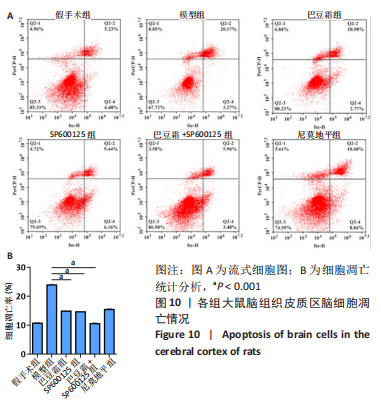
[1] 王娜琳,左艳丽,李占涛,等.失荅剌知丸及其拆方对局灶性脑缺血再灌注大鼠海马区ERK1/2通路的影响[J].湖南中医杂志,2020,36(11):172-178.
[2] ZENG M, ZHOU H, HE Y, et al. Danhong injection alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by improving intracellular energy metabolism coupling in the ischemic penumbra.Biomed Pharmacother.2021;140: 111771.
[3] CAO X, WANG Y, GAO L.CHRFAM7A Overexpression Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting Microglia Pyroptosis Mediated by the NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway.Inflammation.2021; 44: 1023-1034.
[4] 王安琪,李艳楠,左文博,等.巴豆苷药理作用及其机制的研究[J].农业灾害研究,2021,11(3):1-2.
[5] 胡静,秦贝贝,马琳,等.巴豆化学成分、药理作用及其质量标志物预测分析[J].中草药, 2021,52(21):6743-6754.
[6] 李宏伟,孔繁斌,丁婷婷,等.巴豆治疗急性卒中的机制初探[J].河北中医, 2017, 39(11):1735-1739.
[7] 尚津锋,李倩楠,崔一然,等.基于网络药理学探讨巴豆制霜的作用机制[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2022,22(8):923-930.
[8] LINDBLOM RPF, TOVEDAL T, NORLIN B, et al. Mechanical Reperfusion Following Prolonged Global Cerebral Ischemia Attenuates Brain Injury.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021;14:338-347.
[9] 马玉玮,潘佐泱,丁义东,等.巴豆霜对局灶性脑缺血再灌注大鼠海马区ERK5通路的影响[J].中国民族民间医药,2022,31(9):23-29.
[10] 王娜琳. 失荅剌知丸及其拆方对局灶性脑缺血再灌注大鼠海马区ERK1/2、ERK5通路的影响[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2020.
[11] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[12] Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, et al. Intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after stroke in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(11):2682-2688.
[13] 刘春刚,冼文川,罗宋宝,等.氢溴酸樟柳碱注射液治疗急性缺血性脑卒中的效果及安全性[J].广西医学,2019,41(14):1742-1742,1748.
[14] 雷雪,周戈耀,王灵芝,等.脑卒中康复疗法的经济学评价研究进展[J].按摩与康复医学, 2021,12(17):65-76.
[15] 《中国脑卒中防治报告》编写组.《中国脑卒中防治报告2019》概要[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2020,17(5):272-281.
[16] GOLTS E, ONAITIS M.Commentary: Ischemia reperfusion-Looking ahead.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161(2):e124-e125.
[17] Riverol M, Becker JT, López OL, et al. Relationship between Systemic and Cerebral Vascular Disease and Brain Structure Integrity in Normal Elderly Individuals. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;44(1):319-328.
[18] 薛婧. 鞘磷脂合成酶2缺乏对小鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后炎症反应的影响及其机制研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2017.
[19] AMINI F, ZAYERI ZD, NEJAD KH. Potential Mechanism and Pathways in Cerebral Ischemia- Reperfusion Injury: Therapeutic GLANCE. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2019;28(4):88-94.
[20] LU Q, RAU TF, HARRIS V, et al. Increased p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling is involved in the oxidative stress associated with oxygen and glucose deprivation in neonatal hippocampal slice cultures. Eur J Neurosci. 2011;34(7):1093-1101.
[21] ZHENG M, CHEN R, CHEN H, et al. Netrin-1 Promotes Synaptic Formation and Axonal Regeneration via JNK1/c-Jun Pathway after the Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:13.
[22] MOMENABADI S, VAFAEI AA, ZAHEDI KHORASANI M, et al. Pre-Ischemic Oxytocin Treatment Alleviated Neuronal Injury via Suppressing NF-κB, MMP-9, and Apoptosis Regulator Proteins in A Mice Model of Stroke. Cell J. 2022;24(6):337-345.
[23] HUANG LY, SONG JX, CAI H, et al. Healthy Serum-Derived Exosomes Improve Neurological Outcomes and Protect Blood-Brain Barrier by Inhibiting Endothelial Cell Apoptosis and Reversing Autophagy-Mediated Tight Junction Protein Reduction in Rat Stroke Model. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:841544.
[24] ZHAI Y, LIU B, WU L, et al. Pachymic acid prevents neuronal cell damage induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation via miR‑155/NRF2/HO‑1 axis. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2022;82(2):197-206.
[25] YAN Y, LIU Y, YANG Y, et al. Carnosol suppresses microglia cell inflammation and apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44:656-662.
[26] WANG PC, WANG SX, YAN XL, et al. Combination of paeoniflorin and calycosin-7-glucoside alleviates ischaemic stroke injury via the PI3K/AKT signalling pathway. Pharm Biol. 2022;60:1469-1477.
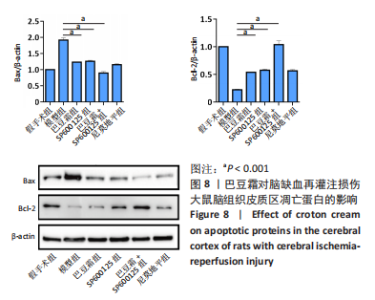
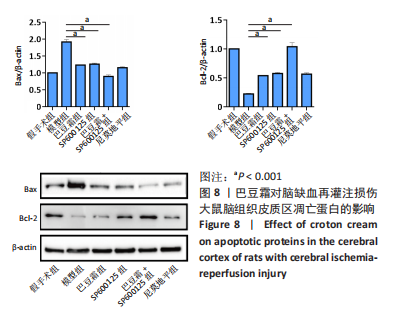
[27] 张萌,张志勇,张蕊,等.白藜芦醇后处理对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤海马CA1区Bax、Bcl-2的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2020,20(19):3644-3648.
[28] ZHANG H, TANG W, WANG S, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Inhibits Platelet Adhesion and Inflammatory Response in Vascular Endothelial Cells by Inhibiting P38 MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Inflammation. 2020; 43(1):286-297.
[29] KOVALSKA M, KOVALSKA L, PAVLIKOVA M, et al. Intracellular signaling MAPK pathway after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res. 2012;37(7):1568-1577.
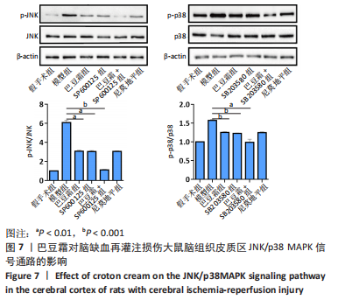
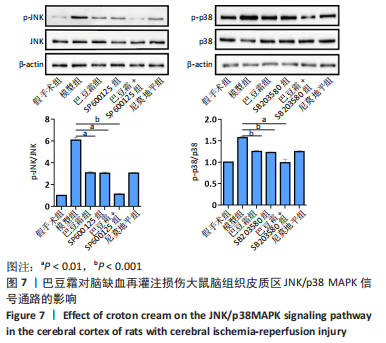
[30] 徐祖清,王诗洋,王枭,等.橄榄苦苷对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠神经元凋亡及JNK/p38 MAPK信号通路的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2021, 41(2):334-338.
[31] Zhen Y, Ding C, Sun J, et al. Activation of the calcium-sensing receptor promotes apoptosis by modulating the JNK/p38 MAPK pathway in focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(2):911-921.
[32] 李明航,田晓翠,安瑞娣,等.全反式维甲酸通过作用于JNK/P38 MAPK信号通路减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注引起的血脑屏障损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(1):112-118.
[33] 郑关毅,陈晓春,杜建,等.没食子酸丙酯对脑缺血大鼠神经元SAPK/JNK及p38 MAPK激活的抑制作用[J].药学学报,2006,41(6):548-554.
|