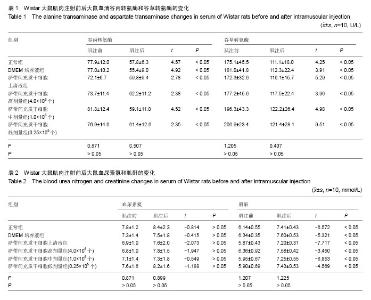
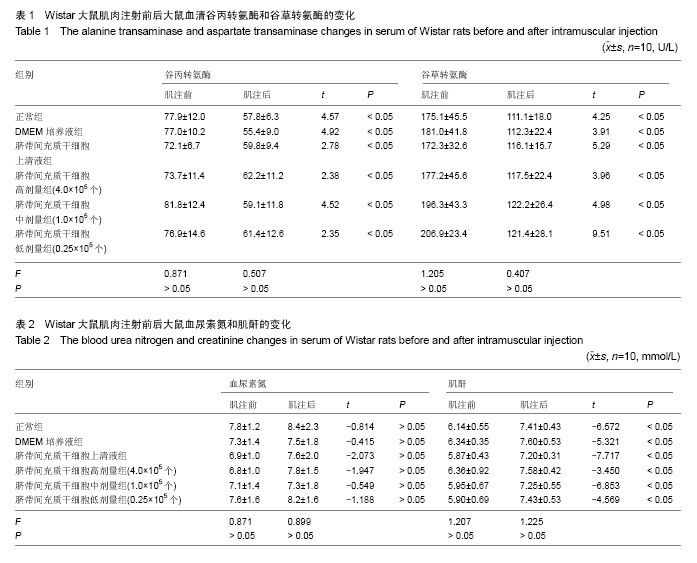
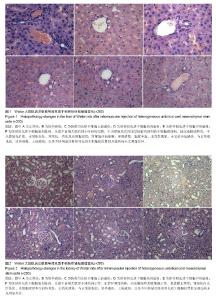
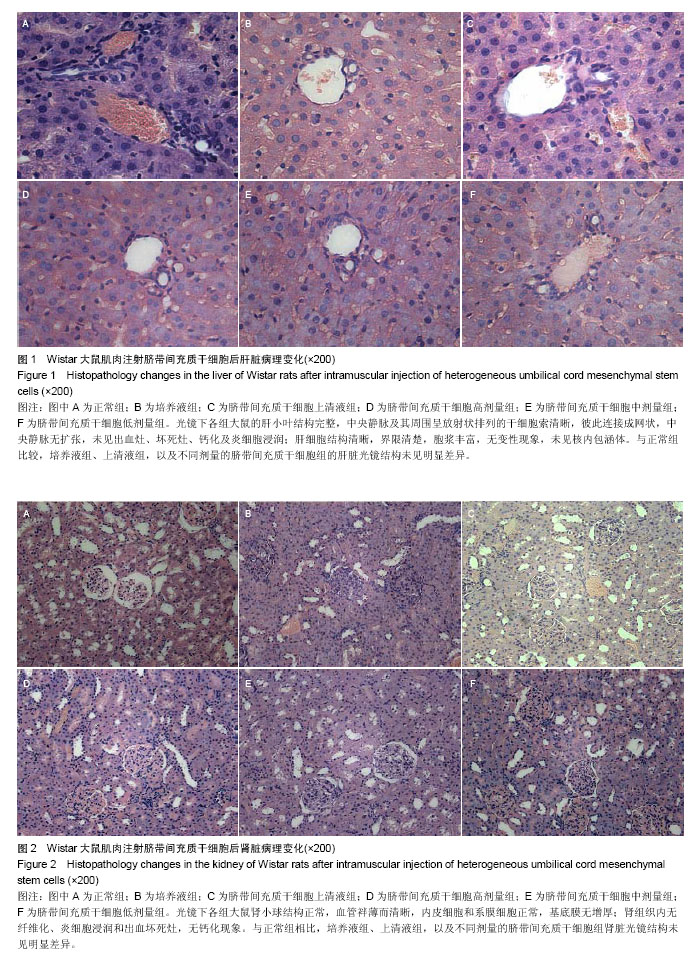
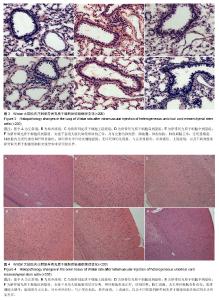
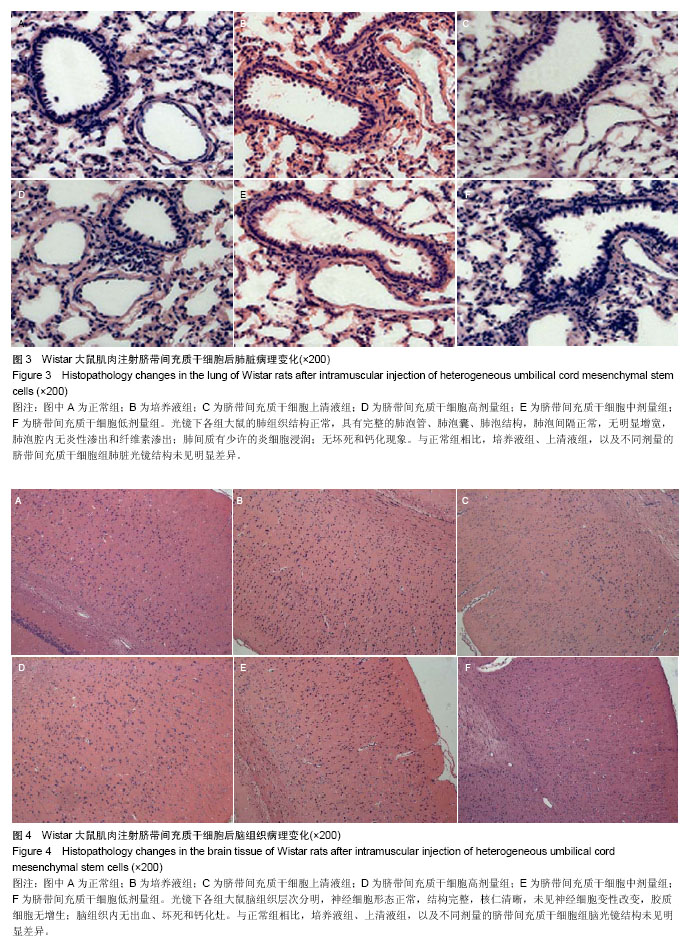
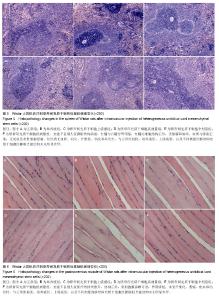
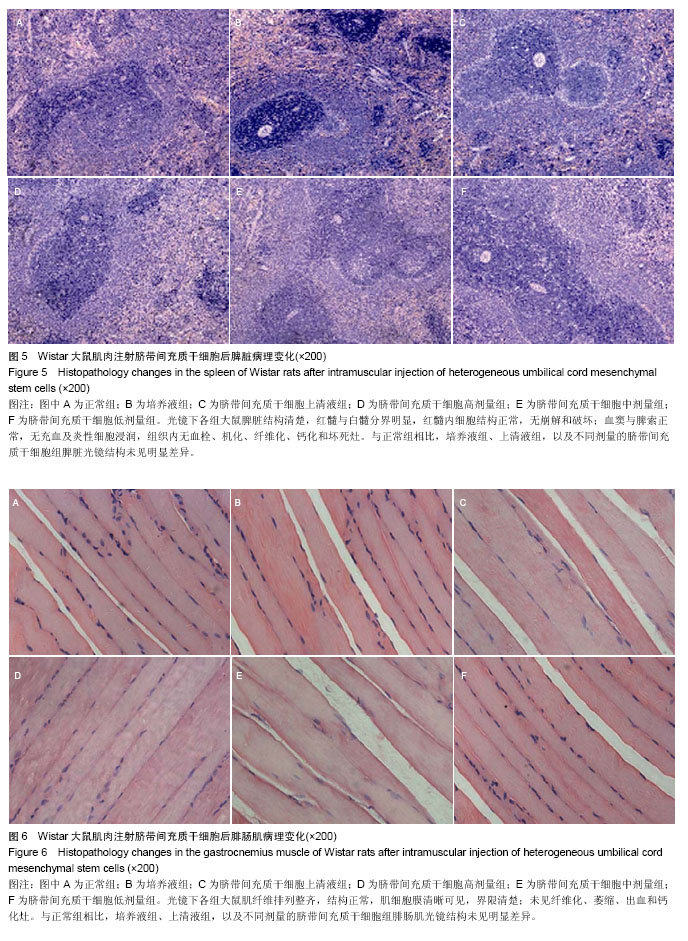
| [1] Barry FP, Murphy JM.Mesenchymal stem cells: clinical applications and biological characterization.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;36(4):568-584.
[2] Fang B, Shi M, Liao L,et al.Multiorgan engraftment and multilineage differentiation by human fetal bone marrow Flk1+/CD31-/CD34- Progenitors.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2003;12(6):603-613.
[3] Fang B, Liao L, Shi M,et al.Multipotency of Flk1CD34 progenitors derived from human fetal bone marrow.J Lab Clin Med. 2004;143(4):230-240.
[4] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL,et al.Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow.Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.
[5] Schwartz RE, Reyes M, Koodie L,et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells.J Clin Invest. 2002;109(10):1291-1302.
[6] 张学峰,张美荣,胡建霞,等.异种脐带间充质干细胞静脉应用的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(32): 5971-5975.
[7] 张美荣,张学峰,胡建霞,等.大鼠肌肉注射移植人脐带间充质干细胞的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(27): 4997-5000.
[8] Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky-Shapiro II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells.J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966;16(3):381-390.
[9] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[10] 肖娟,姜晓蓉,刘靖媛,等.脐带间充质细胞生物学特性及应用研究[J].解剖科学进展,2013,19(4):363-365.
[11] Wang Y, Huso DL, Harrington J,et al.Outgrowth of a transformed cell population derived from normal human BM mesenchymal stem cell culture.Cytotherapy. 2005;7(6): 509-519.
[12] Bochkov NP, Voronina ES, Kosyakova NV,et al.Chromosome variability of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2007;143(1):122-126.
[13] Jeong JO, Han JW, Kim JM,et al.Malignant tumor formation after transplantation of short-term cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in experimental myocardial infarction and diabetic neuropathy.Circ Res. 2011;108(11):1340-1347.
[14] Medicetty S, Bledsoe AR, Fahrenholtz CB,et al.Transplantation of pig stem cells into rat brain: proliferation during the first 8 weeks.Exp Neurol. 2004;190(1):32-41.
[15] Weiss ML, Mitchell KE, Hix JE,et al.Transplantation of porcine umbilical cord matrix cells into the rat brain.Exp Neurol. 2003; 182(2):288-299.
[16] Pirtskhalaishvili G, Shurin GV, Gambotto A,et al.Transduction of dendritic cells with Bcl-xL increases their resistance to prostate cancer-induced apoptosis and antitumor effect in mice.J Immunol. 2000;165(4):1956-1964.
[17] Ludewig B, Graf D, Gelderblom HR,et al.Spontaneous apoptosis of dendritic cells is efficiently inhibited by TRAP (CD40-ligand) and TNF-alpha, but strongly enhanced by interleukin-10.Eur J Immunol. 1995;25(7):1943-1950.
[18] 何君,李洋,陈威,等.人脐带间充质干细胞静脉输注小鼠的安全性[J].中国比较医学杂志,2013,23(9):36-41.
[19] Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS,et al.Marrow-derived stromal cells express genes encoding a broad spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines and promote in vitro and in vivo arteriogenesis through paracrine mechanisms.Circ Res. 2004;94(5):678-685.
[20] Casillas-Ramírez A, Zaouali A, Padrissa-Altés S,et al. Insulin-like growth factor and epidermal growth factor treatment: new approaches to protecting steatotic livers against ischemia-reperfusion injury.Endocrinology. 2009; 150(7):3153-3161.
[21] Gnecchi M, He H, Noiseux N,et al.Evidence supporting paracrine hypothesis for Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac protection and functional improvement. FASEB J. 2006;20(6):661-669.
[22] Tang YL, Zhao Q, Qin X,et al.Paracrine action enhances the effects of autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on vascular regeneration in rat model of myocardial infarction. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80(1):229-236.
[23] 张颖,李娜,辛毅,等.大鼠静脉注射人脐带胶样组织来源间充质干细胞的安全性研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2013,32(6):783-788.
[24] Fazel S, Chen L, Weisel RD,et al.Cell transplantation preserves cardiac function after infarction by infarct stabilization: augmentation by stem cell factor.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130(5):1310.
[25] Burt RK, Loh Y, Pearce W,et al.Clinical applications of blood-derived and marrow-derived stem cells for nonmalignant diseases.JAMA. 2008;299(8):925-936.
[26] Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS,et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart.Circulation. 2002;105(1):93-98.
[27] Dai W, Hale SL, Martin BJ,et al.Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in postinfarcted rat myocardium: short- and long-term effects.Circulation. 2005;112(2):214-223.
[28] Lee H, Bae JS, Jin HK.Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve neurological abnormalities of Niemann-Pick type C mouse by modulation of neuroinflammatory condition.J Vet Med Sci. 2010;72(6): 709-717.
[29] Phinney DG, Prockop DJ.Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair--current views.Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2896-2902.
[30] 陈晓岚,黄仁彬,汤银娟,等.人脐血间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗大鼠局灶性脑缺血的实验研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2007, 10(1):4-7.
[31] Burt RK, Loh Y, Pearce W,et al.Clinical applications of blood-derived and marrow-derived stem cells for nonmalignant diseases.JAMA. 2008;299(8):925-936.
[32] Hare JM.Translational development of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for cardiovascular diseases.Tex Heart Inst J. 2009;36(2):145-147.
[33] Li DH,Wang CH,Shan W,et al. Human amnion tissue injected with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells repairs damaged sciatic nerves in rats. Neural Regen Res.2012;7(23): 1771-1778.
[34] Li Z, Qin HJ, Feng ZS, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell- loaded amniotic membrane for the repair of radial nerve injury. Neural Regen Res.2013; 8(36): 3441-3448.
[35] Koç ON, Gerson SL, Cooper BW,et al.Rapid hematopoietic recovery after coinfusion of autologous-blood stem cells and culture-expanded marrow mesenchymal stem cells in advanced breast cancer patients receiving high-dose chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(2):307-316. |