Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3056-3061.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1251
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of aerobic endurance training on peroxisome proliferators activated receptor gamma expression in white adipose tissue and plasma of obese mice induced by high fat
Ren Zhichao
- (Department of Public Education, Xin Lian College, Henan Normal University, Zhengzhou 451400, Henan Province, China)
-
Received:2019-01-28 -
About author:Ren Zhichao, Master, Lecturer, Department of Public Education, Xin Lian College, Henan Normal University, Zhengzhou 451400, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ren Zhichao. Effect of aerobic endurance training on peroxisome proliferators activated receptor gamma expression in white adipose tissue and plasma of obese mice induced by high fat [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(19): 3056-3061.
share this article
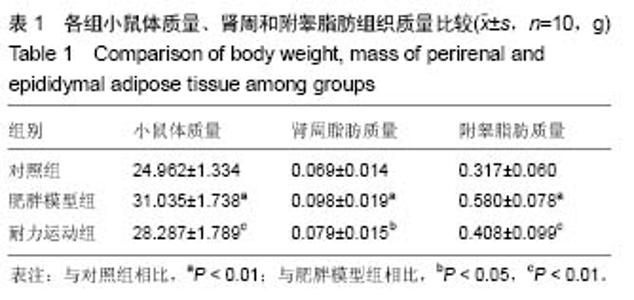
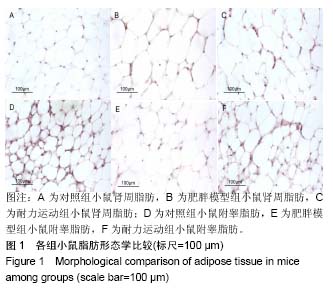
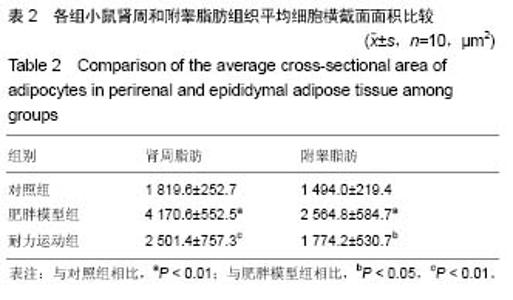
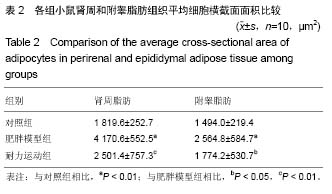
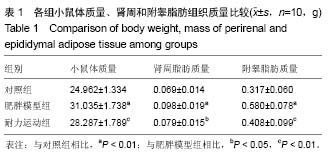
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验初期选取40只4周龄雄性C57BL/6J小鼠,其中10只为对照组,在实验过程中无脱失,全部进入结果分析;剩余30只作为肥胖模型组,在高脂饲料诱导肥胖小鼠模型时舍弃体质量较小的10只,剩余20只体质量较大的进入后续实验,分为肥胖模型组和耐力运动组,每组10只,在实验过程中无脱失,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 耐力运动训练对肥胖小鼠体质量和肾周及附睾脂肪质量的影响 表1结果显示,肥胖模型组体质量明显大于对照组(P < 0.01),表明肥胖小鼠造模成功,耐力运动组体质量明显小于肥胖模型组(P < 0.01),表明耐力运动训练明显减轻了肥胖小鼠的体质量;肥胖模型组肾周脂肪和附睾脂肪质量明显大于对照组(P < 0.01),耐力运动组肾周脂肪质量小于肥胖模型组(P < 0.05)、附睾脂肪质量明显小于肥胖模型组(P < 0.01)。"
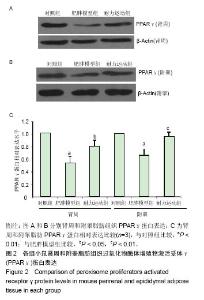
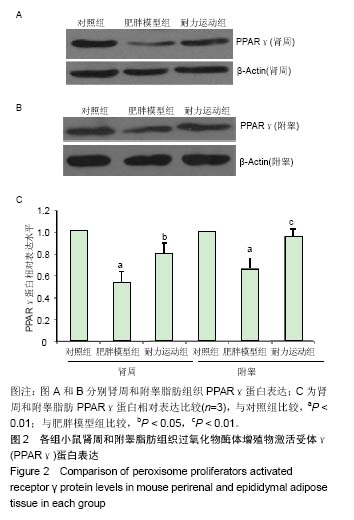
2.4 各组小鼠血浆PPARγ质量浓度比较 肥胖模型组血浆PPARγ质量浓度明显低于对照组[(568.88±75.99),(685.24±77.62) ng/L,P < 0.01)],耐力运动组血浆PPARγ质量浓度(634.28±81.07)ng/L明显高于肥胖模型组(P < 0.05)。 2.5 各组小鼠肾周和附睾脂肪组织PPARγ蛋白水平比较 图2A和2B结果显示,肥胖模型组肾周和附睾脂肪PPARγ蛋白的表达均低于对照组,耐力运动组均高于肥胖模型组。 图2C是对图2A和2B(n=3)结果的统计分析,结果显示,肥胖模型组肾周和附睾脂肪的PPARγ蛋白表达含量均明显低于对照组(P < 0.01);耐力运动组肾周脂肪PPARγ蛋白表达高于肥胖模型组(P < 0.05),附睾脂肪明显高于肥胖模型组(P < 0.01)。"
| [1] 倪国华,张璟,郑风田. 中国肥胖流行的现状与趋势[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2013,19(10): 70-74.[2] Bray GA, Kim KK, Wilding JPH; World Obesity Federation. Obesity: a chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes Rev.2017;18(7): 715-723. [3] Ashish KK, Neha D. Drug treatment of obesity: Current status and future prospects. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(2):89-94.[4] Mitchell NS, Catenacci VA, Wyatt HR, et al. Obesity: overview of an epidemic. Psychiatr Clin North Am.2011; 34(4): 717-732.[5] Whaley-Connell A, Sowers JR. Obesity and kidney disease: from population to basic science and the search for new therapeutic targets. Kidney Int.2017;92(2): 313-323.[6] Kilov D, Kilov G. Philosophical determinants of obesity as a disease. Obes Rev.2018;19(1): 41-48.[7] Guglielmo D, Hootman JM, Murphy LB, et al. Health Care Provider Counseling for Weight Loss Among Adults with Arthritis and Overweight or Obesity - United States, 2002-2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.2018;67(17): 485-490. [8] Wolfe BM, Kvach E, Eckel RH. Treatment of Obesity: Weight Loss and Bariatric Surgery. Circ Res.2016;118(11): 1844-1855. [9] Chin SH, Kahathuduwa CN, Binks M. Physical activity and obesity: what we know and what we need to know. Obes Rev.2016;17(12): 1226-1244. [10] Bae JY, Woo J, Roh HT, et al. The effects of detraining and training on adipose tissue lipid droplet in obese mice after chronic high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis.2017;16(1):13.[11] Chiu CH, Ko MC, Wu LS, et al. Benefits of different intensity of aerobic exercise in modulating body composition among obese young adults: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Health Qual Life Outcomes.2017;15(1):168.[12] Marques CM, Motta VF, Torres TS, et al. Beneficial effects of exercise training (treadmill) on insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat fed C57BL/6 mice. Braz J Med Biol Res.2010;43(5):467-475.[13] Strasser B. Physical activity in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2013;1281:141-159.[14] Lefterova MI, Haakonsson AK,Lazar MA, et al. PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends Endocrinol. Metab.2014;25(6): 293-302.[15] Zhang Y, Li H. Three important transcription factors related to lipogenesis and adipogenesis in mam mal. J Northeast Agric Univ.2010;17(3):62-75.[16] Issemann I, Green S. Activation of a number of steroid receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature.1990;347 (6294): 645-650.[17] Ahmadian M, Suh Jm, Han N, et al. PPARγ Signaling and Metabolism: The Good, the Bad and Future. Nat Med. 2013;19(5): 557-566.[18] Picard F, A uwerx J. PPARγ AND GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS. Annu Rev Nutr.2002;22:167- 97.[19] de la Rosa Rodriguez MA, Kersten S. Regulation of lipid droplet-associated proteins by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids.2017;1862(10 Pt B): 1212-1220.[20] Huang B, Yuan HD, Kim DY, et al. Cinnamaldehyde prevents adipocyte differentiation and adipogenesis via regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and AMP-activated proteinkinase (AMPK) pathways. J Agric Food Chem.2011;59(8): 3666-3673.[21] Lefterova MI, Haakonsson AK, Lazar MA, et al. PPARγ and the global map of adipogenesis and beyond. Trends Endocrinol Metab.2014;25(6): 293-302.[22] Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM. PPARγ: a Nuclear Regulator of Metabolism, Differentiation, and Cell Growth. J Biol Chem.2001; 276(41):37731-37734.[23] Lee JE, Ge K. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of PPARγ expression during adipogenesis. Cell Biosci. 2014;4:29.[24] Li P, Song Y, Zan W, et al. Lack of CUL4B in Adipocytes Promotes PPARγ-Mediated Adipose Tissue Expansion and Insulin Sensitivity. Diabetes.2017;66(2): 300-313. [25] Gross B, Pawlak M, Lefebvre P, et al. PPARs in obesity-induced T2DM, dyslipidaemia and NAFLD. Nat Rev Endocrinol.2017;13(1): 36-49.[26] Barak Y, Nelson MC, Ong ES, et al. PPARγ is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell.1999;4(4): 585-595.[27] Wang F, Mullican SE, DiSpirito JR, et al. Lipoatrophy and severe metabolic disturbance in mice with fat-specific deletion of PPARγ. Proc Natl Acad Sci.2013;110(46): 18656-18661.[28] Akyürek N, Aycan Z, Çetinkaya S, et al. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma concentrations in childhood obesity. Scand J Clin Lab Invest.2013;73(4): 355-360. [29] Ruschke K, Fishbein L, Dietrich A, et al. Gene expression of PPARgamma and PGC-1alpha in human omental and subcutaneous adiposetissues is related to insulin resistance markers and mediates beneficial effects of physical training. Eur J Endocrinol.2010;162(3): 515-23.[30] 夏书宇.不同强度跑台运动对高脂饮食大鼠脂肪组织PPARγ/脂联素/ TNF-αmRNA的影响[J]. 成都体育学院学报, 2015, 41(3): 98-102.[31] Chandler PC, Viana JB, Oswald KD, et al.Feeding response to melanocortin agonist predicts preference for and obesity from a high-fat diet.Physiol Behav.2005;85(02): 221-230.[32] Bedford, Toby G, Charles M, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures[J]. J Appl Physiol, 1979, 47(6): 1278-1283.[33] Kus V, Prazak T, Brauner P, et al. Induction of muscle thermogenesis by high-fat diet in mice: association with obesity-resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2008; 295(2): E356-E367.[34] Gollisch KS, Brandauer J, Jessen N, et al. Effects of exercise training on subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in normal-and high-fat diet-fed rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2009;297: E495-E504.[35] Chen N, Lei T, Xin L, et al. Depot-specific effects of treadmill running and rutin on white adipose tissue fuction in diet-induced obese mice. J Physiol Biochem.2016;72(3): 453-467.[36] Kawamura T, Yoshida K, Sugawara A, et al. Regulation of skeletal muscle peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma expression by exercise and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in fructose-fed hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res.2004;27(1):61-70.[37] 杨星雅,李鹏飞,房国梁,等.有氧和抗阻运动对大鼠白色脂肪棕色化的作用[J].体育科学, 2017, 37(6): 69-74.[38] 李萌,柏友萍,崔建飞,等.不同强度运动处方对青春期肥胖大鼠PPARγ及相关指标的影响[J].卫生研究,2014,43(5):732-737.[39] 刘长金,刘磊,柯大智,等.高果糖引起的脂肪肝大鼠肾脏脂质合成相关基因和蛋白的表达[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2014,36(4): 446-454.[40] 罗祖纯,戴霞,张泰辉,等.有氧、抗阻运动对糖尿病前期人群血清胰高血糖素样肽1、血糖水平的影响[J].山东医药,2017,57(2): 18-21.[41] Hasan AU, Ohmori K, Hashimoto T, et al. PPARγ activation mitigates glucocorticoid receptor-induced excessive lipolysis in adipocytes via homeostatic crosstalk. J Cell Biochem.2018; 119(6): 4627-4635.[42] Engin A. Fat Cell and Fatty Acid Turnover in Obesity[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol.2017;960:135-160. |
| [1] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [2] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [3] | Chai Le, Lü Jianlan, Hu Jintao, Hu Huahui, Xu Qingjun, Yu Jinwei, Quan Renfu. Signal pathway variation after induction of inflammatory response in rats with acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1218-1223. |
| [4] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [5] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [6] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [7] | Wang Hanyue, Li Furong, Yang Xiaofei, Hu Chaofeng. Direct reprogramming hepatocytes into islet-like cells by efficiently targeting and activating the endogenous genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1056-1063. |
| [8] | Xie Yang, Zhang Shujiang, Liu Menglan, Luo Ying, Yang Yang, Li Zuoxiao. Mechanism by which rapamycin protects spinal cord neurons in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 695-700. |
| [9] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [10] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [11] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [12] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [13] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [14] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [15] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||