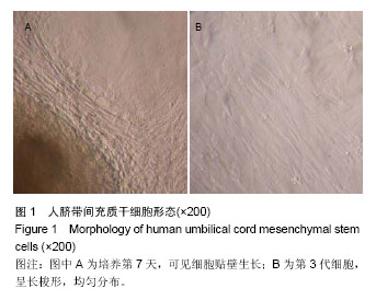
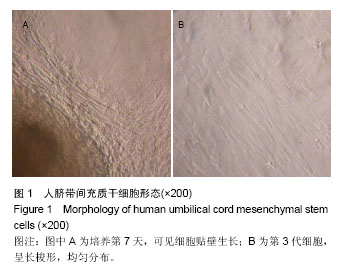
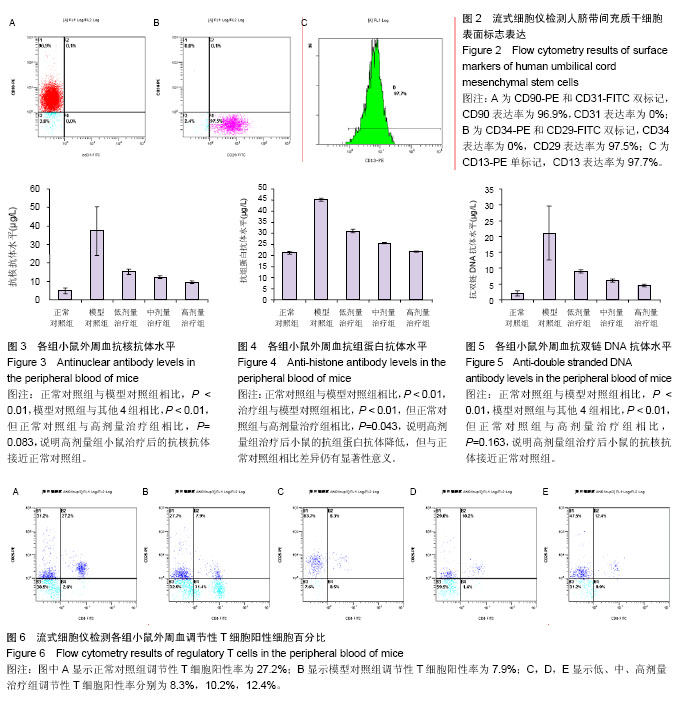
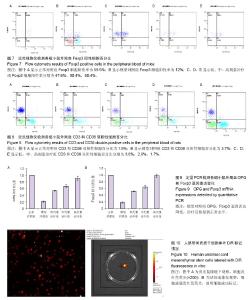
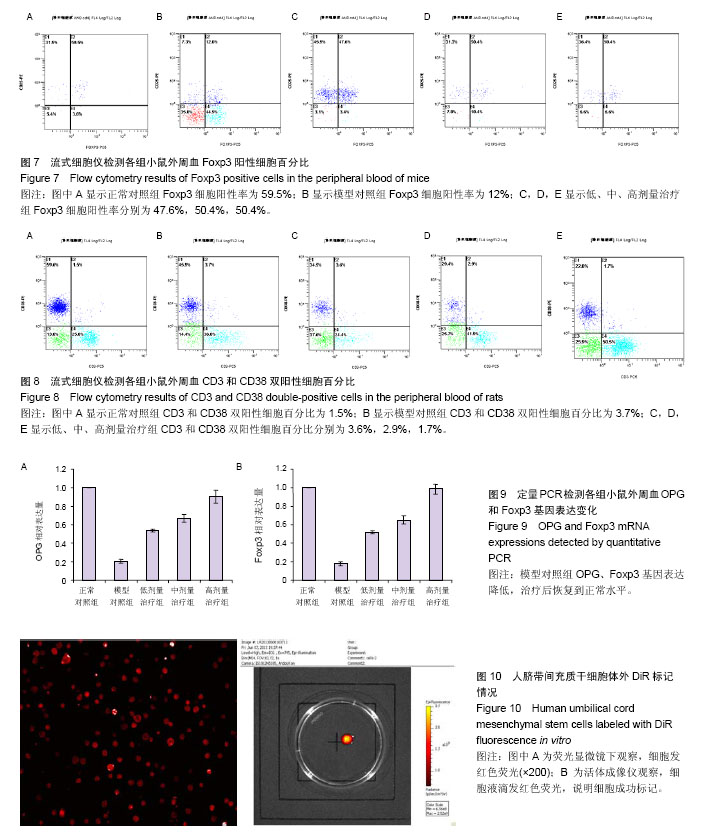
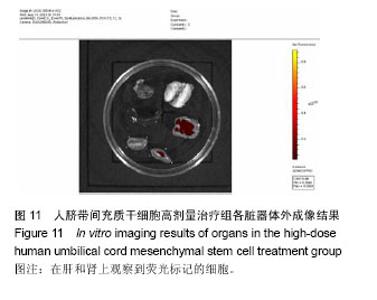
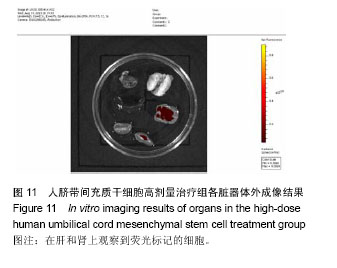
| [1] Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(9):929-939.
[2] Crispín JC, Tsokos GC. Novel molecular targets in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev. 2008;7(3):256-261.
[3] Kyttaris VC, Juang YT, Tsokos GC. Immune cells and cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17(5):518-522.
[4] Ramanujam M, Davidson A. Targeting of the immune system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2008; 10:e2.
[5] Pego-Reigosa JM, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus: pharmacological developments and recommendations for a therapeutic strategy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;17(1):31-41.
[6] Tieng AT, Peeva E. B-cell-directed therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2008;38(3):218-227.
[7] Burt RK, Traynor A, Statkute L,et al. Nonmyeloablative hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for systemic lupus erythematosus. JAMA. 2006;295(5):527-535.
[8] Smith-Berdan S, Gille D, Weissman IL, et al. Reversal of autoimmune disease in lupus-prone New Zealand black/New Zealand white mice by nonmyeloablative transplantation of purified allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2007; 110(4):1370-1378.
[9] Erices A, Conget P, Minguell JJ. Mesenchymal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br J Haematol. 2000; 109(1):235-242.
[10] Romanov YA, Svintsitskaya VA, Smirnov VN. Searching for alternative sources of postnatal human mesenchymal stem cells: candidate MSC-like cells from umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2003;21(1):105-110.
[11] Qiao C, Xu W, Zhu W, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the umbilical cord. Cell Biol Int. 2008;32(1):8-15.
[12] Deans RJ, Moseley AB. Mesenchymal stem cells: biology and potential clinical uses. Exp Hematol. 2000;28(8):875-84.
[13] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74.
[14] Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Latsinik NV, et al. Stromal cells responsible for transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues. Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation. 1974;17(4):331-340.
[15] Cordeiro AC, Isenberg DA. Novel therapies in lupus - focus on nephritis. Acta Reumatol Port. 2008;33(2):157-169.
[16] Chen X, Armstrong MA, Li G. Mesenchymal stem cells in immunoregulation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2006;84(5):413-421.
[17] Han YF, Tao R, Sun TJ, et al. Optimization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods. Cytotechnology. 2013;65(5):819-827.
[18] El-Badri NS, Hakki A, Ferrari A, et al. Autoimmune disease: is it a disorder of the microenvironment. Immunol Res. 2008; 41(1):79-86.
[19] Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004;363 (9419):1439-1441.
[20] Sun L, Wang D, Liang J, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in severe and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(8): 2467-2475.
[21] Wang D, Li J, Zhang Y, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active and refractory systemic lupus erythematosus: a multicenter clinical study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R79. |