Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (6): 841-846.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.06.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Autophagy-related gene Beclin-1 expression in neuron-like differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Yang Yi, Ding Wen-jing, Dong Wan-li
- The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-01-10Online:2014-02-05Published:2014-02-05 -
Contact:Dong Wan-li, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Yang Yi, Studying for master’s degree, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Ding Wen-jing, Studying for master’s degree, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China Yang Yi and Ding Wen-jing contributed equally to this paper. -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. SBK201123617
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yi, Ding Wen-jing, Dong Wan-li. Autophagy-related gene Beclin-1 expression in neuron-like differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 841-846.
share this article
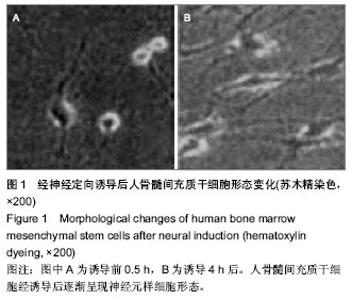
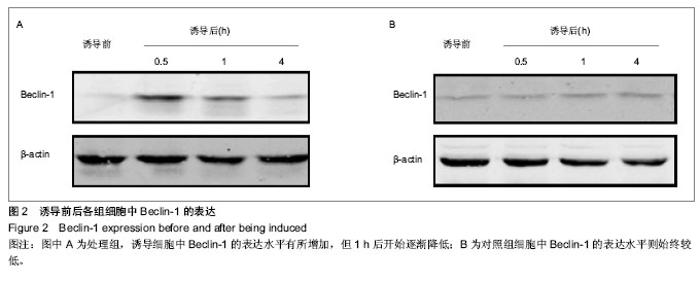
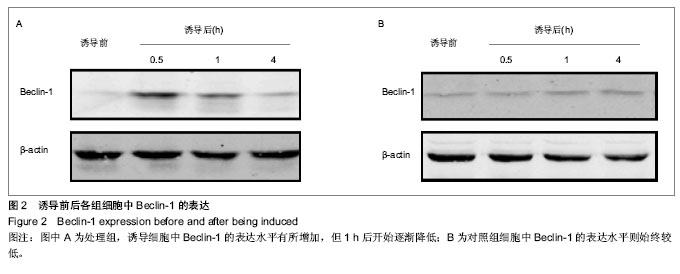
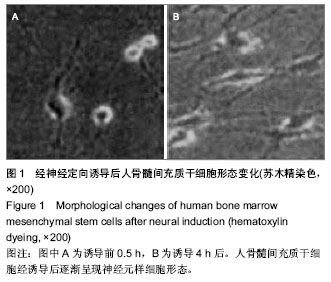
2.1 诱导后人骨髓间充质干细胞的形态变化 在预诱导24 h后,倒置显微镜下可见部分人骨髓间充质干细胞体积变小变圆,继续诱导细胞质开始出现了以胞核为中心的收缩,细胞体更透亮,整体呈球形或是锥形,但部分细胞边缘不对称且有半透明光圈,之后细胞边缘逐渐出现突起,24 h后交汇成网。诱导至6 h时,大部分细胞呈现为典型神经元样细胞,可见部分神经网络开始形成,神经元光晕明显;但6 h后神经元样细胞的比例没有明显增加;诱导至12 h时,细胞仍然是呈现贴壁生长的状态(图1)。 免疫组织化学结果显示,诱导4 h后处理组细胞中神经元特异性烯醇化酶阳性率为78.7%,而胶质纤维酸性蛋白阳性率仅8.1%,而对照组细胞中均不表达神经元特异性烯醇化酶和胶质纤维酸性蛋白。"
| [1] 马林业,戴国友,刘煜昊,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养增殖过程及分化为心肌样细胞后的致瘤性实验[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(14):2661-2666.[2] Xu J, Wang W, Ludeman M, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional alginate gels. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008; 14(5): 667-680. [3] 邓志锋,汪泱,宋书欣,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血区血管新生及神经前体细胞增殖的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2005, 28(5): 500-503.[4] 裴瑛波.骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养和定向分化的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(4):2775-2778.[5] 金辉,张蕾,李伟伟.人骨髓间充质干细胞诱导向多巴胺能神经元的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(36): 6677-6680.[6] Kaushik S, Cuervo AM. Autophagy as a cell-repair mechanism: activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress. Mol Aspects Med. 2006;27(5-6): 444-454. [7] Phadwal K, Watson AS, Simon AK. Tightrope act: autophagy in stem cell renewal, differentiation, proliferation, and aging. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(1):89-103. [8] Salemi S, Yousefi S, Constantinescu MA, et al. Autophagy is required for self-renewal and differentiation of adult human stem cells. Cell Res. 2012;22(2):432-435. [9] Warr MR, Kohli L, Passegué E. Born to survive: autophagy in hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Cell Cycle. 2013; 12(13): 1979-1980. [10] Yoshimori T. Autophagy: a regulated bulk degradation process inside cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 313(2):453-458.[11] Klionsky DJ. The molecular machinery of autophagy: unanswered questions. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 1):7-18.[12] Kunz JB, Schwarz H, Mayer A. Determination of four sequential stages during microautophagy in vitro. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(11):9987-9996. [13] Orenstein SJ, Cuervo AM. Chaperone-mediated autophagy: molecular mechanisms and physiological relevance. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010;21(7):719-726.[14] Kvam E, Goldfarb DS. Nucleus-vacuole junctions and piecemeal microautophagy of the nucleus in S. cerevisiae. Autophagy. 2007;3(2):85-92. [15] Hansen TE, Johansen T. Following autophagy step by step. BMC Biol. 2011;9:39.[16] Simonsen A, Tooze SA. Coordination of membrane events during autophagy by multiple class III PI3-kinase complexes. J Cell Biol. 2009;186(6):773-782. [17] Huang WP, Klionsky DJ. Autophagy in yeast: a review of the molecular machinery. Cell Struct Funct. 2002;27(6):409-420.[18] Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, et al. Induction of autophagy and inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 1999;402(6762):672-676.[19] Aita VM, Liang XH, Murty VV, et al. Cloning and genomic organization of beclin 1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 17q21. Genomics. 1999;59(1):59-65.[20] Scarlatti F, Maffei R, Beau I, et al. Role of non-canonical Beclin 1-independent autophagy in cell death induced by resveratrol in human breast cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(8):1318-1329. [21] Edinger AL, Thompson CB. Defective autophagy leads to cancer. Cancer Cell. 2003;4(6):422-424.[22] 黄平,刘岩峰,托娅,等.大鼠弥漫性脑损伤后S100β表达与损伤时间关系[J].法医学杂志,2006,22(1):4-6.[23] Gaytán M, Morales C, Sánchez-Criado JE, et al. Immunolocalization of beclin 1, a bcl-2-binding, autophagy- related protein, in the human ovary: possible relation to life span of corpus luteum. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331(2):509-517. [24] Kim R, Emi M, Matsuura K, et al. Antisense and nonantisense effects of antisense Bcl-2 on multiple roles of Bcl-2 as a chemosensitizer in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2007; 14(1):1-11.[25] Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G, et al. Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin 1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(12):1809-1820. [26] Furuya D, Tsuji N, Yagihashi A, et al. Beclin 1 augmented cis-diamminedichloroplatinum induced apoptosis via enhancing caspase-9 activity. Exp Cell Res. 2005;307(1): 26-40. [27] 刘全,王建军,潘永成,等.Beclin1在非小细胞肺癌中的表达及临床意义[J].肿瘤防治研究,2008,35(3):184-187. [28] Pickford F, Masliah E, Britschgi M, et al. The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid beta accumulation in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118(6):2190-2199.[29] Long X, Olszewski M, Huang W, et al. Neural cell differentiation in vitro from adult human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2005;14(1):65-69.[30] Oliver L, Hue E, Priault M, et al. Basal autophagy decreased during the differentiation of human adult mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(15):2779-2788. [31] Wirawan E, Vanden Berghe T, Lippens S, et al. Autophagy: for better or for worse. Cell Res. 2012;22(1):43-61. [32] Tang Z, Lin MG, Stowe TR, et al. Autophagy promotes primary ciliogenesis by removing OFD1 from centriolar satellites. Nature. 2013;502(7470):254-257. [33] Leveque L, Vu T, Kuns RD, et al. Autophagy is required for long-term hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) function and G-CSF-induced HSC mobilization. Blood. 2013;122(21):892.[34] Mortensen M, Watson AS, Simon AK. Lack of autophagy in the hematopoietic system leads to loss of hematopoietic stem cell function and dysregulated myeloid proliferation. Autophagy. 2011;7(9):1069-1070.[35] Graziotto JJ, Cao K, Collins FS, et al. Rapamycin activates autophagy in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome: implications for normal aging and age-dependent neurodegenerative disorders. Autophagy. 2012;8(1):147-151. [36] Essick EE, Sam F. Oxidative stress and autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010;3(3):168-177.[37] Copetti T, Bertoli C, Dalla E, et al. p65/RelA modulates BECN1 transcription and autophagy. Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 29(10): 2594-2608.[38] Wang B, Ling S, Lin WC. 14-3-3Tau regulates Beclin 1 and is required for autophagy. PLoS One. 2010;5(4):e10409. [39] Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, et al. Regulation of autophagy by a beclin 1-targeted microRNA, miR-30a, in cancer cells. Autophagy. 2009;5(6):816-823. [40] 苏冀.Beclin 1表达下调与肝细胞癌不良预后关系的研究[D].长沙:中南大学.2006.[41] 刘贵红.Beclin 1在膀胱癌组织中的表达及临床意义[D].广州:广州医学院.2012.[42] 王赞宏.自噬基因Beclin 1与宫颈癌相关性的实验研究[D].成都:四川大学.2007.[43] 段振玲.上皮性卵巢癌中自噬基因Beclin1的表达及调控其相关信号途径PI3K/PKB的实验研究[D].成都:四川大学.2007.[44] 余守和,洪岸.Runx2通过抑制细胞巨自噬以诱导C2C12细胞向成骨细胞分化[J].中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(3):481-487.[45] 王赞宏,彭芝兰,段振玲,等.自噬基因Beclin 1在宫颈鳞癌中的蛋白表达及其临床意义[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2006,37(6): 860-863.[46] 段振玲,彭芝兰,王赞宏.上皮性卵巢癌中自噬基因Beclin 1的表达及其调控相关信号传导途径的研究[J].四川大学学报:医学版, 2007,38(2):239-242.[47] 郭长青,邵经浩,卢瑞利,等.胃癌组织中Beclin 1和PTEN蛋白的表达[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2010,45(3):463-465.[48] 肖瑜,龙驰,张明慧,等.Beclin-1在非小细胞肺癌中的表达与意义[J].第三军医大学学报, 2013,35(12):1271-1273.[49] 眭怡群,冯一中.自噬相关基因LC3、Beclin-1与凋亡相关基因p53、BCL-2在大肠癌中的表达及意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2012,28(3):282-286.[50] 黄莉.自噬基因Beclin 1在喉鳞状细胞癌中的表达及意义[D].长沙:中南大学.2008. |
| [1] | Wang Jian-ji, Yang Long, Li Jing, Sun Qi, Zuo Wei-min, Ren Qi-feng, Sun Yu, Wu Zhan-yu, Zou Qiang, Ma Min-xian, Ye Chuan. Development and application of special-purpose grafter by femoral head decompression combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation based on three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6636-6642. |
| [2] | Zhou Chang-yan, Zhou Qing-huan, Bian Jing, Chen Ke, Chen Wen. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with calcium phosphate cement to repair articular cartilage defects in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1195-1199. |
| [3] | Xu Xiang, Yin He-ping. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2144-2148. |
| [4] | Du Qing-hua, Cao Jun-kai, Dong Xi-xi, E Ling-ling, Wei Li-jun. Osteogenic differentiation of pluripotent stem cells induced by akermanite extracts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2236-2242. |
| [5] | Rao Li-jia, Li Qi-meng, Li Jin-ling, Xu Qiong. Expression pattern of ten-eleven translocation family during differentiation of human dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2261-2266. |
| [6] | Gao Zhuo-yue, Liu Yong-qi, He Jian-xin, Wu Zhi-wei, Luo Ya-li, Su Yun, Zhang Li-ying, Zhang Qi, Wu You-ming, Zhou Ni-na. Regulatory effects of warming yang and invigorating qi treatment on the inflammatory balance and genetic stability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under tumor microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2267-2272. |
| [7] | Han Xiang-zhen, He Hui-yu, Hu Yang, Ba Jiao-jiao, Wang Huan-huan, Mi Xue, Abulizi•Abudula. Recombinant lentiviral vector transfected sheep bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteogenic gene expression changes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 821-828. |
| [8] | Huang Jian-feng, Huang Ji-feng, Zhang Wei-cai. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuron-like cells induced by combination of two cytokines [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 829-834. |
| [9] | Zou Bin, Zong Shao-hui, Zeng Gao-feng, Fang Ye, Gao Tai-hang. Effects of alpha-zearalanol on the osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 835-840. |
| [10] | Su Xue-lian, Bao Guang-jie, Kang Hong, Liu Lin, Kong Nan-nan. Morphological changes of goat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into fibrochondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 860-865. |
| [11] | Nie De-zhi, Wan Ying, Ben Liang, Wang Ying-jun, Liu Xiang-zhu, Wang Li-hui, Li Chao, Zhang Shi-dong. Stem cell tumorigenicity in Balb/c nude mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 888-893. |
| [12] | Fan Yan, Wang Jian-jun, Wei Feng, Fan Xiao-hai, Ma Ai-qun. Effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on inflammatory response and ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 900-905. |
| [13] | Zhao Xiao-jian, Lu Cai-ping, Chu Wei-wei, Zhen Qiang, Tan Guo-liang, Zhang Ya-xiao, Wang Ren-feng, Zhang Bing, Liu Jia-bao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation suppresses emphysema-induced inflammation and apoptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 906-911. |
| [14] | Yuan Shu-fang, Hu Lan-ying, Jiang Tao, Sun Li-hua, Zheng Rong-jiong, Zhao Jin-yan, Zhang Yue-xin . Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on the expression of CD163 and interleukin-10 in rats with acute hepatic liver failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 919-925. |
| [15] | Wang Yan, Zhao Xin-li, Zhang Jun-yan, Tan Jun. Therapeutic applications of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 932-937. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||