[1] MARTIROSYAN NL, PATEL AA,CAROTENUTO A, et al. Genetic alterations in intervertebral disc disease .Front Surg.2016;21(2):59.
[2] ZHAO GS, ZHANG Q, QUAN ZX. Mid-term efficacy and safety of cervical disc arthroplasty versus fusion in cervical spondylosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Biomed Rep. 2017;6(2):159-166.
[3] PHILLIPS KL, CULLEN K, CHIVERTON N, et al. Potential roles of cytokines and chemokines in human intervertebral disc degeneration: interleukin-1 is a master regulator of catabolic processes.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(7):1165-1177.
[4] DAHIA CL, MAHONEY EJ, DURRANI AA, et al. Postnatal growth, differentiation, and aging of the mouse intervertebral disc.Spine. 2009; 34(5):447.
[5] MILLWARD S J, COSTELLO P W, FREEMONT A J, et al. Regulation of catabolic gene expression in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc cells: implications for the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration.J Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):243.
[6] 张雪梅,江维.血红素氧合酶-1通过NF-κB信号通路抑制人退变椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡[J].第三军医大学学报,2018,40(7):561-568.
[7] 赵英伦,马元,李东冉,等. 凋亡促进因子TFAR19,Apaf-1与腰椎间盘突出症的关系研究[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2017,32(2):30-32.
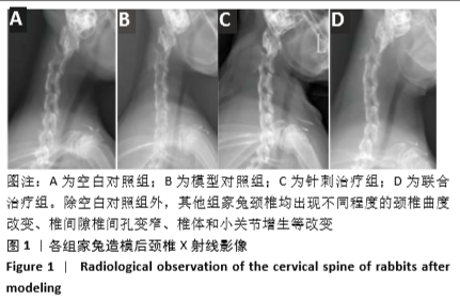
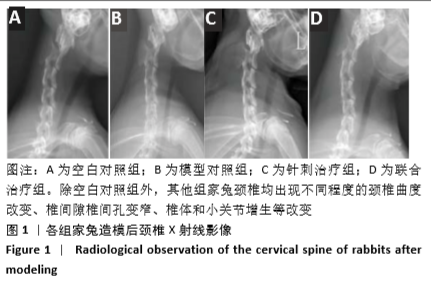
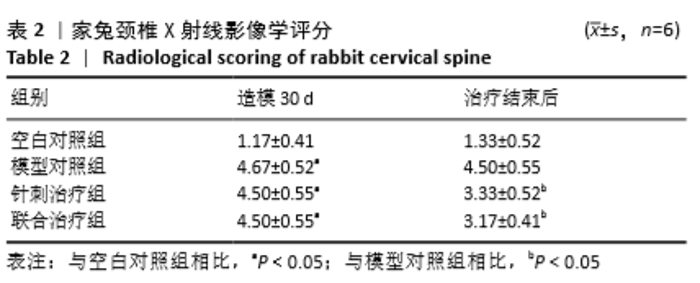
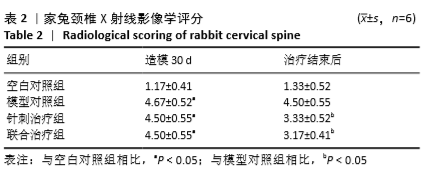
[8] 张欣,李殿宁,李开平,等.无创兔颈型颈椎病动物模型的建立[J].中华中医药学刊,2015,33(4): 913.
[9] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2003: 314 -325.
[10] 余家阔,吴毅文,戴先进,等.颈椎病生物力学发病机制实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报, 1990, 25 (1) :47-51.
[11] MASUDA K, AOTA Y, MUEHLEMAN C, et al. A Novel Rabbit Model of Mild, Reproducible Disc Degeneration by an Anulus Needle Puncture: Correlation Between the Degree of Disc Injury and Radiological and Histological Appearances of Disc Degeneration. Spine. 2005; 30(1): 5-14.
[12] EVA S, JAVIER P E, JOHAN H, et al. Healthy lifestyle behavior and risk of long duration troublesome neck pain or low back pain among men and women: results from the Stockholm Public Health Cohort.Dove Press. 2017;9: 491-500.
[13] 吴炳轩,刘宝戈,刘振宇,等. 颈椎曲度和活动度参数的影响因素[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(4):380-386.
[14] 买小军,王学琦,卢万春,等.X线平片、CT、MRI诊断颈椎病的价值[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2009,17(3):220-222.
[15] 杨平.青年型颈椎病X线诊断的临床分析[J].中国医药指南,2015, 13(9):98-99.
[16] 常献,陈斌,李长青.髓核细胞老化机制研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(1):40-42.
[17] 孟祥宇,夏建龙.椎间盘退变的机制及修复[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(11):1768-1773.
[18] 李文举,李亦梅.椎间盘退变机制研究现状及生物治疗展望[J].中国骨与关节外科,2014,7(1):66-69.
[19] HASCHTMANN D, FERGUSON SJ, STOYANOV JV. Apoptosis and gene expression of collagenases but not gelatinases in rabbit disc fragment cultures.J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(6):552.
[20] 邹璟,姜梦雅,李解,等.细胞凋亡参与电针对退变椎间盘保护作用的研究[J].时珍国医国药,2017,28(9):2271-2273.
[21] DING F, SHAO ZW, YANG SH, et al. Role of mitochondrial pathway in compression induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. Apoptosis. 2012;17 (6) :579-590.
[22] 陈琪, 石芳芳, 杨曦, 等. 不同代次髓核细胞生物学特性的比较研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(6):660-667.
[23] 黄秀芳,原向伟.Sox9和Ⅱ型胶原蛋白在人腰椎间盘退变中的表达及意义[J].中国医药科学,2014,4(3):18-21.
[24] MA K, CHEN S, LI Z, et al. Mechanisms of endogenous repair failure during intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019; 27(1): 41-48.
[25] MAZUMDER S, PLESCA D, ALMASAN A. Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis . Methods Mol Biol. 2008;414:13-21.
[26] 尹东亮,卢沛林,尹润龙,等.过表达PRRX1通过p53介导的线粒体凋亡途径诱导肝癌SMMC7721细胞凋亡[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2019,26(6):662-668.
[27] 陆洋,孔灵菲,耿秀娟.Caspase-3、Caspase-9在哮喘大鼠模型嗜酸性粒细胞中的表达及糖皮质激素的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2008,24(11):1033-1035.
[28] ABOUTALEB N, SHAMSAEI N, RAJABI H, et al. Protection of hippocampal CA1 neurons against ischemia/reperfusion injury by exercise preconditioning via modulation of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and prevention of caspase-3 activation.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2016;7(1): 21-29.
[29] XIA Z, DICKENS M, RAINGEAUD J, et al. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis.Science. 1995;270(5240): 1326-1331.
[30] KLUCK RM, BOSSY-WETZEL E, GREEN DR, et al. The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis.Science. 1997;275(5303):1132-1136.
[31] OLTVAI ZN, MILLIMAN CL, KORSMEYER SJ. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death.Cell.1993;74(4): 609-619.
[32] 丁实,赵学荣,李宝群, 等.基于Bcl-2/Beclin-1复合体探讨黄连素对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠模型的保护作用[J].中国实验动物学报, 2019,27(5):651-657.
[33] 肖飞,刘鹏,程光宇,毕海洋,于楠楠.天麻素穴位注射对戊四氮致痫模型大鼠脑内海马区凋亡调控因子Bcl-2、Caspase-3表达的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2019,35(10):66-70.
[34] LIU G, WANG T, WANG T, et al. Effects of apoptosis-related proteins caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 on cerebral ischemia rats. Biomedical Reports. 2013;1(6):861-867.
[35] 袁效智. 中药热敷联合针灸治疗腰椎间盘突出症的效果分析[J]. 医学信息, 2015,28(40):21-21.
[36] 江明,张宏波.局部针刺联合中药包热敷治疗神经根型颈椎病的疗效[J].医学信息,2019,32(15):149-151.
[37] 李峰.按摩推拿配合中药热敷治疗坐骨神经痛临床效果观察[J].河南医学研究,2016,25(10):1819-1819.
[38] 李毅敏,伍永灼,郑文诺.针灸推拿配合中药湿热敷治疗椎动脉型颈椎病60例临床研究[J].云南中医中药杂志,2018,39(9):61-62.
[39] 赵荣华.针灸推拿分期施用治疗颈椎病的研究[J].中国急救医学, 2016,36(z2):118-119.
[40] 杨凤云,邓许勇,王丽华,等.中药热奄包配合正脊手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[J].中国当代医药,2017,24(36):114-116.
[41] 罗先意,黄少炎,史红美,等.中药热奄包外敷干预颈型颈椎病家兔的实验研究[J].贵州医科大学学报,2017,42(11):1258-1261.
|