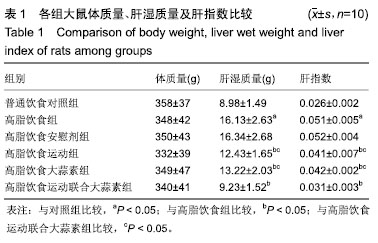
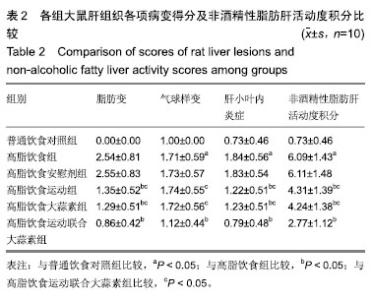
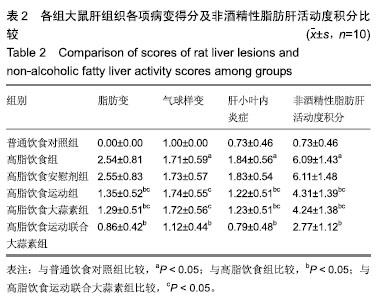
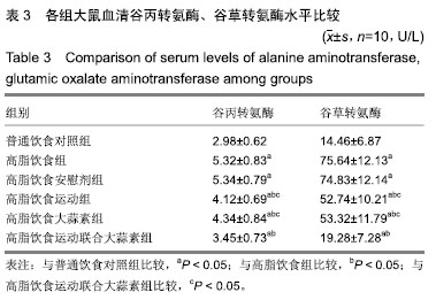
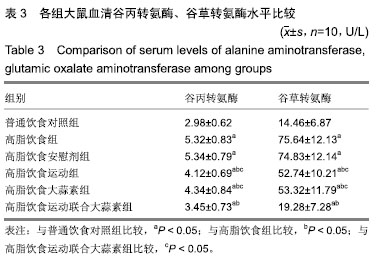
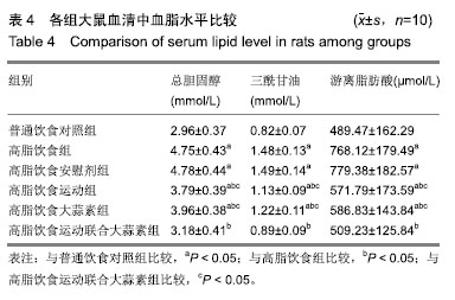
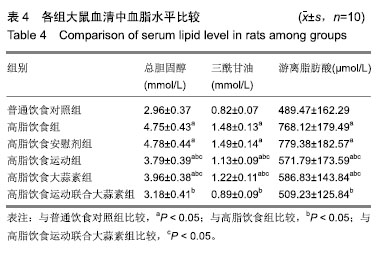
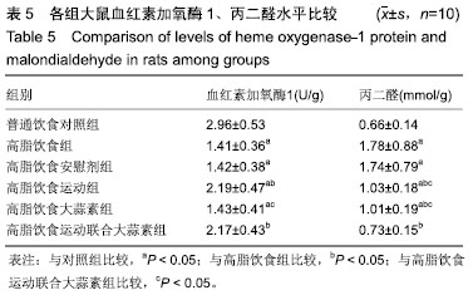
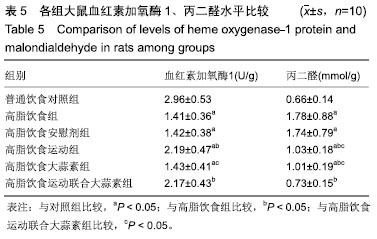
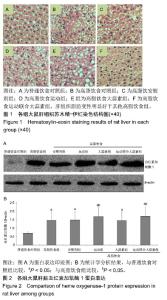
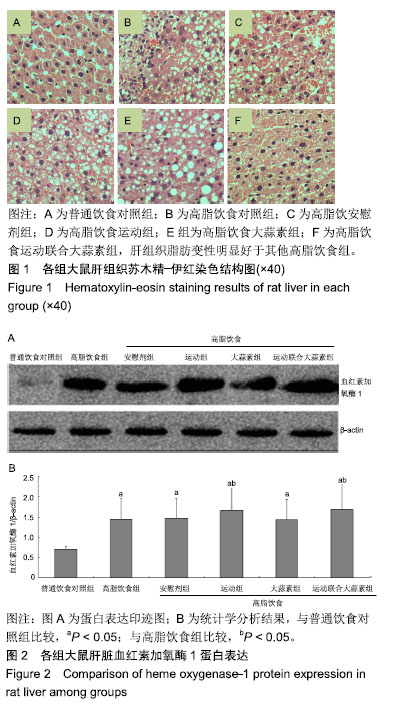
| [1]娜日苏,包纳日斯.非酒精性脂肪肝的发病机制与流行病学的研究进展[J].中国医药指南,2016,14(3):39-40.[2]Shen F,Zheng R,Shi J,et al. Impact of skin capsular distance on the performance of controlled attenuation parameter in patients with chronic liver disease. Liver Int.2015;35(11):2392-2400.[3]范建高.非酒精性脂肪性肝病的研究现状与展望[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2015,31(7):999-1001.[4]El-Kashef DH,El-Kenawi AE,Suddek GM,et al. Protective effect of allicin against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int Immunopharmacol.2015;29(2):679-686.[5]许思毛,王蕊,刑荣鑫,等.大蒜素预处理对大负荷运动后大鼠心肌保护作用及其机制探讨[J].体育科学,2018,38(11):66-74.[6]Pérez-Köhler B,García-Moreno F,Bayon Y,et al. Inhibition of staphylococcus aureus adhesion to the surface of a reticular heavyweight polypropylenemesh soaked in a combination of chlorhexidine and allicin:an in vitro study. PloS One.2015;10(5):e0126711.[7]周媛媛,刘春杰,楚宪襄,等.大蒜素对非酒精性脂肪性肝病模型大鼠的治疗作用及TNF-α蛋白,SREBP-1c 蛋白的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2016,22(13):127-130.[8]Gao XY,Geng XJ,Zhai WL,et al. Effect of combined treatment with cyclophosphamidum and allicin on neurobloma-bearing mice. Asian Pac J Trop Med.2015;8(2):137-141.[9]Elkayam A,Peleg E,Grossman E,et al. Effects of allicin on cardiovascular risk factors in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Isr Med Assoc J.2013;15(3):170-173.[10]Beadford TG,Tipton CM,Wilson NC,et al.Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures.J Appl Physiol. 1979;47(6):1278-1283.[11]American College of Sports Medicine.ACSM's guidelines for exercise testing and prescription.9th ed. Philadelphia(PA): Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.2013.[12]Kleiner DE,Brunt EM,Van Natta M,et al.Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41(6):1313-1321.[13]李海玲,彭书明,李凛,等.4种常用蛋白浓度测定方法的比较[J].中国生化药物杂志,2008,29(4):277-278,282.[14]杨家耀,时昭红,马威,等.附子理中汤通过激活 AMPK 通路及抑制NF-κB p65通路降低非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠肝脏损伤[J].中国中药杂志,2018,43(15): 3176-3183.[15]徐正婕,范建高,王国良,等.高脂饮食致大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝炎肝纤维化模型[J].世界华人消化杂志,2002,10(4):392-396.[16]张建民,张娜娜,崔璀,等.薏苡仁提取物改善大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝游离脂肪酸的代谢机制研究[J].中国药师,2017,20(1): 25-29.[17]穆杰,王庆国,王雪茜,等.非酒精性脂肪肝机制及其与慢性应激相关性的研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志,2016,24(5):692-698.[18]李青艳,王绩凯,冯哲伟,等. 非酒精性脂肪肝患者脂质过氧化与肝功能的相关性研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2012,41(16):1591-1592.[19]张艳,卢洁,周莹群,等.非酒精性脂肪性肝病与氧化应激[J].世界临床药物, 2013, 34(8): 459-463.[20]李颖.“二次打击”假说与非酒精性脂肪肝[J].医学综述, 2013,19(4): 594-596.[21]Vergnes L,Chin RG,DE Aguiar Vallim T,et al. SREBP -2- deficient and hypomorphic mice reveal roles for SREBP -2 in embryonic development and SREBP-1c expression.J Lipid Res.2016;57(3): 410-421.[22]Lai SJ, Li Y, Kuang Y, et al. PKC delta silencing alleviates saturated fatty acid induced ER stress by enhancing SERCA activity.Biosci Rep.2017;37(6):1-10. [23]杜杰.有氧运动结合燕麦β-葡聚糖对高脂仓鼠降低胆固醇的作用及机制[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(1):97-103.[24]苗华,张旭,赵英永.基于代谢组学研究有氧运动对高脂血症的治疗作用及其生物化学作用机制[J]北京体育大学学报,2015, 38(12):78-82,101.[25]Guo R,Liong EC,So KF,et al. Beneficial mechanisms of aerobic exercise on hepatic lipid metabolism in non -alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015;14(2):139-444[26]Sertie RA,Andreotti,Proena AR,et al. Cessation of physical exercise changes metabolism and modifies the adipocyte cellularity of the periepididymal white adipose tissue in rats. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;115(3):394-402. [27]Elkayam A,Peleg E,Grossman E,et al.Effects of allicin on cardiovascular risk factors in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Isr Med Assoc J.2013;15(3): 170-173.[28]杨莉.大蒜改善血脂代谢紊乱研究进展[J].中成药,2016,38(3): 634-638.[29]李国峰,许思毛.运动经PKC-Nfr2途径调节肝血红素加氧酶-1表达及抗氧化能力的研究[J].广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 35(1):113-118. |