Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (41): 6591-6596.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.41.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Zhang Lian-fang1, Kang Hui2, Deng Lian-fu2, Yang Hui-lin1
- 1Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopeadic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Department of Orthopedics of Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
-
Revised:2014-09-04Online:2014-10-01Published:2014-10-01 -
Contact:Yang Hui-lin, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopeadic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Zhang Lian-fang, M.D., Physician, Department of Orthopaedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Orthopeadic Institute of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81061160510
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Lian-fang, Kang Hui, Deng Lian-fu, Yang Hui-lin. Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6591-6596.
share this article
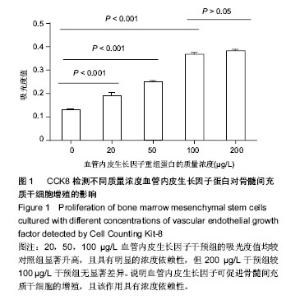
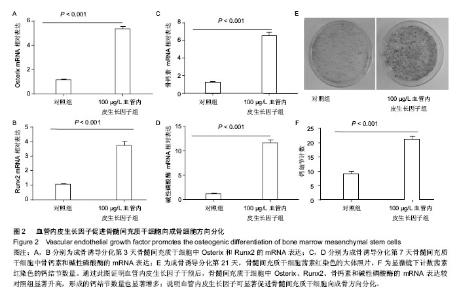
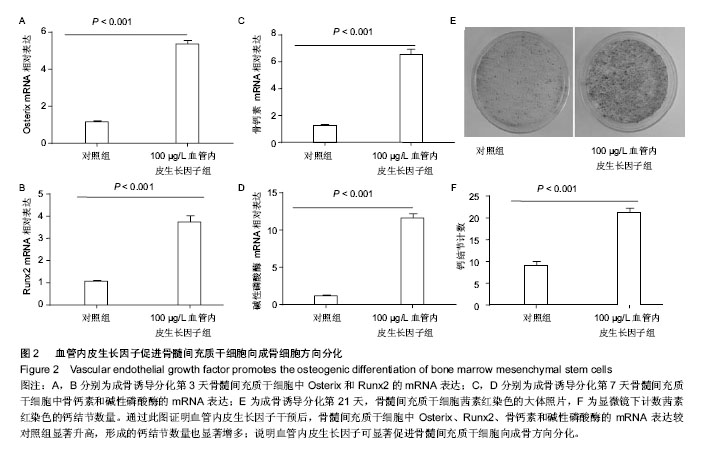
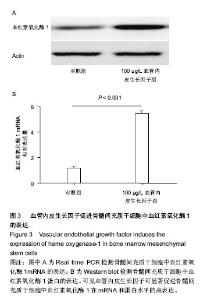
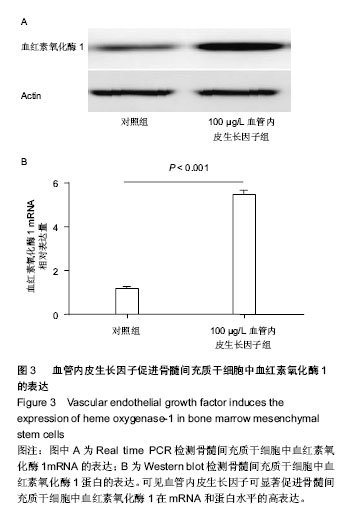
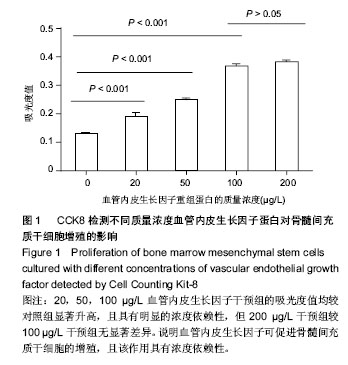
2.1 血管内皮生长因子促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖 CCK8试剂盒检测在含不同质量浓度重组血管内皮生长因子蛋白的培养液下骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖情况,发现20,50,100,200 μg/L重组血管内皮生长因子蛋白培养下骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖率分别是对照组的1.44倍、1.90倍、2.81倍和2.92倍,可见骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖随培养液中血管内皮生长因子蛋白质量浓度的增加而增加,100 μg/L促增殖作用最显著,而200 μg/L较100 μg/L对骨髓间充质干细胞的促增殖作用无差异(图1)。这说明血管内皮生长因子对骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖有促进作用,且有浓度依赖性;200 μg/L组较100 μg/L组无差异,可能是因为在100 μg/L这一质量浓度时受体已经饱和的缘故,因而后面的实验选用100 μg/L这一质量浓度。 2.2 血管内皮生长因子促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化 骨髓间充质干细胞在有成骨细胞分化诱导剂的培养液中培养第3天,Real-time PCR方法检测其成骨细胞分化早期基因Osterix和Runx2的表达;培养第7天检测碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的表达。发现培养3 d后100 μg/L血管内皮生长因子组骨髓间充质干细胞的Osterix和Runx2表达分别是对照组的4.61倍(P < 0.001)和3.52倍(P < 0.001) (图2A,B);培养第7天,100 μg/L血管内皮生长因子组骨髓间充质干细胞中碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的表达分别是对照组的9.79倍(P < 0.001)和5.25倍(P < 0.001)(图2C,D)。成骨诱导培养下第21天,对骨髓间充质干细胞行茜素红染色(图2E),镜下计数钙结节,100 μg/L血管内皮生长因子组钙结节数量(31.78±3.14)是对照组(9.22±1.41)的3.45倍(P < 0.001)(图2 F)。结果证实血管内皮生长因子可显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞方向分化。 2.3 血管内皮生长因子促进骨髓间充质干细胞内血红素氧化酶1的表达 为研究血管内皮生长因子对血红素氧化酶1表达的影响,实验检测骨髓间充质干细胞中血红素氧化酶1的mRNA和蛋白表达。研究发现100 μg/L血管内皮生长因子组骨髓间充质干细胞中血红素氧化酶1的mRNA是对照组的4.45倍(P < 0.001)(图3A)。 Western blot检测结果同Real time PCR结果一致:血管内皮生长因子明显促进骨髓间充质干细胞中血红素氧化酶1的蛋白表达(图3B)。 "
| [1] Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK, Lalykina KS.The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells.Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970;3(4):393-403. [2] Castro-Malaspina H, Gay RE, Resnick G,et al. Characterization of human bone marrow fibroblast colony-forming cells (CFU-F) and their progeny.Blood. 1980;56(2):289-301. [3] Caplan AI.Mesenchymal stem cells.J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5): 641-650. [4] Caplan AI.Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine.J Cell Physiol. 2007; 213(2):341-347. [5] Bianco P, Robey PG, Simmons PJ.Mesenchymal stem cells: revisiting history, concepts, and assays.Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(4):313-319. [6] Liu Y, Teoh SH, Chong MS,et al.Vasculogenic and osteogenesis-enhancing potential of human umbilical cord blood endothelial colony-forming cells.Stem Cells. 2012; 30(9):1911-1924. [7] Liu CH, Hwang SM.Cytokine interactions in mesenchymal stem cells from cord blood.Cytokine. 2005;32(6):270-279. [8] Busletta C, Novo E, Valfrè Di Bonzo L,et al. Dissection of the biphasic nature of hypoxia-induced motogenic action in bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells. 2011 Jun;29(6):952-963. [9] 王培蕊,马学玲,王心蕊,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养及血管内皮生长因子对其产生的诱导分化作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(46):9250-9254. [10] 刘傥,张湘生,张庆,等.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中血管内皮生长因子和骨形态发生蛋白2的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(36):6651-6657. [11] Wang Y, Wan C, Deng L,et al.The hypoxia-inducible factor alpha pathway couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during skeletal development.J Clin Invest. 2007;117(6): 1616-1626. [12] Bakken AF, Thaler MM, Schmid R.Metabolic regulation of heme catabolism and bilirubin production. I. Hormonal control of hepatic heme oxygenase activity.J Clin Invest. 1972;51(3): 530-536. [13] Pimstone NR, Engel P, Tenhunen R,et al.Inducible heme oxygenase in the kidney: a model for the homeostatic control of hemoglobin catabolism.J Clin Invest. 1971;50(10): 2042-2050. [14] Tenhunen R, Marver HS, Schmid R.Microsomal heme oxygenase. Characterization of the enzyme.J Biol Chem. 1969;244(23):6388-6394. [15] Tenhunen R, Marver HS, Schmid R.The enzymatic conversion of heme to bilirubin by microsomal heme oxygenase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968;61(2):748-755. [16] Vanella L, Kim DH, Asprinio D,et al.HO-1 expression increases mesenchymal stem cell-derived osteoblasts but decreases adipocyte lineage.Bone. 2010;46(1):236-243. [17] Barbagallo I, Vanella A, Peterson SJ,et al.Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 increases human osteoblast stem cell differentiation.J Bone Miner Metab. 2010;28(3):276-288. [18] Vanella L, Sanford C Jr, Kim DH,et al. Oxidative stress and heme oxygenase-1 regulated human mesenchymal stem cells differentiation.Int J Hypertens. 2012;2012:890671. [19] Soleimani M, Nadri S.A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow.Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):102-106. [20] Hsiao FS, Cheng CC, Peng SY,et al.Isolation of therapeutically functional mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells within 3 h by an effective single-step plastic-adherent method.Cell Prolif. 2010;43(3):235-248. [21] Dai J, Rabie AB.VEGF: an essential mediator of both angiogenesis and endochondral ossification.J Dent Res. 2007;86(10):937-950. [22] Drake CJ, LaRue A, Ferrara N,et al.VEGF regulates cell behavior during vasculogenesis.Dev Biol. 2000;224(2): 178-188. [23] Engsig MT, Chen QJ, Vu TH,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase 9 and vascular endothelial growth factor are essential for osteoclast recruitment into developing long bones.J Cell Biol. 2000;151(4):879-889. [24] Hiltunen MO, Ruuskanen M, Huuskonen J,et al. Adenovirus- mediated VEGF-A gene transfer induces bone formation in vivo. FASEB J. 2003;17(9):1147-1149. [25] Claffey KP, Abrams K, Shih SC, et al.Fibroblast growth factor 2 activation of stromal cell vascular endothelial growth factor expression and angiogenesis.Lab Invest. 2001;81(1):61-75. [26] Deckers MM, van Bezooijen RL, van der Horst G,et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins stimulate angiogenesis through osteoblast-derived vascular endothelial growth factor A. Endocrinology. 2002;143(4):1545-1553. [27] Peng H, Wright V, Usas A,et al.Synergistic enhancement of bone formation and healing by stem cell-expressed VEGF and bone morphogenetic protein-4.J Clin Invest. 2002;110(6): 751-759. [28] Yeh LC, Lee JC.Osteogenic protein-1 increases gene expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in primary cultures of fetal rat calvaria cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1999; 153(1-2):113-124. [29] Ball SG, Shuttleworth CA, Kielty CM.Vascular endothelial growth factor can signal through platelet-derived growth factor receptors.J Cell Biol. 2007;177(3):489-500. [30] Abraham NG, Kappas A.Pharmacological and clinical aspects of heme oxygenase.Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60(1):79-127. [31] Komatsu DE, Hadjiargyrou M.Activation of the transcription factor HIF-1 and its target genes, VEGF, HO-1, iNOS, during fracture repair.Bone. 2004;34(4):680-688. [32] Bussolati B, Ahmed A, Pemberton H,et al.Bifunctional role for VEGF-induced heme oxygenase-1 in vivo: induction of angiogenesis and inhibition of leukocytic infiltration.Blood. 2004;103(3):761-766. [33] Lin HH, Lai SC, Chau LY.Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression via p38 kinase-dependent activation of Sp1.J Biol Chem. 2011;286(5):3829-3838. [34] Vanella L, Kim DH, Asprinio D,et al.HO-1 expression increases mesenchymal stem cell-derived osteoblasts but decreases adipocyte lineage.Bone. 2010;46(1):236-243. [35] Barbagallo I, Vanella A, Peterson SJ,et al.Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 increases human osteoblast stem cell differentiation.J Bone Miner Metab. 2010;28(3):276-288. [36] Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S,et al.Stimulation of bone formation in vitro and in rodents by statins.Science. 1999; 286(5446):1946-1949. [37] Armour KE, Armour KJ, Gallagher ME,et al.Defective bone formation and anabolic response to exogenous estrogen in mice with targeted disruption of endothelial nitric oxide synthase.Endocrinology. 2001;142(2):760-766. [38] Garrett IR, Gutierrez G, Mundy GR.Statins and bone formation.Curr Pharm Des. 2001;7(8):715-736. [39] Penna C, Perrelli MG, Karam JP,et al.Pharmacologically active microcarriers influence VEGF-A effects on mesenchymal stem cell survival.J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(1): 192-204. |
| [1] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [2] | Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199. |
| [3] | Jing Cai-xia, Liu Chang-kui, Tan Xin-ying, Luo Jin-chao, Hu Min. Bone mesenchymal stem cells with allogeneic bone to repair canine mandibular defects: detection of osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2138-2143. |
| [4] | Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148. |
| [5] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhang Ya-xiao, Zhang Bing, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Wang Ren-feng, Liu Jia-bao, Wu Lin. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treatment of emphysema: intravenous versus intratracheal approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2211-2215. |
| [6] | Liang Jian-ji, He Zhi-yong, Liu Kang, Li Xiao-ling, Cheng Wei-min, Yu Xin-ping, Chen Er-dong. Intraarticular injection of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for mild-to-moderate osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2216-2223. |
| [7] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [8] | Han Xiang-zhen, He Hui-yu, Hu Yang, Ba Jiao-jiao, Wang Huan-huan, Mi Xue, Abulizi•Abudula. Recombinant lentiviral vector transfected sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteogenic gene expression changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 821-828. |
| [9] | Huang Jian-feng, Huang Ji-feng, Zhang Wei-cai. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuron-like cells induced by combination of two cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 829-834. |
| [10] | Zou Bin, Zong Shao-hui, Zeng Gao-feng, Fang Ye, Gao Tai-hang. Effects of alpha-zearalanol on the osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 835-840. |
| [11] | Yang Yi, Ding Wen-jing, Dong Wan-li. Autophagy-related gene Beclin-1 expression in neuron-like differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 841-846. |
| [12] | Su Xue-lian, Bao Guang-jie, Kang Hong, Liu Lin, Kong Nan-nan. Morphological changes of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into fibrochondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 860-865. |
| [13] | Nie De-zhi, Wan Ying, Ben Liang, Wang Ying-jun, Liu Xiang-zhu, Wang Li-hui, Li Chao, Zhang Shi-dong. Stem cell tumorigenicity in Balb/c nude mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 888-893. |
| [14] | Fan Yan, Wang Jian-jun, Wei Feng, Fan Xiao-hai, Ma Ai-qun. Effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on inflammatory response and ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 900-905. |
| [15] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Zhang Ya-xiao, Wang Ren-feng, Zhang Bing, Liu Jia-bao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation suppresses emphysema-induced inflammation and apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 906-911. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||