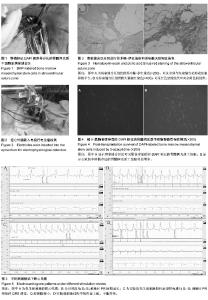
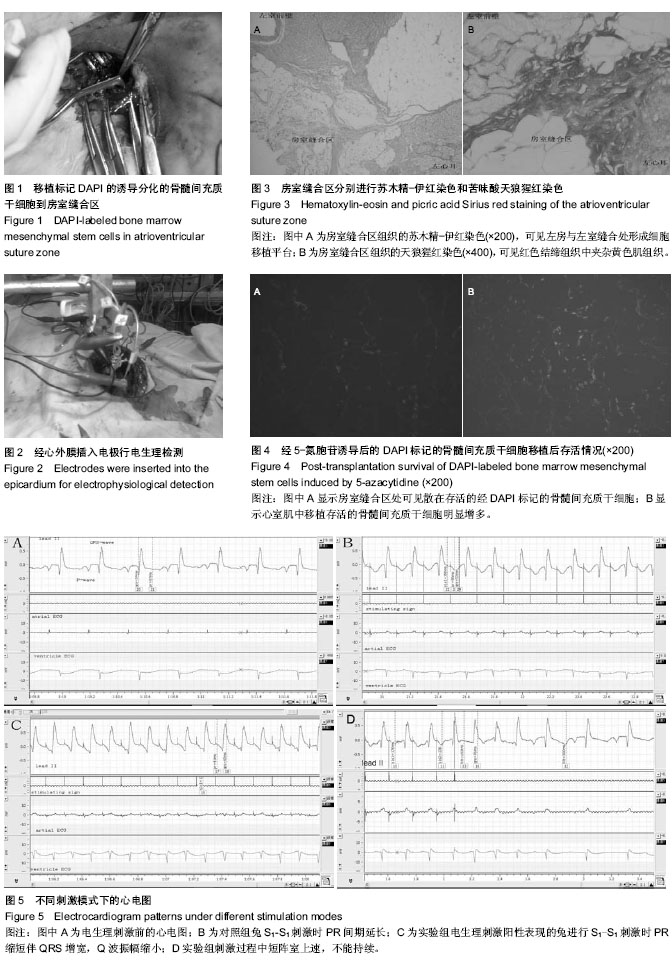
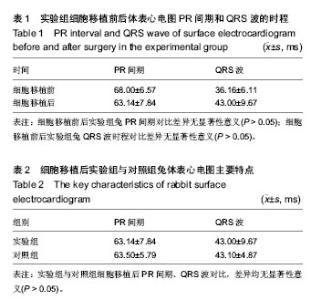
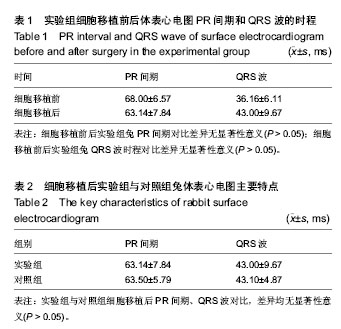
| [1] Wollert KC, Meyer GP, Lotz J, et al. Intracoronary autologous bone-marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: the BOOST randomised controlled clinical trial.Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):141-148.
[2] Tse HF, Kwong YL, Chan JK, et al.Angiogenesis in ischaemic myocardium by intramyocardial autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell implantation.Lancet. 2003;361(9351):47-49.
[3] Fuchs S, Satler LF, Kornowski R,et al.Catheter-based autologous bone marrow myocardial injection in no-option patients with advanced coronary artery disease: a feasibility study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(10):1721-1724.
[4] Beeres SL, Atsma DE, van der Laarse A,et al. Human adult bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repair experimental conduction block in rat cardiomyocyte cultures.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(10):1943-1952.
[5] Choi YH, Stamm C, Hammer PE,et al.Cardiac conduction through engineered tissue.Am J Pathol. 2006;169(1):72-85.
[6] Siminiak T, Kalawski R, Fiszer D,et al.Autologous skeletal myoblast transplantation for the treatment of postinfarction myocardial injury: phase I clinical study with 12 months of follow-up.Am Heart J. 2004;148(3):531-537.
[7] Abraham MR, Henrikson CA, Tung L,et al.Antiarrhythmic engineering of skeletal myoblasts for cardiac transplantation. Circ Res. 2005;97(2):159-167.
[8] 张奇峰.自体骨髓间质干细胞诱导分化移植构建房室间电传递新通道治疗房室传导阻滞的初步研究[D]. 汕头:汕头人学,2007.
[9] Junqueira LC, Bignolas G, Brentani RR.Picrosirius staining plus polarization microscopy, a specific method for collagen detection in tissue sections.Histochem J. 1979;11(4):447-455.
[10] Mills WR, Mal N, Kiedrowski MJ,et al.Stem cell therapy enhances electrical viability in myocardial infarction.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2007;42(2):304-314.
[11] Breitbach M, Bostani T, Roell W,et al. Potential risks of bone marrow cell transplantation into infarcted hearts.Blood. 2007; 110(4):1362-1369.
[12] Li W, Ma N, Ong LL,et al.Bcl-2 engineered MSCs inhibited apoptosis and improved heart function.Stem Cells. 2007; 25(8):2118-2127.
[13] Tang YL, Tang Y, Zhang YC,et al.Improved graft mesenchymal stem cell survival in ischemic heart with a hypoxia-regulated heme oxygenase-1 vector.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(7):1339-1350.
[14] Rosen MR, Robinson RB, Brink P,et al. Recreating the biological pacemaker.Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol. 2004;280(2):1046-1052.
[15] Anghel TM, Pogwizd SM.Creating a cardiac pacemaker by gene therapy.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2007;45(2):145-155.
[16] 周浩粤,邱汉婴,卢炯斌,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外向心肌样细胞诱导分化:缝隙连接蛋白43的表达变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2010, 14(19):3431-3435.
[17] Hofshi A, Itzhaki I, Gepstein A,et al.A combined gene and cell therapy approach for restoration of conduction.Heart Rhythm. 2011;8(1):121-130.
[18] 董皓,李萍,李璇.细胞工程和基因技术修复已损害的房室传导或建立人工房室通路[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(1): 167-170.
[19] 任晓庆,浦介麟,张澍,等.自体骨髓间叶干细胞诱导分化移植治疗房室阻滞的初步观察[J].中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志,2005, 19(1):48-52.
[20] 李家一,王海昌,李成祥.5-氮杂胞苷诱导兔骨髓间充质细胞分化为心肌样细胞的实验[J].中国临床康复, 2005,9(46):18-20.
[21] Josephson ME.临床心脏电生理学技术和理论[M].3版. 天津:天津科学技术翻译出版公司,2005:305-400.
[22] 马健,唐海沁,翟志敏,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外纯化及心肌样细胞定向诱导分化后的特征分析[J].中国老年学杂志,2007, 27(9):817-820.
[23] 任鹏,孙发,李洪辉. 苦味酸天狼猩红偏振光法检测阴茎白膜损伤愈合过程中胶原纤维类型分布的动态变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(11):2187-2190.
[24] Li W, Ma N, Ong LL,et al.Bcl-2 engineered MSCs inhibited apoptosis and improved heart function.Stem Cells. 2007; 25(8):2118-2127.
[25] Tang YL, Tang Y, Zhang YC,et al.Improved graft mesenchymal stem cell survival in ischemic heart with a hypoxia-regulated heme oxygenase-1 vector.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(7):1339-1350.
[26] Qi CM, Ma GS, Liu NF,et al.Transplantation of magnetically labeled mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in a swine myocardial infarction model.Chin Med J (Engl). 2008; 121(6):544-550.
[27] Bayes-Genis A, Roura S, Soler-Botija C,et al.Identification of cardiomyogenic lineage markers in untreated human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Transplant Proc. 2005;37(9):4077-4079.
[28] Zhang N, Li J, Luo R,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce angiogenesis and attenuate the remodeling of diabetic cardiomyopathy.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2008; 116(2):104-111.
[29] Nakanishi C, Yamagishi M, Yamahara K,et al.Activation of cardiac progenitor cells through paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;374(1):11-16.
[30] Xu RX, Chen X, Chen JH,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in vitro through hypoxia-induced paracrine mechanisms.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009;36(2):176-180. |