Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2120-2125.doi: 10.12307/2024.153
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of adipose tissue and its derivative on wound repair and vascularization
Zhao Lixin1, Tang Qingxi2, Zhang Kezhong1
- 1The Central Hospital of Jiamusi City, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-29Accepted:2023-05-15Online:2024-05-08Published:2023-08-29 -
Contact:Zhao Lixin, Master, Associate chief physician, The Central Hospital of Jiamusi City, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Zhao Lixin, Master, Associate chief physician, The Central Hospital of Jiamusi City, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Lixin, Tang Qingxi, Zhang Kezhong. Influence of adipose tissue and its derivative on wound repair and vascularization[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2120-2125.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
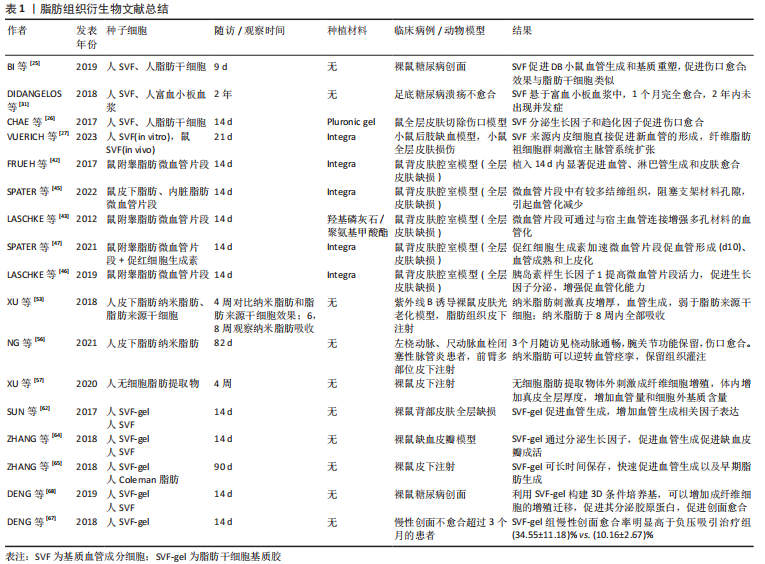
2.1 软组织损伤修复中的血管再生 软组织创伤愈合过程大致可分为3个相互重叠的阶段:炎症反应阶段、增生纤维化阶段、重塑成熟阶段[2,5-6]。 伤口修复的第一个阶段,即炎症反应阶段,在组织损伤之后立即开始,涉及凝血及炎症过程。血小板聚集形成凝血块以闭合伤口,同时血管收缩发挥止血作用。血小板激活并分泌细胞因子,募集免疫细胞聚集到损伤部位,发挥免疫功能,清除死亡或失去活力的组织[2]。在伤口修复的第二阶段,各种细胞增殖并迁移,新组织形成,包括表皮细胞再生、血管再生、细胞外基质的形成等[5]。在伤口修复的最后阶段,出现胶原蛋白逐渐分解、合成以及重塑等,伤口完全愈合或形成瘢痕组织[5]。 在组织增殖阶段,新生血管的形成发挥至关重要的作用。正常组织中,微血管处于稳定状态,将营养和氧气输送到组织中,并带走代谢废物和CO2。组织损伤后,局部微血管被破坏,引起局部液体积聚、形成缺氧环境,新生毛细血管迅速向伤口处生长,形成大量杂乱的新生血管网络,具有许多死端血管,通常此时的血管量远远大于正常组织的血管量,可达两三倍甚至10倍以上[7]。伤口修复中的血管生成受多个因素的影响,包括局部缺氧条件和细胞因子的分泌等[8]。多种生长因子可激活血管生成,如血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)、血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β1、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α等[2]。缺氧诱导因子1α通过多种机制促进血管生成,包括调节血管生成相关基因和促血管生成因子,如血管生成素2、干细胞因子和VEGF-A等[9]。在血管密度达到顶峰后,抗血管生成因子的表达开始增加,如Sprouty2和色素上皮原因子,可诱导组织血管恢复到正常数量[8,10-11]。血小板衍生生长因子BB可以募集并促进周细胞分化,可以促进血管网络的稳定。同时,血管生成素1、血管生成素2以及Tie2在调节血管生成和成熟起到复杂的作用[12]。在一些慢性愈合或不愈合伤口中,血管生成的减少更明显,例如:糖尿病足溃疡不愈合中分离出的渗出物可检测出更多抗血管生成蛋白[8];慢性静脉溃疡中,VEGF-A的水解也有所增加[13]。 尽管伤口的血管化被认为有着重要的作用,但过度未成熟的血管化似乎会对组织愈合产生不利的影响。一些研究表明,当血管生成减少时,皮肤伤口仍可以完全闭合,且瘢痕增生更少[7,14-15]。几种皮肤伤口可以快速愈合且没有或很少的瘢痕增生,如子宫内胎儿的伤口以及口腔黏膜的伤口,这些伤口能在毛细血管减少的情况下快速愈合,得益于毛细血管的结构和功能。许多软组织伤口中快速形成的毛细血管大多功能不高,主要表现为血管通透性较低,不能形成有效的血液灌注[10,16]。 在某些相对较薄的皮肤缺损(包括含真皮层的损伤)中,移植组织的血管化通常是多余的,因为受损部位可以直接快速形成血管达到损伤部位提供营养并维持移植物存活[2,17]。然而,要修复具有更厚更复杂的结构将需要一个成熟血管网络来维持细胞存活[18]。因此,在软组织愈合过程中,快速建立足够的有效的血运至关重要,而快速有效的组织愈合并不意味着大量的血管生成,而是需要适当数量的成熟有功能的毛细血管。如果能加速成熟血管形成,组织将愈合更快,且形成更少的瘢痕,这意味着愈合皮肤的弹性及韧性更强。 2.2 脂肪组织及其衍生成分在血管化中的作用 目前已有许多通过血管化加速软组织修复的方法,从基因治疗、蛋白治疗到(干)细胞治疗,从单纯使用生物细胞成分到添加组织工程材料治疗,移植物的体外预血管化,药物治疗,物理刺激治疗如机械刺激和缺氧诱导刺激等。虽然方法多样,但由于制备方法不一,治疗效果不稳定,以及一些细胞治疗的市场监管应用方面的原因,很多治疗手段并不能直接进行临床转化,仍停留在实验室阶段。此外,涉及到复杂的细胞操作及耗时且昂贵的治疗程序只能由少数高度专业化的临床中心来实现[3]。 2.2.1 脂肪组织及其衍生成分 在再生医学领域中,脂肪组织是人体中最大最重要的再生细胞库[19]。将脂肪组织进行不同的方法处理,可以获得有着不同用途的脂肪成分。从脂肪组织经过特殊处理获得的多种细胞成分混合物,一般称为间质血管成分(stromal vascular fraction,SVF)细胞。脂肪组织的处理主要有2种形式:脂肪组织中加入胶原酶分解可以获得以细胞为最小单元的间质血管成分,为cSVF;以及通过纯机械破碎手段获得的以组织为最小单元的间质血管成分,为tSVF[20]。 cSVF中包含多种细胞成分,如脂肪干细胞,各类前体细胞如血管前体细胞、血管内皮前体细胞;以及各种成熟细胞如成纤维细胞、血管内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞、周细胞以及巨噬细胞等[21-22]。将cSVF进一步过滤纯化提取,可获得脂肪干细胞或脂肪来源微血管片段(adipose tissue-derived microvascular fragments,ad-MVF)等。 tSVF现普遍指通过物理方式获得的脂肪混合物,其中细胞间、细胞与基质之间的连接并未完全打破。在组织再生的应用中,可以提供完整的结构成分,即间质细胞和细胞外基质,这对细胞的存活和功能有积极影响[3,20]。与cSVF类似,通过改变纯机械处理过程中的破碎、离心等步骤的时间与次数,可以获得microfat、纳米脂肪或脂肪来源干细胞基质胶(stromal vascular fraction gel,SVF-gel)等组织。考虑到应用胶原酶的安全性、市场监管条件以及制备时间效率,纯机械分离得到的tSVF更适合在临床中应用。 2.2.2 SVF细胞 SVF细胞是取自脂肪组织的多种细胞群的总称,既可以通过胶原酶消化得到(cSVF),也可以通过单纯机械分离方式取得(tSVF)。目前普遍认为在没有强调脂肪成分的类型时,SVF被默认为是通过胶原酶充分消化得到的细胞产物。一般处理过程如下:将吸脂或其他方法得到的脂肪与胶原酶或胰蛋白酶混合,在37 ℃下连续摇晃约60 min,促进脂肪组织与酶充分接触并消化。随后加入完全培养基终止消化,振荡混匀后过滤、离心,弃去上层脂肪,最终获得SVF混悬液。从得到脂肪抽吸液到获得可以使用的SVF整个过程不超过4 h,在手术前获得脂肪,手术进行的同时进行SVF制备工作,一期手术可直接植入。SVF中包含多种细胞成分,如脂肪干细胞,各类前体细胞如血管前体细胞、血管内皮前体细胞;以及各种成熟细胞如成纤维细胞、平滑肌细胞、血管内皮细胞、巨噬细胞以及周细胞等[21-23]。因为含有多种细胞群,使得SVF只能用于自身组织[22]。幸运的是,人体脂肪存量相对丰富,可以通过微创抽脂的方法从适合的部位大量获得脂肪组织。也正因有除脂肪干细胞以外的细胞存在,SVF可以更好地发挥细胞间的沟通作用,从而提高其修复能力。 SVF的促进血管再生能力已被证明优于脂肪干细胞[3,24]。研究证明SVF可有效促进血管新生、减少组织缺血缺氧、促进组织再生,已被广泛应用于各种类型的组织再生修复中,如软组织创伤[25-28]、瘢痕修复[29]、难治性溃疡[30-32]、骨软骨缺损等[33-34]。SVF的促血管再生能力与其中富含大量的细胞因子和生长因子有关,它们可以通过旁分泌效应刺激血管生成[3,35-36]。此外,SVF中的各类细胞在体内能够自发地自组装成完整、有功能的血管网络[27,37-38]。因此,cSVF是一种有吸引力的、易于制备的分离物,可用于再生医学中的各种应用,如创面愈合和骨修复等[33-34,39]。 2.2.3 ad-MVF 通过缩短胶原酶暴露时间(8-10 min),可以避免血管细胞的充分分离,保留了组织的微血管形态,经过过滤、搅拌、离心等处理,可获得ad-MVF[23,40]。ad-MVF中含有包括动脉、静脉以及毛细血管片段,长度在40-50 μm之间[41],以及一些淋巴管片段及内皮细胞等[42]。在修复过程中,与脂肪干细胞和SVF不同,微血管片段(microvascular fragment,MVF)不需要重新募集内皮细胞形成血管形态,而是通过内部连接吻合直接将现有的微血管进行连接重组。同时,形成的微血管通过向外链接吻合与移植部位周围组织结合[23,43],省略了细胞到血管的组装过程,利用现有血管进行连接,这无疑加速了血管再生的过程。FRUEH等[42]的研究表明,在修复软组织的过程中,MVF可以在3-5 d内形成有功能的血管。不仅如此,除了血管片段,MVF中还含有各类成体干细胞、内皮细胞和细胞因子等,为血管片段提供了必须的支持细胞和适宜血管再生的微环境,进一步提高了血管生成和再生的潜力。相应地,血管碎片为干细胞提供了合适的微环境,从而更好地保留了干细胞的存活、自我分化、增殖、动员和分化能力[41-42]。 有关MVF的文献目前均从小鼠体内提取,如小鼠附睾脂肪[42,44]、腹股沟脂肪[45]、皮下脂肪或内脏脂肪等[45],尚无人MVF提取和实验的报道,亦无临床应用的报道。MVF可用于血管再生、淋巴再生以及全层皮肤修复等[42],将来可能用于血管化组织替代,淋巴水肿治疗和促进生物材料整合等[41]。 MVF的血管再生能力可以通过加入各类其他细胞及生物成分而进一步增强。例如,LASCHKE等[46]将胰岛素样生长因子1与MVF共培养后移植,发现胰岛素样生长因子1可以在不影响MVF细胞组成的情况下明显提高VEGF/VEGFR2和基质金属蛋白酶2的表达,而且适当浓度的胰岛素样生长因子1还可以保护MVF中内皮细胞和周细胞的凋亡。进一步地,该团队在尝试移植MVF后全身注射低剂量的促红细胞生成素,发现可以达到同样的血管化效果,同时避免了长时间的体外预培养过程[47]。除了血管再生能力,MVF还可以减少移植干细胞的凋亡和衰老。XU等[48]将ad-MVFs和牙髓干细胞联合移植用于促进牙髓再生,发现ad-MVFs在体内或体外均能有效抑制移植牙髓干细胞的凋亡和衰老,促进移植血管网络的形成。 MVF中含有多种细胞和组织成分,这不仅加速了血管移植部位的血管再生过程,还为局部细胞提供合适的微环境,减少其衰老和凋亡。除此之外,MVF还拥有脂肪组织的共同优势,即成分来自患者自身,且取得方法简便。在未来的研究和应用中,MVF的应用范围会逐渐扩大,包括各类组织修复、各类实体器官移植以及一些疾病的治疗等方面。虽然针对不同治疗目的可能有着不同的制备方法,但制定一个统一的制备标准仍然是必须的。与SVF类似,MVF也将发展出完全自动化的术中制备器械,方便临床使用。 2.2.4 纳米脂肪 起初,用于脂肪移植的填充物称为微脂肪(microfat),但因其颗粒直径较大,无法用于精细的移植填充操作。直到2013年TONNARD 等[49]将抽脂获得的脂肪组织进行机械乳化(将脂肪在2个由鲁尔接头连接注射器中来回移动)和过滤,获得了液体状态的脂肪组织,称为纳米脂肪。经过上述机械操作,纳米脂肪中脂肪细胞被破碎,而容易阻塞细针头的结缔组织残余被过滤,从而获得了易经细针(27G)注射的脂肪组织,并直接在临床治疗中验证了其脂肪填充和皮肤年轻化的治疗效果[49]。纳米脂肪可通过纯物理制备方法取得,属于tSVF中的一种[3,50]。因其制备简单,取材来源于患者自身,制备过程中不需要加入胶原酶等其他生物制剂且无需进行额外的培养扩增步骤,很快便用于临床试验及治疗中,并在血管再生、皮肤年轻化、瘢痕修复、皮瓣移植以及软组织损伤修复中取得令人印象深刻的成就[13,49-58]。值得一提的是,由于其颗粒直径(400-600 μm)远大于纳米级计量单位,因此用“nano”对其修饰并不准确[19,51]。此外,纳米脂肪中没有有效的脂肪细胞,所以用“fat”对其命名亦不准确。然而,各研究机构学者已习惯使用nanofat一词,进一步基于其制备方法衍生出其他脂肪成分,如nanofat2.0、vivo nanofat等[59-60]。 对于纳米脂肪制备过程中基质细胞的生存能力改变,不同实验室得出的结果有一定差异[61]。一些研究者认为纳米脂肪乳化过程中不会显著影响基质细胞的生存能力;其他人认为,基质细胞的生存能力减半,制备率是cSVF的10-12倍[13,61]。造成结果差异的原因主要是制备方案的差异以及检测方法的不同,纳米脂肪的制备效率很大程度上取决于术者机械乳化操作过程中的力度和时间等[61],因此建立一套标准化的制备流程将有助于治疗和研究的标准化。 纳米脂肪中所包含的组织成分与SVF类似,包括各类细胞,如脂肪干细胞、血管内皮细胞、周细胞等;各类细胞因子及生长因子如骨形态发生蛋白2、白细胞介素4、白细胞介素8、VEGF、血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子β1以及MVF等[13,51,53]。纳米脂肪可以在不产生任何可见瘢痕的情况下促进新血管生成,并在整形手术中为乳房、面部年轻化和面部填充提供了良好的结果[51]。纳米脂肪的成血管功能不仅体现在细胞成分上,与MVF相似,未经过胶原酶分解的纳米脂肪中也有未完全分解的血管片段。WEINZIERL等[55]的研究证明了这一点:在纳米脂肪移植后第6天就可以检测到nanofat来源的微血管,作者推测在短时间内形成的血管不应是干细胞来源,而是MVP。 虽然纳米脂肪是细胞、血管段和细胞外基质化合物的异质混合物,但它仍然表现出液体稠度和小颗粒大小。因此,它不仅可以用作皮下填充物,还可以与生物多孔材料结合。纳米脂肪中的细胞及血管成分会加速生物材料的融合;相反地,为纳米脂肪提供不同的生物材料可以向不同方向发挥纳米脂肪的细胞异质性特点,以在不同条件下加速和改善其组织修复能力[3,50,55]。 2.2.5 脂肪干细胞来源基质胶 由纳米脂肪开启的纯机械制备脂肪组织治疗在整形外科和再生医学中取得巨大进展。但纳米脂肪为液体成分,填充能力较差,且细胞密度小,在组织再生应用中能力有限。如果通过物理浓缩的手段提高细胞密度,可减少或消除体外扩增步骤,从而更快地得到目标产品。SVF-gel则达到了这一目的,其由南方医科大学鲁峰教授团队开发,将脂肪组织离心、分离、机械乳化等,可得到去除了油脂的SVF细胞和细胞外基质的浓缩物,称为SVF-gel[62-63]。 与其他脂肪组织衍生物类似,SVF-gel也有强大的血管再生和软组织修复功能,且远高于SVF[62,64-66];SUN等[62]的实验表明,移植了SVF-gel的伤口中VEGF和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子表达量在移植后14 d内全程高于SVF移植组。SVF-gel移植后会引起局部强烈炎症反应,大量巨噬细胞浸润,分泌大量细胞因子[62,65];然而在伤口愈合后期,炎症迅速消退,这可能与SVF-gel中含有大量脂肪干细胞从而发挥的免疫调节作用有关[62]。此外,SVF-gel中也有一些血管碎片被保留下来,移植后互相连接并最后与宿主血管连接,发挥血管再生的作用[65]。由于细胞外基质的大量保留,使得SVF细胞在移植后能长期大量保存,并持续发挥作用[65]。SVF-gel在一些慢性创面中也有着良好的治疗前景。DENG等[67]将SVF-gel与伤口密闭负压治疗慢性创面进行对比,结果表明SVF-gel的创面治疗效果明显优于常规治疗手段,且创面血管化明显增强。必须指出的是,该临床调查中常规治疗组的初始创面面积(23.36±12.54) cm2高于SVF-gel组(8.79±5.65) cm2,这可能对治疗效果和实验结果产生影响,但作者并未对此进行比较和说明。ZHANG等[64]评估了SVF-gel对小鼠缺血皮瓣的治疗效果,结果显示SVF-gel组皮瓣缺血区最小,且VEGF和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子表达比对照组多了约3倍。DENG等[68]对SVF-gel与SVF进行了横向比较,结果显示在糖尿病慢性创面治疗方面SVF-gel优于SVF。 从相同体积的脂肪组织中获得高浓度的脂肪产物意味着制备率的降低。与纳米脂肪相比,制备相同体积的SVF-gel需要大量的脂肪组织。一项最新研究表明,纳米脂肪与SVF-gel的制备率分别为(82.82±3.8)%及(20.15±2.92)%,但SVF-gel中的活性细胞量明显大于纳米脂肪,前者约4.56×105 cells/mL,后者约4.12×104 cells/mL[69]。SVF-gel具有高细胞浓度的特点,组织呈凝胶状态,填充注射效果优于纳米脂肪。在各种横向对比实验中,SVF-gel显示出更强大的血管再生和促进组织修复的功能,但相关文献数量仍相对较少,产品未在研究者之间普及,研究通常在有限的研究团队中展开。需要更多的研究来完善SVF-gel的制备和应用策略,设计标准化制备流程或器械,基于其临床应用便捷、治疗效果明显,SVF-gel治疗的普及似乎只是时间问题。 脂肪组织衍生物文献总结见表1。"
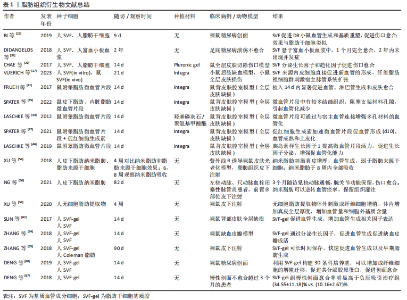
| [1] BAIGUERA S, RIBATTI D. Endothelialization approaches for viable engineered tissues. Angiogenesis. 2013;16(1):1-14. [2] MASSON-MEYERS DS, TAYEBI L. Vascularization strategies in tissue engineering approaches for soft tissue repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(9):747-762. [3] LASCHKE MW, MENGER MD. The simpler, the better: tissue vascularization using the body’s own resources. Trends Biotechnol. 2022;40(3):281-290. [4] ZUK PA, ZHU M, MIZUNO H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [5] GURTNER GC, WERNER S, BARRANDON Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321. [6] FINNSON KW, MCLEAN S, DI GUGLIELMO GM, et al.Dynamics of Transforming Growth Factor Beta Signaling in Wound Healing and Scarring. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013;2(5):195-214. [7] DIPIETRO LA. Angiogenesis and wound repair: when enough is enough. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(5):979-984. [8] VEITH AP, HENDERSON K, SPENCER A, et al. Therapeutic strategies for enhancing angiogenesis in wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019;146: 97-125. [9] AHLUWALIA A, TARNAWSKI AS. Critical role of hypoxia sensor--HIF-1alpha in VEGF gene activation. Implications for angiogenesis and tissue injury healing. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(1):90-97. [10] WIETECHA MS, KROL MJ, MICHALCZYK ER, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor as a multifunctional regulator of wound healing. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309(5):H812-H826. [11] WIETECHA MS, CHEN L, RANZER MJ, et al. Sprouty2 downregulates angiogenesis during mouse skin wound healing. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300(2):H459-H467. [12] HAKANPAA L, SIPILA T, LEPPANEN VM, et al. Endothelial destabilization by angiopoietin-2 via integrin beta1 activation. Nat Commun. 2015;6:5962. [13] SESE B, SANMARTIN JM, ORTEGA B, et al. Nanofat Cell Aggregates: A Nearly Constitutive Stromal Cell Inoculum for Regenerative Site-Specific Therapies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(5):1079-1088. [14] LANGE-ASSCHENFELDT B, VELASCO P, STREIT M, et al. The angiogenesis inhibitor vasostatin does not impair wound healing at tumor-inhibiting doses. J Invest Dermatol. 2001;117(5):1036-1041. [15] WILGUS TA, FERREIRA AM, OBERYSZYN TM, et al. Regulation of scar formation by vascular endothelial growth factor. Lab Invest. 2008;88(6): 579-590. [16] ERBA P, OGAWA R, ACKERMANN M, et al. Angiogenesis in wounds treated by microdeformational wound therapy. Ann Surg. 2011;253(2):402-409. [17] DATTA P, AYAN B, OZBOLAT IT. Bioprinting for vascular and vascularized tissue biofabrication. Acta Biomater. 2017;51:1-20. [18] MIN S, KO IK, YOO JJ. State-of-the-Art Strategies for the Vascularization of Three-Dimensional Engineered Organs. Vasc Specialist Int. 2019;35(2):77-89. [19] COPCU HE, OZTAN S. Not Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) or Nanofat, but Total Stromal-Cells (TOST): A New Definition. Systemic Review of Mechanical Stromal-Cell Extraction Techniques. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(1):25-36. [20] ALEXANDER RW. Biocellular Regenerative Medicine: Use of Adipose-Derived Stem/Stromal Cells and It’s Native Bioactive Matrix. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2016;27(4):871-891. [21] COHEN SR, HEWETT S, ROSS L, et al. Regenerative Cells For Facial Surgery: Biofilling and Biocontouring. Aesthet Surg J. 2017;37(suppl_3):S16-S32. [22] BORA P, MAJUMDAR AS. Adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction in regenerative medicine: a brief review on biology and translation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):145. [23] FRUEH FS, MENGER MD, LINDENBLATT N, et al. Current and emerging vascularization strategies in skin tissue engineering. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017;37(5):613-625. [24] SUN Y, CHEN S, ZHANG X, et al. Significance of Cellular Cross-Talk in Stromal Vascular Fraction of Adipose Tissue in Neovascularization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(6):1034-1044. [25] BI H, LI H, ZHANG C, et al. Stromal vascular fraction promotes migration of fibroblasts and angiogenesis through regulation of extracellular matrix in the skin wound healing process. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):302. [26] CHAE DS, HAN S, SON M, et al. Stromal vascular fraction shows robust wound healing through high chemotactic and epithelialization property. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(4):543-554. [27] VUERICH R, GROPPA E, VODRET S, et al. Ischemic wound revascularization by the stromal vascular fraction relies on host-donor hybrid vessels. NPJ Regen Med. 2023;8(1):8. [28] 朱琳,李薇薇,刘志凯.人血管基质片段联合脂肪干细胞促进裸鼠放射性皮肤损伤的愈合[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版),2017,55(9):66-72. [29] STACHURA A, PASKAL W, PAWLIK W, et al. The Use of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) in Skin Scar Treatment-A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. J Clin Med. 2021;10(16):3637. [30] ZHAO X, GUO J, ZHANG F, et al. Therapeutic application of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction in diabetic foot. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):394. [31] DIDANGELOS T, KOLIAKOS G, KOUZI K, et al. Accelerated healing of a diabetic foot ulcer using autologous stromal vascular fraction suspended in platelet-rich plasma. Regen Med. 2018;13(3):277-281. [32] TAN SS, YEO XY, LIANG ZC, et al. Stromal vascular fraction promotes fibroblast migration and cellular viability in a hyperglycemic microenvironment through up-regulation of wound healing cytokines. Exp Mol Pathol. 2018;104(3):250-255. [33] ROATO I, BELISARIO DC, COMPAGNO M, et al. Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction/Xenohybrid Bone Scaffold: An Alternative Source for Bone Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:4126379. [34] KAMENAGA T, KURODA Y, NAGAI K, et al. Cryopreserved human adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction maintains fracture healing potential via angiogenesis and osteogenesis in an immunodeficient rat model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):110. [35] MAZO M, CEMBORAIN A, GAVIRA JJ, et al. Adipose stromal vascular fraction improves cardiac function in chronic myocardial infarction through differentiation and paracrine activity. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(5):1023-1037. [36] 袁艺, 鲁峰, 高建华. 血管基质片段辅助游离脂肪移植早期移植物组织学变化及相关实验研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(4):449-453. [37] RAMAKRISHNAN VM, BOYD NL. The Adipose Stromal Vascular Fraction as a Complex Cellular Source for Tissue Engineering Applications. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;24(4):289-299. [38] 鲁峰, 常强, 詹炜卿, 等. 血管基质片段促进体内组织工程室血管和组织新生的初步研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(5):644-648. [39] FRANCOIS P, GIRAUDO L, VERAN J, et al. Development and Validation of a Fully GMP-Compliant Process for Manufacturing Stromal Vascular Fraction: A Cost-Effective Alternative to Automated Methods. Cells. 2020;9(10):2158. [40] FRUEH FS, SPATER T, SCHEUER C, et al. Isolation of Murine Adipose Tissue-derived Microvascular Fragments as Vascularization Units for Tissue Engineering. J Vis Exp. 2017;(122):55721. [41] LASCHKE MW, SPATER T, MENGER MD. Microvascular Fragments: More Than Just Natural Vascularization Units. Trends Biotechnol. 2021;39(1):24-33. [42] FRUEH FS, SPATER T, LINDENBLATT N, et al. Adipose Tissue-Derived Microvascular Fragments Improve Vascularization, Lymphangiogenesis, and Integration of Dermal Skin Substitutes. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(1):217-227. [43] LASCHKE MW, KLEER S, SCHEUER C, et al. Vascularisation of porous scaffolds is improved by incorporation of adipose tissue-derived microvascular fragments. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;24:266-277. [44] ORTH M, ALTMEYER MAB, SCHEUER C, et al. Effects of locally applied adipose tissue-derived microvascular fragments by thermoresponsive hydrogel on bone healing. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:201-211. [45] SPATER T, MARSCHALL JE, BRUCKER LK, et al. Vascularization of Microvascular Fragment Isolates from Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue of Mice. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022;19(1):161-175. [46] LASCHKE MW, KONTAXI E, SCHEUER C, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 stimulates the angiogenic activity of adipose tissue-derived microvascular fragments. J Tissue Eng. 2019;10:2041731419879837. [47] SPATER T, WORRINGER DM, MENGER MM, et al. Systemic low-dose erythropoietin administration improves the vascularization of collagen-glycosaminoglycan matrices seeded with adipose tissue-derived microvascular fragments. J Tissue Eng. 2021;12:20417314211000304. [48] XU X, LIANG C, GAO X, et al. Adipose Tissue-derived Microvascular Fragments as Vascularization Units for Dental Pulp Regeneration. J Endod. 2021;47(7):1092-1100. [49] TONNARD P, VERPAELE A, PEETERS G, et al. Nanofat grafting: basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132(4):1017-1026. [50] KAMAT P, FRUEH FS, MCLUCKIE M, et al. Adipose tissue and the vascularization of biomaterials: Stem cells, microvascular fragments and nanofat-a review. Cytotherapy. 2020;22(8):400-411. [51] JEYARAMAN M, MUTHU S, SHARMA S, et al. Nanofat: A therapeutic paradigm in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(11):1733-1746. [52] TONNARD P, VERPAELE A, CARVAS M. Fat Grafting for Facial Rejuvenation with Nanofat Grafts. Clin Plast Surg. 2020;47(1):53-62. [53] XU P, YU Q, HUANG H, et al. Nanofat Increases Dermis Thickness and Neovascularization in Photoaged Nude Mouse Skin. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2018;42(2):343-351. [54] DING P, LU E, LI G, et al. Research progress on preparation, mechanism, and clinical application of nanofat. J Burn Care Res. 2022;43(5):1140-1144. [55] WEINZIERL A, HARDER Y, SCHMAUSS D, et al. Boosting Tissue Vascularization: Nanofat as a Potential Source of Functional Microvessel Segments. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:820835. [56] NG KLB, HSIEH MW, LIN YN, et al. Application of nanofat grafting to rescue a severe ischaemic hand with thromboangiitis obliterans: A case report about promising salvage procedure. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(42):e27577. [57] XU Y, DENG M, CAI Y, et al. Cell-Free Fat Extract Increases Dermal Thickness by Enhancing Angiogenesis and Extracellular Matrix Production in Nude Mice. Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40(8):904-913. [58] RAGEH MA, EL-KHALAWANY M, IBRAHIM SMA. Autologous nanofat injection in treatment of scars: A clinico-histopathological study. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;20(10):3198-3204. [59] LO FURNO D, TAMBURINO S, MANNINO G, et al. Nanofat 2.0: experimental evidence for a fat grafting rich in mesenchymal stem cells. Physiol Res. 2017;66(4):663-671. [60] BI HS, ZHANG C, NIE FF, et al. Basic and Clinical Evidence of an Alternative Method to Produce Vivo Nanofat. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(5):588-593. [61] TRIVISONNO A, ALEXANDER RW, BALDARI S, et al. Intraoperative Strategies for Minimal Manipulation of Autologous Adipose Tissue for Cell- and Tissue-Based Therapies: Concise Review. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(12):1265-1271. [62] SUN M, HE Y, ZHOU T, et al. Adipose Extracellular Matrix/Stromal Vascular Fraction Gel Secretes Angiogenic Factors and Enhances Skin Wound Healing in a Murine Model. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:3105780. [63] YAO Y, DONG Z, LIAO Y, et al. Adipose Extracellular Matrix/Stromal Vascular Fraction Gel: A Novel Adipose Tissue-Derived Injectable for Stem Cell Therapy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(4):867-879. [64] ZHANG P, FENG J, LIAO Y, et al. Ischemic flap survival improvement by composition-selective fat grafting with novel adipose tissue derived product - stromal vascular fraction gel. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495(3):2249-2256. [65] ZHANG Y, CAI J, ZHOU T, et al. Improved Long-Term Volume Retention of Stromal Vascular Fraction Gel Grafting with Enhanced Angiogenesis and Adipogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;141(5):676e-686e. [66] DENG C, HE Y, FENG J, et al. Extracellular matrix/stromal vascular fraction gel conditioned medium accelerates wound healing in a murine model. Wound Repair Regen. 2017;25(6):923-932. [67] DENG C, WANG L, FENG J, et al. Treatment of human chronic wounds with autologous extracellular matrix/stromal vascular fraction gel: A STROBE-compliant study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(32):e11667. [68] DENG C, HE Y, FENG J, et al. Conditioned medium from 3D culture system of stromal vascular fraction cells accelerates wound healing in diabetic rats. Regen Med. 2019;14(10):925-937. [69] YANG Z, JIN S, HE Y, et al. Comparison of Microfat, Nanofat, and Extracellular Matrix/Stromal Vascular Fraction Gel for Skin Rejuvenation: Basic Research and Clinical Applications. Aesthet Surg J. 2021;41(11):NP1557-NP1570. |
| [1] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [2] | Zhang Ya, Mu Qiuju, Wang Zilin, Liu Hongjie, Zhu Lili. Hydrogel loaded with platelet-rich plasma promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 690-696. |
| [3] | Shen Ziqing, Xia Tian, Shan Yibo, Zhu Ruijun, Wan Haoxin, Ding Hao, Pan Shu, Zhao Jun. Vascularized tracheal substitutes constructed by exosome-load hydrogel-modified 3D printed scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 697-705. |
| [4] | Dong Hongfei, Huang Xi, Li Xianhui, Zhang Yanbiao, Wang Xuyang, Wang Bing, Sun Hongyu. Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in promoting acute skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2047-2053. |
| [5] | Bei Ying, Li Wenjing, Li Meiyun, Su Meng, Zhang Jin, Huang Yu, Zhu Yanzhao, Li Jiali, Wu Yan. Prussian blue nanoparticles promote wound healing of diabetic skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1526-1532. |
| [6] | Jiao Wencheng, Dai Jing, Yan Wenrui, Shen Jintao, Hu Jinglu, Jin Yiguang, Du Lina. 3D-printed multifunctional wound dressing for combined radiation and wound injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(10): 1562-1567. |
| [7] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [8] | Li Yujiao, Su Kunxia. High-intensity endurance exercise influences browning of white adipose tissue in a mouse model of high-fat diet induced obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 707-713. |
| [9] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [10] | Cao Congcong, Ling Gengfei, Yang Chunhua. Local injection of ginsenoside Rg1 nanoparticles in the treatment of myocardial infarction in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 3977-3983. |
| [11] | Liu Jichao, Zhao Jinlong, Yu Yang. Silk fibroin collagen composite scaffold combined with platelet-rich plasma for repairing skin injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(25): 3971-3976. |
| [12] | Cao Jin, Wang Ansu, Huang Nijiao, Wu Fujun, Chen Ping, Li Chengmei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of polyphosphate in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(21): 3375-3381. |
| [13] | Zhou Lanxi, Shao Lu, Dong Shiwu, Yu Zhengwen. Molecular mechanism of angiogenesis promoted by medical metal materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2616-2624. |
| [14] | Zhu Hong, Lin Ziheng, He Rouye, Pan Jinbin, Liu Xiaochuan, He Xiaoling, Zhang Jingying. Antibacterial and hemostatic properties of chitosan collagen sponge [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(16): 2525-2533. |
| [15] | Chen Di, Xue Yu, Tang Yu, Fei Xiaoming, Zhuang Qin, Zhou Wenwen, Lyu Demin, Shi Wentao, Zhang Zhijian, Zheng Wenjuan, Jiang Yu. Ecto-mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium lyophilized powder combined with fibrin glue to repair skin injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2350-2355. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||