Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (14): 2179-2185.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.14.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via intramuscular injection influence the expression of cytokines related to dilated cardiomyopathy in rats
Jiang Yan-jie1, Mao Cheng-gang2, Ning Xian-feng3, Li Rong4, Li Zi-pu2
- 1Department of Pediatric Medicine, Taian Central Hospital, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China; 2Departmnet of Pediatric Medicine, 3Department of Cardiology, 4Department of Ultrasound, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China
-
Revised:2015-03-06Online:2015-04-02Published:2015-04-02 -
Contact:Li Zi-pu, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Departmnet of Pediatric Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266003, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Jiang Yan-jie, Master, Physician, Department of Pediatric Medicine, Taian Central Hospital, Taian 271000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Scientific Development Project of the Economic and Technological Development Zone of Qingdao, No. 2012-2-63
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Yan-jie, Mao Cheng-gang, Ning Xian-feng, Li Rong, Li Zi-pu. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via intramuscular injection influence the expression of cytokines related to dilated cardiomyopathy in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2179-2185.
share this article
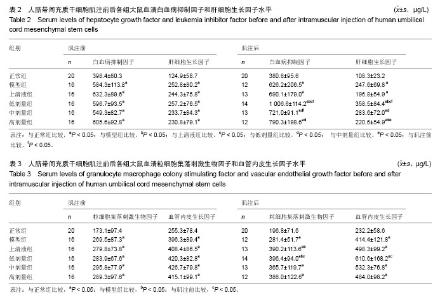
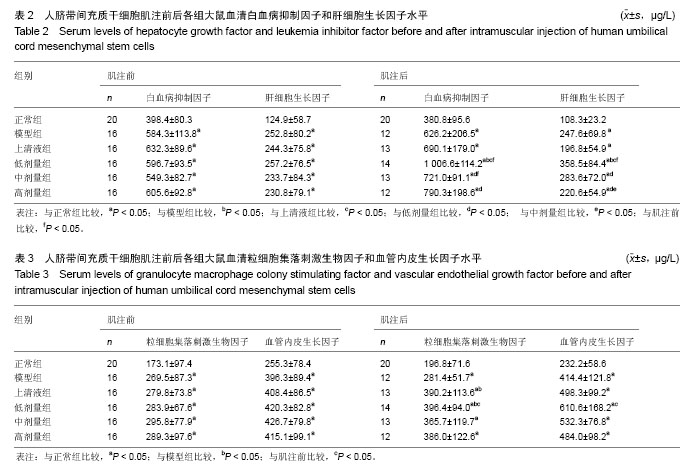
2.1 实验动物数量分析 参加实验动物数量160只,于建立扩张型心肌病模型阶段死亡60只,于2次肌肉注射观察阶段死亡16只。 2.2 人脐带间充质干细胞肌肉注射后各组大鼠血清HGF和LIF水平 肌注前,模型组、上清液组及不同剂量组间HGF和LIF水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),均较正常组明显升高(P < 0.05);肌注后,模型组、上清液组及不同剂量组仍较正常组明显升高(P < 0.05),其低剂量组不仅较肌注前显著升高(P < 0.05),且较模型组和上清液组明显升高(P < 0.05),同时中剂量组LIF水平亦较肌注前明显升高 (P < 0.05),高剂量组HGF和LIF水平肌注前后无明显差异(P > 0.05);3个剂量组间无明显的量效关系(P > 0.05), 见表2。 2.3 人脐带间充质干细胞肌注后各组大鼠血清GM-CSF和VEGF水平 肌注前,模型组、上清液组及不同剂量组间GM-CSF和VEGF差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),均较正常组明显升高(P < 0.05);肌注后,模型组、上清液组及不同剂量组仍较正常组高(P < 0.05),同时低剂量组GM-CSF和VEGF水平均较肌注前明显升高(P < 0.05),中、高剂量组GM-CSF和VEGF水平肌注前后均无明显差异(P > 0.05);3个剂量组间无明显量效关系(P > 0.05),见表3。"
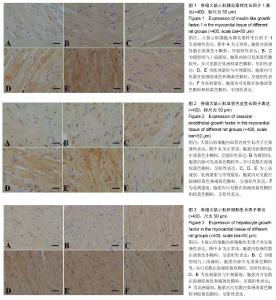
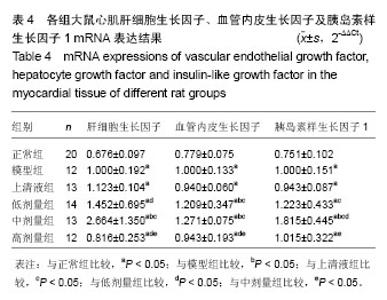
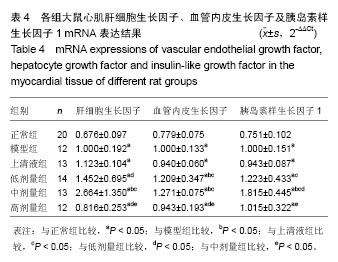
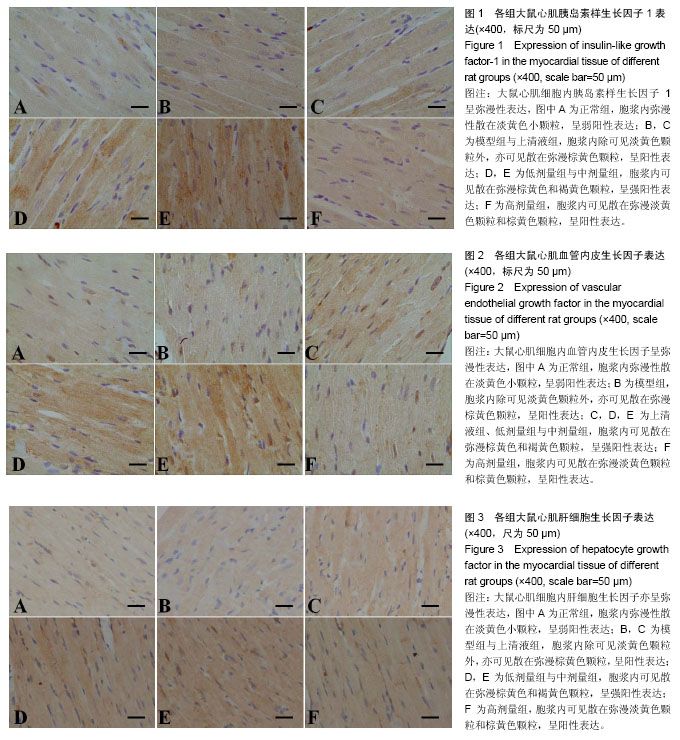
2.4 人脐带间充质干细胞肌注后大鼠心肌IGF-1、VEGF、HGF表达情况 大鼠心肌IGF-1、HGF和VEGF的表达部位主要在细胞胞浆内,高倍镜下胞浆内有棕黄色小颗粒即为阳性。正常组和模型组大鼠心肌胞浆内可见少量棕黄色小颗粒,IGF-1、HGF和VEGF表达均呈弱阳性;上清液组及不同剂量组大鼠心肌细胞胞浆可见多量棕黄色颗粒,IGF-1、HGF和VEGF表达明显增多,其中低剂量组、中剂量组呈强阳性表达,见图1-3。 2.5 人脐带间充质干细胞肌注后各组大鼠心肌IGF-1、HGF、VEGF mRNA表达结果 模型组、上清液组及不同剂量组HGF、VEGF和IGF-1 mRNA表达均较正常组明显增加(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,上清液组IGF-1、HGF和VEGF mRNA的表达无变化(P > 0.05),低剂量组HGF和VEGF mRNA的表达、中剂量组VEGF和IGF-1 mRNA的表达明显升高(P < 0.05),但高剂量组HGF、VEGF和IGF-1 mRNA表达无变化(P > 0.05)。与低剂量组比较,中剂量组HGF和IGF-1 mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05),高剂量组HGF和VEGF mRNA明显下降(P < 0.05);与中剂量组比较,高剂量组HGF、VEGF和IGF-1 mRNA表达均明显下降(P < 0.05),见表4。"
| [1] Garg R, Yusuf S. Overview of randomized trials of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on mortality and morbidity in patients with heart failure. Collaborative Group on ACE Inhibitor Trials. JAMA. 1995;273(18):1450-1456. [2] Pitt B, Poole-Wilson PA, Segal R, et al. Effect of losartan compared with captopril on mortality in patients with symptomatic heart failure: randomised trial--the Losartan Heart Failure Survival Study ELITE II. Lancet. 2000; 355 (9215):1582-1587. [3] Solomon SD, Wang D, Finn P, et al. Effect of candesartan on cause-specific mortality in heart failure patients: the Candesartan in Heart failure Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. Circulation. 2004; 110(15):2180-2183. [4] Poole-Wilson PA, Swedberg K, Cleland JG, et al. Comparison of carvedilol and metoprolol on clinical outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure in the Carvedilol Or Metoprolol European Trial (COMET): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;362(9377):7-13. [5] Dandel M, Weng Y, Siniawski H, et al. Long-term results in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy after weaning from left ventricular assist devices.Circulation. 2005;112 (9 Suppl): I37-45. [6] Sun CK, Chang LT, Sheu JJ, et al. Bone marrow-derived mononuclear cell therapy alleviates left ventricular remodeling and improves heart function in rat-dilated cardiomyopathy. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(4):1197-1205. [7] 何红燕,林晓波,应文娟,等.人脐带间充质干细胞经体内定植并向心肌样细胞分化的研究[J].中国输血杂志,2009,22(3):188-191. [8] 林晓波,何红燕,罗敏杰,等.人脐带间充质干细胞向心肌样细胞分化的研究[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2007, 22(13):971-973. [9] Noiseux N, Gnecchi M, Lopez-Ilasaca M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing Akt dramatically repair infarcted myocardium and improve cardiac function despite infrequent cellular fusion or differentiation. Mol Ther. 2006;14(6):840-850. [10] 杨德忠,王伟,王薇,等.旁分泌机制在脂肪间充质干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死中的作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2013,35(9):874-879. [11] Huang J, Zhang Z, Guo J, et al. Genetic modification of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing CCR1 increases cell viability, migration, engraftment, and capillary density in the injured myocardium. Circ Res. 2010;106(11):1753-1762. [12] 张文祥,王思平,锡洪敏,等.Wistar 大鼠肌肉注射异种脐带间充质干细胞的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(41): 6620-6627. [13] 王思平,聂娜娜,王丽,等.肌肉注射异种脐带间充质干细胞大鼠心肌肌钙蛋白 I 及血清相关因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(10): 1566-1572. [14] 王琪,张文祥,王思平,等. 肌肉注射人脐带间充质干细胞健康大鼠心肌组织ki-67, phh3及cTnT 的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(41): 6671-6677. [15] 王本臻. 肌肉注射人脐带间充质干细胞对阿霉素诱导扩张型心肌病大鼠心功能及心肌超微结构的影响[D]. 青岛:青岛大学, 2014. [16] Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402-408. [17] Gnecchi M, Danieli P, Cervio E. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for heart disease. Vascul Pharmacol. 2012;57(1):48-55. [18] van den Akker F, Deddens JC, Doevendans PA, et al. Cardiac stem cell therapy to modulate inflammation upon myocardial infarction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(2):2449-2458. [19] Mohammadi Gorji S, Karimpor Malekshah AA, Hashemi-Soteh MB, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on Doxorubicin-induced fibrosis. Cell J. 2012;14(2):142-151. [20] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E, et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):319-331. [21] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al. Mobilized bone marrow cells repair the infarcted heart, improving function and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(18):10344-10349. [22] Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart. Circulation. 2002;105(1):93-98. [23] Gnecchi M, He H, Noiseux N, et al. Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. FASEB J. 2006;20(6):661-669. [24] Tang YL, Zhao Q, Qin X, et al. Paracrine action enhances the effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on vascular regeneration in rat model of myocardial infarction. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80(1):229-236. [25] Tögel F, Hu Z, Weiss K, et al. Administered mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischemic acute renal failure through differentiation-independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;289(1):F31-42. [26] Breitbach M, Bostani T, Roell W, et al. Potential risks of bone marrow cell transplantation into infarcted hearts. Blood. 2007; 110(4):1362-1369. [27] Vulliet PR, Greeley M, Halloran SM, et al. Intra-coronary arterial injection of mesenchymal stromal cells and microinfarction in dogs. Lancet. 2004;363(9411):783-784. [28] Widimsky P, Penicka M. Complications after intracoronary stem cell transplantation in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 2006;111(1):178-179. [29] Yoon YS, Park JS, Tkebuchava T, et al. Unexpected severe calcification after transplantation of bone marrow cells in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2004;109(25): 3154-3157. [30] Barbash IM, Chouraqui P, Baron J, et al. Systemic delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to the infarcted myocardium: feasibility, cell migration, and body distribution. Circulation. 2003;108(7):863-868. [31] Menasché P, Hagège AA, Vilquin JT, et al. Autologous skeletal myoblast transplantation for severe postinfarction left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(7): 1078-1083. [32] Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, et al. Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature. 2001;410(6829): 701-705. [33] Lin H, Shabbir A, Molnar M, et al. Adenoviral expression of vascular endothelial growth factor splice variants differentially regulate bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells .J Cell Physiol. 2008;216(2):458-468. [34] Vacanti V, Kong E, Suzuki G, et al. Phenotypic changes of adult porcine mesenchymal stem cells induced by prolonged passaging in culture. J Cell Physiol. 2005;205(2):194-201. [35] Yoon YS, Wecker A, Heyd L, et al. Clonally expanded novel multipotent stem cells from human bone marrow regenerate myocardium after myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115(2):326-338. [36] Nagaya N, Kangawa K, Itoh T, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in a rat model of dilated cardiomyopathy.Circulation. 2005 ;112(8): 1128-1135. |
| [1] | Jing Cai-xia, Liu Chang-kui, Tan Xin-ying, Luo Jin-chao, Hu Min. Bone mesenchymal stem cells with allogeneic bone to repair canine mandibular defects: detection of osteogenic ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2138-2143. |
| [2] | Lv Pin-lei, Su Yue-han, Cao Yun, Wang Zheng. Treatment of osteoarthritis using colony-forming cells in stromal vascular fraction of adipose tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2149-2154. |
| [3] | Ruan Guang-ping, Yao Xiang, Liu Ju-fen, Wang Jin-xiang, Hu Yuan-yuan, Li Zi-an, Yang Jian-yong, Pang Rong-qing, Pan Xing-hua. Transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2172-2178. |
| [4] |
Liu Yu-liang, Li Jun, He Yu-qin, Zhuo Feng, Wei Kai-bin.
Transplantation of human umbilical cord derived-mesenchymal stem cells by different ways for the treatment of spinal cord injury
|
| [5] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhang Ya-xiao, Zhang Bing, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Wang Ren-feng, Liu Jia-bao, Wu Lin. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treatment of emphysema: intravenous versus intratracheal approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2211-2215. |
| [6] | Liang Jian-ji, He Zhi-yong, Liu Kang, Li Xiao-ling, Cheng Wei-min, Yu Xin-ping, Chen Er-dong. Intraarticular injection of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for mild-to-moderate osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2216-2223. |
| [7] | Huang Jian-feng, Huang Ji-feng, Zhang Wei-cai. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuron-like cells induced by combination of two cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 829-834. |
| [8] | Qu Xin, Wang Xin-chao, Han Lu, Zhang Hai-chao. Different sources of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of liver fibrosis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 926-931. |
| [9] | Li Hui-zhen, Li Meng, Li Rui-yu, Wu Li-ping. Effects of epimedium on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 979-984. |
| [10] | Yan Hao-ran, Cai Jun-feng, Shen Bin, Wen Jun-xiang, Tan Jun. Sodium hyaluronate for treatment of chondromalacia patella syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8525-8528. |
| [11] | Yang Bei-bei, Chen Jiang-tao, Song Xing-hua. Proteome changes in a rat model of spinal cord injury after intrathecal injection of methylprednisolone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7897-7902. |
| [12] | Ruan Guang-ping, Yao Xiang, Liu Ju-fen, Shu Fan, He Jie, Yang Jian-yong, Pang Rong-qing, Pan Xing-hua. Role of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: cell transplantation, immuoregulation and target cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6714-6718. |
| [13] | Zhou Hao-yue, Lu Jiong-bin, Qiu Han-ying. Construction of cardiac atrioventricular electrical conduction pathway by rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6597-6602. |
| [14] | Zhang Fei, Wang Yi-xiong, Wu Zhong-yan, Li Gui-cai, Cao Peng, Wang Wu. Biological characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: cold trypsin digestion versus tissue explant method in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6614-6619. |
| [15] | Zhang Wen-xiang, Wang Si-ping, Xi Hong-min, Li Zi-pu. Security of heterogeneous umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via intramuscular injection in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6620-6627. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||