[1] LANE NE. Epidemiology, etiology, and diagnosis of osteoporosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;194(2):S3-11.
[2] 张超,吴斌,陈懿.骨质疏松诊疗现状及发展前景探讨[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(5):727-728.
[3] 邱贵兴,裴福兴,胡侦明,等.中国骨质疏松性骨折诊疗指南[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015,8(5):371-374。
[4] MONZÓN DG, ISERSON KV, JAUREGUI J, et al. Total hip arthroplasty for hip fractures: 5-year follow-up of functional outcomes in the oldest independent old and very old patients. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2014;5(1):3-8.
[5] BHANDARI M, BAJAMMAL S, GUYATT GH, et al. Effect of bisphosphonates on periprosthetic bone mineral density after total joint arthroplasty.A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg(Am). 2005;87(2): 293-301.
[6] SCOTT DF, WOLTZ JN, SMITH RR. Effect of zoledronic acid on reducing femoral bone mineral density loss following total hip arthroplasty: preliminary results of a prospective randomized trial. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(4):671-675.
[7] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006; 17(12):1726-1733.
[8] 周伟,郭晓斌,刘禹,等.唑来膦酸对绝经后骨质疏松症患者假体周围骨密度的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(4):488-494.
[9] 王友强.髋关节置换治疗晚期股骨头缺血性坏死64例分析[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(9):56-57.
[10] 王巍,郭金库,何飞熊,等.单次静脉滴注唑来膦酸对全髋关节置换术后假体早期移位及临床疗效的影响[J].浙江医学,2019,41(11): 1143-1146.
[11] SURATWALA SJ, CHO SK, VAN RAALTE JJ, et al. Enhancement of periprosthetic bone quality with topical hydroxyapatite-bisphosphonate composite. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(10):2189-2196.
[12] JAKOBSEN T, KOLD S, SHIGUETOMI-MEDINA J, et al. Topical zoledronic acid decreases micromotion induced bone resorption in a sheep arthroplasty model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):441.
[13] 王凌斌,陆龙卫,赵凯.唑来膦酸在骨科领域的相关研究与应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(7):639-643.
[14] BLACK DM, DELMUS PD, EASTELL R, et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356(18):1809-1822.
[15] DEMPSTER DW, ROSCHGER P, MISOF BM, et al. Differential effects of teriparatide and zoledronic acid on bone minerallization density distribution at 6 and 24 months in short study. J Bone Miner Res. 2016; 31(8):1527-1535.
[16] KELLESARIAN SV, SUBHI AL, HARTHI S, et al. Effect of local zoledronate delivery on osseointegration: a systematic review of preclinical studies. Acta Odontol Scand. 2017;75(7): 530-541.
[17] 魏更生,吴京亮,吴磊.老年骨质疏松性髋部骨折患者的药物起始率及依从性分析[J].临床骨科杂志,2017,20(2):175-178.
[18] 袁宏,陆琳松,钟惠琴,等.唑来膦酸对骨质疏松患者全髋关节置换术后假体周围骨密度的影响[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,8(3):278-285.
[19] JAKOBSEN T, BECHTOLD JE, SØBALLE K, et al. Local delivery of zoledronate from a poly (d, l- lactide)- coating increases fixation of hydroxy-coated implants. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(5):974-979.
[20] JAKOBSEN T, BECHTOLD JE, SØBALLE K, et al. Local delivery of zoledronate from a poly (D, L- lactide) - Coating increases fixation of press-fit implants. J Orthop Res. 2016;34(1):65-71.
[21] 任民,甄平,李旭升,等.人工全髋关节置换术后髋臼松动的诊断策略[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(12):1148-1149.
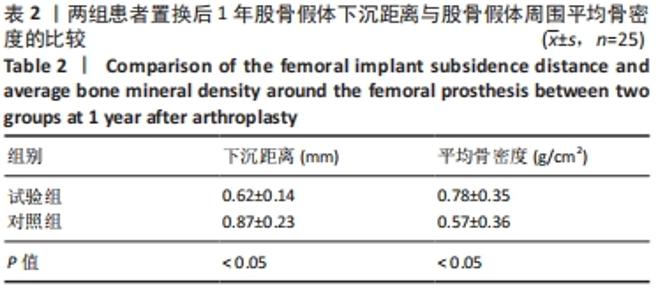
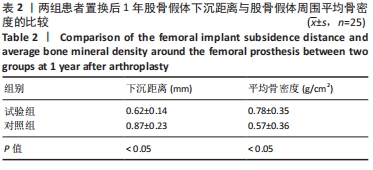
|