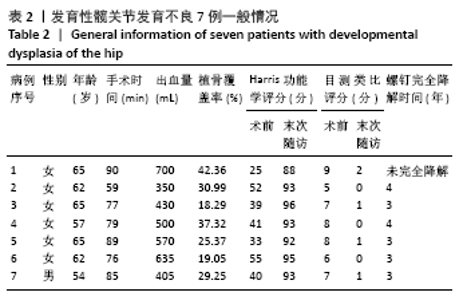
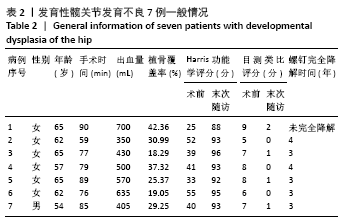
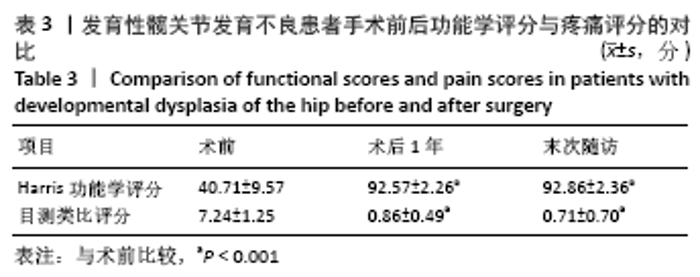
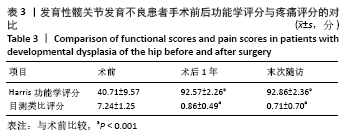
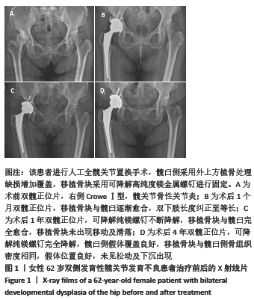
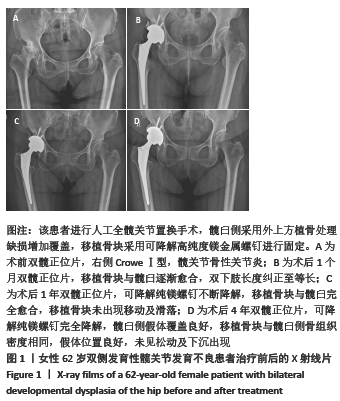
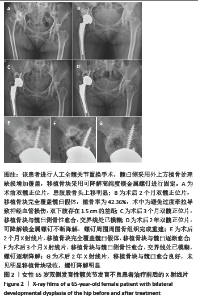
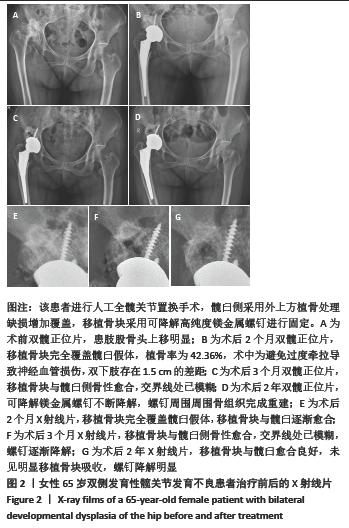
[1] 程亮亮,赵德伟.成人发育性髋关节发育不良的诊治现状[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(7):516-520.
[2] 林传松,杨爱勇,关钦强,等.全髋关节置换治疗髋臼发育不良继发骨性关节炎的临床研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(2): 145-146.
[3] 吴立东,熊炎,严世贵,等.非骨水泥白杯加自体股骨头植骨全髋关节置换术治疗髋白发育不良伴骨性关节炎中华外科杂志,2004, 42(16):1006-1009.
[4] 朱俊峰,陈晓东,沈超,等.髋臼结构植骨在Crowe Ⅲ或Ⅳ型髋关节发育不良关节置换术中的应用[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2014, 19(1):15-18.
[5] CHEN M, LUO ZL, WU KR, et al. Cementless total hip arthroplasty with a high hip center for hartofilakidis type B developmental dys- plasia of the hip: results of midterm follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(5): 1027-1034.
[6] IWASE T, MORITA D, ITO T, et al. Favorable results of primary total hip arthroplasty with acetabular impaction bone grafting for large segmental bone defects in dysplastic hips. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31 (10):2221-2226.
[7] ISHIDOU Y, MATSUYAMA K, SAKUMA D, et al. Osteoarthritis ofthe hip joint in elderly patients is most commonly atrophic, with low parameters of acetabular dysplasia and possibleinvolvement of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2017;12(1):30.
[8] KOMIYAM K, NAKASHIMA Y, HIRATA M, et al. Does High Hip Center Decrease Range of Motion in Total Hip Arthroplasty? A ComputerSimulation Study. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10):2342-2347.
[9] AL-AMIRY B, MAHMOOD S, KRUPIC F, et al. Leg lengthening and femoral-offset reduction after total hip arthroplasty: where is theproblem-stem or cup positioning? Acta Radiol. 2017;58(9):1125-1131.
[10] 彭阳,杨柳,陈光兴,等.Crowe Ⅲ及Ⅳ型髋关节发育不良全髋关节置换术中髋臼骨缺损的重建[J].中华外科杂志,2014,52(1):25-29.
[11] ABOLGHASEMIAN M, SAMIEZADEH S, JAFARI D, et al. Displacement of the hip center of rotation after arthroplasty of Crowe III and IV dysplasia: a radiological and biomechanical study. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(6):1031-1035.
[12] NOVIANA D, PARAMITHA D, ULUM MF, et al. The effect of hydrogen gas evolution of magnesium implant on the postimplantation mortality of rats. J Orthop Transl. 2016;5:9-15.
[13] 陈及非,阎作勤,陈云苏,等.利用股骨头结构性植骨人工全髋关节置换治疗Crowe Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型髋关节发育不良[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(3):270-273.
[14] 翟吉良,翁习生,林进,等.自体股骨头重建髋臼治疗髋关节发育不良的中期疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(4):401-406
[15] 陈焕杰,杨洪泉.髋臼内壁穿透法行全髋关节置换术治疗髋关节发育不良的疗效[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(11):1024-1026.
[16] COLO E, RIJNEN WH, GARDENIERS JW, et al. Satisfying Results of Primary Hip Arthroplasty in Patients With Hip Dysplasia at a Mean Followup of 20 Years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(11):2462-2468.
[17] ZHENG X, GUO KJ, ZHAO FC, et al. Medial Protrusio Technique in Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Prospective 6- to 9-Year Follow-Up of 43 Consecutive Patients. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(8):1761-1766.
[18] 尹诗九,钟航,李锐博,等.CroweⅢ型髋关节发育不良人工全髋关节置换术中自体股骨头结构植骨重建髋臼疗效分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(1):20-24.
[19] SEAGRAVE KG, TROELSEN A, MALCHAU H, et al. Acetabular cup position and risk of dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2016;(1):10-17.
[20] 查国春,冯硕,马桥桥,等.髋关节发育不良全髋关节置换术中髋臼覆盖率对臼杯初始稳定性的影响[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(19): 1215-1221.
[21] 胡兴,冯华明,黄笃,等.髋臼加盖技术行全髋关节置换术治疗发育性髋脱位[J].临床骨科杂志,2020,23(1):55-57.
[22] 杨鉴,梁灿,张会忠.严重髋臼缺损髋关节发育不良患者全髋置换中采用结构性植骨重建髋臼的有效性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(32):5092-5096.
[23] 刘宏鸣,朱吉桂,叶峥,等.植骨加盖行生物学固定型全髋关节置换治疗严重成人髋关节发育不良[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(26):4120-4124.
[24] HUANG S, WANG B, ZHANG X, et al. High-purity weight-bearing magnesium screw:Translational application in the healing of femoral-neck-fracture. Biomaterials. 2020;238:119829.
[25] ZHANG XZ, ZU HY, ZHAO DW, et al. Ion channel functional protein kinase TRPM7 regulates Mg ions to promote the osteoinduction of human osteoblast via PI3K pathway: In vitro simulation of the bone-repairing effect of Mg-based alloy implant. Acta Biomater. 2017;63: 369-382.
[26] CHENG PF, HAN P, ZHAO CL, et al. High-purity magnesium interference screws promote fibrocartilaginous entheses regeneration in the anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction rabbit model via accumulation of BMP-2 and VEGF. Biomaterials. 2016;81:14-26.
[27] TANG TT, QIN L. Translational study of orthopaedic biomaterials and devices. J Orthop Transl. 2016;5:69-71.
[28] WITTE F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: a review. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:1680-1692.
[29] ZHAO DW, WITTE F, LU F, et al. Current status on clinical applications of magnesium-based orthopaedic implants: A review from clinical translational perspective. Biomaterials. 2017;112:287e302.
[30] ZHAO D, HUANG S, LU F, et al. Vascularized bone grafting fixed by biodegradable magnesium screw for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biomaterials. 2016;81:84-92. |