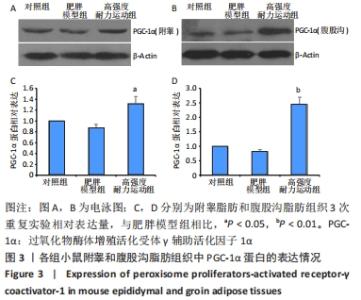
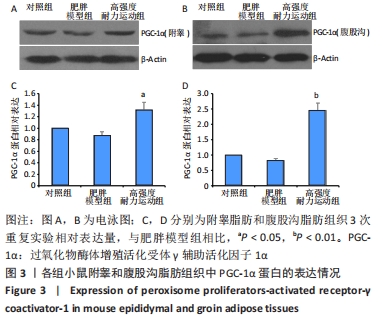
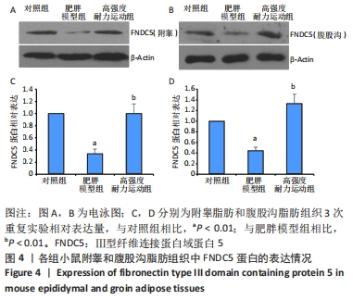
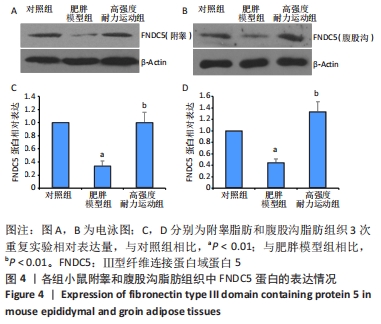
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 707-713.doi: 10.12307/2023.065
Previous Articles Next Articles
High-intensity endurance exercise influences browning of white adipose tissue in a mouse model of high-fat diet induced obesity
Li Yujiao, Su Kunxia
- Public Education Department of Zhongyuan Institute of Science and Technology, Zhengzhou 451400, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-06Accepted:2022-04-18Online:2023-02-18Published:2022-07-22 -
Contact:Su Kunxia, PhD candidate, Associate professor, Public Education Department of Zhongyuan Institute of Science and Technology, Zhengzhou 451400, Henan Province, China -
About author:Li Yujiao, Lecturer, Public Education Department of Zhongyuan Institute of Science and Technology, Zhengzhou 451400, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yujiao, Su Kunxia. High-intensity endurance exercise influences browning of white adipose tissue in a mouse model of high-fat diet induced obesity[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 707-713.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
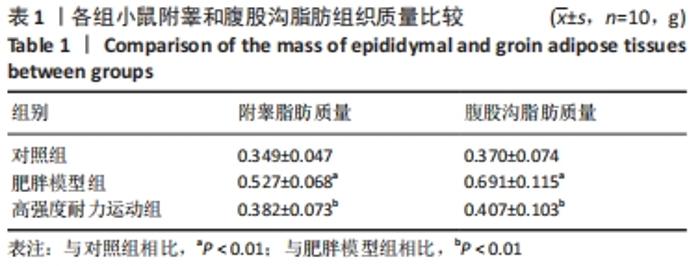
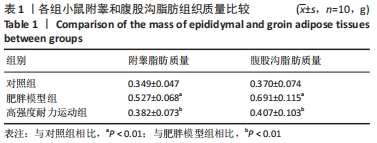
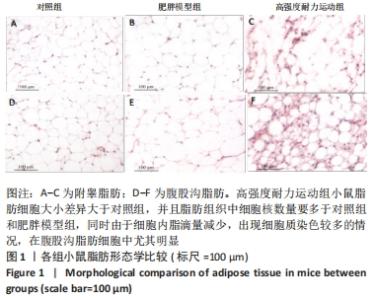
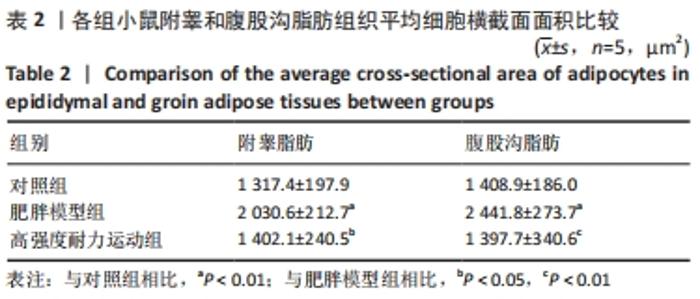
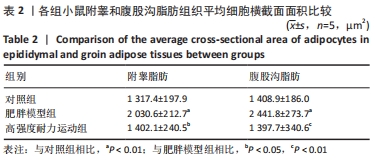
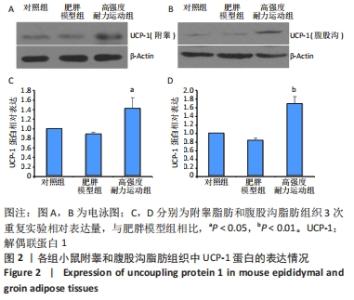
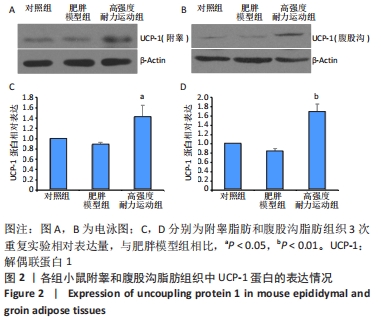
| [1] CINTI S. Adipose Organ Development and Remodeling. Compr Physiol. 2018;8(4):1357-1431. [2] SHAPIRA SN, SEALE P. Transcriptional Control of Brown and Beige Fat Development and Function. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019;27(1):13-21. [3] CINTI S. Transdifferentiation properties of adipocytes in the adipose organ. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;297(5):E977-986. [4] ZINGARETTI MC, CROSTA F, VITALI A, et al. The presence of UCP1 demonstrates that metabolically active adipose tissue in the neck of adult humans truly represents brown adipose tissue. FASEB J. 2009; 23(9):3113-3120. [5] FLETCHER LA, KIM K, LEITNER BP, et al. Sexual Dimorphisms in Adult Human Brown Adipose Tissue. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2020;28(2):241-246. [6] LOELIGER R C, MAUSHART C I, GASHI G, et al. Relation of diet-induced thermogenesis to brown adipose tissue activity in healthy men. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021;320(1):E93-E101. [7] KEUPER M, JASTROCH M. The good and the BAT of metabolic sex differences in thermogenic human adipose tissue. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;533111337. [8] CYPESS AM, WHITE AP, VERNOCHET C, et al. Anatomical localization, gene expression profiling and functional characterization of adult human neck brown fat. Nat Med. 2013;19(5):635-639. [9] CHU D T, GAWRONSKA-KOZAK B. Brown and brite adipocytes: Same function, but different origin and response. Biochimie. 2017;138102-138105. [10] BARBATELLI G, MURANO I, MADSEN L, et al. The emergence of cold-induced brown adipocytes in mouse white fat depots is determined predominantly by white to brown adipocyte transdifferentiation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;298(6):E1244-1253. [11] SIDOSSIS L, KAJIMURA S. Brown and beige fat in humans: thermogenic adipocytes that control energy and glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(2):478-486. [12] ALTINOVA AE. Beige Adipocyte As The Flame Of White Adipose Tissue: Regulation Of Browning And Impact Of Obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022;107(5):e1778-e1788. [13] BLÜHER M. Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019;15(5):288-298. [14] STANFORD KI, MIDDELBEEK RJ, GOODYEAR LJ. Exercise Effects on White Adipose Tissue: Beiging and Metabolic Adaptations. Diabetes. 2015;64(7):2361-2368. [15] ALDISS P, BETTS J, SALE C, et al. Exercise-induced ‘browning’ of adipose tissues. Metabolism. 2018;81:63-70. [16] TAPIA P, FERNANDEZ-GALILEA M, ROBLEDO F, et al. Biology and pathological implications of brown adipose tissue: promises and caveats for the control of obesity and its associated complications. 2018;93(2):1145-1164. [17] JAKICIC JM, ROGERS RJ, DAVIS KK, et al. Role of Physical Activity and Exercise in Treating Patients with Overweight and Obesity. Clin Chem. 2018;64(1):99-107. [18] KLENTROU P, PLYLEY M. Onset of puberty, menstrual frequency, and body fat in elite rhythmic gymnasts compared with normal controls. Br J Sports Med. 2003;37(6):490-494. [19] ARGENTATO PP, DE CÁSSIA CÉSAR H, ESTADELLA D, et al. Programming mediated by fatty acids affects uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) in brown adipose tissue. Br J Nutr. 2018;120(6):619-627. [20] DEMINE S, RENARD P, ARNOULD T. Mitochondrial Uncoupling: A Key Controller of Biological Processes in Physiology and Diseases. Cells. 2019;8(8):795. [21] KHALAFI M, MOHEBBI H, SYMONDS ME. The Impact of Moderate-Intensity Continuous or High-Intensity Interval Training on Adipogenesis and Browning of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue in Obese Male Rats. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):925. [22] PICOLI CC, GILIO GR, HENRIQUES F, et al. Resistance exercise training induces subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue browning in Swiss mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020;129(1):66-74. [23] LI J, YI X, LI T, et al. Effects of exercise and dietary intervention on muscle, adipose tissue, and blood IRISIN levels in obese male mice and their relationship with the beigeization of white adipose tissue. Endocr Connect. 2022;11(3):e210625. [24] TSILOULIS T, CAREY A L, BAYLISS J, et al. No evidence of white adipocyte browning after endurance exercise training in obese men. Int J Obes (Lond). 2018;42(4):721-727. [25] SON M J, OH K J, PARK A, et al. GATA3 induces the upregulation of UCP-1 by directly binding to PGC-1α during adipose tissue browning. Metabolism. 2020;109:154280. [26] SENAMONTREE S, LAKTHAN T, CHAROENPANICH P, et al. Betulinic acid decreases lipid accumulation in adipogenesis-induced human mesenchymal stem cells with upregulation of PGC-1α and UCP-1 and post-transcriptional downregulation of adiponectin and leptin secretion. PeerJ. 2021;9:e12321. [27] HEIAT F, HEIAT M, SHOJAEIFARD M. Changes in mitochondrial biogenesis and fatty liver indicators in rat following continuous and high intensity interval training.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2021;61(10):1416-1422. [28] LIU Y, GUO C, LIU S, et al. Eight Weeks of High-Intensity Interval Static Strength Training Improves Skeletal Muscle Atrophy and Motor Function in Aged Rats via the PGC-1α/FNDC5/UCP1 Pathway. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:811-821. [29] RODRIGUEZ LANZI C, PERDICARO DJ, GAMBARTE TUDELA J, et al. Grape pomace extract supplementation activates FNDC5/irisin in muscle and promotes white adipose browning in rats fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2020;11(2):1537-1546. [30] 苏坤霞. 不同强度耐力运动影响高脂诱导肥胖模型小鼠血清Irisin含量、骨骼肌PGC-1α、FNDC5、PPARδ蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(3):427-434. [31] JANDOVA T, BUENDÍA-ROMERO A. Long-Term Effect of Exercise on Irisin Blood Levels-Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare (Basel). 2021;9(11):1438. [32] 苏坤霞. 运动训练联合奥利司他对肥胖小鼠减肥及运动能力的影响[J]. 河南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018,4(2):89-94. [33] GARCIA-HERMOSO A, RAMIREZ-VELEZ R, RAMIREZ-CAMPILLO R, et al. Concurrent aerobic plus resistance exercise versus aerobic exercise alone to improve health outcomes in paediatric obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(3):161-166. [34] GOPALAN V, YALIGAR J, MICHAEL N, et al. A 12-week aerobic exercise intervention results in improved metabolic function and lower adipose tissue and ectopic fat in high-fat diet fed rats.Biosci Rep. 2021;41(1): BSR20201707. [35] BAE JY, WOO J, ROH HT, et al. The effects of detraining and training on adipose tissue lipid droplet in obese mice after chronic high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2017;16(1):13. [36] BAILEY JW, BARKER RL, BEAUCHENE RE. Age-related changes in rat adipose tissue cellularity are altered by dietary restriction and exercise. J Nutr. 1993;123(1):52-58. [37] KALINOVICH AV, DE JONG JM, CANNON B, et al. UCP1 in adipose tissues: two steps to full browning. Biochimie. 2017;134127-134137. [38] PUIGSERVER P, WU Z, PARK CW, et al. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell. 1998; 92(6):829-839. [39] WU MV, BIKOPOULOS G, HUNG S, et al. Thermogenic capacity is antagonistically regulated in classical brown and white subcutaneous fat depots by high fat diet and endurance training in rats: impact on whole-body energy expenditure. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(49):34129-34140. [40] SLOCUM N, DURRANT JR, BAILEY D, et al. Responses of brown adipose tissue to diet-induced obesity, exercise, dietary restriction and ephedrine treatment. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013;65(5):549-557. [41] STANFORD KI, MIDDELBEEK RJ, TOWNSEND KL, et al. A novel role for subcutaneous adipose tissue in exercise-induced improvements in glucose homeostasis. Diabetes. 2015;64(6):2002-2014. [42] TCHKONIA T, LENBURG M, THOMOU T, et al. Identification of depot-specific human fat cell progenitors through distinct expression profiles and developmental gene patterns. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2007;292(1):E298-307. [43] LI H, ZHANG Y, WANG F, et al. Effects of irisin on the differentiation and browning of human visceral white adipocytes. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(12):7410-7421. [44] MAAK S, NORHEIM F, DREVON CA, et al. Progress and Challenges in the Biology of FNDC5 and Irisin. Endocr Rev. 2021;42(4):436-456. [45] ROCA-RIVADA A, CASTELAO C, SENIN LL, et al. FNDC5/irisin is not only a myokine but also an adipokine. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e60563. [46] MORENO-NAVARRETE JM, ORTEGA F, SERRANO M, et al. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(4):E769-778. [47] PEREZ-SOTELO D, ROCA-RIVADA A, BAAMONDE I, et al. Lack of Adipocyte-Fndc5/Irisin Expression and Secretion Reduces Thermogenesis and Enhances Adipogenesis.Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16289. |
| [1] | Chen Xianghe, Liu Bo, Yang Kang, Lu Pengcheng, Yu Huilin. Treadmill exercise improves the myocardial fibrosis of spontaneous type 2 diabetic mice: an exploration on the functional pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1210-1215. |
| [2] | Lin Jiayu, Huang Huibin, Liang Bo, Chen Lijun. Changes in irisin, leptin, adiponectin and visceral fat in obese rats undergoing high-intensity intermittent exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5583-5588. |
| [3] | Wang Ao, Chu Hongshang, Wu Hongguang, Li Ke, Liu Huijuan. Expression of leptin receptor in mouse skin and the role of leptin receptor-positive cells in skin development and wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3993-3998. |
| [4] | Ye Erbai, Xiao Xiaoling, He Ziyu, Yang Chun, Du Yikuan. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor signaling pathway is involved in the metabolic regulation of obesity by intestinal flora and brown adipose tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5222-5226. |
| [5] | Wang Bo, Bai Shengchao, Li Wenbo, Wang Lin. A rabbit model of high-intensity jumping-induced tendon injury followed by post-exercise cold water immersion: inflammations and collagen remodeling in the patellar tendon [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4619-4625. |
| [6] | Zhang Shuang, Tan Rui, Wang Chunxiao, Wu Fengyu, Guo Hongyu. MicroRNAs for assessing the motion control of human skeletal muscles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2755-2760. |
| [7] | Shi Xiaoyu, Feng Ziyang, Liu Ziming, Li Lin, Wang Zhen, Liu Xiaoran, Yu Liang. Effect of high-intensity interval training on fat reduction and irisin expression in obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2137-2141. |
| [8] | Chen Zegang, Ding Haili, Li Long, Wang Chun. Changes of bone metabolism after different intensity endurance exercises in growing rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5582-5588. |
| [9] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| [10] | Yang Zhongya, Su Hao, Wang Ji, Zhang Yimin, Kong Zhenxing, Zhang Juan, Zhang Long. High-intensity interval training improves cardiorespiratory endurance in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1708-1713. |
| [11] | Cao Meng, Quan Minghui, Zhuang Jie. Similar effect of high-intensity interval training with moderate-intensity continuous training on body composition and cardiovascular health of obesity children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5732-5740. |
| [12] | Yang Zhongming1, Jiang Manyi2, Xu Simao3 . Synergistic resistance of moderate-intensity endurance exercise and allicin to rat models of fatty liver induced by high-fat diet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5030-5035. |
| [13] | Li Shuoqi1, Wang Cong1, Zhang Tiantian2, Wang Mengjun1, Zhu Xiangui1. Energy and substrate consumption characteristics of different intermittent forms of high-intensity interval training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(23): 3729-3733. |
| [14] | Jin Shanhu, Hu Yazhe. Effect of early different intensities of exercise on the modelling rate and blood glucose level of rats with late-stage type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3092-3096. |
| [15] | Ren Zhichao. Effect of aerobic endurance training on peroxisome proliferators activated receptor gamma expression in white adipose tissue and plasma of obese mice induced by high fat [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3056-3061. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||