Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (25): 3993-3998.doi: 10.12307/2022.404
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of leptin receptor in mouse skin and the role of leptin receptor-positive cells in skin development and wound healing
Wang Ao, Chu Hongshang, Wu Hongguang, Li Ke, Liu Huijuan
- Bio-X Institutes, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
-
Received:2021-04-07Accepted:2021-05-14Online:2022-09-08Published:2022-01-26 -
Contact:Liu Huijuan, MD, Associate researcher, Master's supervisor, Bio-X Institutes, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China -
About author:Wang Ao, Master, Bio-X Institutes, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ao, Chu Hongshang, Wu Hongguang, Li Ke, Liu Huijuan. Expression of leptin receptor in mouse skin and the role of leptin receptor-positive cells in skin development and wound healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3993-3998.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
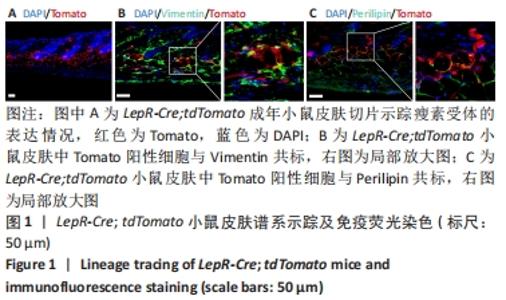
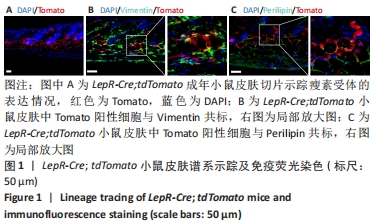
2.1 瘦素受体在小鼠皮肤中的谱系示踪 首先将LepR-Cre小鼠与Rosa26a-tdTomato小鼠杂交,构建LepR-Cre; tdTomato小鼠[25-26]。取2月龄LepR-Cre; tdTomato小鼠背部皮肤,进行冰冻切片观察Tomato阳性细胞在皮肤中的分布情况,结果显示Tomato阳性细胞存在于小鼠皮肤的真皮乳头、真皮层和真皮白色脂肪层中,见图1A。由于真皮乳头、真皮层和真皮白色脂肪层都属于皮肤间质,由此表明瘦素受体主要标记小鼠皮肤中的间质。Vimentin是一个常用的间质标记物,Perilipin是白色脂肪中脂肪细胞的常用标记物。Vimentin以及Perilipin免疫荧光染色结果显示Tomato阳性细胞可以与少量Vimentin阳性细胞共标,且在Tomato阳性细胞中Vimentin阳性细胞占比为(27.37±5.39)%,见图1B。Tomato阳性细胞与部分Perilipin阳性细胞共标,且共标比例为(25.26±4.54)%,见图1C。由此推测瘦素受体所标记的细胞类群很有可能是皮肤间充质干细胞中的一个谱系。"
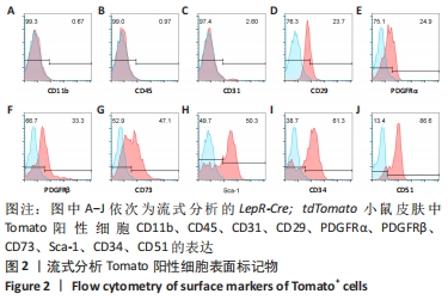
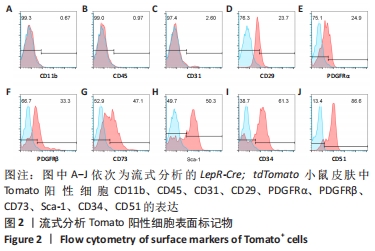
2.2 LepR-Cre; tdTomato小鼠皮肤细胞表面标记物流式分析 谱系示踪实验和免疫荧光染色显示,瘦素受体可能标记皮肤间充质干细胞中的一个亚群。在研究中鉴别一类细胞是否属于间充质干细胞,常常采用流式细胞表面标记物分析。该研究将2月龄LepR-Cre; tdTomato小鼠背部皮肤消化得到分散的细胞,使用经典的间充质干细胞表面标记物和其他间质标记物进行流式分析,结果显示Tomato阳性细胞CD11b、CD45、CD31呈阴性表达(0.67%, 0.97%, 2.60%)。Tomato阳性细胞表达典型的间充质干细胞标记物CD29、CD73、Sca-1(23.7%,47.1%,50.3%),且间质标记物PDGFRα、PDGFRβ、CD34、CD51呈阳性表达(24.9%,33.3%,61.3%,86.6%),见图2。之前的谱系示踪实验发现瘦素受体标记皮肤真皮白色脂肪层,而以往研究发现脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞高度表达CD34,这与流式鉴定的结果相吻合。以上结果表明,瘦素受体谱系细胞符合间充质干细胞的特征,并且还表达一些骨髓间充质干细胞标记物和其他常见的间质标记物,由此说明皮肤中瘦素受体阳性细胞属于一类间充质干细胞。"
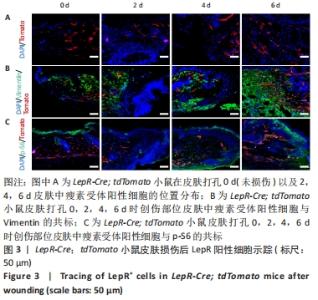
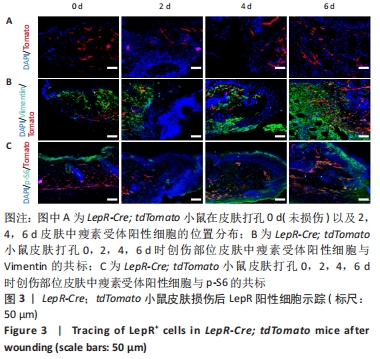
2.3 瘦素受体谱系细胞参与皮肤创伤愈合的进程 已知皮肤中的间充质干细胞在创伤愈合中发挥着关键作用,既然瘦素受体可以标记皮肤中的一类间充质干细胞,那么瘦素受体所标记的细胞谱系可能会参与到皮肤损伤修复的进程。因此,为了进一步探究瘦素受体谱系细胞在小鼠皮肤创伤愈合中的作用,该研究利用LepR-Cre; tdTomato小鼠构建小鼠背部直径为5 mm的皮肤全层切除创伤模型(此模型小鼠7 d创伤可以基本愈合)。在对小鼠皮肤打孔后的0 d(未损伤的正常皮肤)以及2,4,6 d分别取伤口部位皮肤,固定包埋进行冰冻切片,结果显示被Tomato红色荧光所标记的瘦素受体阳性细胞在伤口边缘及伤口中央都有分布,瘦素受体阳性细胞在伤口边缘部位增殖并迁移到伤口中央,并且细胞数量随时间逐渐增多,见图3A。通过免疫荧光染色染Vimentin,部分瘦素受体阳性细胞可以与Vimentin共标,即一部分瘦素受体阳性细胞以成纤维细胞的形式参与损伤修复,见图3B。免疫荧光染色显示在创伤愈合进程中瘦素受体谱系细胞表达p-S6,见图3C,在损伤修复过程中瘦素受体谱系细胞的mTOR信号通路被激活。小鼠皮肤损伤后的谱系示踪结果表明,在皮肤创伤愈合后瘦素受体标记的间质细胞被激活,通过增殖和迁移参与真皮层的重建,即瘦素受体谱系细胞参与皮肤损伤后的修复。"

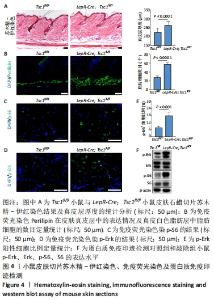
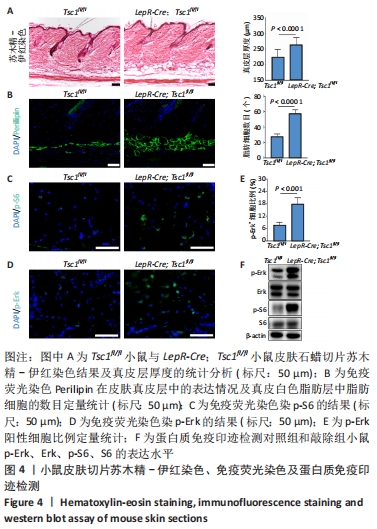
与对照组相比,敲除组小鼠的体型、体质量及生理状态无明显差异且发育正常。取2月龄对照组和敲除组小鼠背部均处于静息期的皮肤,进行组织固定包埋石蜡切片,经苏木精-伊红染色并借助图像软件测量统计,结果显示敲除组小鼠真皮层和真皮白色脂肪层厚度增加,见图4A。Perilipin免疫荧光染色显示敲除组小鼠Perilipin所标记的白色脂肪细胞数量增多,见图4B。免疫荧光染色结果显示敲除组小鼠真皮层中p-S6表达高于对照组小鼠,见图4C。此外,免疫荧光染色结果显示敲除组小鼠p-Erk阳性细胞比例明显高于对照组,见图4D,4E。Western blot检测结果也显示,与对照组相比,敲除组小鼠S6磷酸化水平和Erk磷酸化水平均明显上调,见图4F。以上结果表明,瘦素受体阳性细胞中敲除Tsc1后影响小鼠皮肤的发育,mTOR信号通路和MAPK信号通路激活,真皮层和真皮白色脂肪层结构受到影响。"

| [1] PAN WW, MYERS MG JR. Leptin and the maintenance of elevated body weight. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2018;19(2):95-105. [2] TRINH T, BROXMEYER HE. Role for Leptin and Leptin Receptors in Stem Cells During Health and Diseases. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(2):511-522. [3] FRIEDMAN JM. Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat Metab. 2019;1(8):754-764. [4] FU X, LIU G, HALIM A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration and Tissue Repair. Cells. 2019;8(8):784. [5] KFOURY Y, SCADDEN DT. Mesenchymal cell contributions to the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(3):239-253. [6] TARTAGLIA LA. The leptin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(10):6093-6096. [7] TRINH T, ROPA J, ALJOUFI A, et al. Leptin receptor, a surface marker for a subset of highly engrafting long-term functional hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia. 2020 Nov 7. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01079-z. [8] ZHOU BO, YUE R, MURPHY MM, et al. Leptin-receptor-expressing mesenchymal stromal cells represent the main source of bone formed by adult bone marrow. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15(2):154-168. [9] DING L, SAUNDERS TL, ENIKOLOPOV G, et al. Endothelial and perivascular cells maintain haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2012;481(7382):457-462. [10] COMAZZETTO S, MURPHY MM, BERTO S, et al. Restricted Hematopoietic Progenitors and Erythropoiesis Require SCF from Leptin Receptor+ Niche Cells in the Bone Marrow. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;24(3):477-486. [11] DECKER M, MARTINEZ-MORENTIN L, WANG G, et al. Leptin-receptor-expressing bone marrow stromal cells are myofibroblasts in primary myelofibrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(6):677-688. [12] ZHANG D, ZHANG S, WANG J, et al. LepR-Expressing Stem Cells Are Essential for Alveolar Bone Regeneration. J Dent Res. 2020;99(11):1279-1286. [13] ROGNONI E, WATT FM. Skin Cell Heterogeneity in Development, Wound Healing, and Cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2018;28(9):709-722. [14] FUCHS E. Skin Stem Cells in Silence, Action, and Cancer. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(5):1432-1438. [15] HORSLEY V. Skin in the Game: Stem Cells in Repair, Cancer, and Homeostasis. Cell. 2020;181(3):492-494. [16] DEKONINCK S, BLANPAIN C. Stem cell dynamics, migration and plasticity during wound healing. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):18-24. [17] GUERRERO-JUAREZ CF, PLIKUS MV. Emerging nonmetabolic functions of skin fat. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(3):163-173. [18] HU MS, BORRELLI MR, LORENZ HP, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review of the Background, Role, and Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:6901983. [19] RODRIGUES M, KOSARIC N, BONHAM CA, et al. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(1):665-706. [20] BOOTHBY IC, COHEN JN, ROSENBLUM MD. Regulatory T cells in skin injury: At the crossroads of tolerance and tissue repair. Sci Immunol. 2020;5(47): eaaz9631. [21] SAXTON RA, SABATINI DM. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell. 2017;168(6):960-976. [22] LAPLANTE M, SABATINI DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149(2):274-293. [23] KIM J, GUAN KL. mTOR as a central hub of nutrient signalling and cell growth. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):63-71. [24] CRINO PB, NATHANSON KL, HENSKE EP. The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(13):1345-1356. [25] KRETZSCHMAR K, WATT FM. Lineage tracing. Cell. 2012;148(1-2):33-45. [26] HORIE T, PARK G, INABA Y, et al. MAPK Erk5 in Leptin Receptor‒Expressing Neurons Controls Body Weight and Systemic Energy Homeostasis in Female Mice. Endocrinology. 2019;160(12):2837-2848. [27] DING X, BLOCH W, IDEN S, et al.mTORC1 and mTORC2 regulate skin morphogenesis and epidermal barrier formation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13226. [28] CIBRIAN D, DE LA FUENTE H, SÁNCHEZ-MADRID F. Metabolic Pathways That Control Skin Homeostasis and Inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(11): 975-986. [29] KRAMANN R, SCHNEIDER RK, DIROCCO DP, et al. Perivascular Gli1+ progenitors are key contributors to injury-induced organ fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(1): 51-66. [30] CURRIE JD, GROSSER L, MURAWALA P, et al. The Prrx1 limb enhancer marks an adult subpopulation of injury-responsive dermal fibroblasts. Biol Open. 2019; 8(7):bio043711. [31] LEAVITT T, HU MS, BORRELLI MR, et al. Prrx1 Fibroblasts Represent a Pro-fibrotic Lineage in the Mouse Ventral Dermis. Cell Rep. 2020;33(6):108356. [32] ABBASI S, SINHA S, LABIT E, et al. Distinct Regulatory Programs Control the Latent Regenerative Potential of Dermal Fibroblasts during Wound Healing. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27(3):396-412.e6. [33] TIKHONOVA AN, DOLGALEV I, HU H, et al. The bone marrow microenvironment at single-cell resolution. Nature. 2019;569(7755):222-228. [34] BLANPAIN C, SIMONS BD. Unravelling stem cell dynamics by lineage tracing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013;14(8):489-502. [35] EL AGHA E, KRAMANN R, SCHNEIDER RK, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Fibrotic Disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2017;21(2):166-177. [36] SEROWOKY MA, ARATA CE, CRUMP JG, et al. Skeletal stem cells: insights into maintaining and regenerating the skeleton. Development. 2020;147(5): dev179325. [37] RIFFAULT M, JOHNSON GP, OWEN MM, et al. Loss of Adenylyl Cyclase 6 in Leptin Receptor-Expressing Stromal Cells Attenuates Loading-Induced Endosteal Bone Formation. JBMR Plus. 2020;4(11):e10408. [38] FUCHS E, BLAU HM. Tissue Stem Cells: Architects of Their Niches. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27(4):532-556. [39] MACHADO L, GEARA P, CAMPS J, et al. Tissue damage induces a conserved stress response that initiates quiescent muscle stem cell activation. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(6):1125-1135.e7. [40] WELLS JM, WATT FM. Diverse mechanisms for endogenous regeneration and repair in mammalian organs. Nature. 2018;557(7705):322-328. [41] LIU GY, SABATINI DM. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(4):183-203. [42] HENSKE EP, JÓŹWIAK S, KINGSWOOD JC, et al. Tuberous sclerosis complex. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16035. [43] MENG D, FRANK AR, JEWELL JL. mTOR signaling in stem and progenitor cells. Development. 2018;145(1):dev152595. [44] XIANG X, ZHAO J, XU G, et al. mTOR and the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011;43(7):501-510. [45] HE D, WU H, XIANG J, et al. Gut stem cell aging is driven by mTORC1 via a p38 MAPK-p53 pathway. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):37. [46] ROBB KP, FITZGERALD JC, BARRY F, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy: progress in manufacturing and assessments of potency. Cytotherapy. 2019; 21(3):289-306. [47] GOLCHIN A, FARAHANY TZ, KHOJASTEH A, et al. The Clinical Trials of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in Skin Diseases: An Update and Concise Review. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(1):22-33. [48] ZHANG R, MA J, HAN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell related therapies for cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(10):6275-6289. [49] STAFF NP, JONES DT, SINGER W. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(5):892-905. [50] CAPLAN AI, CORREA D. The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(1): 11-15. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [5] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [6] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [7] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [8] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [9] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [10] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Li Weiming, Xu Qingwen, Li Yijun, Sun Yanbo, Cui Jin, Xu Pengyuan . Deep seawater promotes wound healing in diabetic mice by activating PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 724-729. |
| [13] | Huang Chuanjun, Zou Yu, Zhou Xiaoting, Zhu Yangqing, Qian Wei, Zhang Wei, Liu Xing. Transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in RADA16-BDNF hydrogel promotes neurological recovery in an intracerebral hemorrhage rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 510-515. |
| [14] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [15] | Huang Shibo, Xie Hui, Wang Zongpu, Wang Weidan, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Application of degradable high-purity magnesium screw in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 493-498. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||