Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (28): 4553-4561.doi: 10.12307/2022.313
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and role of human platelet lysate in tissue repair and regeneration
Xie Xingqin1, Nie Yuqi2, Zhang Yi1
- 1National and Local Joint Research and Engineering Center for Aging Diseases, Tian Qing Stem Cell Co., Ltd., Harbin 150028, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Collabera Inc, NJ 07920, USA
-
Received:2021-02-23Accepted:2021-03-31Online:2022-10-08Published:2022-03-23 -
Contact:Zhang Yi, PhD, Professorial senior engineer, National and Local Joint Research and Engineering Center for Aging Diseases, Tian Qing Stem Cell Co., Ltd., Harbin 150028, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Xie Xingqin, Senior engineer, National and Local Joint Research and Engineering Center for Aging Diseases, Tian Qing Stem Cell Co., Ltd., Harbin 150028, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:Technical Research Project of Industrial Information Technology Bureau of Songbei District, Harbin, No. HSGK201913 (to ZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Xingqin, Nie Yuqi, Zhang Yi. Application and role of human platelet lysate in tissue repair and regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4553-4561.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1.1 血小板来源 制备人血小板裂解液的血小板来源大体分为两种,自体血液来源或异体血液来源。自体血液来源的富血小板血浆或浓缩血小板制备获得的人血小板裂解液具有安全可控和无免疫排斥反应的特点,多用于临床试验和疾病治疗[13]。缺点是自体血液制备的人血小板裂解液受患者身体素质的影响,新生儿、老年患者或有传染性疾病的患者因血液有限、血管弱、服用过抗凝血药物、曾发生过脑血管疾病、存在炎症、有传染性微生物等问题而无法获得自体血液[14],这种情况则可以通过捐献的异体血液制备无血缘关系的血小板裂解液以进行临床应用。异体人血小板裂解液可以通过成人单采机富集的血小板或脐血来源的血小板浓缩物[3,15]。为了获得足够的异体来源的人血小板裂解液,2018年BAIGGER等[16]通过诱导性干细胞分化的巨核细胞来生产人血小板裂解液,脐血来源和诱导型干细胞分化法获得的人血小板裂解液被认为是用于儿童和老年人疾病治疗的良好选择。如果采用异体来源的血小板,在制备人血小板裂解液过程还需要增加一个除去病毒和病原体的过程,确保治疗过程的风险性最低。 2.1.2 人血小板裂解液制备方法 人血小板裂解液制备方法包括冷冻/融化、超声破碎、表面活性剂法和凝血酶/氯化钙激活法等四大类[17-19]。2020年DELILA等[20]报道了不同生产方式获得的人血小板裂解液中不仅蛋白质、生长因子、细胞因子含量有区别,而且其生化特征、凝血酶生成能力、凝血酶相关的蛋白水解活性、磷脂相关的促凝血潜能、细胞外囊泡及抗氧化特性有很大差异,将会对临床治疗的安全性和功效造成潜在不良影响。冻融法通常设定为几个循环的-80 ℃/37 ℃温度改变,以便彻底将血小板裂解后内容物释放,然后在室温进行高速离心去除细胞碎片,上清再通过0.22 μm过滤后获得人血小板裂解液。近年来的几个对比试验证实,储存4个月的血小板浓缩物冻融后制备出来的人血小板裂解液与新鲜制备的结果无差别[21],但制备温度对因子影响有差别,在-80 ℃/37 ℃下制备人血小板裂解液可能会影响生长因子的质量,而-196 ℃/-4 ℃的方法能更好地保存人血小板裂解液中的生长因子活性[22-23]。冻融次数是控制血小板中因子释放充分与否的关键,冻融循环次数3-5次是文献报道中常见的方案[24],CaCl2和低分子肝素激活与传统冻融法结合可进一步获得超活化血小板裂解液[25-26]。超声处理法也是临床研究中制备人血小板裂解液常用方法之一。通过20 kHz左右频率的超声仪处理30 min可充分实现血小板脱颗粒效果[27],其结果比超声15 min能更多地释放生长因子,超声裂解后的样本经56 ℃30 min处理可消除可引起炎症的补体、纤维蛋白原和可能的病毒携带风险[28]。表面活性剂方法制备人血小板裂解液是将浓缩血小板在25℃的1%磷酸三丁酯和1%Triton-45中连续温和搅拌培养1 h后,加上10%豆油充分混合、离心去除上层油相,残余表面活性剂经C18处理后去除[29]。采用凝血酶/氯化钙激活法制备人血小板裂解液通常是将经几个冻融循环后的血小板与CaCl2和玻璃珠室温混合1 h启动血小板的激活和脱颗粒激活,释放生长因子,将纤维蛋白原在玻璃珠上转变为纤维蛋白凝胶,再经过离心和过滤后形成人血小板裂解液[30]。4种方法中冻融法是最简单、廉价、快速生产人血小板裂解液的方法,过程不添加任何可能会导致不良反应的物质,因此为更多的研究者所采用。 2.1.3 人血小板裂解液组成成分 临床起效的人血小板裂解液组分主要包含血浆来源的成分和血小板来源的成分。血浆的主要蛋白是起到大分子载体的白蛋白和球蛋白及起到凝血功能的纤维蛋白原[31],这些蛋白不会因为人血小板裂解液制备过程而浓缩,因此在人血小板裂解液中起到的作用较小。人血小板裂解液中起关键修复作用的成分源自血小板。血小板源的产物在血小板激活裂解后产生,这个过程可释放超过4 000种物质,其中致密颗粒可释放出血清素、肾上腺素、组胺、Ca2+、二磷酸腺苷和三磷酸腺苷;溶酶体能释放出弹性蛋白酶、胶原蛋白酶、cathepsin、α-阿拉伯糖苷、β-半乳糖苷酶、β-葡萄糖醛酸酶和正乙酰葡糖胺酶;α-颗粒可释放出大量的生长因子、细胞因子、黏附因子、凝血因子和趋化因子等参与损伤修复过程[32]。2019年ZAMANI等[33]荟萃了近十年的人血小板裂解液文献发现,制备工艺不同将导致人血小板裂解液中起损伤修复性关键作用的组分波动较大,血小板源生长因子AB质量浓度在30-44 μg/L之间,血小板源生长因子BB质量浓度为3.3-24.0 μg/L,血小板源生长因子AA质量浓度为11-34 μg/L,胰岛素样生长因子质量浓度在32-140 μg/L,转化生长因子β1质量浓度在24-103 μg/L范围。含量较少的为脑源生长因子、内皮细胞生长因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和血管内皮生长因子,其质量浓度分别约为18,1.7-3.4,0.07-0.57,0.1-11 μg/L,这些损伤修复性蛋白将对细胞生长、分化、成熟、迁移、免疫调节和调节毛细血管形成、神经保护等起到作用。多种因子的协调作用能更好地激发下游信号通路,例如成纤维细胞生长因子、内皮细胞生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、转化生长因子β和血小板源生长因子协同作用下才能促进血管内皮生长因子的血管形成作用[34],血管内皮生长因子与血小板源生长因子共同作用促进了间充质干细胞的迁移[35]。人血小板裂解液中还含有多种血小板源的异质性微囊体,包括细胞膜来源的微粒和多囊体来源的外泌体,这两种微囊体均在血小板激活过程产生。2014年TORREGGIANI等[36]发现骨髓间充质干细胞的分化和迁移与人血小板裂解液中的外泌体浓度成显著相关性。当然,人血小板裂解液的成分和对细胞的影响除了与制备工艺有关,也与供者的年龄有关。2019年BERGER等[37]研究发现,年龄大于50岁供者来源的人血小板裂解液对肌腱细胞扩增和迁移的影响随着人血小板裂解液量的增加而增加,而年轻供者则无量效关系,可见临床老年患者应用中需要考虑人血小板裂解液的使用浓度。 2.2 人血小板裂解液单独用于组织再生修复 人血小板裂解液在组织再生修复中的应用以骨科相关疾病为主,近年来发展到了疼痛、眼部疾病、皮肤黏膜疾病、周围血管病变、新冠肺炎、男性勃起功能障碍及美容等多个领域的疾病治疗。"
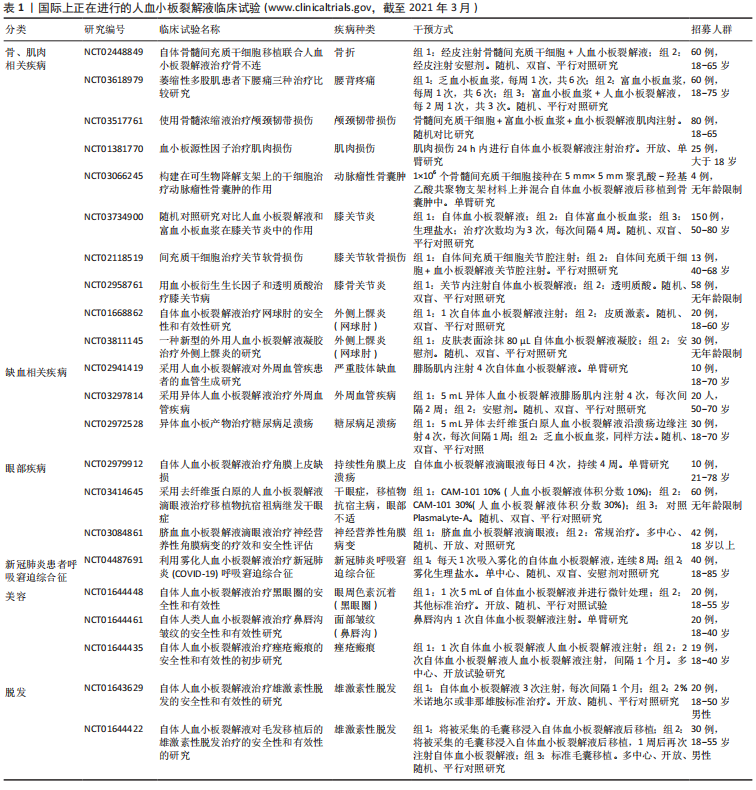
2.2.1 人血小板裂解液单独用于组织再生修复 治疗疼痛:2016年TAN等[38]采用自体人血小板裂解液原位注射治疗56例顽固性肱骨外上髁炎,目测类比评分和Mayo 量表分析显示,所有患者均在12个月治疗后恢复了正常的肘部功能。2016年严伟等[39]将人血小板裂解液联合体外冲击波后,3个月目测类比评分由7.58±0.82降至2.61±0.53,Mayo评分由61.8±5.5提高到91.6±6.5,彩色多普勒超声强信号区明显减小,均未出现感染、血管和神经损伤等并发症。2017年CENTENO等[40]对470例腰椎放射性神经痛患者进行硬膜外注射人血小板裂解液治疗,并通过数值疼痛评分、功能评分指数和修改后的单一评估数值评价评分进行24个月随访分析,结果发现接受人血小板裂解液治疗的患者72%疼痛显著缓解,数值疼痛评分和功能评分指数变化得分较基线显著降低,修改后的单一评估数值评价评分在治疗后24个月显示49.7%改善。2019年刘广亚等[41]观察40例跟腱炎患者采用富血小板血浆或改良的人血小板裂解液治疗1,3,6个月后的目测类比评分改善效果,结果两组患者与治疗前比较目测类比评分显著降低,两组间差异无统计学意义;超声影像学显示人血小板裂解液组较富血小板血浆组有更多的跟腱病变部位改善,使用改良的人血小板裂解液可能比富血小板血浆具有更好的应用前景。 治疗骨性关节炎:2015年AL-AJLOUNI等[42]报告了在关节中注射自体人血小板裂解液治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床研究,48例双膝慢性疼痛和肿胀的骨性关节炎患者,K/L分级Ⅰ-Ⅱ级,经皮每隔3周注射自体人血小板裂解液共3次,随访分析人血小板裂解液治疗后其KOOS分数在32,52周较治疗之前明显提高,证明自体人血小板裂解液经皮局部注射对治疗膝骨性关节炎安全且有效。2016年SAMARA等[43]报道了应用自体人血小板裂解液经皮注射治疗15例早中期骨性关节炎患者的案例,患者经过2次治疗,每次间隔3周,1年后发现经过人血小板裂解液治疗患者胫骨和股骨两侧的软骨厚度均有明显改善。2017年严伟等[44]报道了106例(141膝)KLⅠ-Ⅱ期膝骨性关节炎患者采用每周2次关节腔内注射自体人血小板裂解液连续5次的治疗结果,经过平均16.7个月的随访,与治疗前相比,人血小板裂解液治疗后WOMAC评分显著降低、疼痛减轻、僵硬程度减轻、关节功能受限程度降低;AKS评分比较结果显示治疗后患者临床症状明显减轻,关节功能包括活动度和稳定性得到一定程度的恢复。在3个前瞻性对比临床研究中,人血小板裂解液也显示出了较好的临床效果[45-47]。2017年侯燕等[45]报告的100例膝骨性关节炎患者中人血小板裂解液和对照组(透明质酸钠)关节腔内注射的前瞻性对照研究结果,人血小板裂解液治疗组WOMAC评分明显低于对照组,KSS评分和 Lysholm评分均高于对照组。2018年鞠昌军等[46]将100例膝骨性关节炎患者随机分为单纯人血小板裂解液组和体外支具联合人血小板裂解液组,结果证明联合治疗组目测类比评分及WOMAC评分均低于单独人血小板裂解液组,联合治疗组股胫角和内侧间室宽度治疗后6个月与治疗前相比明显改善。体外人工膝支具辅助人血小板裂解液治疗膝骨性关节炎在缓解症状、改善下肢力线方面能够取得较好的临床效果。2020年鞠昌军等[47]在人血小板裂解液、富血小板血浆、透明质酸钠治疗膝骨性关节炎的前瞻性随机对照研究中,一共150例患者,随访点为治疗后1,3,6个月,结果证明人血小板裂解液治疗膝骨性关节炎能够取得与富血小板血浆同样的治疗效果,均优于玻璃酸钠,同时不良反应发生率低。 治疗骨折:2016年JIANG等[48]报道1例采用自体人血小板裂解液治疗骨不连案例,该患者胫腓骨骨折钢板内固定后9个月胫骨仍不愈合且钢板断裂错位,二次手术采用复位联合自体人血小板裂解液注射骨折部位3次,间隔1周,每月进行影像学拍照,患者骨痂在第二次术后4-6个月后逐渐显现生成,在第8个月后实现骨折完全愈合,期间没有不良反应发生。2020年YU等[49]报道了从2016年6月至2018年6月接受了人血小板裂解液治疗的radius骨和尺骨骨折不愈合9例患者,在5例不愈合和延迟愈合的患者中有3例实现了临床骨愈合,1例骨不连患者好转,通过复查观察到骨赘形成,骨髓腔未闭合,复查显示愈伤组织生长,下肢患者仍无法承受体质量。 治疗腰间盘突出:腰椎间盘突出症是导致显著的轴向腰背和辐射腿痛的常见原因,这种情况可能会造成潜在的永久性神经系统损害,包括麻木、无力及肠和膀胱功能障碍。药物、硬膜外类固醇和手术等传统治疗策略均具有医源性后遗症的潜在风险。2020年RAWSON[50]报告了2例L4-L5腰间盘突出患者采用富血小板血浆和人血小板裂解液联合治疗案例,研究者将1 mL富血小板血浆用于腰椎L4-L5位置的脊柱韧带和面关节,目的为脊柱提供额外的稳定性和减压,而将3 mL自体人血小板裂解液注射在脊柱硬膜外,第一位患者注射后4周疼痛得到了50%的缓解,而第二次治疗后4周随访MRI显示突出的腰间盘近乎完全吸收;第二位患者第一次治疗后2个月随访发现左腿疼痛明显改善,第二次注射后3个月随访患者自述疼痛、麻木、刺痛和无力的症状完全缓解,行动功能改善,MRI可见突出的间盘完全吸收。由此推测注射血小板溶解产物可能是通过细胞因子和生长因子的相互作用促进了新血管形成及巨噬细胞诱导的吞噬作用,从而促进脊柱结构的恢复。 治疗脱发:2017年COLE等[27]研究报道了3例年龄在27-55岁之间的雄性激素性脱发患者,每位头顶3个2 cm×2 cm的位置分别用1 mL 人血小板裂解液、葡萄糖酸钙激活的富血小板血浆或生理盐水处理过的毛囊进行移植,术后 3.5 个月时,人血小板裂解液、葡萄糖酸钙激活的富血小板血浆或生理盐水处理的部位有分别(89±9)%,(74±7)%和(57±10)%的毛囊再生;4个月时人血小板裂解液、葡萄糖酸钙激活的富血小板血浆或生理盐水位置的毛囊存活率分别达到99%,75%和71%,人血小板裂解液能实现最佳的毛囊成活率;第4位雄性激素性脱发患者移植的是人血小板裂解液处理的毛囊,术后7个月可见脱发处毛囊单位增加50%、头发密度增加122%。研究者认为人血小板裂解液效果好的原因是通过超声波处理的人血小板裂解液比葡萄糖酸钙激活的富血小板血浆含有更多的血管内皮生长因子、血小板源生长因子BB和转化生长因子β1。 治疗眼角膜损伤:2016年FEA等[51]研究揭示了使用自体人血小板裂解液滴眼液治疗20例原发性干燥综合征患者的效果,自体人血小板裂解液通过降低朗格汉斯细胞密度、促进角膜、神经细胞再生,有效恢复角膜损伤。2019年ABU-AMEERH等[52]对10例持续性角膜上皮损伤患者采用自体人血小板裂解液滴眼液,每天使用4次,在治疗后的第7,14,21,28天进行评估,总共70%的患者在28 d内完全重新上皮化,其中40%的患者在14 d内治愈,30%的患者在28 d内治愈。2020年SAMARKANOVA等[53]在一项多中心、回顾性、连续病例研究中评估了33例(46眼)对常规治疗无效且需要紧急干预的严重的眼表病变(神经营养性溃疡:Ⅰ组;其他角膜溃疡:Ⅱ组;角膜烧伤:Ⅲ组)和慢性病(眼移植物抗宿主病:Ⅳ组;严重干眼症:Ⅴ组)患者经同种异体脐血血小板裂解液滴眼液连续治疗19 d,结果Ⅰ-Ⅲ组中患者78%获得康复、19%获得部分改善,Ⅳ-Ⅴ组有85%改善,没有严重的不良事件直接归因于脐血血小板裂解液滴眼液,针对神经营养性角膜炎的一项前瞻性临床试验(NCT03084861)正在进行中,以确认脐血血小板裂解液滴眼液的有效性和安全性数据,见表1。"

治疗眼部移植物抗宿主病:同种异体骨髓移植后出现移植物抗宿主病的发病率万分之一,其中60%出现眼部移植物抗宿主病。移植物抗宿主病导致眼表和泪腺的损害,有发红、发炎、烧灼痛感觉和眼部干燥症,以全身免疫抑制方案和局部疗法(主要是人工泪液和皮质类固醇)为主的眼部移植物抗宿主病治疗效果并不理想。2016年PEZZOTTA等[54]继2012年发表对23例经标准疗法无反应的难治性眼部移植物抗宿主病(Ⅱ-Ⅳ级)患者采用自体人血小板裂解液治疗的30 d有效性随访效果后,再次发表了31例患者自体人血小板裂解液滴眼液治疗6-36个月的随访结果,在6个月时患者GSS症状评分中位数从70降至41(36个月时为33),GSS功能中位数从68降低至46(36个月时为33);泪崩试验中位时间从6个月后的3 s延长到36个月的6 s,没有发生严重的不良事件,证明长期使用人血小板裂解液滴剂进行治疗对于眼部移植物抗宿主病是安全有效的。2016年VALENTINI等[55]报道,用自体血小板衍生的眼药水有效治疗慢性移植物抗宿主病患者,在有反应和有抵抗力的患者中,滴眼液都富含各种生长因子,其数量与血小板计数呈正比,无反应的患者滴眼液表现出最高水平的血浆来源趋化因子(CXC基序)配体(CXCL)10,表明患者采用人血小板裂解液滴眼液的有效性和血小板因子直接相关。2016年ZALLIO等[56]进行了单中心前瞻性试验研究,以评估使用由裂解血小板浓缩物制成的滴眼剂的疗效和安全性,26例慢性眼部移植物抗宿主病患者中24例完成了1年治疗;在30 d评估访谈中,有91%患者报告其症状有所改善,有86%患者角膜损害得到缓解,NIH评分提高了73%,其中8%患者的最佳得分为0(即非干眼症)。在以后的时间点也看到了类似的结果,表明人血小板裂解液滴眼液是一种安全、实用、效果良好的治疗选择。 治疗皮肤、黏膜损伤:2019年AHMED等[57]评估了局部用人血小板裂解液与丙酸氯倍他索相比在甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎患者口腔溃疡的随机对照临床试验,30例患者分为人血小板裂解液组和丙酸氯倍他索对照组,与最有效的局部皮质类固醇激素之一丙酸氯倍他索相比,人血小板裂解液在减轻类风湿关节炎患者甲氨蝶呤引起的口腔溃疡疼痛和临床症状方面具有更好的效果。2020年JAFAR 等[58]报道了2例采用人血小板裂解液治疗长期糖尿病足溃疡的愈合研究,经过在溃疡周边注射治疗,2例早期8周都不愈合的患者得到痊愈。 2.2.2 人血小板裂解液与细胞联合使用 治疗骨科相关疾病:2016年LABIBZADEH等[59]报道了人长骨骨不连治疗中采用间充质干细胞结合人血小板裂解液的治疗效果,在18例长骨骨不连患者中入组7例进行间充质干细胞(2×107)结合人血小板裂解液治疗,并随访1,3,6,12个月,所有患者都在12个月内耐受治疗,有4例患者实现了骨完全愈合。在2016-2020年间,CENTENO团队进行了多组人血小板裂解液临床对比研究[60-63]。其中,2016年报道了18个医疗中心采用经皮注射人血小板裂解液联合培养的骨髓干细胞或人血小板裂解液联合骨髓浓缩细胞治疗各种骨科相关疾病的2 372例患者,进行了长达9年的不良反应跟踪[60],病患部位包括膝盖、臀部、脚踝/脚、手/腕、肘部、肩膀和脊柱,总计325次不良事件,大多数为手术后疼痛(n=93,占3.9%)和进行性退行性关节疾病引起的疼痛(n=90,占3.8%),注射骨髓浓缩细胞+人血小板裂解液的患者中不良事件发生率最低;有7例报告了肿瘤,发病率低于一般人群,因此没有临床证据表明该研究中使用任何类型的人血小板裂解液联合细胞治疗会增加发生肿瘤的风险。在2018年报道的前交叉韧带撕裂研究中,29例患者采用经皮在前交叉韧带处注射自体骨髓浓缩细胞联合自体人血小板裂解液产品方式(人血小板裂解液或富血小板血浆)进行前交叉韧带撕裂治疗后,77%患者前交叉韧带完整性显著改善,骨髓浓缩细胞和血小板产品的经皮前交叉韧带治疗有望成为手术的替代方案[61]。在2018年报道的膝骨性关节炎临床研究中,48例膝骨关节炎患者被随机分为运动疗法对照组或注射自体骨髓浓缩细胞+人血小板裂解液的治疗组,对照组患者可在3个月后转用骨髓浓缩细胞+人血小板裂解液治疗,结果表明,运动组所有患者在3个月后转换成治疗组方式治疗,转换组在3个月后的KSS膝关节、SF-12体能和LEAS评分较运动组有显著改善,与治疗组接近[62]。在2020年报道的肩袖撕裂研究中,年龄在18-65岁之间肩袖部分或未回缩型撕裂患者被分成运动治疗和骨髓浓缩细胞联合自体血小板产品(人血小板裂解液或富血小板血浆)经皮治疗组,至少接受3个月的运动疗法后,运动组患者可转而接受骨髓浓缩细胞联合血小板产品治疗,中期随访(至少随访12个月)显示,25例入组患者中没有严重不良反应的报道,骨髓浓缩细胞+血小板产品组3,6个月的疼痛、功能评分比运动疗法组有显著改善,在24个月时平均改善89%,并持续获得功能增强和疼痛减轻,MRI复查显示骨髓浓缩细胞联合血小板产品治疗后大多数撕裂减小[63]。 治疗勃起功能障碍:2019年PROTOGEROU等[64]将8例患者分为2组,A组患者接受脂肪间充质干细胞联合人血小板裂解液治疗,B组患者只接受人血小板裂解液治疗,随访结果表明,两组均在随访1个月和3个月后出现勃起功能改善,两组治疗前后的国际勃起功能指数IIEF-5评分具有统计学差异,但IIEF-5评分无统计学意义上的差异。说明不论是人血小板裂解液联合间充质干细胞还是单独使用人血小板裂解液均可获得良好的勃起功能障碍治疗效果。2020年该团队进一步发表了自体脂肪间充质干细胞联合血小板裂解液血浆治疗5例勃起功能障碍患者的长期随访结果,治疗后第1,3,6,12个月的勃起功能评价发现,所有患者IIEF-5、Peak Systolic Velocity(PSV)在第6个月均得到改善,结论是脂肪间充质干细胞与血小板裂解液血浆结合对勃起功能障碍有一定改善作用,且短期内不良反应很小[65]。 2.2.3 国际上正在进行的hPL临床试验 截至2021年3月,在NIH的clinicaltrials.gov网站上注册的正在招募或进行的采用人血小板裂解液进行疾病治疗临床试验有22项,大部分为骨科相关疾病研究,见表1,包括用人血小板裂解液治疗骨科相关疾病10项,其中骨不连(NCT02448849)、颅颈韧带损伤(NCT03517761)、骨性关节炎(NCT02118519)、动脉瘤性骨囊肿(NCT03066245)4项的治疗组采用了间充质干细胞联合人血小板裂解液的治疗方案。单独使用人血小板裂解液治疗缺血相关疾病的试验有3项,分别针对严重下肢缺血、周围血管病变和糖尿病足溃疡。正在进行的眼部相关临床试验有2项,为局部采用人血小板裂解液滴眼液治疗持续性角膜上皮溃疡研究和不同浓度剂量人血小板裂解液对干眼症、眼部移植物抗宿主病及眼部不适适应证研究。面部修复和脱发治疗一共5项,均是采用单独人血小板裂解液制剂。 新冠肺炎(COVID-19)疫情是自2020年初爆发至今的全球性新型疾病,重症COVID-19后呼吸窘迫综合征的有效治疗方法很少。近年来,研究发现血小板与抵抗病毒和肺部生理功能具有直接相关性的证据[66],使得人血小板裂解液实现新冠肺炎后呼吸窘迫征患者肺部病毒控制、炎症控制、肺部损伤和纤维化控制具有合理的理论依据[67],相关细胞学研究已经证明,人血小板裂解液的抗炎性作用和雾化的人血小板裂解液对肺纤维细胞生长的促进作用[8],2020年新注册的1项单中心、随机、双盲、安慰剂对照研究(NCT04487691),将招募40例新冠肺炎患者,抽取约520 mL的自体静脉血制备56瓶血小板裂解液,每天1次吸入雾化的自体人血小板裂解液,连续治疗8周以确定雾化吸入的人血小板裂解液对伴有呼吸窘迫综合征新冠肺炎患者肺功能的影响。 2.2.4 人血小板裂解液与生物材料联合使用 近年来研究负载人血小板裂解液的生物工程材料,包括生物水凝胶、3D支架及线、膜材料等已经成为再生修复领域的研究发展趋势。 2015年SANTO等[68]研究稳定负载人血小板裂解液材料的3D纳米结构水凝胶对软骨再生修复的影响,将脂肪来源的干细胞包埋在负载人血小板裂解液的3D水凝胶中并在成软骨条件下培养,组织切片、免疫组化和基因表达分析表明,人血小板裂解液可以既作为组织载体又作为细胞因子应用来源,可以促进I型、Ⅱ型胶原、聚糖蛋白等新软骨细胞外基质的形成,从而起到软骨修复作用。 2016年ROBINSON等[69]发现,人血小板裂解液水凝胶能够持续释放内源性血小板源生长因子BB长达20 d,并且对蛋白酶降解具有抵抗力。人血小板裂解液水凝胶通过在3D环境中促进人间充质干细胞的生长和迁移,对后肢缺血鼠模型中用激光多普勒灌注成像评估,与对照组相比,人血小板裂解液和人间充质干细胞的组合水凝胶材料在8 d后改善了局部组织灌注。2018年ALMEIDA等[70]提出了一种基于透明质酸和人血小板裂解液的可光交联的水凝胶材料,掺入人血小板裂解液的透明质酸水凝胶可通过人牙髓干细胞促进细胞代谢并刺激矿化的基质沉积,为修复受损的牙髓/牙本质组织和牙髓再生提供了清晰的证据。2018年BABO等[71]构建了人血小板裂解液、磷酸钙水泥结合人血小板裂解液及透明质酸微球的双层结构材料,旨在再生软组织和矿化的牙周组织,研究表明,基于人血小板裂解液的双层材料有利于减少上皮组织的下移并促进整体牙周组织的愈合和再生。2019年COSTA-ALMEIDA等[72]将人血小板裂解液均匀包被的丝线上封装了人脂肪干细胞,形成了生物功能复合活性水凝胶纤维,人血小板裂解液水凝胶使封装的人脂肪干细胞可以在培养中存活长达14 d,并且能够在核心纤维的表面对齐并沉积I型和Ⅲ型胶原,从而人血小板裂解液-人脂肪干细胞水凝胶包被的缝合线成为具有生物学活性的纤维材料。2020年FRAZER等[73]开发了基于人血小板裂解液的生物墨水,将人血小板裂解液、纤维蛋白原和凝血酶结合在一起可以生成透明且具有黏性的生物墨水,与9种生物墨水相比,由10%人血小板裂解液构建的生物墨水具有所有所需的机械和细胞特性,并且能够在体外再生全厚度上皮,可直接应用于人角膜以促进角膜上皮再生。2020年HUANG等[74]采用负载超活化血小板裂解液的同轴纳米生物复合材料促进了大鼠颅骨缺陷的修复。2021年TANG 等[75]构建了负载人血小板裂解液生长因子的聚赖氨酸和透明质酸聚电解质多层膜,交联或不交联构建的透明质酸/聚赖氨酸薄膜都成功地吸收了血小板裂解液,表现出高亲水性和血小板裂解液吸收率,薄膜的血小板裂解液释放曲线持续时间长达2周,负载血小板裂解液的聚电解质多层膜中低氧诱导因子1/血管内皮生长因子的激活促进了缺损区域的肉芽组织形成、胶原蛋白沉积和新生血管,从而实现皮肤的快速再上皮化和再生。2021年MENDES等[76]将透明质酸与人血小板裂解液进行光交联结合形成了能够从注射器中推出并通过3D打印出稳定的3D结构,与没有人血小板裂解液的透明质酸水凝胶相比,这些可注射交联水凝胶支持细胞黏附并增强了细胞与微凝胶结构的相互作用。2021年DAIKUARA等[77]研制的由人血小板裂解液和明胶甲基丙烯酰基组成的3D打印生物墨水,用于制造多功能3D打印的真皮产品,这种生物墨水在流变特性和形状保真度方面满足了可印刷性的基本要求,而且可以容易地调节其机械性能,以实现与天然皮肤组织相当的刚度,在长达2周的研究中,以可持续的方式成功释放与生物有关的因子。"

| [1] BOHONEK M, KUTAC D, ACKER JP, et al. Optimizing the supply of whole blood-derived bioproducts through the combined implementation of cryopreservation and pathogen reduction technologies and practices: An overview. Transfus Apher Sci. 2020;59(2):102754. [2] VIAU S, LAGRANGE A, CHABRAND L, et al. A highly standardized and characterized human platelet lysate for efficient and reproducible expansion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2019;21(7):738-754. [3] SCHALLMOSER K, HENSCHLER R, GABRIEL C, et al. Production and quality requirements of human platelet lysate: A position statement from the working party on cellular therapies of the international society of blood transfusion. Trends Biotechnol. 2019;17:S0167-7799. [4] GUIOTTO M, RAFFOUL W, HART AM, et al. Human platelet lysate to substitute fetal bovine serum in hMSC expansion for translational applications: a systematic review. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):351. [5] LANER-PLAMBERGER S, OELLER M, MRAZEK C, et al. Upregulation of mitotic bookmarking factors during enhanced proliferation of human stromal cells in human platelet lysate. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):432. [6] BARRO L, BURNOUF PA, CHOU ML, Human platelet lysates for human cell propagation. Platelets. 2021;32(2):152-162. [7] VENNILA R, RAJA SUNDARI M SUNDARAM, SELVARAJ S, et al. Effect of human platelet lysate in differentiation of Wharton’s Jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2019; 19(8):1177-1191. [8] BEITIA M, DELGADO D, SNCHEZ P, et al. Platelet lysate nebulization protocol for the treatment of COVID-19 and its sequels: Proof of concept and scientific rationale. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1856. [9] NGUYEN VT, NARDINI M, RUGGIU A, et al. Platelet lysate induces in human osteoblasts resumption of cell proliferation and activation of pathways relevant for revascularization and regeneration of damaged bone. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):5123. [10] HUANG CT, CHU HS, HUNG KC, et al. The effect of human platelet lysate on corneal nerve regeneration. Br J Ophthalmol. 2021;105(6):884-890. [11] BIEBACK K, FERNANDEZ-MUÑOZ B, PATI S, et al. Gaps in the knowledge of human platelet lysate as a cell culture supplement for cell therapy: A joint publication from the American Association of Blood Banks and the International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy. Transfusion. 2019;59(11): 3448-3460. [12] MEFTAHPOUR V, MALEKGHASEMI S, BAGHBANZADEH A, et al. Platelet lysate: a promising candidate in regenerative medicine. Regen Med. 2021; 16(1):71-85. [13] SHIH DT, BURNOUF T. Preparation, quality criteria, and properties of human blood platelet lysate supplements for ex vivo stem cell expansion. N Biotechnol. 2015;32:199-211. [14] DREW VJ, TSENG CL, SEGHATCHIAN J, et al. Reflections on dry eye syndrome treatment: Therapeutic role of blood products.Front Med (Lausanne). 2018; 5:33. [15] LOSI P, BARSOTTI MC, FOFFA I, et al. In vitro human cord blood platelet lysate characterisation with potential application in wound healing. Int Wound J. 2020;17(1):65-72. [16] BAIGGER A, EICKE D, YUZEFOVYCH Y, et al. Characterization of induced pluripotent stemcell-derived megakaryocyte lysates for potential regenerative applications. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22:4545-4549. [17] BURNOUF T, STRUNK D, KOH MB, et al. Human platelet lysate: Replacing fetal bovine serum as a gold standard for human cell propagation? Biomaterials. 2016;76:371-387. [18] SHANBHAG S, STAVROPOULOS A, SULIMAN S, et al. Efficacy of humanized mesenchymal stem cell cultures for bone tissue engineering: A systematic review with a focus on platelet derivatives. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017; 23(6):552-569. [19] STRUNK D, LOZANO M, MARKS DC, et al. International Forum on GMP-grade human platelet lysate for cell propagation: summary. Vox Sang. 2018; 113(1):80-87. [20] DELILA L, WU YW, NEBIE O, et al. Extensive characterization of the composition and functional activities of five preparations of human platelet lysates for dedicated clinical uses. Platelets. 2020;27:1-14. [21] SHANBHAG S, MOHAMED-AHMED S, LUNDE THF, et al. Influence of platelet storage time on human platelet lysates and platelet lysate-expanded mesenchymal stromal cells for bone tissue engineering. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):351. [22] ALTAIE A, OWSTON H, JONES E. Use of platelet lysate for bone regeneration-Are we ready for clinical translation? World J Stem Cells. 2016;8(2):47-55. [23] KLATTE-SCHULZ F, SCHMIDT T. Comparative analysis of different platelet lysates and platelet rich preparations to stimulate tendon cell biology: An in vitro study.Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):212. [24] STRANDBERG G, SELLBERG F, SOMMAR P, et al. Standardizing the freeze-thaw preparation of growth factors from platelet lysate. Transfusion. 2017; 57(4):1058-1065. [25] ZHANG Y, ZHUANG D, ZHANG Y, et al. Super activated platelet lysate, a novel autologous Platelet lysate, regulates the expression of inflammasome and cytokine in the experimental periodontitis in rats. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:5535-5543. [26] 刘春香,王博昊,张怡.超活化富血小板裂解液的制备及其对雄激素性脱发小鼠模型毛囊再生作用[J]. 国际生物制品学杂志,2020,43(1):16-19. [27] COLE JP, COLE MA, INSALACO C, et al. Alopecia and platelet-derived therapies. Stem Cell Investig. 2017;4:88. [28] CHEN LW, HUANG CJ, TU WH, et al. The corneal epitheliotrophic abilities of lyophilized powder form human platelet lysates. PLoS One. 2018;13(3): e0194345. [29] CHEN MS, WANG TJ, LIN HC, et al. Four types of human platelet lysate, including one virally inactivated by solvent-detergent, can be used to propagate Wharton jelly mesenchymal stromal cells. N Biotechnol. 2019; 49:151-160. [30] WANG TJ, CHEN MS, CHOU ML, et al. Comparison of three human platelet lysates used as supplements for in vitro expansion of corneal endothelium cells. Transfus Apher Sci. 2017;56(5):769-773. [31] SANTOS SCNDS, SIGURJONSSON ÓE, CUSTÓDIO CA, et al. Blood plasma derivatives for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine therapies. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2018;24(6):454-462. [32] LEE HW, CHOI KH, KIM JY, et al. Proteomic classification and identification of proteins related to tissue healing of platelet-rich plasma. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020;12(1):120-129. [33] ZAMANI M, YAGHOUBI Y,MOVASSAGHPOUR A, et al. Novel therapeutic approaches in utilizing platelet lysate in regenerative medicine: Are we ready for clinical use? J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):17172-17186. [34] ITO R, MORIMOTO N, PHAM LH, et al. Efficacy of the controlled release of concentrated platelet lysate from a collagen/gelatin scaffold for dermis-like tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(11-12):1398-1405. [35] LEOTOT J, COQUELIN L, BODIVIT G, et al. Platelet lysate coating on scaffolds directly and indirectly enhances cell migration, improving bone and blood vessel formation. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(5):6630-6640. [36] TORREGGIANI E, PERUT F, RONCUZZI L, et al. Exosomes: Novel effectors of human platelet lysate activity. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;28:137-151. [37] BERGER DR, CENTENO CJ, STEINMETZ NJ. Platelet lysates from aged donors promote human tenocyte proliferation and migration in a concentration-dependent manner. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(1):32-40. [38] TAN XX, JU HY, YAN W, et al. Autologous platelet lysate local injections for the treatment of refractory lateral epicondylitis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:17. [39] 严伟,谭训香,姜红江,等.体外冲击波联合血小板裂解液局部注射治疗难治性肱骨外上髁炎[J].中医正骨,2016,28(8):52-55. [40] CENTENO C, MARKLE J, DODSON E, et al. The use of lumbar epidural injection of platelet lysate for treatment of radicular pain. J Exp Orthop. 2017;4(1):38. [41] 刘广亚,许育兵,张喻,等.富血小板血浆与血小板裂解液治疗跟腱炎的比较研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(10):22-25. [42] AL-AJLOUNI J, AWIDI A, SAMARA O, et al. Safety and efficacy of autologous intra-articular platelet lysates in early and intermediate knee osteoarthrosis in humans: A prospective open-label study. Clin J Sport Med. 2015;25(6):524-528. [43] SAMARA O, AL-AJLOUNI J, AL-NAJAR M, et al. Intra-articular autologous platelet lysates produce positive MRI structural changes in early and intermediate knee osteoarthrosis. PJR. 2016;27(1):14-18. [44] 严伟,刘海宁,宋修刚,等.关节腔内重复注射血小板裂解液治疗早期膝骨关节炎疗效观察[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(10):906-909. [45] 侯燕,秦立武,鞠昌军,等.血小板裂解液关节腔注射治疗膝骨性关节炎的临床观察[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(11):29-32. [46] 鞠昌军,姜红江,高广凌,等.体外人工膝支具辅助血小板裂解液治疗膝关节骨性关节炎的临床疗效分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志, 2018,4(4):224-227. [47] 鞠昌军,严伟,赵锦伟,等.血小板裂解液与富血小板血浆治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2020,14(5):565-571. [48] JIANG HJ, TAN XX, JU HY, et al. Autologous platelet lysates local injections for treatment of tibia non-union with breakage of the nickelclad: a case report. Springerplus. 2016;5(1):2013. [49] YU DM, ZHANG T, LIU JH, et al. The molecular mechanism of platelet lysate promotes transformation of non-union cells into osteoblasts. Transl Cancer Res. 2020;9(3):1985-1992. [50] RAWSON B. Platelet-rich Plasma and epidural platelet lysate: Novel treatment for lumbar disk herniation. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2020;120(3):201-207. [51] FEA AM, ARAGNO V, TESTA V, et al. The effect of autologous platelet lysate eye drops: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:8406832. [52] ABU-AMEERH MA, JAFAR HD, HASAN MH, et al. Platelet lysate promotes re-epithelialization of persistent epithelial defects: A pilot study. Int Ophthalmol. 2019;39(7):1483-1490. [53] SAMARKANOVA D, MARTIN S, BISBE L, et al. Clinical evaluation of allogeneic eye drops from cord blood platelet lysate. Blood Transfus. 2020. doi: 10.2450/2020.0130-20. [54] PEZZOTTA S, DEL FANTE C, SCUDELLER L. Long-term safety and efficacy of autologous platelet lysate drops for treatment of ocular GvHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;52(1):101-106. [55] VALENTINI CG, NUZZOLO ER, ORLANDO N, et al. Cytokine profile of autologous platelet‐ derived eye drops in patients with ocular chronic graft ‐versus‐ host disease. Vox Sanguinis. 2016;110(2):189-192. [56] ZALLIO F, MAZZUCCO L, MONACO F, et al. Single-center pilot prospective study of topical application of platelet-derived eye drops for patients with ocular chronic graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(9):1664-1670. [57] AHMED EM, ALI S, GAAFAR SM, et al. Evaluation of topical human platelet lysate versus topical clobetasol in management of methotrexate-induced oral ulceration in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Randomized-controlled clinical trial. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;73:389-394. [58] JAFAR H, HASAN M, AL-HATTAB D, et al. Platelet lysate promotes the healing of long-standing diabetic foot ulcers: A report of two cases and in vitro study. Heliyon. 2020;6(5):e03929. [59] LABIBZADEH N, EMADEDIN M, FAZELI R, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells implantation in combination with platelet lysate product is safe for reconstruction of human long bone nonunion. Cell J. 2016;18(3):302-309. [60] CENTENO CJ, AL-SAYEGH H, FREEMAN MD, et al. A multi-center analysis of adverse events among two thousand, three hundred and seventy two adult patients undergoing adult autologous stem cell therapy for orthopaedic conditions. Int Orthop. 2016;40(8):1755-1765. [61] CENTENO C, MARKLE J, DODSON E, et al. Symptomatic anterior cruciate ligament tears treated with percutaneous injection of autologous bone marrow concentrate and platelet products: a non-controlled registry study. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):246. [62] CENTENO C, SHEINKOP M, DODSON E, et al. A specific protocol of autologous bone marrow concentrate and platelet products versus exercise therapy for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial with 2 year follow-up. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):355. [63] CENTENO C, FAUSEL Z, STEMPER I, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the treatment of rotator cuff tears with bone marrow concentrate and platelet products compared to exercise therapy: A midterm analysis. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:5962354. [64] PROTOGEROU V, MICHALOPOULOS E, MALLIS P, et al. Administration of adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet lysate in erectile dysfunction: A single center pilot study. Bioengineering (Basel). 2019;6(1):21. [65] PROTOGEROU V, BESHARI SE, MICHALOPOULOS E, et al. The combined use of stem cells and platelet lysate plasma for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: A pilot study-6 months results. Medicines (Basel). 2020;7(3):14. [66] MIDDLETON EA, WEYRICH AS, ZIMMERMAN GA. Platelets in pulmonary immune responses and inflammatory lung diseases. Physiol Rev. 2016;96: 1211-1259. [67] JEYARAMAN M, RANJAN R, KUMAR R, et al. Cellular Therapy: Shafts of Light Emerging for COVID-19. Stem Cell Investig. 2020;7:11. [68] SANTO VE, POPA EG, MANO JF, et al. Natural assembly of platelet lysate-loaded nanocarriers into enriched 3D hydrogels for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2015;19:56-65. [69] ROBINSON ST, DOUGLAS AM, CHADID T, et al. A novel platelet lysate hydrogel for endothelial cell and mesenchymal stem cell-directed neovascularization. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:86-98. [70] ALMEIDA LDF, BABO PS, SILVA CR, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels incorporating platelet lysate enhance human pulp cell proliferation and differentiation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(6):88. [71] BABO PS, CAI X, PLACHOKOVA AS, et al. Evaluation of a platelet lysate bilayered system for periodontal regeneration in a rat intrabony three-wall periodontal defect. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):e1277-e1288. [72] COSTA-ALMEIDA R, CALEJO I, ALTIERI R, et al. Exploring platelet lysate hydrogel-coated suture threads as biofunctional composite living fibers for cell delivery in tissue repair. Biomed Mater. 2019;14(3):034104. [73] FRAZER H, YOU J, CHEN Z, et al. Development of a platelet lysate-based printable, transparent biomaterial with regenerative potential for epithelial corneal injuries. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2020;9(13):40. [74] HUANG ZP, WANG WT, WANG QL, et al. Coaxial nanofiber scaffold with super-active platelet lysate to accelerate the repair of bone defects. RSC Adv. 2020;10:35776-35786. [75] TANG Q, LIM T, SHEN LY, et al. Well-dispersed platelet lysate entrapped nanoparticles incorporate with injectable PDLLA-PEG-PDLLA triblock for preferable cartilage engineering application. Biomaterials. 2021;268:120605. [76] MENDES BB, DALY AC, REIS RL, et al. Injectable hyaluronic acid and platelet lysate-derived granular hydrogels for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2021;119:101-113. [77] DAIKUARA LY, YUE Z, SKROPETA D, et al. In vitro characterisation of 3D printed platelet lysate-based bioink for potential application in skin tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2021;7:36. [78] CHOU ML, WU JW, GOUEL F, et al. Tailor-made purified human platelet lysate concentrated in neurotrophins for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Biomaterials. 2017;142:77-89. [79] LEITER O, WALKER TL. Platelets in Neurodegenerative Conditions-Friend or Foe? Front Immunol. 2020;11:747. |
| [1] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [2] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [3] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [4] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [5] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [8] | Guo Xiaohui, Song Xizheng, Xiang Hanrui, Kang Zhaorong, Li Daming, Kang Yu, Hu Jun, Sheng Kai. External spinal fixation elastic stress in the treatment of jumping spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 919-923. |
| [9] | Li Weiming, Xu Qingwen, Li Yijun, Sun Yanbo, Cui Jin, Xu Pengyuan . Deep seawater promotes wound healing in diabetic mice by activating PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 724-729. |
| [10] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [11] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [12] | Yang Feng, Zhao Qian, Zhang Shixuan, Zhao Tienan, Feng Bo. Effectiveness and safety of rapamycin combined with CD133 antibody stent in preventing vascular restenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 579-584. |
| [13] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [14] | Maihemuti•Yakufu, Sun Qinqin, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yiliyaer•Abudusimu, Abudushalamu•Abudukelimu, Liu Jianjiang. Tension of 3D printed controllable tension band and skin regeneration of skin defect model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 371-375. |
| [15] | He Yiheng, Cheng Mingwei, Zhu Peijun, Xu Yan, Chen Jiahao, Lai Chunhua, Xu Shulan. Electroactive membrane promotes bone formation in rats in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4446-4451. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||