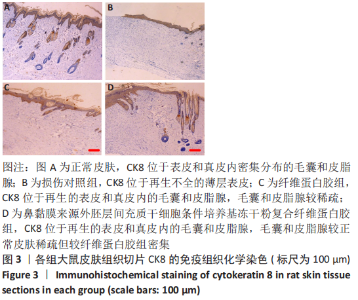
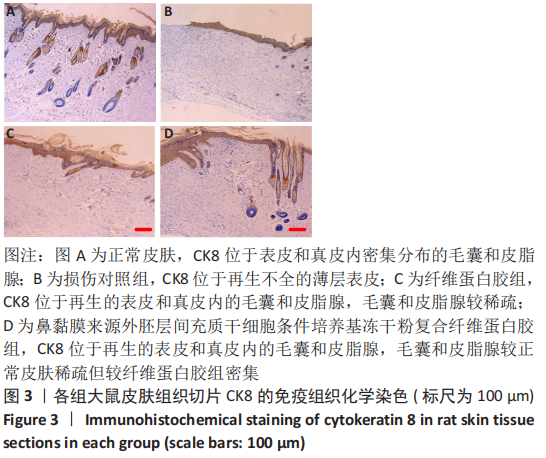
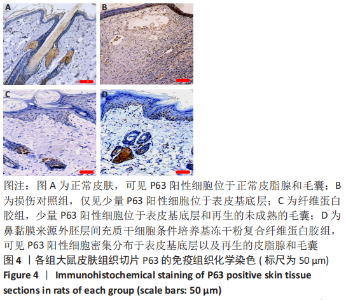
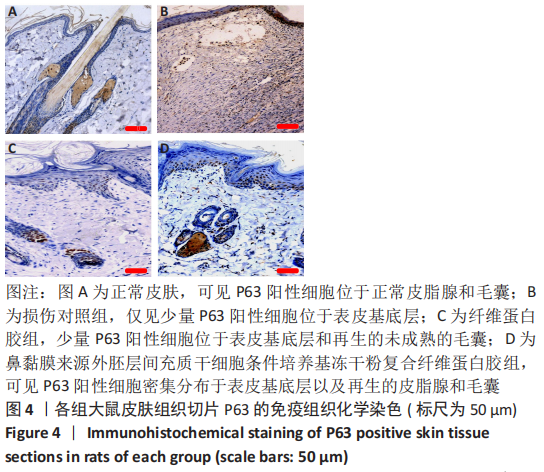
[1] JACKSON WM, NESTI LJ, TUAN RS. Concise review: clinical translation of wound healing therapies based on mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(1):44-50.
[2] KOLIOS G, MOODLEY Y. Introduction to stem cells and regenerative medicine. Respiration. 2013;85(1):3-10.
[3] MA S, XIE N, LI W, et al. Immunobiology of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(2):216-225.
[4] BOGATCHEVA NV, COLEMAN ME. Conditioned Medium of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: A New Class of Therapeutics. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019; 84(11):1375-1389.
[5] DENG W, SHAO F, HE Q, et al. EMSCs Build an All-in-One Niche via Cell-Cell Lipid Raft Assembly for Promoted Neuronal but Suppressed Astroglial Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells. Adv Mater. 2019;31(10): e1806861.
[6] FORNI PE, WRAY S. Neural crest and olfactory system: new prospective. Mol Neurobiol. 2012;46(2):349-360.
[7] VERON AD, BIENBOIRE-FROSINI C, FERON F, et al. Isolation and characterization of olfactory ecto-mesenchymal stem cells from eight mammalian genera. BMC Vet Res. 2018;14(1):17.
[8] 丁志,杨松林.间充质干细胞生物学特性及其分化潜能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(1):147-150.
[9] SASAKI M, ABE R, FUJITA Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells are recruited into wounded skin and contribute to wound repair by transdifferentiation into multiple skin cell type. J Immunol. 2008;180(4): 2581-2587.
[10] WU Y, CHEN L, SCOTT PG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis. Stem Cells. 2007;25(10):2648-2659.
[11] BAGHER Z, ATOUFI Z, ALIZADEH R, et al. Conductive hydrogel based on chitosan-aniline pentamer/gelatin/agarose significantly promoted motor neuron-like cells differentiation of human olfactory ecto-mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;101: 243-253.
[12] RUI K, LIN X, TIAN J, et al. Ecto-mesenchymal stem cells: a new player for immune regulation and cell therapy. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018;15(1): 82-84.
[13] STAMEGNA JC, GIRARD SD, VERON A, et al. A unique method for the isolation of nasal olfactory stem cells in living rats. Stem Cell Res. 2014; 12(3):673-679.
[14] VIG K, CHAUDHARI A, TRIPATHI S, et al. Advances in Skin Regeneration Using Tissue Engineering. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):789.
[15] MACNEIL S. Progress and opportunities for tissue-engineered skin. Nature. 2007;445(7130):874-880.
[16] KIM JW, LEE JH, LYOO YS, et al. The effects of topical mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in canine experimental cutaneous wounds. Vet Dermatol. 2013;24(2):242-253.
[17] JOSEPH A, BAIJU I, BHAT IA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media: A novel alternative of stem cell therapy for quality wound healing. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(7-8):5555-5569.
[18] MEIRELLES LDA S, FONTES AM, COVAS DT, et al. Mechanisms involved in the therapeutic properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(5-6):419-427.
[19] LIANG X, DING Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: current status and perspectives. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(9):1045-1059.
[20] DELORME B, NIVET E, GAILLARD J, et al. The human nose harbors a niche of olfactory ectomesenchymal stem cells displaying neurogenic and osteogenic properties. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(6):853-866.
[21] RUI K, ZHANG Z, TIAN J, et al. Olfactory ecto-mesenchymal stem cells possess immunoregulatory function and suppress autoimmune arthritis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2016;13(3):401-408.
[22] SHABBIR A, COX A, RODRIGUEZ-MENOCAL L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Induce Proliferation and Migration of Normal and Chronic Wound Fibroblasts, and Enhance Angiogenesis In Vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(14):1635-1647.
[23] CHEN B, LI Q, ZHAO B, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Potential Therapeutic Tool for Tissue Repair. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(9):1753-1758.
[24] JANMEY PA, WINER JP, WEISEL JW. Fibrin gels and their clinical and bioengineering applications. J R Soc Interface. 2009;6(30):1-10.
[25] ZHANG Z, HE Q, DENG W, et al. Nasal ectomesenchymal stem cells: multi-lineage differentiation and transformation effects on fibrin gels. Biomaterials. 2015;49:57-67.
[26] DAVIS NE, DING S, FORSTER RE, et al. Modular enzymatically crosslinked protein polymer hydrogels for in situ gelation. Biomaterials. 2010; 31(28):7288-7297.
[27] LEI H, ZHU C, FAN D. Optimization of human-like collagen composite polysaccharide hydrogel dressing preparation using response surface for burn repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;239:116249.
[28] REINKE JM, SORG H. Wound repair and regeneration. Eur Surg Res. 2012;49(1):35-43.
[29] MOLL R, DIVO M, LANGBEIN L. The human keratins: biology and pathology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;129(6):705-733.
[30] PELLEGRINI G, DELLAMBRA E, GOLISANO O, et al. p63 identifies keratinocyte stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(6):3156-3161.
[31] OWENS DW, LANE EB. The quest for the function of simple epithelial keratins. Bioessays. 2003;25(8):748-758.
[32] MILLS AA, ZHENG B, WANG XJ, et al. p63 is a p53 homologue required for limb and epidermal morphogenesis. Nature. 1999;398(6729): 708-713.
[33] YANG A, SCHWEITZER R, SUN D, et al. p63 is essential for regenerative proliferation in limb, craniofacial and epithelial development. Nature. 1999;398(6729):714-718.
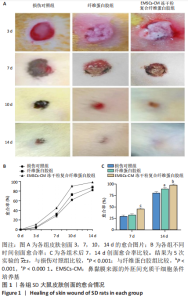
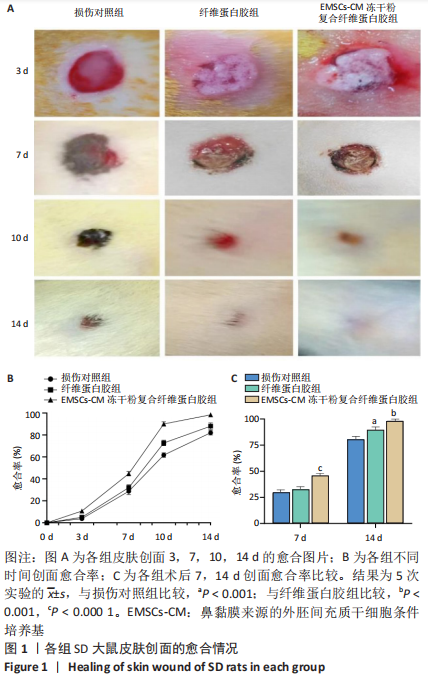
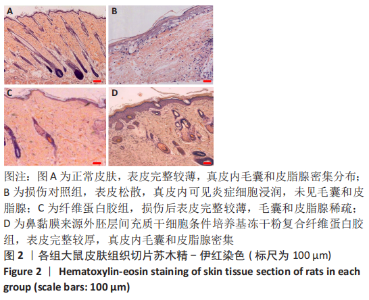
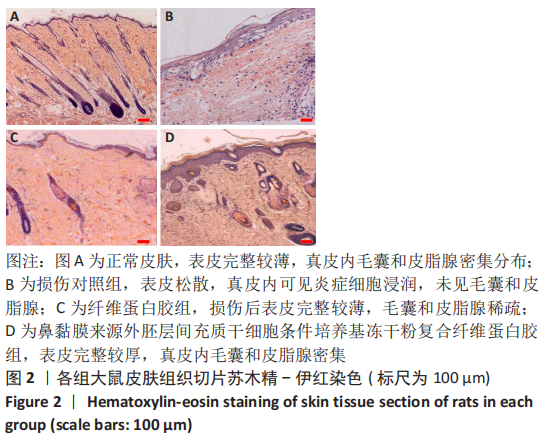
|